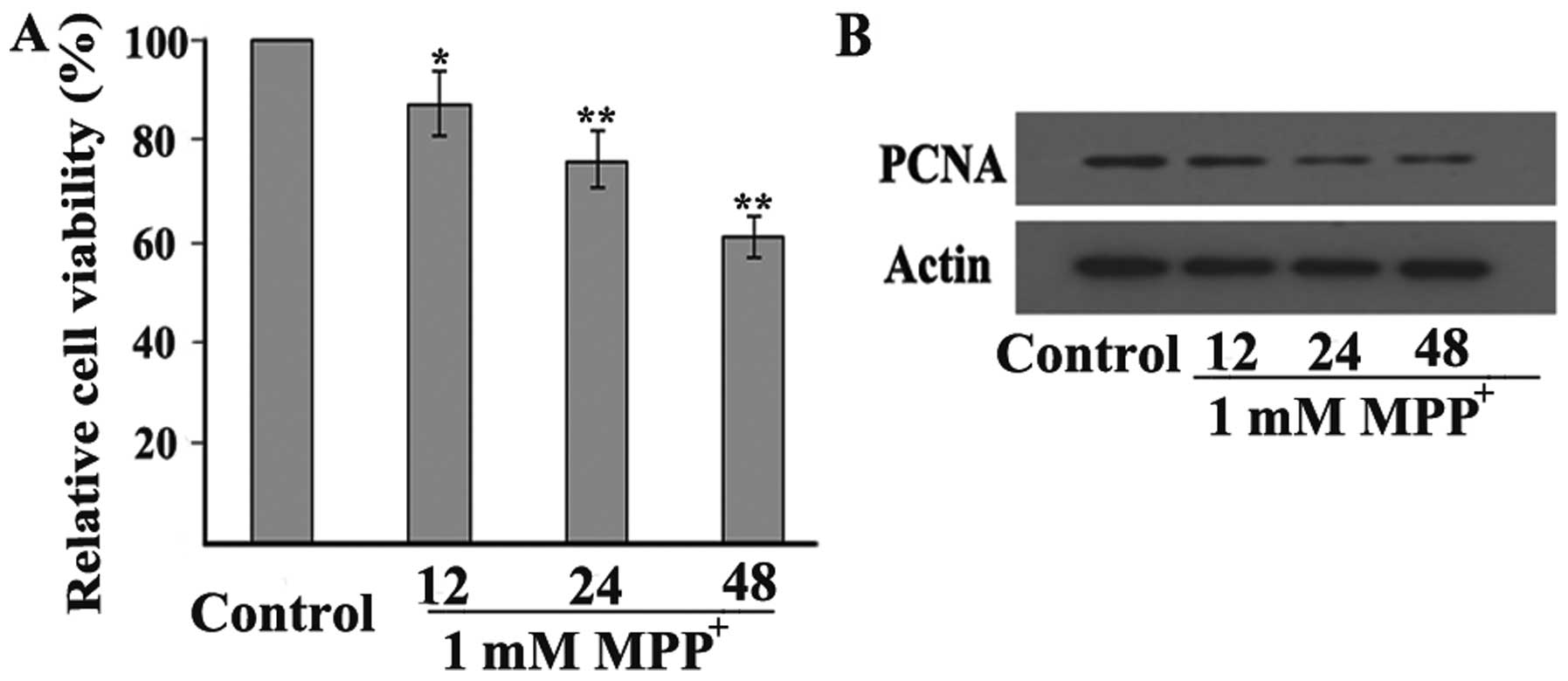
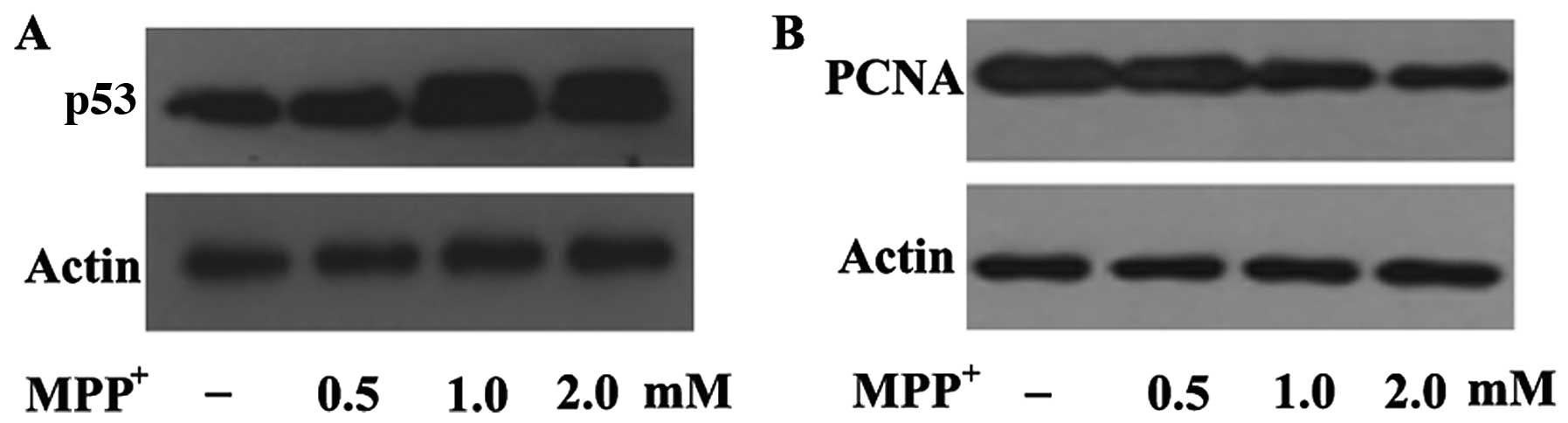
|
1
|
Forno LS: Neuropathology of Parkinson's
disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 55:259–272. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Langston JW and Irwin I: MPTP: Current
concepts and controversies. Clin Neuropharmacol. 9:485–507. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kopin IJ and Markey SP: MPTP toxicity:
implications for research in Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 11:81–96. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heikkila RE, Sieber BA, Manzino L and
Sonsalla PK: Some features of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic
neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in
the mouse. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 10:171–183. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Calon F, Lavertu N, Lemieux AM, Morissette
M, Goulet M, Grondin R, Blanchet PJ, Bédard PJ and Di Paolo T:
Effect of MPTP-induced denervation on basal ganglia GABA(B)
receptors: correlation with dopamine concentrations and dopamine
transporter. Synapse. 40:225–234. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiba K, Trevor A and Castagnoli N Jr:
Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain
monoamine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 120:574–578. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Javitch JA, D'Amato RJ, Strittmatter SM
and Snyder SH: Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin,
N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the
metabolite N-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains
selective toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:2173–2177. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Akaneya Y, Takahashi M and Hatanaka H:
Involvement of free radicals in MPP+ neurotoxicity
against rat dopaminergic neurons in culture. Neurosci Lett.
193:53–56. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jenner P: Oxidative mechanisms in nigral
cell death in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 13(Suppl 1): 24–34.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Przedborski S and Vila M: The
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetra-hydropyridine mouse model: a tool
to explore the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 991:189–198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Segura Aguilar J and Kostrzewa RM:
Neurotoxins and neurotoxic species implicated in neurodegeneration.
Neurotox Res. 6:615–630. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Schapira AH and Jenner P: Etiology and
pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 26:1049–1055.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu J and Chu CT: Mitochondrial
dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 20(Suppl 2):
S325–S334. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Parker WD Jr, Parks JK and Swerdlow RH:
Complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease frontal cortex. Brain
Res. 1189:215–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jenner P and Olanow CW: The pathogenesis
of cell death in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 66(Suppl 4):
S24–S36. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jenner P: Oxidative stress in Parkinson's
disease. Ann Neurol. 53(Suppl 3): S26–S38. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoritaka A, Hattori N, Uchida K, Tanaka M,
Stadtman ER and Mizuno Y: Immunohistochemical detection of
4-hydroxynonenal protein adducts in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:2696–2701. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Floor E and Wetzel MG: Increased protein
oxidation in human substantia nigra pars compacta in comparison
with basal ganglia and prefrontal cortex measured with an improved
dinitrophenyl-hydrazine assay. J Neurochem. 70:268–275. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Callio J, Oury TD and Chu CT: Manganese
superoxide dismutase protects against 6-hydroxydopamine injury in
mouse brains. J Biol Chem. 280:18536–18542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vila M and Przedborski S: Targeting
programmed cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 4:365–375. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perier C, Bové J, Vila M and Przedborski
S: The rotenone model of Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci.
26:345–346. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun SY, An CN and Pu XP: DJ-1 protein
protects dopaminergic neurons against 6-OHDA/MG-132-induced
neurotoxicity in rats. Brain Res Bull. 88:609–616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heikkila RE, Hess A and Duvoisin RC:
Dopaminergic neurotoxicity of
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice. Science.
224:1451–1453. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mattson MP: Apoptosis in neurodegenerative
disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:120–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Alam ZI, Jenner A, Daniel SE, Lees AJ,
Cairns N, Marsden CD, Jenner P and Halliwell B: Oxidative DNA
damage in the parkinsonian brain: an apparent selective increase in
8-hydroxyguanine levels in substantia nigra. J Neurochem.
69:1196–1203. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Perry G, Smith MA, Robertson D,
Olson SJ, Graham DG and Montine TJ: Parkinson's disease is
associated with oxidative damage to cytoplasmic DNA and RNA in
substantia nigra neurons. Am J Pathol. 154:1423–1429. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mandir AS, Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V,
Wang ZQ, Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Smulson ME, Hoffman BE, Guastella
DB, Dawson VL and Dawson TM: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activation
mediates 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2,3,6-tetra-hydropyridine
(MPTP)-induced parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:5774–5779.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tan CK, Castillo C, So AG and Downey KM:
An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf
thymus. J Biol Chem. 261:12310–12316. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Prelich G, Tan CK, Kostura M, Mathews MB,
So AG, Downey KM and Stillman B: Functional identity of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta
auxiliary protein. Nature. 326:517–520. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burkovics P, Hajdú I, Szukacsov V, Unk I
and Haracska L: Role of PCNA-dependent stimulation of
3′-phosphodiesterase and 3′-5′ exonuclease activities of human Ape2
in repair of oxidative DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4247–4255.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Amoroso A, Concia L, Maggio C, Raynaud C,
Bergounioux C, Crespan E, Cella R and Maga G: Oxidative DNA damage
bypass in Arabidopsis thaliana requires DNA polymerase λ and
proliferating cell nuclear antigen 2. Plant Cell. 23:806–822. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirata H and Cadet JL: p53-knockout mice
are protected against the long-term effects of methamphetamine on
dopaminergic terminals and cell bodies. J Neurochem. 69:780–790.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duan W, Zhu X, Ladenheim B, Yu QS, Guo Z,
Oyler J, Cutler RG, Cadet JL, Greig NH and Mattson MP: p53
inhibitors preserve dopamine neurons and motor function in
experimental parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 52:597–606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trimmer PA, Smith TS, Jung AB and Bennett
JP Jr: Dopamine neurons from transgenic mice with a knockout of the
p53 gene resist MPTP neurotoxicity. Neurodegeneration. 5:233–239.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moldovan GL, Pfander B and Jentsch S:
PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 129:665–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Samii A, Nutt JG and Ransom BR:
Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 363:1783–1793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li DW, Yao M, Dong YH, Tang MN, Chen W, Li
GR and Sun BQ: Guanosine exerts neuroprotective effects by
reversing mitochondrial dysfunction in a cellular model of
Parkinson's disease. Int J Mol Med. 34:1358–1364. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martinon F: Signaling by ROS drives
inflammasome activation. Eur J Immunol. 40:616–619. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA,
Masood A, Sofi MA and Ganie SA: Oxidative stress, mitochondrial
dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight.
Biomed Pharmacother. 74:101–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He F and Zuo L: Redox roles of reactive
oxygen species in cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
16:27770–27780. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lotharius J and Brundin P: Pathogenesis of
Parkinson's disease: dopamine, vesicles and alpha-synuclein. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 3:932–942. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Montine KS, Quinn JF, Zhang J, Fessel JP,
Roberts LJ II, Morrow JD and Montine TJ: Isoprostanes and related
products of lipid peroxidation in neurodegenerative diseases. Chem
Phys Lipids. 128:117–124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nagatsu T and Sawada M: Molecular
mechanism of the relation of monoamine oxidase B and its inhibitors
to Parkinson's disease: possible implications of glial cells. J
Neural Transm Suppl. 71:53–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kumar MJ and Andersen JK: Perspectives on
MAO-B in aging and neurological disease: where do we go from here?
Mol Neurobiol. 30:77–89. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Norris EH, Giasson BI, Hodara R, Xu S,
Trojanowski JQ, Ischiropoulos H and Lee VM: Reversible inhibition
of alpha-synuclein fibrillization by dopaminochrome-mediated
conformational alterations. J Biol Chem. 280:21212–21219. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zecca L, Wilms H, Geick S, Claasen JH,
Brandenburg LO, Holzknecht C, Panizza ML, Zucca FA, Deuschl G,
Sievers J and Lucius R: Human neuromelanin induces
neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the rat substantia
nigra: implications for Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol.
116:47–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sadrzadeh SM and Saffari Y: Iron and brain
disorders. Am J Clin Pathol. 121(Suppl): S64–S70. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jomova K and Valko M: Advances in
metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology.
283:65–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Núñez MT, Urrutia P, Mena N, Aguirre P,
Tapia V and Salazar J: Iron toxicity in neurodegeneration.
Biometals. 25:761–776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lan J and Jiang DH: Desferrioxamine and
vitamin E protect against iron and MPTP-induced neurodegeneration
in mice. J Neural Transm. 104:469–481. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fang J, Seki T and Maeda H: Therapeutic
strategies by modulating oxygen stress in cancer and inflammation.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:290–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fruehauf JP and Meyskens FL Jr: Reactive
oxygen species: a breath of life or death? Clin Cancer Res.
13:789–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Day BJ: Catalytic antioxidants: A radical
approach to new therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 9:557–566. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nikitaki Z, Hellweg CE, Georgakilas AG and
Ravanat JL: Stress-induced DNA damage biomarkers: applications and
limitations. Front Chem. 3:352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Aziz K, Nowsheen S, Pantelias G, Iliakis
G, Gorgoulis VG and Georgakilas AG: Targeting DNA damage and
repair: embracing the pharmacological era for successful cancer
therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 133:334–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Smolarz B, Wilczyński J and Nowakowska D:
DNA repair mechanisms and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection.
Folia Microbiol (Praha). 60:199–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Mailand N, Gibbs-Seymour I and
Bekker-Jensen S: Regulation of PCNA-protein interactions for genome
stability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:269–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Koundrioukoff S, Jónsson ZO, Hasan S, de
Jong RN, van der Vliet PC, Hottiger MO and Hübscher U: A direct
interaction between proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and
Cdk2 targets PCNA-interacting proteins for phosphorylation. J Biol
Chem. 275:22882–22887. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D and Stillman B:
The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA
replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 369:574–578. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Witko-Sarsat V, Mocek J, Bouayad D,
Tamassia N, Ribeil JA, Candalh C, Davezac N, Reuter N, Mouthon L,
Hermine O, et al: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen acts as a
cytoplasmic platform controlling human neutrophil survival. J Exp
Med. 207:2631–2645. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature.
389:300–305. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mirza A, Wu Q, Wang L, McClanahan T,
Bishop WR, Gheyas F, Ding W, Hutchins B, Hockenberry T, Kirschmeier
P, et al: Global transcriptional program of p53 target genes during
the process of apoptosis and cell cycle progression. Oncogene.
22:3645–3654. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhao R, Gish K, Murphy M, Yin Y, Notterman
D, Hoffman WH, Tom E, Mack DH and Levine AJ: Analysis of
p53-regulated gene expression patterns using oligonucleotide
arrays. Genes Dev. 14:981–993. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: Dissecting
p53-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 13:994–1002. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Culmsee C and Mattson MP: p53 in neuronal
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:761–777. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Morris GF, Bischoff JR and Mathews MB:
Transcriptional activation of the human proliferating-cell nuclear
antigen promoter by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:895–899. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shivakumar CV, Brown DR, Deb S and Deb SP:
Wild-type human p53 transactivates the human proliferating cell
nuclear antigen promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 15:6785–6793. 1995z.
View Article : Google Scholar
|