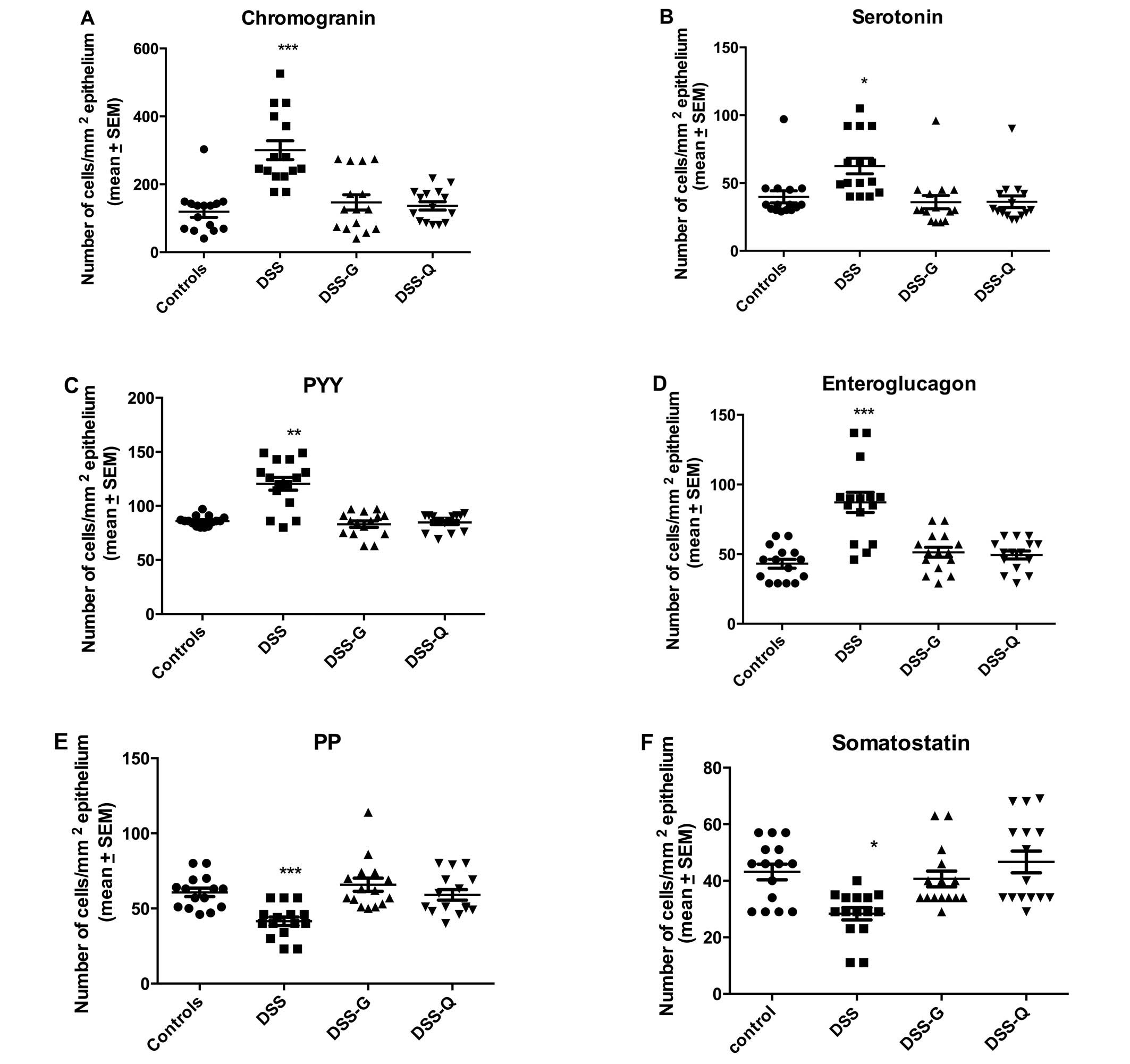
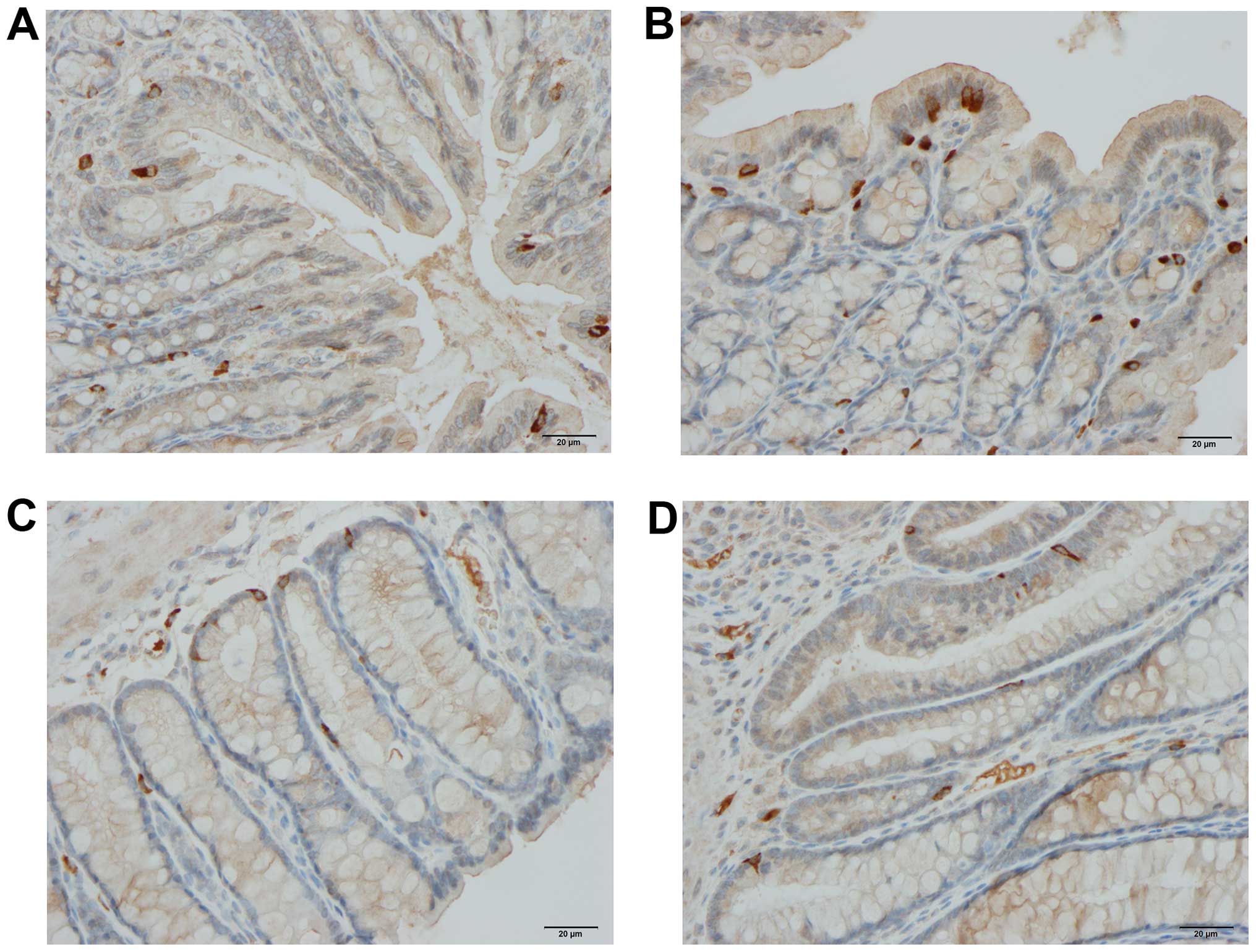
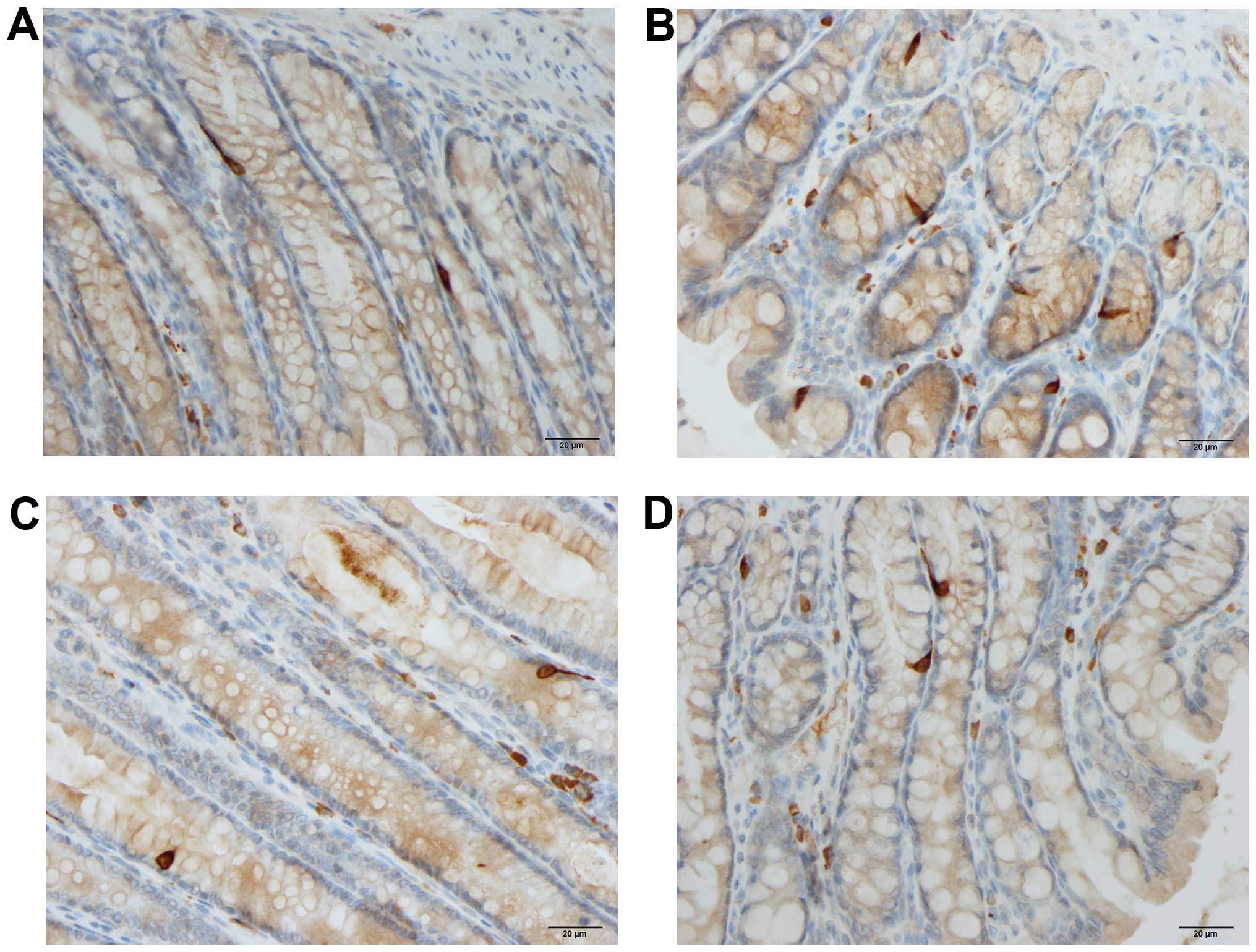
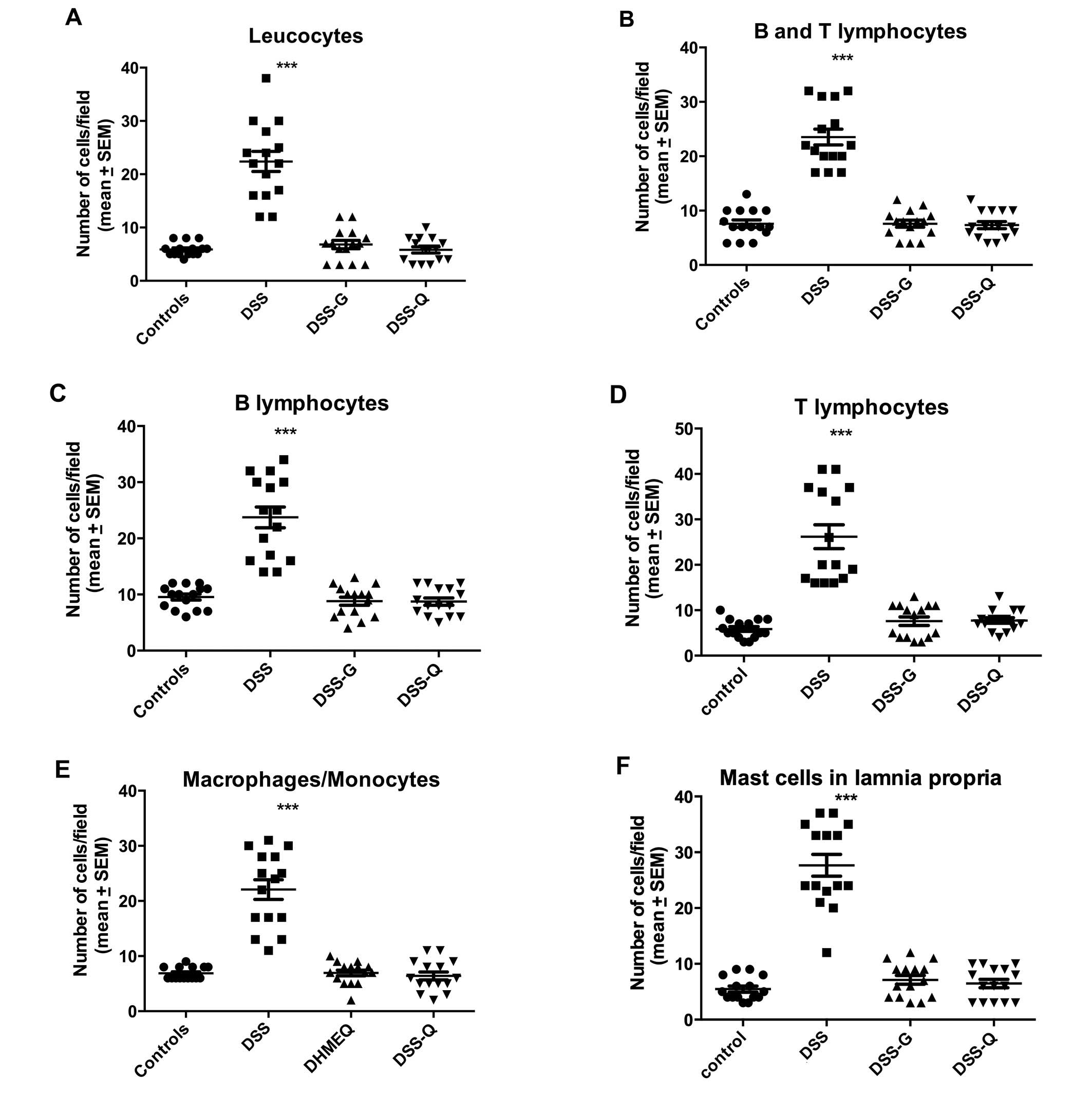
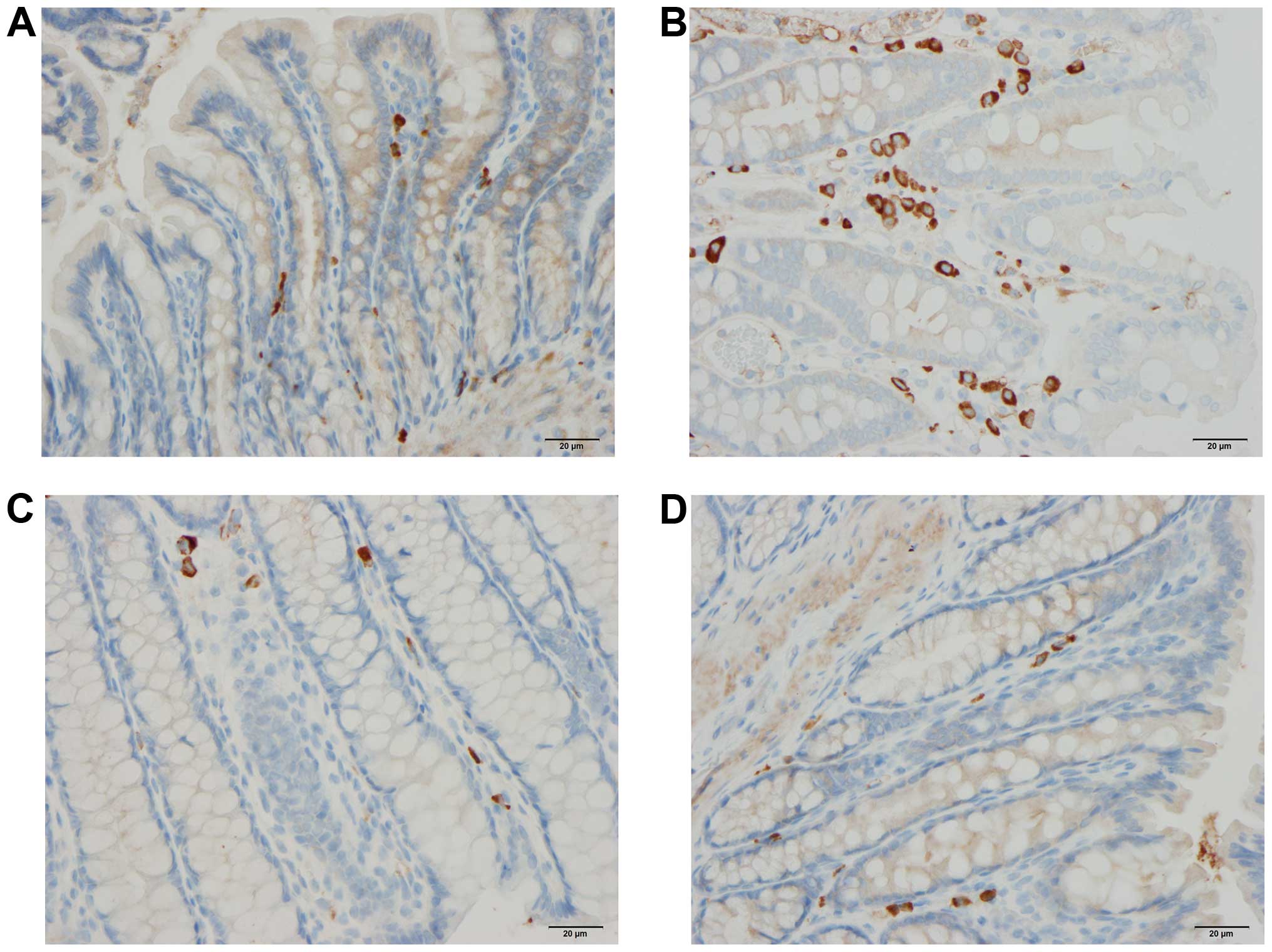
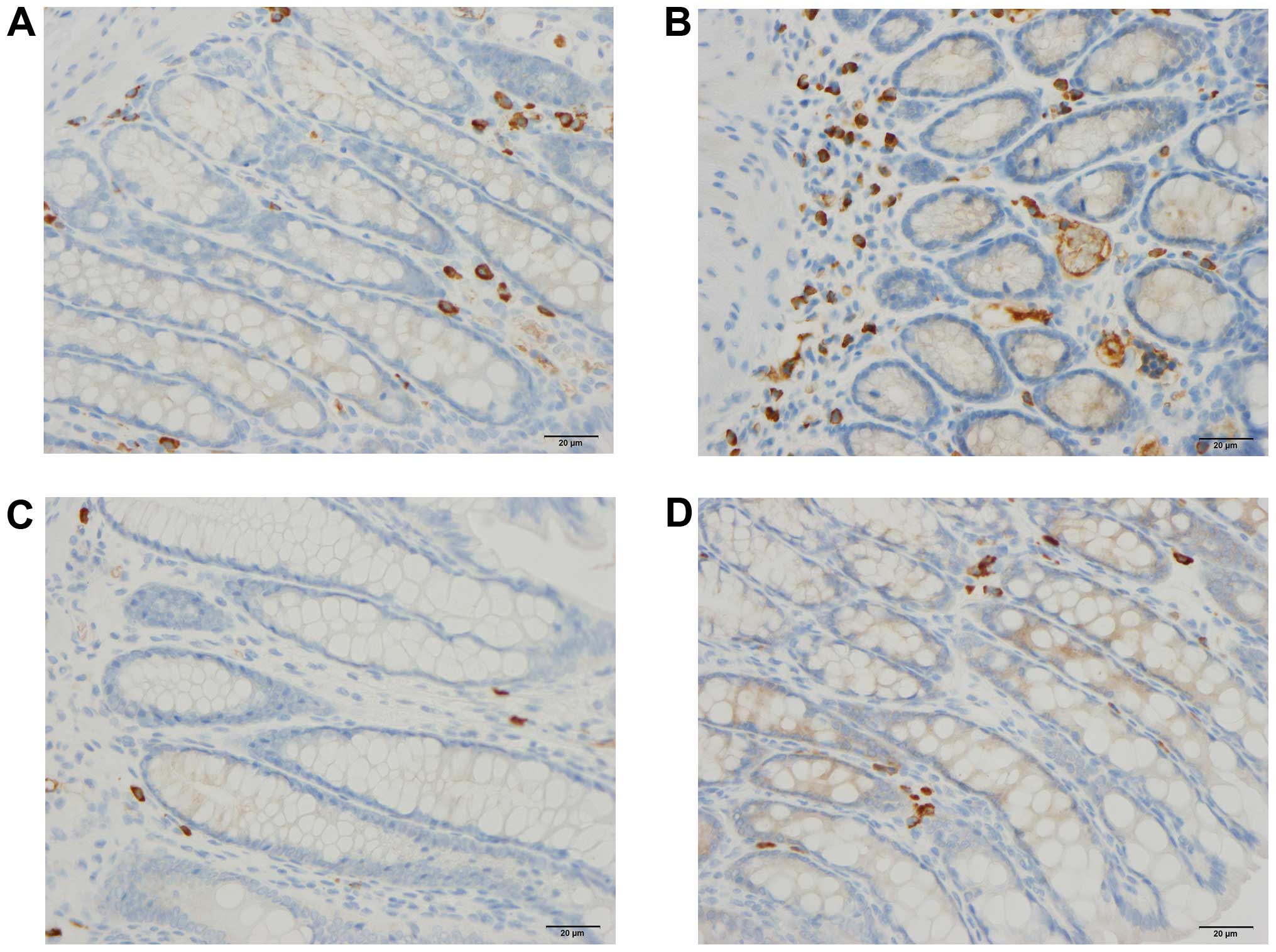
|
1
|
El-Salhy M, Danielsson A, Stenling R and
Grimelius L: Colonic endocrine cells in inflammatory bowel disease.
J Intern Med. 242:413–419. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Chromogranin A cell density as a diagnostic marker for
lymphocytic colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 57:3154–3159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: High densities of serotonin and peptide YY cells in the
colon of patients with lymphocytic colitis. World J Gastroenterol.
18:6070–6075. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
El-Salhy M, Lomholt-Beck B and Gundersen
TD: High chromogranin A cell density in the colon of patients with
lymphocytic colitis. Mol Med Rep. 4:603–605. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moran GW, Pennock J and McLaughlin JT:
Enteroendocrine cells in terminal ileal Crohn's disease. J Crohn's
Colitis. 6:871–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moran GW, Leslie FC and McLaughlin JT:
Crohn's disease affecting the small bowel is associated with
reduced appetite and elevated levels of circulating gut peptides.
Clin Nutr. 32:404–411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Besterman HS, Mallinson CN, Modigliani R,
Christofides ND, Pera A, Ponti V, Sarson DL and Bloom SR: Gut
hormones in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol.
18:845–852. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
El-Salhy M, Mazzawi T, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: The role of peptide YY in
gastrointestinal diseases and disorders (review). Int J Mol Med.
31:275–282. 2013.Review. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirotani Y, Mikajiri K, Ikeda K, Myotoku M
and Kurokawa N: Changes of the peptide YY levels in the intestinal
tissue of rats with experimental colitis following oral
administration of mesalazine and prednisolone. Yakugaku Zasshi.
128:1347–1353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vona-Davis LC and McFadden DW: NPY family
of hormones: clinical relevance and potential use in
gastrointestinal disease. Curr Top Med Chem. 7:1710–1720. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Salhy M, Suhr O and Danielsson A:
Peptide YY in gastrointestinal disorders. Peptides. 23:397–402.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tari A, Teshima H, Sumii K, Haruma K,
Ohgoshi H, Yoshihara M, Kajiyama G and Miyachi Y: Peptide YY
abnormalities in patients with ulcerative colitis. Jpn J Med.
27:49–55. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sciola V, Massironi S, Conte D, Caprioli
F, Ferrero S, Ciafardini C, Peracchi M, Bardella MT and Piodi L:
Plasma chromogranin a in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 15:867–871. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bishop AE, Pietroletti R, Taat CW,
Brummelkamp WH and Polak JM: Increased populations of endocrine
cells in Crohn's ileitis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol.
410:391–396. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manocha M and Khan WI: Serotonin and GI
Disorders: an update on clinical and experimental studies. Clin
Transl Gastroenterol. 3:e132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stoyanova II and Gulubova MV: Mast cells
and inflammatory mediators in chronic ulcerative colitis. Acta
Histochem. 104:185–192. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto H, Morise K, Kusugami K, Furusawa
A, Konagaya T, Nishio Y, Kaneko H, Uchida K, Nagai H, Mitsuma T, et
al: Abnormal neuropeptide concentration in rectal mucosa of
patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol.
31:525–532. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Payer J, Huorka M, Duris I, Mikulecky M,
Kratochvílová H, Ondrejka P and Lukác L: Plasma somatostatin levels
in ulcerative colitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 41:552–553.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watanabe T, Kubota Y, Sawada T and Muto T:
Distribution and quantification of somatostatin in inflammatory
disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 35:488–494. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koch TR, Carney JA, Morris VA and Go VL:
Somatostatin in the idiopathic inflammatory bowel diseases. Dis
Colon Rectum. 31:198–203. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khan WI and Ghia JE: Gut hormones:
emerging role in immune activation and inflammation. Clin Exp
Immunol. 161:19–27. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Margolis KG and Gershon MD: Neuropeptides
and inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
25:503–511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ota E, Takeiri M, Tachibana M, Ishikawa Y,
Umezawa K and Nishiyama S: Synthesis and biological evaluation of
molecular probes based on the 9-methylstreptimidone derivative
DTCM-glutarimide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:164–167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shibasaki S, Yamashita K, Goto R, Wakayama
K, Tsunetoshi Y, Zaitsu M, Igarashi R, Haga S, Ozaki M, Umezawa K
and Todo S: Immunosuppressive effects of DTCM-G, a novel inhibitor
of the mTOR downstream signaling pathway. Transplantation.
95:542–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Funakoshi T, Yamashita K, Ichikawa N,
Fukai M, Suzuki T, Goto R, Oura T, Kobayashi N, Katsurada T,
Ichihara S, et al: A novel NF-κB inhibitor,
dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, ameliorates inflammatory colonic
injury in mice. J Crohn's Colitis. 6:215–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
El-Salhy M, Umezawa K, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk
JG, Gundersen D and Hausken T: Amelioration of severe TNBS induced
colitis by novel AP-1 and NF-κB inhibitors in rats. Scientific
World Journal. 2014:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Takeiri M, Tachibana M, Kaneda A, Ito A,
Ishikawa Y, Nishiyama S, Goto R, Yamashita K, Shibasaki S, Hirokata
G, et al: Inhibition of macrophage activation and suppression of
graft rejection by DTCM-Glutarimide, a novel piperidine derived
from the antibiotic 9-methylstreptimidone. Inflamm Res. 60:879–888.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishikawa Y, Tachibana M, Matsui C, Obata
R, Umezawa K and Nishiyama S: Synthesis and biological evaluation
on novel analogs of 9-methylstreptimidone, an inhibitor of
NF-kappaB. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:1726–1728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ueki S, Yamashita K, Aoyagi T, Haga S,
Suzuki T, Itoh T, Taniguchi M, Shimamura T, Furukawa H, Ozaki M, et
al: Control of allograft rejection by applying a novel nuclear
factor-kappaB inhibitor, dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin.
Transplantation. 82:1720–1727. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Matsumoto N, Ariga A, To-e S, Nakamura H,
Agata N, Hirano S, Inoue J and Umezawa K: Synthesis of NF-kappaB
activation inhibitors derived from epoxyquinomicin C. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 10:865–869. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Umezawa N, Matsumoto N, Iwama S, Kato N
and Higuchi T: Facile synthesis of peptide-porphyrin conjugates:
towards artificial catalase. Bioorg Med Chem. 18:6340–6350. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
El-Salhy M, Gilja OH, Gundersen D,
Hatlebakk JG and Hausken T: Endocrine cells in the ileum of
patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol.
20:2383–2391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Hatlebakk JG and
Hausken T: Low-Grade inflammation in the rectum of patients with
sporadic irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep. 7:1081–1085.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS and
Riddell RH: Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease.
Gastroenterology. 109:1344–1367. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Low D, Nguyen DD and Mizoguchi E: Animal
models of ulcerative colitis and their application in drug
research. Drug Des Devel Ther. 7:1341–1357. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Spiller R: Serotonin and GI clinical
disorders. Neuropharmacology. 55:1072–1080. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Egger M, Beer AG, Theurl M, Schgoer W,
Hotter B, Tatarczyk T, Vasiljevic D, Frauscher S, Marksteiner J,
Patsch JR, et al: Monocyte migration: a novel effect and signaling
pathways of catestatin. Eur J Pharmacol. 598:104–111. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feistritzer C, Mosheimer BA, Colleselli D,
Wiedermann CJ and Kähler CM: Effects of the neuropeptide
secretoneurin on natural killer cell migration and cytokine
release. Regul Pept. 126:195–201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ferrero E, Magni E, Curnis F, Villa A,
Ferrero ME and Corti A: Regulation of endothelial cell shape and
barrier function by chromogranin A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 971:355–358.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Steeds J, Motomura Y, Deng Y,
Verma-Gandhu M, El-Sharkawy RT, McLaughlin JT, Grencis RK and Khan
WI: CD4+ T cell-mediated immunological control of
enterochro-maffin cell hyperplasia and 5-hydroxytryptamine
production in enteric infection. Gut. 56:949–957. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cloëz-Tayarani I and Changeux JP: Nicotine
and serotonin in immune regulation and inflammatory processes: a
perspective. J Leukoc Biol. 81:599–606. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stefulj J, Cicin-Sain L, Schauenstein K
and Jernej B: Serotonin and immune response: effect of the amine on
in vitro proliferation of rat lymphocytes. Neuroimmunomodulation.
9:103–108. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Betten A, Dahlgren C, Hermodsson S and
Hellstrand K: Serotonin protects NK cells against oxidatively
induced functional inhibition and apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol.
70:65–72. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Laberge S, Cruikshank WW, Beer DJ and
Center DM: Secretion of IL-16 (lymphocyte chemoattractant factor)
from serotonin-stimulated CD8+ T cells in vitro. J
Immunol. 156:310–315. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Soga F, Katoh N, Inoue T and Kishimoto S:
Serotonin activates human monocytes and prevents apoptosis. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:1947–1955. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|