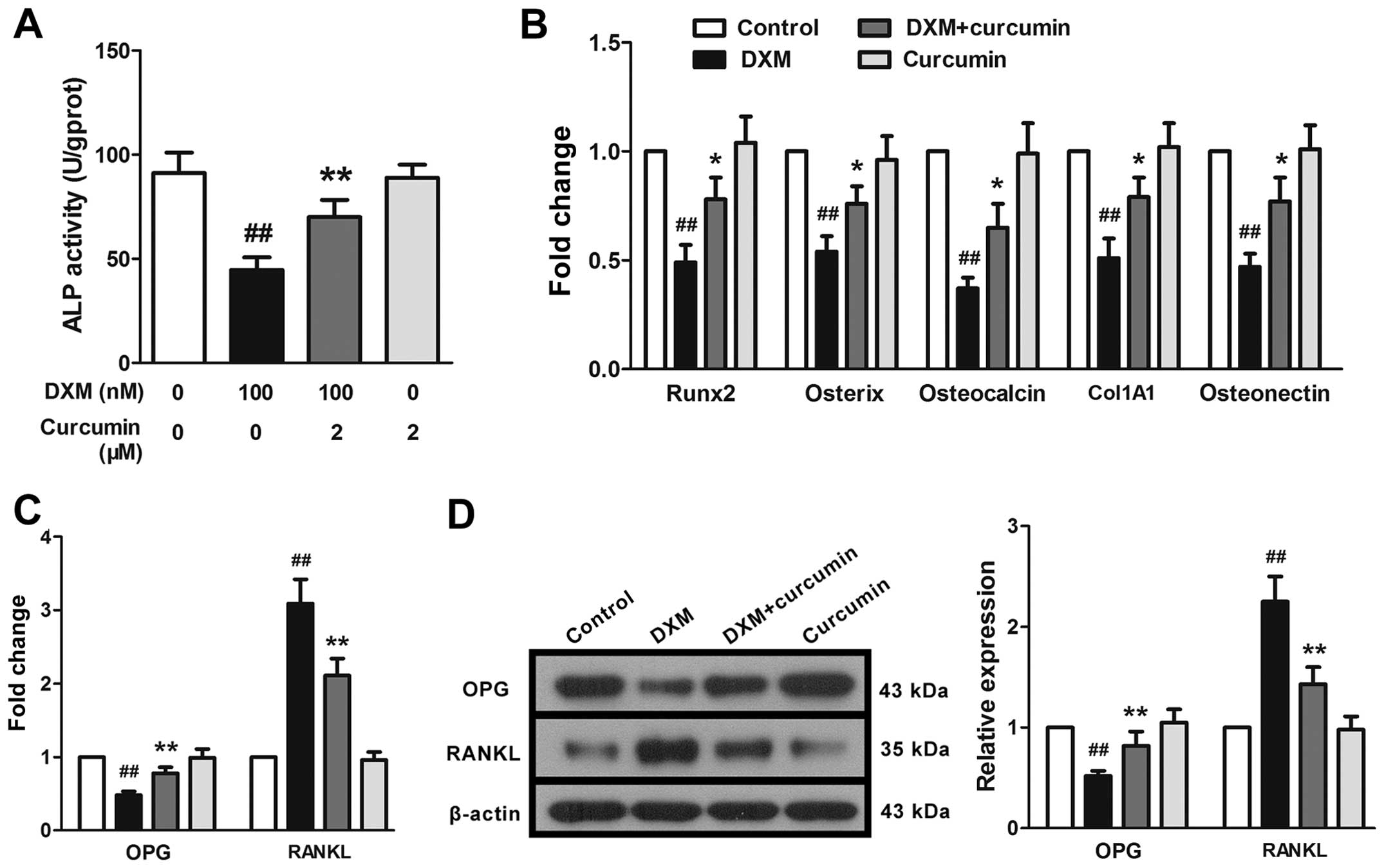
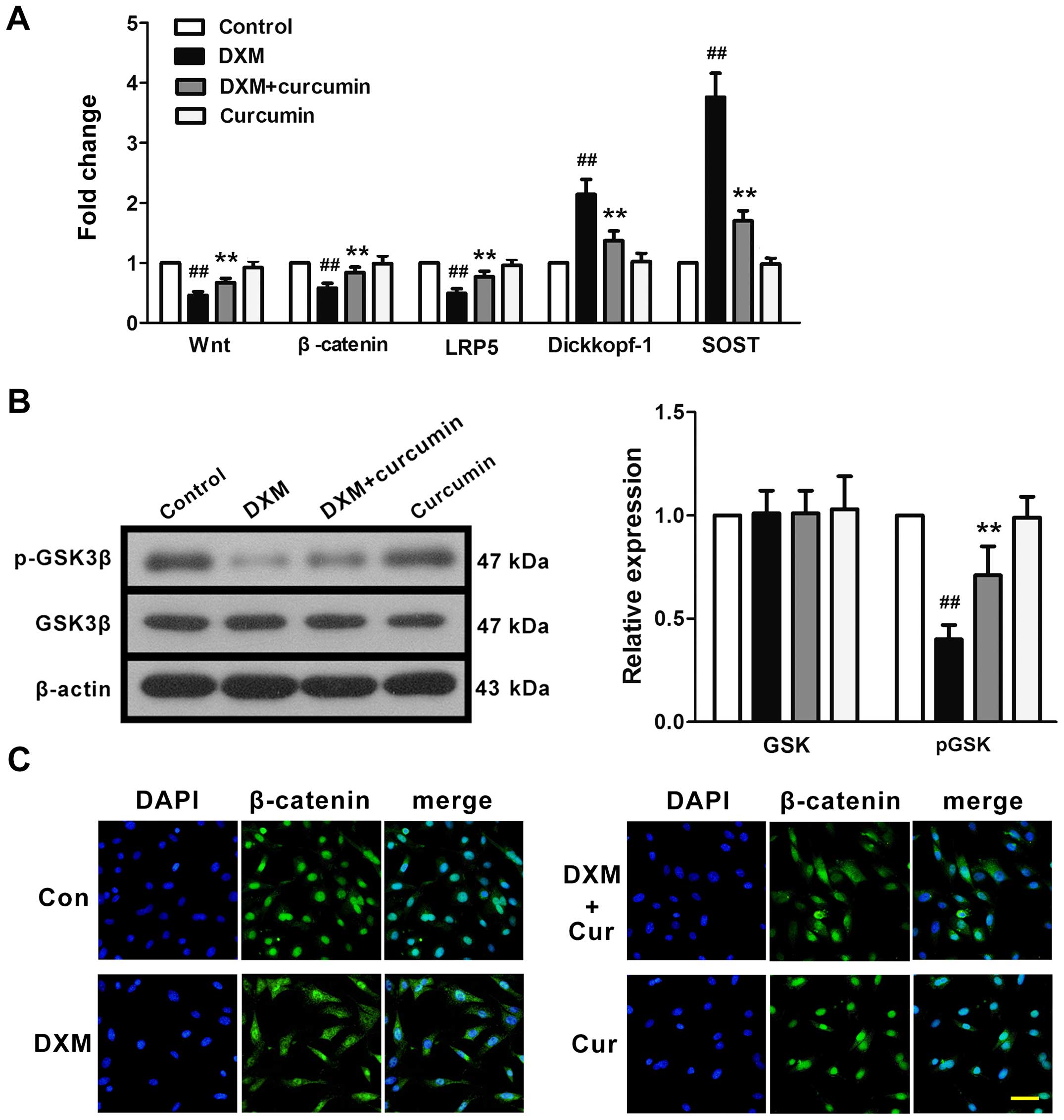
|
1
|
Buttgereit F, Burmester GR and Lipworth
BJ: Optimised glucocorticoid therapy: the sharpening of an old
spear. Lancet. 365:801–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
den Uyl D, Bultink IE and Lems WF:
Advances in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Curr Rheumatol
Rep. 13:233–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hallberg I, Bachrach-Lindström M, Hammerby
S, Toss G and Ek AC: Health-related quality of life after vertebral
or hip fracture: a seven-year follow-up study. BMC Musculoskelet
Disord. 10:1352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Ensrud KC, Scott
JC and Black D: Risk of mortality following clinical fractures.
Osteoporos Int. 11:556–561. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weinstein RS: Glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2:65–73. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Recommendations for the prevention and
treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: 2001 update.
American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis. Arthritis Rheum. 44:1496–1503.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Adler RA and Hochberg MC: Suggested
guidelines for evaluation and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis for the Department of Veterans Affairs. Arch Intern
Med. 163:2619–2624. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nawata H, Soen S, Takayanagi R, Tanaka I,
Takaoka K, Fukunaga M, Matsumoto T, Suzuki Y, Tanaka H, Fujiwara S,
et al: Guidelines on the management and treatment of
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis of the Japanese Society for
Bone and Mineral Research (2004). J Bone Miner Metab. 23:105–109.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sambrook PN, Diamond T, Ferris L,
Fiatarone-Singh M, Flicker L, MacLennan A, Nowson C, O'Neill S and
Greville H; Osteoporosis Australia; National Asthma Campaign:
Corticosteroid induced osteoporosis. Guidelines for treatment. Aust
Fam Physician. 30:793–796. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lestari ML and Indrayanto G: Curcumin.
Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol. 39:113–204. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jurenka JS: Anti-inflammatory properties
of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of
preclinical and clinical research. Altern Med Rev. 14:141–153.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim WK, Ke K, Sul OJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Lee
MH, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Chung HT and Choi HS: Curcumin protects against
ovariectomy-induced bone loss and decreases osteoclastogenesis. J
Cell Biochem. 112:3159–3166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Folwarczna J, Zych M and Trzeciak HI:
Effects of curcumin on the skeletal system in rats. Pharmacol Rep.
62:900–909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hussan F, Ibraheem NG, Kamarudin TA, Shuid
AN, Soelaiman IN and Othman F: Curcumin protects against
ovariectomy-induced bone changes in rat model. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:1749162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho DC, Jung HS, Kim KT, Jeon Y, Sung JK
and Hwang JH: Therapeutic advantages of treatment of high-dose
curcumin in the ovariectomized rat. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
54:461–466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang MW, Wang TH, Yan PP, Chu LW, Yu J,
Gao ZD, Li YZ and Guo BL: Curcumin improves bone microarchitecture
and enhances mineral density in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Phytomedicine. 18:205–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen Z, Xue J, Shen T, Ba G, Yu D and Fu
Q: Curcumin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by
protecting osteoblasts from apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. Oct 30–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: a
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Glass DA II, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M,
Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA and
Karsenty G: Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts
controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 8:751–764. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song L, Liu M, Ono N, Bringhurst FR,
Kronenberg HM and Guo J: Loss of wnt/β-catenin signaling causes
cell fate shift of preosteoblasts from osteoblasts to adipocytes. J
Bone Miner Res. 27:2344–2358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pinson KI, Brennan J, Monkley S, Avery BJ
and Skarnes WC: An LDL-receptor-related protein mediates Wnt
signalling in mice. Nature. 407:535–538. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, Spokony R, Liu
C, Katsuyama Y, Hess F, Saint-Jeannet JP and He X:
LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature.
407:530–535. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G,
Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, et
al: Osteoporosis-Pseudoglioma Syndrome Collaborative Group: LDL
receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye
development. Cell. 107:513–523. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Little RD, Carulli JP, Del Mastro RG,
Dupuis J, Osborne M, Folz C, Manning SP, Swain PM, Zhao SC, Eustace
B, et al: A mutation in the LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene
results in the autosomal dominant high-bone-mass trait. Am J Hum
Genet. 70:11–19. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L,
Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K and Lifton RP: High bone
density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl
J Med. 346:1513–1521. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tiwari SK, Agarwal S, Seth B, Yadav A,
Nair S, Bhatnagar P, Karmakar M, Kumari M, Chauhan LK, Patel DK, et
al: Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles potently induce adult
neurogenesis and reverse cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease
model via canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. ACS Nano. 8:76–103.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tiwari SK, Agarwal S, Tripathi A and
Chaturvedi RK: Bisphenol-A mediated inhibition of hippocampal
neurogenesis attenuated by curcumin via canonical Wnt pathway. Mol
Neurobiol. May 12–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen F, Wang H, Xiang X, Yuan J, Chu W,
Xue X, Zhu H, Ge H, Zou M, Feng H and Lin J: Curcumin increased the
differentiation rate of neurons in neural stem cells via wnt
signaling in vitro study. J Surg Res. 192:298–304. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He M, Li Y, Zhang L, Li L, Shen Y, Lin L,
Zheng W, Chen L, Bian X, Ng HK and Tang L: Curcumin suppresses cell
proliferation through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in medulloblastoma. Oncol Rep. 32:173–180. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui L, Jia X, Zhou Q, Zhai X, Zhou Y and
Zhu H: Curcumin affects β-catenin pathway in hepatic stellate cell
in vitro and in vivo. J Pharm Pharmacol. 66:1615–1622. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Albaum JM, Levesque LE, Gershon AS, Liu G
and Cadarette SM: Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis management
among seniors, by year, sex, and indication, 1996–2012. Osteoporos
Int. 26:2845–2852. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baofeng L, Zhi Y, Bei C, Guolin M,
Qingshui Y and Jian L: Characterization of a rabbit osteoporosis
model induced by ovariectomy and glucocorticoid. Acta Orthop.
81:396–401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Castañeda S, Calvo E, Largo R,
González-González R, de la Piedra C, Díaz-Curiel M and
Herrero-Beaumont G: Characterization of a new experimental model of
osteoporosis in rabbits. J Bone Miner Metab. 26:53–59. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Reid IR, Evans MC, Wattie DJ, Ames R and
Cundy TF: Bone mineral density of the proximal femur and lumbar
spine in glucocorticoid-treated asthmatic patients. Osteoporos Int.
2:103–105. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sambrook P, Birmingham J, Kempler S, Kelly
P, Eberl S, Pocock N, Yeates M and Eisman J: Corticosteroid effects
on proximal femur bone loss. J Bone Miner Res. 5:1211–1216. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Feng M, Zhang R, Gong F, Yang P, Fan L, Ni
J, Bi W, Zhang Y, Wang C and Wang K: Protective effects of
necrostatin-1 on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rats. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 144B:455–462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Samir SM and Malek HA: Effect of
cannabinoid receptors 1 modulation on osteoporosis in a rat model
of different ages. J Physiol Pharmacol. 65:687–694. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ehrlich PJ and Lanyon LE: Mechanical
strain and bone cell function: a review. Osteoporos Int.
13:688–700. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Laan RF, Buijs WC, van Erning LJ, Lemmens
JA, Corstens FH, Ruijs SH, van de Putte LB and van Riel PL:
Differential effects of glucocorticoids on cortical appendicular
and cortical vertebral bone mineral content. Calcif Tissue Int.
52:5–9. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reid IR and Heap SW: Determinants of
vertebral mineral density in patients receiving long-term
glucocorticoid therapy. Arch Intern Med. 150:2545–2548. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim HJ, Zhao H, Kitaura H, Bhattacharyya
S, Brewer JA, Muglia LJ, Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL: Glucocorticoids
suppress bone formation via the osteoclast. J Clin Invest.
116:2152–2160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miyazaki T, Matsunaga T, Miyazaki S,
Hokari S and Komoda T: Changes in receptor activator of nuclear
factor-kappaB, and its ligand, osteoprotegerin, bone-type alkaline
phosphatase, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in
ovariectomized rats. J Cell Biochem. 93:503–512. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wysokinski D, Pawlowska E and Blasiak J:
RUNX2: A master bone growth regulator that may be involved in the
DNA damage response. DNA Cell Biol. 34:305–315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sinha KM and Zhou X: Genetic and molecular
control of osterix in skeletal formation. J Cell Biochem.
114:975–984. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Komori T: Regulation of skeletal
development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J Cell
Biochem. 95:445–453. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z,
Deng JM, Behringer RR and de Crombrugghe B: The novel zinc
finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 108:17–29.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Feng JQ, Dusevich VM,
Sinha K, Zhang H, Darnay BG and de Crombrugghe B: Multiple
functions of Osterix are required for bone growth and homeostasis
in postnatal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:12919–12924. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi
K, Kinosaki M, Goto M, Mochizuki SI, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Udagawa
N, et al: A novel molecular mechanism modulating osteoclast
differentiation and function. Bone. 25:109–113. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsuda E, Goto M, Mochizuki S, Yano K,
Kobayashi F, Morinaga T and Higashio K: Isolation of a novel
cytokine from human fibroblasts that specifically inhibits
osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 234:137–142. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Buckley KA and Fraser WD: Receptor
activator for nuclear factor kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin:
regulators of bone physiology and immune responses/potential
therapeutic agents and biochemical markers. Ann Clin Biochem.
39:551–556. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kim JH, Liu X, Wang J, Chen X, Zhang H,
Kim SH, Cui J, Li R, Zhang W, Kong Y, et al: Wnt signaling in bone
formation and its therapeutic potential for bone diseases. Ther Adv
Musculoskelet Dis. 5:13–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rossini M, Gatti D and Adami S:
Involvement of WNT/β-catenin signaling in the treatment of
osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 93:121–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Amrein K, Amrein S, Drexler C, Dimai HP,
Dobnig H, Pfeifer K, Tomaschitz A, Pieber TR and Fahrleitner-Pammer
A: Sclerostin and its association with physical activity, age,
gender, body composition, and bone mineral content in healthy
adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:148–154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sheng Z, Tong D, Ou Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z,
Li S, Zhou J, Zhang J and Liao E: Serum sclerostin levels were
positively correlated with fat mass and bone mineral density in
central south Chinese postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
76:797–801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sutherland MK, Geoghegan JC, Yu C, Winkler
DG and Latham JA: Unique regulation of SOST, the sclerosteosis
gene, by BMPs and steroid hormones in human osteoblasts. Bone.
35:448–454. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yao W, Cheng Z, Pham A, Busse C,
Zimmermann EA, Ritchie RO and Lane NE: Glucocorticoid-induced bone
loss in mice can be reversed by the actions of parathyroid hormone
and risedronate on different pathways for bone formation and
mineralization. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3485–3497. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A and
Aaronson SA: Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated
by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat Cell Biol.
3:683–686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rawadi G, Vayssière B, Dunn F, Baron R and
Roman-Roman S: BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and
osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner
Res. 18:1842–1853. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mak W, Shao X, Dunstan CR, Seibel MJ and
Zhou H: Biphasic glucocorticoid-dependent regulation of Wnt
expression and its inhibitors in mature osteoblastic cells. Calcif
Tissue Int. 85:538–545. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ohnaka K, Taniguchi H, Kawate H, Nawata H
and Takayanagi R: Glucocorticoid enhances the expression of
dickkopf-1 in human osteoblasts: novel mechanism of
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
318:259–264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang FS, Ko JY, Yeh DW, Ke HC and Wu HL:
Modulation of Dickkopf-1 attenuates glucocorticoid induction of
osteoblast apoptosis, adipocytic differentiation, and bone mass
loss. Endocrinology. 149:1793–1801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lin X, Farooqi AA and Ismail M: Recent
progress in fungus-derived bioactive agents for targeting of
signaling machinery in cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther.
9:1797–1804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang FS, Chuang PC, Lin CL, Chen MW, Ke
HJ, Chang YH, Chen YS, Wu SL and Ko JY: MicroRNA-29a protects
against glucocorticoid-induced bone loss and fragility in rats by
orchestrating bone acquisition and resorption. Arthritis Rheum.
65:1530–1540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Smith E and Frenkel B: Glucocorticoids
inhibit the transcriptional activity of LEF/TCF in differentiating
osteoblasts in a glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-dependent and
-independent manner. J Biol Chem. 280:2388–2394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wang FS, Ko JY, Weng LH, Yeh DW, Ke HJ and
Wu SL: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta attenuates
glucocorticoid-induced bone loss. Life Sci. 85:685–692. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|