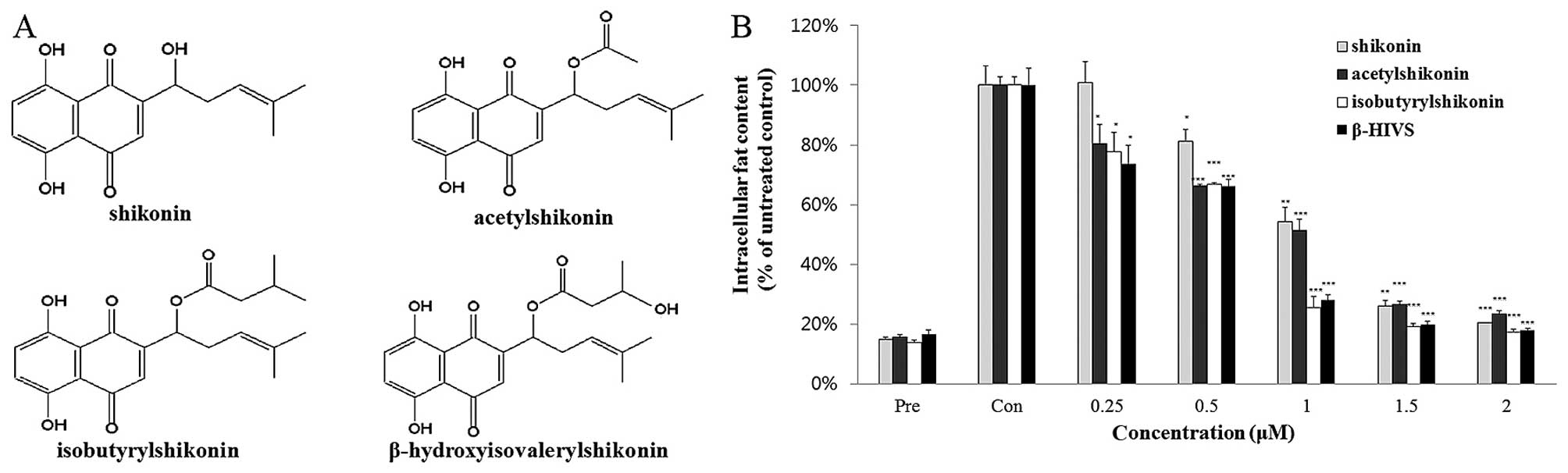
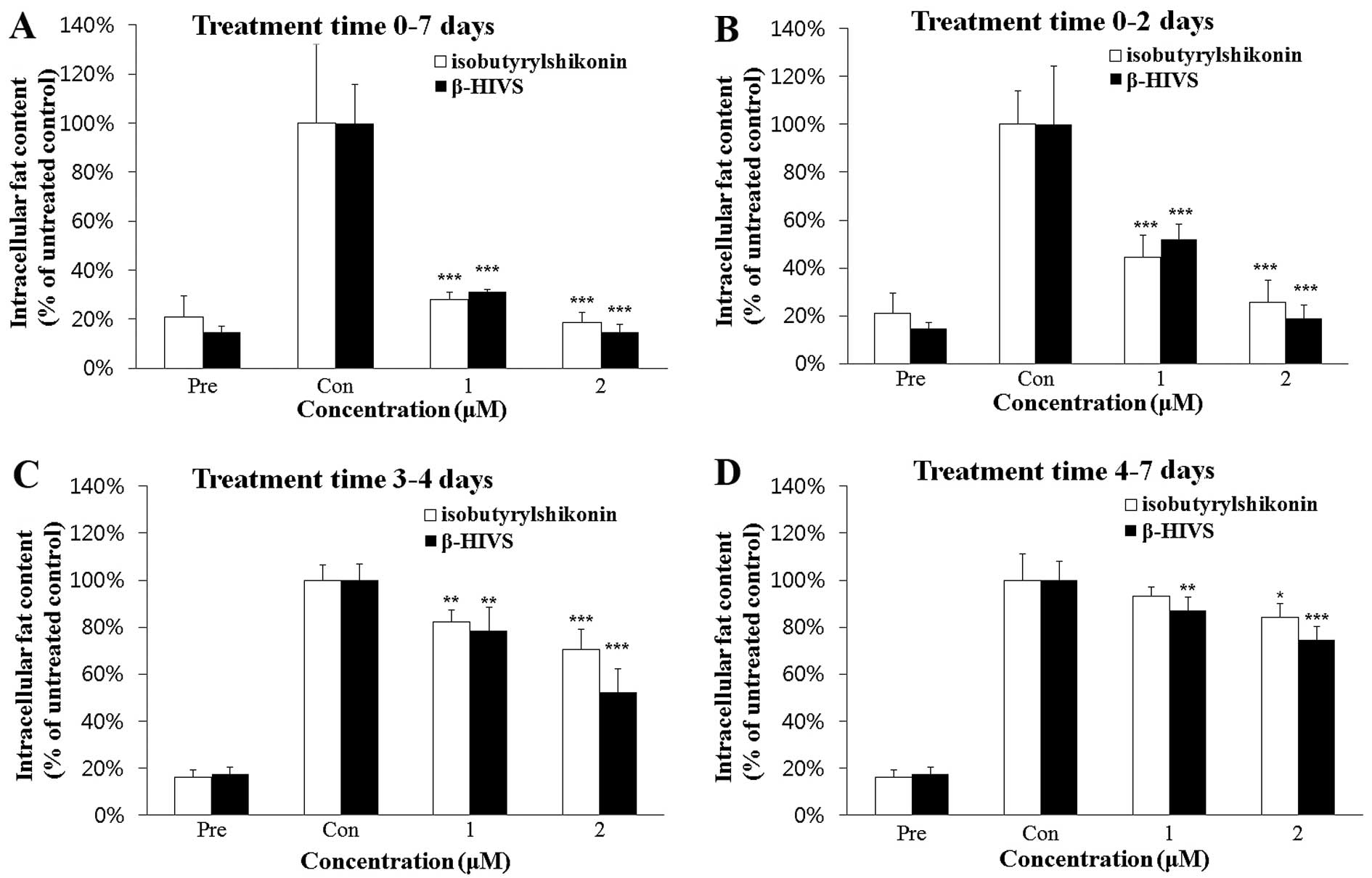
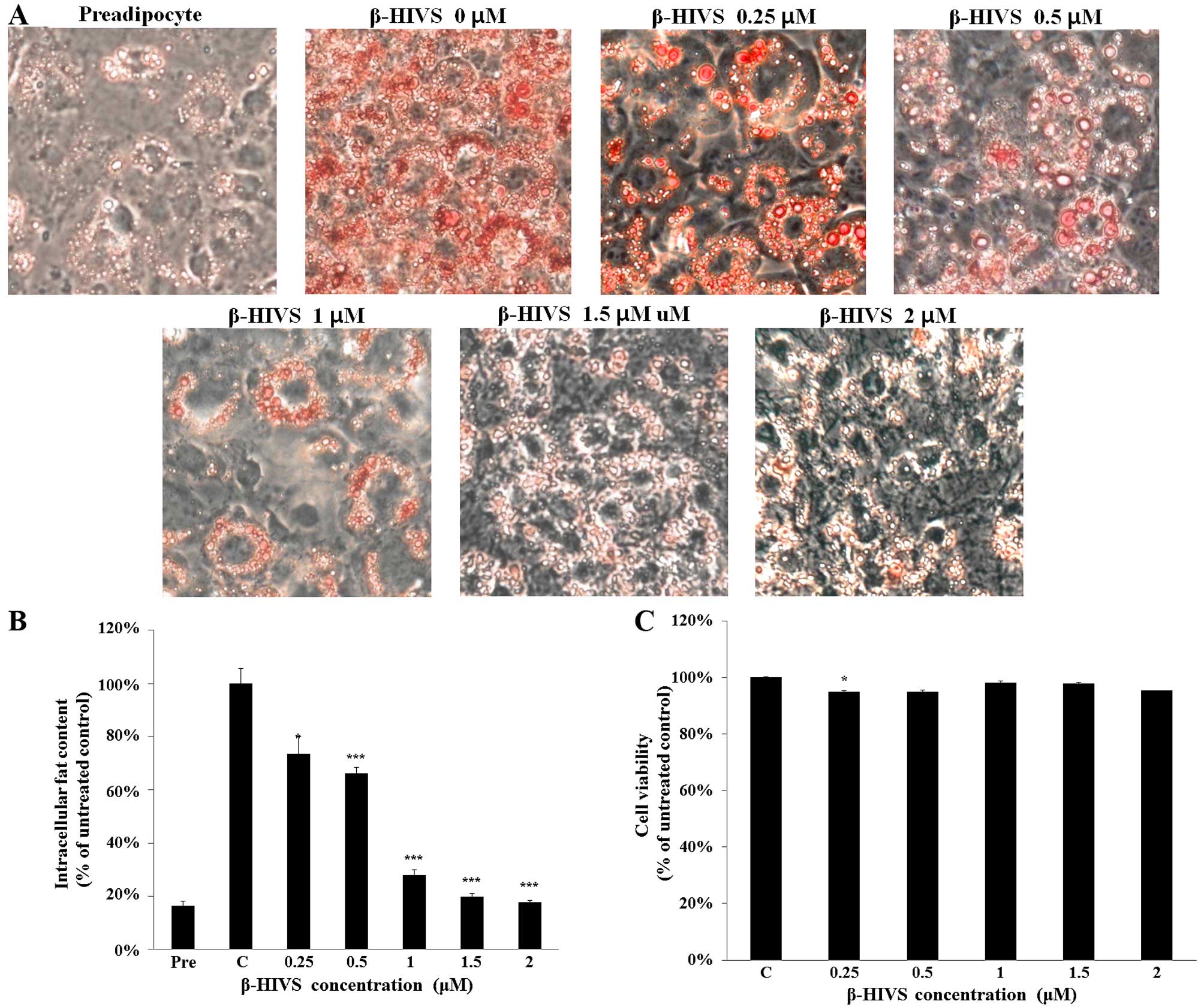
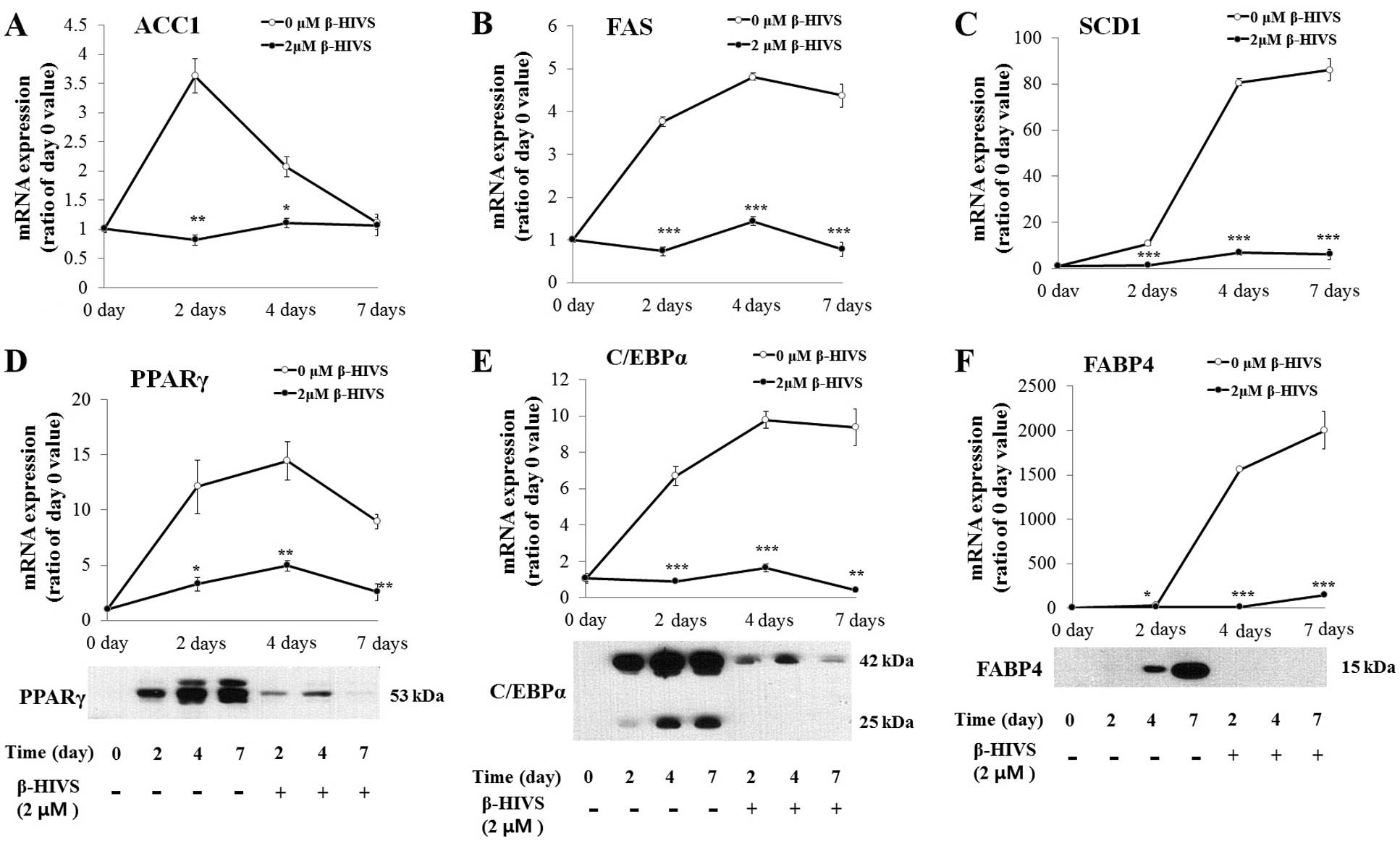
|
1
|
Grundy SM: Obesity, metabolic syndrome,
and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:2595–2600.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farmer SR: Transcriptional control of
adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 4:263–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosen ED and MacDougald OA: Adipocyte
differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
7:885–896. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P and
Spiegelman BM: Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes
Dev. 14:1293–1307. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: a
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Makinde AO, Gamble J and Lopaschuk GD:
Upregulation of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase is responsible for
the increase in myocardial fatty acid oxidation rates following
birth in the newborn rabbit. Circ Res. 80:482–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ojuka EO, Jones TE, Nolte LA, Chen M,
Wamhoff BR, Sturek M and Holloszy JO: Regulation of GLUT4
biogenesis in muscle: evidence for involvement of AMPK and
Ca2+. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 282:E1008–E1013.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fazakerley DJ, Holman GD, Marley A, James
DE, Stöckli J and Coster ACF: Kinetic evidence for unique
regulation of GLUT4 trafficking by insulin and AMP-activated
protein kinase activators in L6 myotubes. J Biol Chem.
285:1653–1660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X,
Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, et al: AMPK
phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic
steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant
mice. Cell Metab. 13:376–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JB, Wright HM, Wright M and Spiegelman
BM: ADD1/SREBP1 activates PPARgamma through the production of
endogenous ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:4333–4337. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ and Howard
MZ: Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives.
Phytother Res. 16:199–209. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ito Y, Onobori K, Yamazaki T and Kawamura
Y: Tigloylshikonin, a new minor Shikonin derivative, from the roots
and the commercial root extract of Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Chem
Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 59:117–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li J, Zhang D, Ward KM, Prendergast GC and
Ayene IS: Hydroxyethyl disulfide as an efficient metabolic assay
for cell viability in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 26:603–612. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gustafson B and Smith U: Cytokines promote
Wnt signaling and inflammation and impair the normal
differentiation and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J
Biol Chem. 281:9507–9516. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Paton CM and Ntambi JM: Biochemical and
physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 297:E28–E37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Shimomura I, Bashmakov Y, Ikemoto S,
Horton JD, Brown MS and Goldstein JL: Insulin selectively increases
SREBP-1c mRNA in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced
diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:13656–13661. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magaña MM, Lin SS, Dooley KA and Osborne
TF: Sterol regulation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase promoter
requires two interdependent binding sites for sterol regulatory
element binding proteins. J Lipid Res. 38:1630–1638.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fajas L, Schoonjans K, Gelman L, Kim JB,
Najib J, Martin G, Fruchart JC, Briggs M, Spiegelman BM and Auwerx
J: Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
expression by adipocyte differentiation and determination factor
1/sterol regulatory element binding protein 1: implications for
adipocyte differentiation and metabolism. Mol Cell Biol.
19:5495–5503. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bijland S, Mancini SJ and Salt IP: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in adipose tissue metabolism and
inflammation. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:491–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee H, Kang R, Bae S and Yoon Y: AICAR, an
activator of AMPK, inhibits adipogenesis via the WNT/β-catenin
pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Med. 28:65–71.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang C, Shin DJ and Osborne TF: A simple
promoter containing two Sp1 sites controls the expression of
sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein 1a (SREBP-1a). Biochem J.
386:161–168. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Yoshikawa T,
Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y,
Ohashi K, et al: Promoter analysis of the mouse sterol regulatory
element-binding protein-1c gene. J Biol Chem. 275:31078–31085.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rayalam S, Della-Fera MA and Baile CA:
Phytochemicals and regulation of the adipocyte life cycle. J Nutr
Biochem. 19:717–726. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shirwany NA and Zou MH: AMPK in
cardiovascular health and disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:1075–1084. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao X and Song BL: SREBP: a novel
therapeutic target. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:2–10.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eberlé D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, Ferré P
and Foufelle F: SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of
lipid homeostasis. Biochimie. 86:839–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hwang JT, Kwon DY and Yoon SH:
AMP-activated protein kinase: A potential target for the diseases
prevention by natural occurring polyphenols. N Biotechnol.
26:17–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen YC, Zeng XY, He Y, Liu H, Wang B,
Zhou H, Chen JW, Liu PQ, Gu LQ, Ye JM and Huang ZS: Rutaecarpine
analogues reduce lipid accumulation in adipocytes via inhibiting
adipogenesis/lipogenesis with AMPK activation and UPR suppression.
ACS Chem Biol. 8:2301–2311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He Y, Li Y, Zhao T, Wang Y and Sun C:
Ursolic acid inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through
LKB1/AMPK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e701352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|