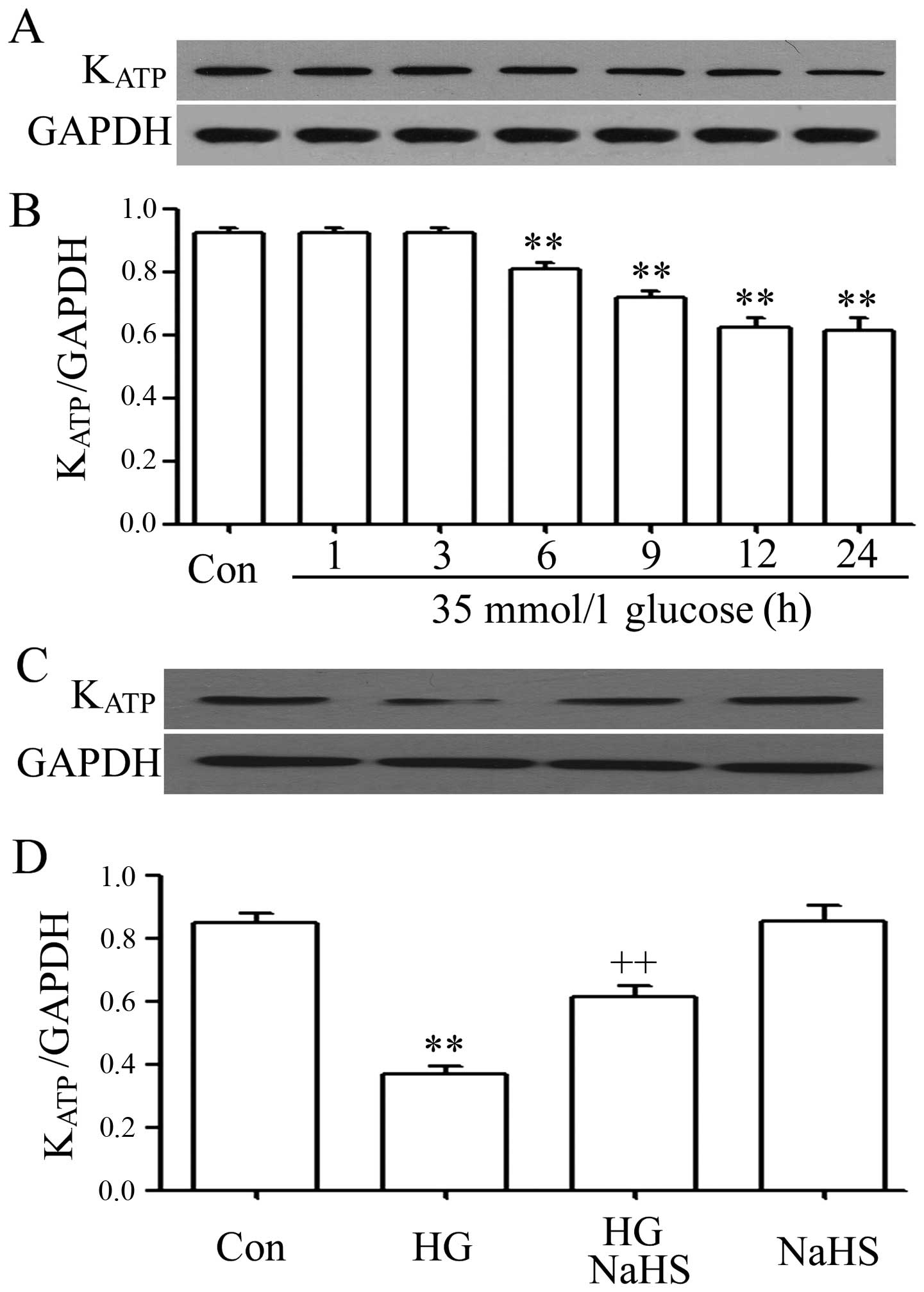
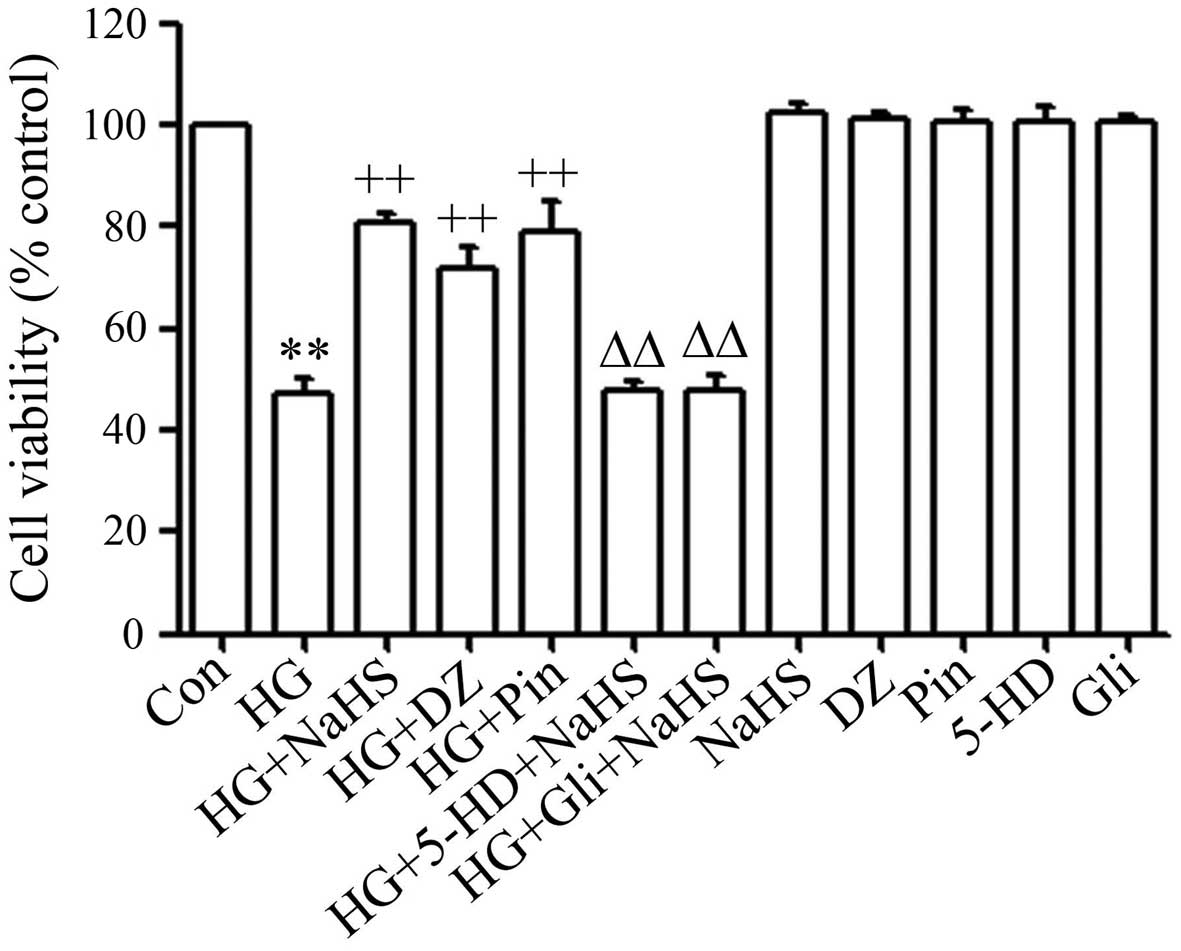
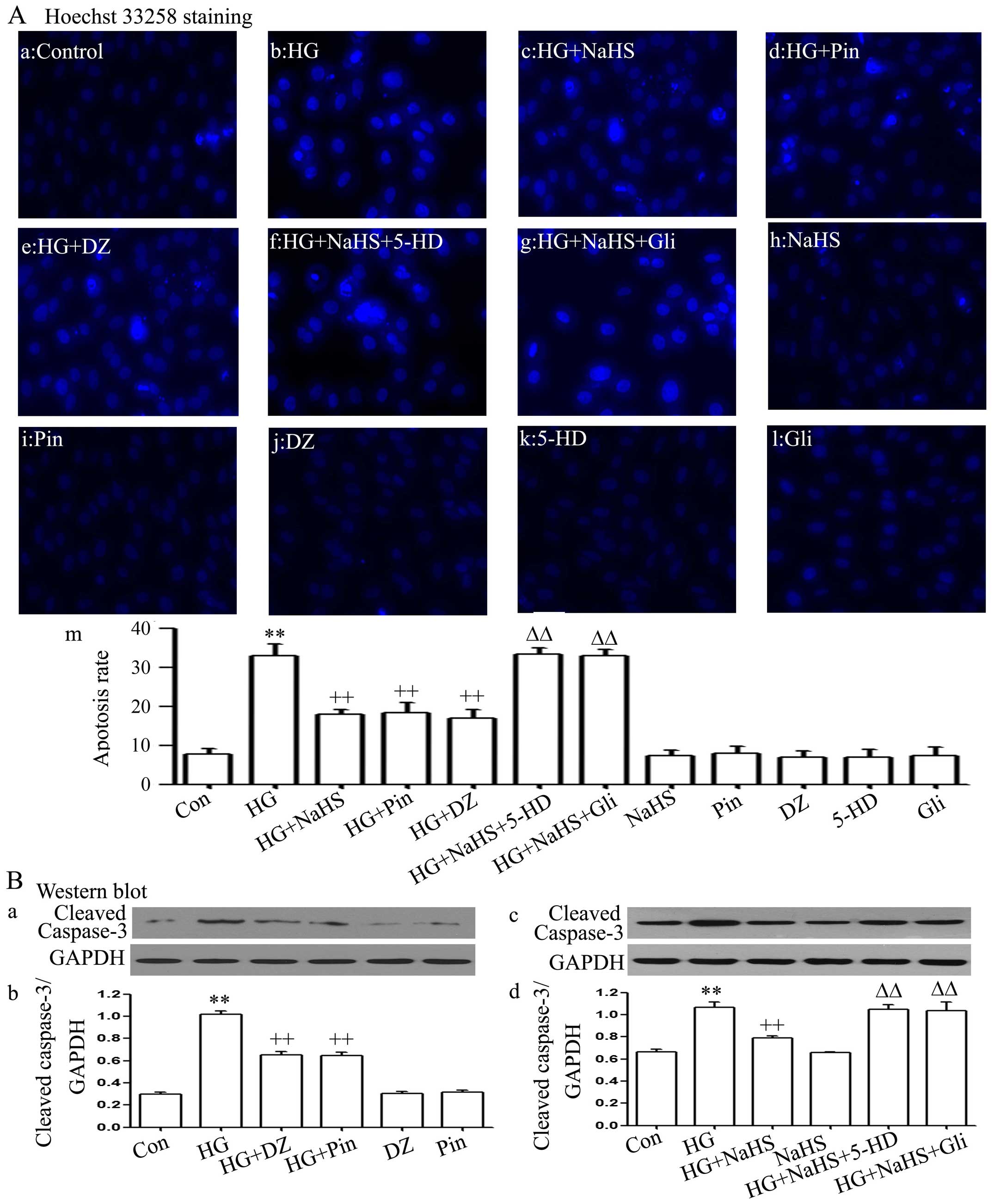
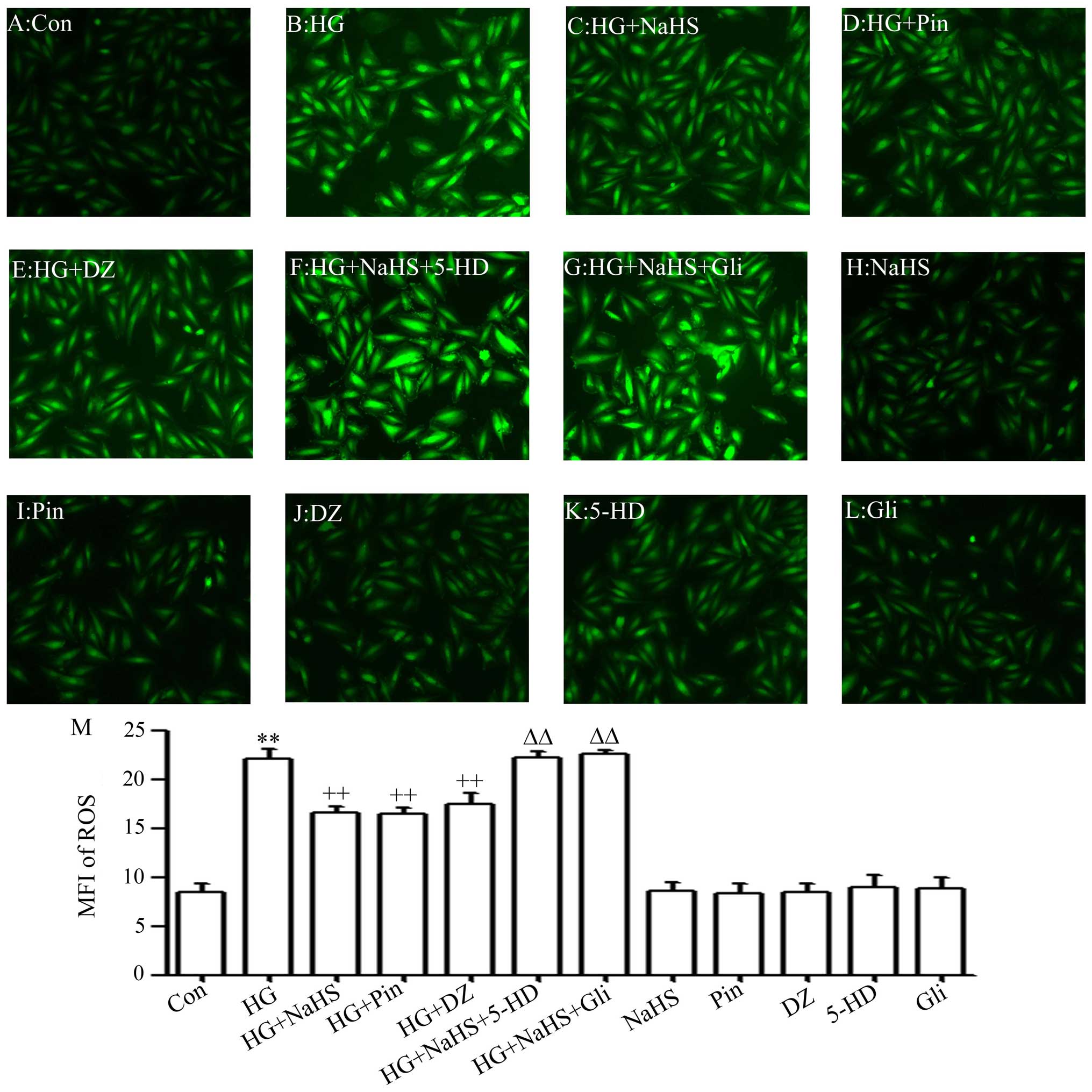
|
1
|
Wang R: Two's company, three's a crowd:
can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter?
FASEB J. 16:1792–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fiorucci S, Distrutti E, Cirino G and
Wallace JL: The emerging roles of hydrogen sulfide in the
gastrointestinal tract and liver. Gastroenterology. 131:259–271.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Szabo C: Hydrogen sulphide and its
therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:917–935. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li L and Moore PK: Putative biological
roles of hydrogen sulfide in health and disease: a breath of not so
fresh air? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:84–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jain SK, Bull R, Rains JL, Bass PF, Levine
SN, Reddy S, McVie R and Bocchini JA Jr: Low levels of hydrogen
sulfide in the blood of diabetes patients and
streptozotocin-treated rats causes vascular inflammation? Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1333–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Whiteman M, Gooding KM, Whatmore JL, Ball
CI, Mawson D, Skinner K, Tooke JE and Shore AC: Adiposity is a
major determinant of plasma levels of the novel vasodilator
hydrogen sulphide. Diabetologia. 53:1722–1726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calvert JW, Elston M, Nicholson CK,
Gundewar S, Jha S, Elrod JW, Ramachandran A and Lefer DJ: Genetic
and pharmacologic hydrogen sulfide therapy attenuates
ischemia-induced heart failure in mice. Circulation. 122:11–19.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Wang Q, Guo W and Zhu YZ: Hydrogen
sulfide attenuates cardiac dysfunction in a rat model of heart
failure: a mechanism through cardiac mitochondrial protection.
Biosci Rep. 31:87–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu MH,
Liu LS and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide, the next potent preventive
and therapeutic agent in aging and age-associated diseases. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:1104–1113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen SL, Yang CT, Yang ZL, Guo RX, Meng
JL, Cui Y, Lan AP, Chen PX and Feng JQ: Hydrogen sulphide protects
H9c2 cells against chemical hypoxia-induced injury. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 37:316–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang Z, Yang C, Xiao L, Liao X, Lan A,
Wang X, Guo R, Chen P, Hu C and Feng J: Novel insights into the
role of HSP90 in cytoprotection of H2S against chemical
hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cardiac myocytes. Int J Mol Med.
28:397–403. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang XY, Yang CT, Zheng DD, Mo LQ, Lan AP,
Yang ZL, Hu F, Chen PX, Liao XX and Feng JQ: Hydrogen sulfide
protects H9c2 cells against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell
Biochem. 363:419–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guo R, Lin J, Xu W, Shen N, Mo L, Zhang C
and Feng J: Hydrogen sulfide attenuates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity by inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway in H9c2 cells.
Int J Mol Med. 31:644–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J, Mo L, Hua X, Zheng D,
Chen P, Chen G, Xu W and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity
by inhibiting p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1668–1680. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Suzuki K, Olah G, Modis K, Coletta C, Kulp
G, Gero D, Szoleczky P, Chang T, Zhou Z, Wu L, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide replacement therapy protects the vascular endothelium in
hyperglycemia by preserving mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:13829–13834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahmad FU, Sattar MA, Rathore HA, Abdullah
MH, Tan S, Abdullah NA and Johns EJ: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
(H2S) reduces blood pressure and prevents the
progression of diabetic nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Ren Fail. 34:203–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Peake BF, Nicholson CK, Lambert JP, Hood
RL, Amin H, Amin S and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide preconditions
the db/db diabetic mouse heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury
by activating Nrf2 signaling in an Erk-dependent manner. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1215–H1224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao Y, Yao X, Zhang Y, Li W, Kang K, Sun L
and Sun X: The protective role of hydrogen sulfide in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in diabetic rats. Int J
Cardiol. 152:177–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu W, Wu W, Chen J, Guo R, Lin J, Liao X
and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury by inhibiting the activities of
the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Mol Med. 32:917–925.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhuang XD, Hu X, Long M, Dong XB, Liu DH
and Liao XX: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates high
glucose-induced cardiotoxicity via inhibition of leptin signaling
in H9c2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 391:147–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu W, Chen J, Lin J, Liu D, Mo L, Pan W,
Feng J, Wu W and Zheng D: Exogenous H2S protects H9c2
cardiac cells against high glucose-induced injury and inflammation
by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and IL-1β pathways. Int J
Mol Med. 35:177–186. 2015.
|
|
22
|
Geng B, Yang J, Qi Y, Zhao J, Pang Y, Du J
and Tang C: H2S generated by heart in rat and its
effects on cardiac function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:362–368. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, Feng ZN, Ali MY,
Zhou S and Moore PK: Role of hydrogen sulfide in the
cardioprotection caused by ischemic preconditioning in the rat
heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 316:670–678.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H(2)S as a novel endogenous gaseous K(ATP)
channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eisen A, Fisman EZ, Rubenfire M, Freimark
D, McKechnie R, Tenenbaum A, Motro M and Adler Y: Ischemic
preconditioning: nearly two decades of research. A comprehensive
review. Atherosclerosis. 172:201–210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akao M, Ohler A, O'Rourke B and Marban E:
Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels inhibit apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress in cardiac cells. Circ Res.
88:1267–1275. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamada S, Kane GC, Behfar A, Liu XK, Dyer
RB, Faustino RS, Miki T, Seino S and Terzic A: Protection conferred
by myocardial ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pressure
overload-induced congestive heart failure revealed in KCNJ11
Kir6.2-null mutant. J Physiol. 577:1053–1065. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zingman LV, Alekseev AE, Hodgson-Zingman
DM and Terzic A: ATP-sensitive potassium channels: Metabolic
sensing and cardioprotection. J Appl Physiol. 103:1888–1893. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sierra A, Zhu Z, Sapay N, Sharotri V,
Kline CF, Luczak ED, Subbotina E, Sivaprasadarao A, Snyder PM,
Mohler PJ, et al: Regulation of cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium
channel surface expression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein
kinase II. J Biol Chem. 288:1568–1581. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Nichols CG and Lederer WJ: Adenosine
triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in the cardiovascular
system. Am J Physiol. 261:H1675–H1686. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Noma A: ATP-regulated K+
channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 305:147–148. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garlid KD, Paucek P, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Sun
X and Schindler PA: The mitochondrial KATP channel as a receptor
for potassium channel openers. Biol Chem. 271:8796–8799. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Sato T, O'Rourke B and Marban E:
Mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channels: novel effectors of
cardioprotection? Circulation. 97:2463–2469. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Findlay I: Interactive regulation of the
ATP-sensitive potassium channel of cardiac muscle. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 24:S6–S11. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
López JR, Ghanbari RA and Terzic A: A KATP
channel opener protects cardiomyocytes from Ca2 waves: a
laser confocal microscopy study. Am J Physiol. 270:H1384–H1389.
1996.
|
|
36
|
Grover GJ: Pharmacology of ATP-sensitive
potassium channel (KATP) openers in models of myocardial ischemia
and reperfusion. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 75:309–315. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Holmuhamedov EL, Jovanović S, Dzeja PP,
Jovanović A and Terzic A: Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+
channels modulate cardiac mitochondrial function. Am J Physiol.
275:H1567–H1576. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yellon DM and Downey JM: Preconditioning
the myocardium: from cellular physiology to clinical cardiology.
Physiol Rev. 83:1113–1151. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gross GJ and Peart JN: KATP channels and
myocardial preconditioning: an update. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 285:H921–H930. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weintraub NL: Impaired hypoxic coronary
vasodilation and ATP-sensitive potassium channel function: a
manifestation of diabetic microangiopathy in humans? Circ Res.
92:127–129. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miura H, Wachtel RE, Loberiza FR Jr, Saito
T, Miura M, Nicolosi AC and Gutterman DD: Diabetes mellitus impairs
vasodilation to hypoxia in human coronary arterioles: reduced
activity of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Circ Res. 92:151–158.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kinoshita H, Azma T, Nakahata K, Iranami
H, Kimoto Y, Dojo M, Yuge O and Hatano Y: Inhibitory effect of high
concentration of glucose on relaxations to activation of
ATP-sensitive K+ channels in human omental artery.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:2290–2295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kinoshita H, Azma T, Iranami H, Nakahata
K, Kimoto Y, Dojo M, Yuge O and Hatano Y: Synthetic peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists restore impaired
vasorelaxation via ATP-sensitive K+ channels by high
glucose. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 318:312–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Seino S and Miki T: Physiological and
pathophysiological roles of ATP-sensitive K+ channels.
Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 81:133–176. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Flagg TP, Enkvetchakul D, Koster JC and
Nichols CG: Muscle KATP channels: recent insights to
energy sensing and myoprotection. Physiol Rev. 90:799–829. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zingman LV, Zhu Z, Sierra A, Stepniak E,
Burnett CM, Maksymov G, Anderson ME, Coetzee WA and Hodgson-Zingman
DM: Exercise-induced expression of cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium
channels promotes action potential shortening and energy
conservation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:72–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu Z, Burnett CM, Maksymov G, Stepniak E,
Sierra A, Subbotina E, Anderson ME, Coetzee WA, Hodgson-Zingman DM
and Zingman LV: Reduction in number of sarcolemmal KATP channels
slows cardiac action potential duration shortening under hypoxia.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:637–641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pearson ER, Flechtner I, Njølstad PR,
Malecki MT, Flanagan SE, Larkin B, Ashcroft FM, Klimes I, Codner E,
Iotova V, et al: Switching from insulin to oral sulfonylureas in
patients with diabetes due to Kir6.2 mutations. N Engl J Med.
355:467–477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Han H, Wang J, Wang H, Yang B and
Wang Z: Impairment of human ether-à-go-go-related gene (HERG)
K+ channel function by hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Similar phenotypes but different mechanisms. J Biol Chem.
278:10417–10426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Smogorzewski M, Galfayan V and Massry SG:
High glucose concentration causes a rise in [Ca2+]i of
cardiac myocytes. Kidney Int. 53:1237–1243. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gribble FM and Reimann F: Sulphonylurea
action revisited: the post-cloning era. Diabetologia. 46:875–891.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Trube G, Rorsman P and Ohno-Shosaku T:
Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent
K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers
Arch. 407:493–499. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ozcan C, Bienengraeber M, Dzeja PP and
Terzic A: Potassium channel openers protect cardiac mitochondria by
attenuating oxidant stress at reoxygenation. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 282:H531–H539. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|