|
1
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Docheva D, Popov C, Mutschler W and
Schieker M: Human mesenchymal stem cells in contact with their
environment: surface characteristics and the integrin system. J
Cell Mol Med. 11:21–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vidane AS, Zomer HD, Oliveira BM,
Guimarães CF, Fernandes CB, Perecin F, Silva LA, Miglino MA,
Meirelles FV and Ambrósio CE: Reproductive stem cell
differentiation: extracellular matrix, tissue microenvironment, and
growth factors direct the mesenchymal stem cell lineage commitment.
Reprod Sci. 20:1137–1143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
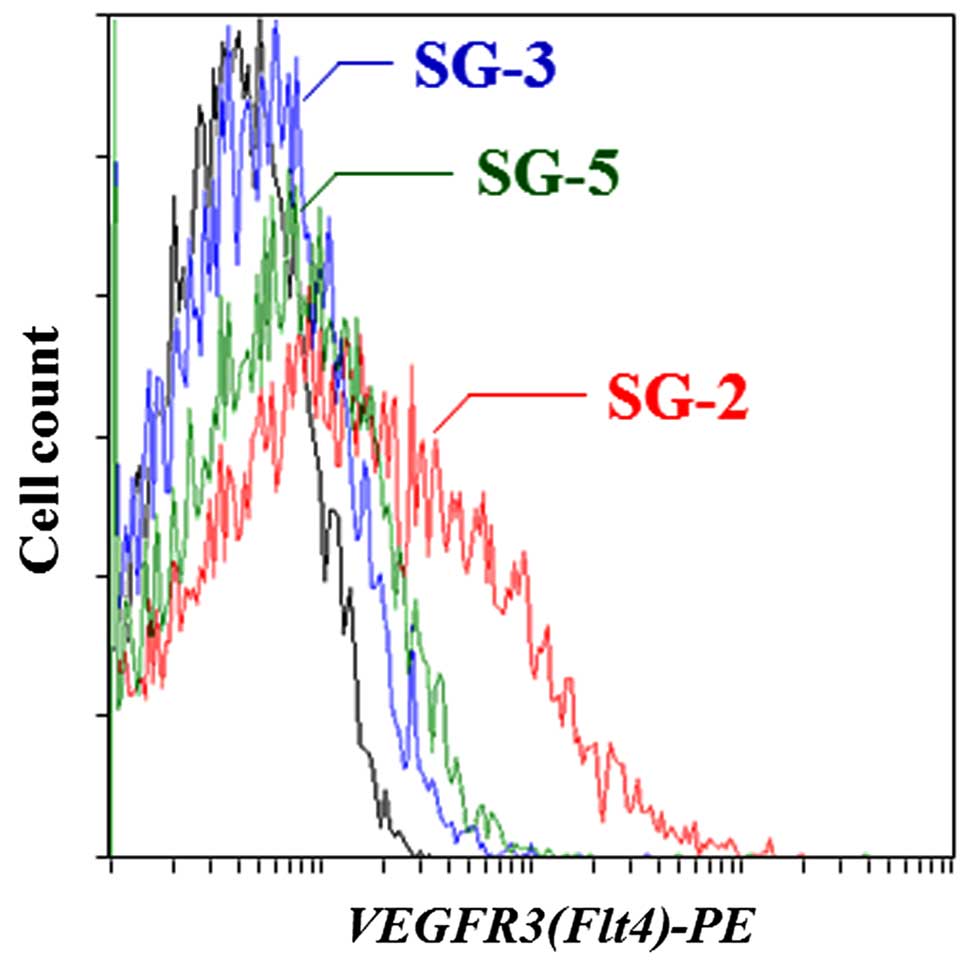
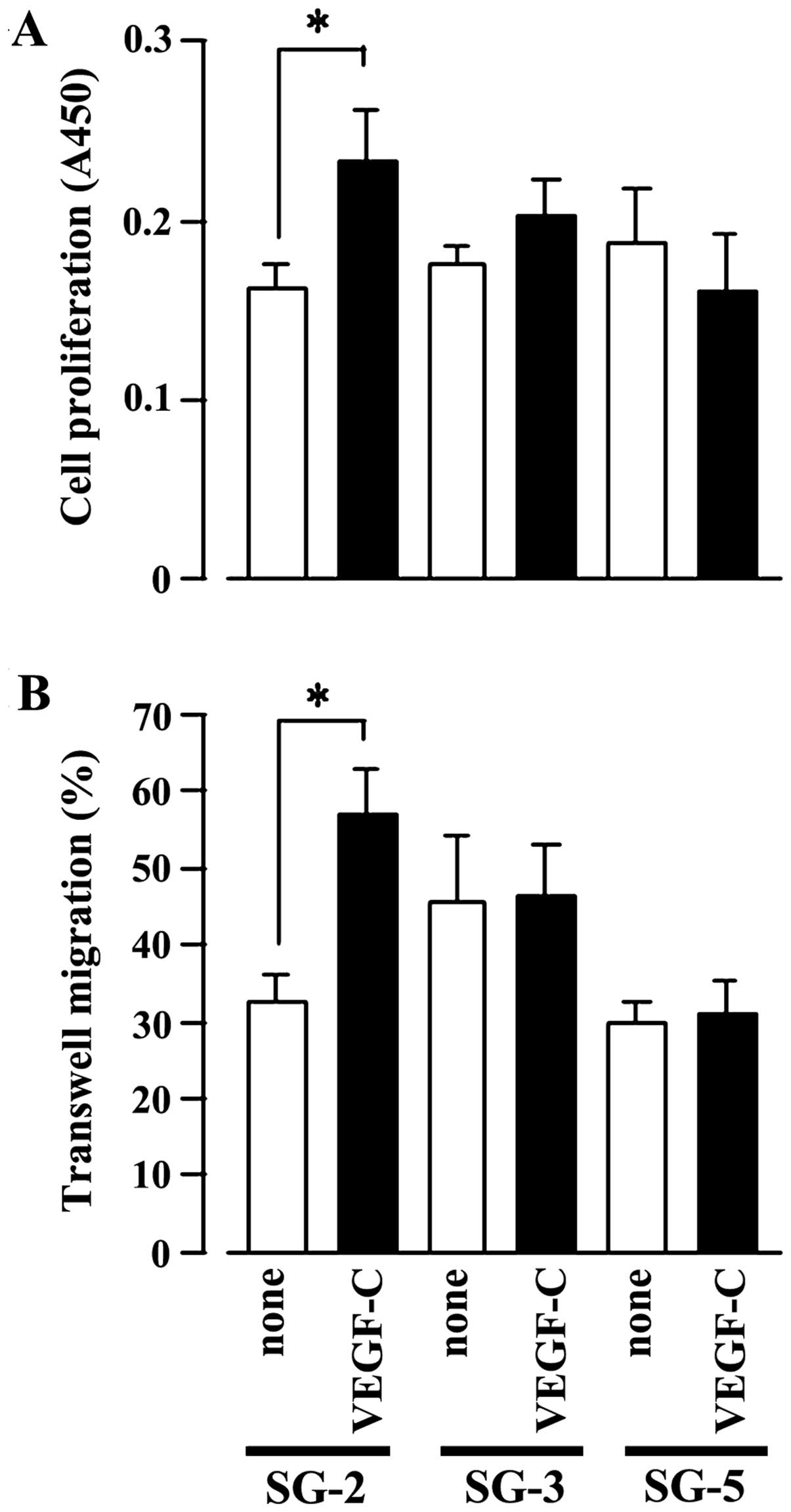
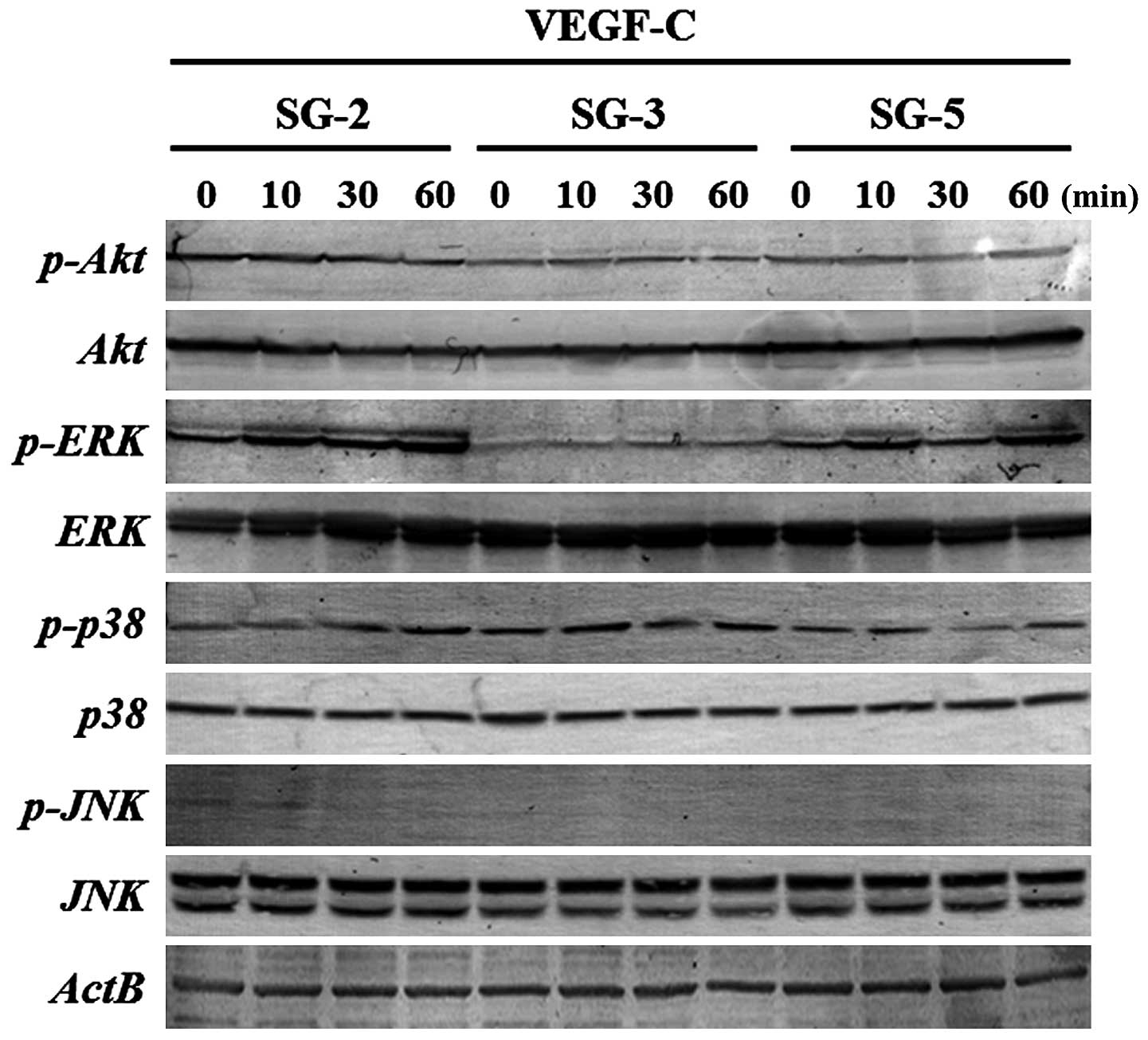
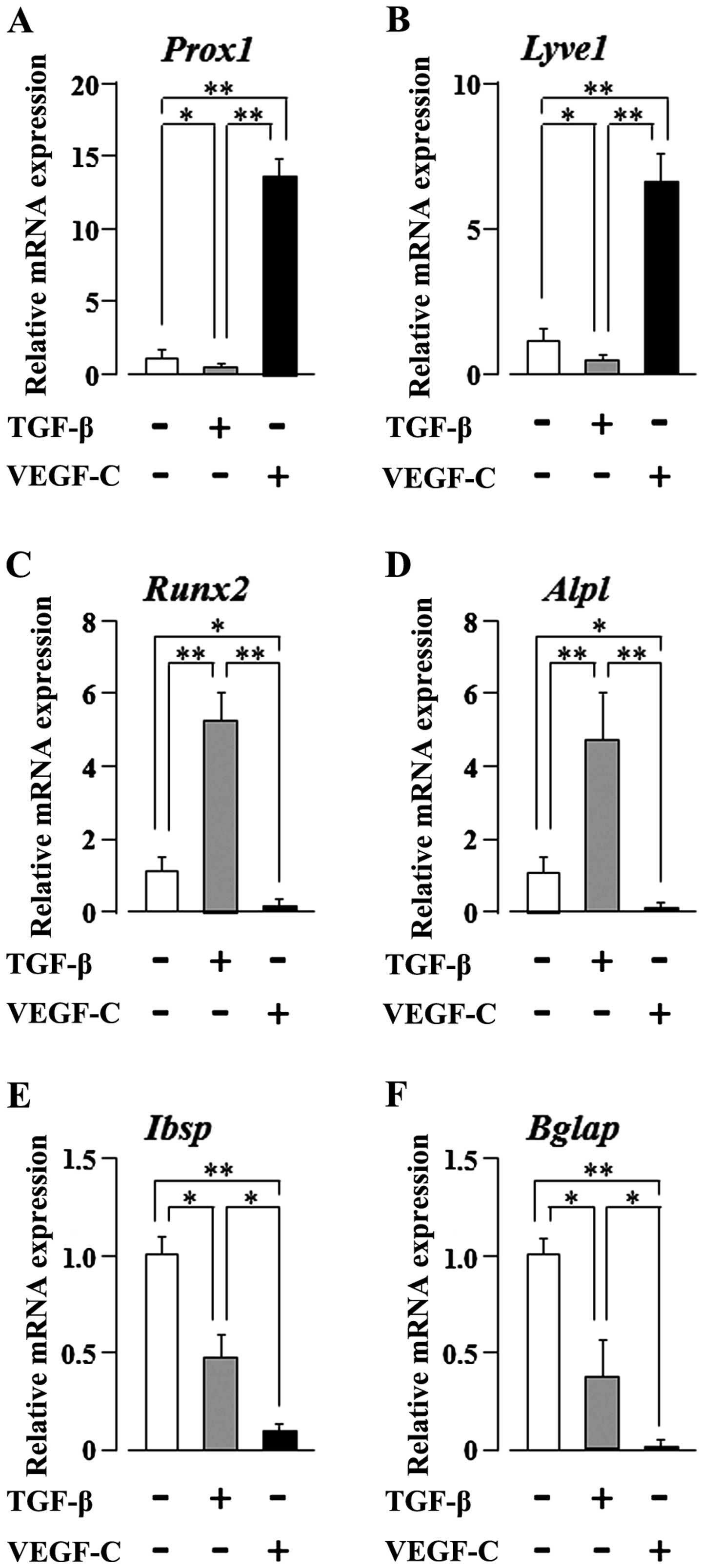
|
Chen BY, Wang X, Chen LW and Luo ZJ:
Molecular targeting regulation of proliferation and differentiation
of the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells or mesenchymal
stromal cells. Curr Drug Targets. 13:561–571. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soleymaninejadian E, Pramanik K and
Samadian E: Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells:
cytokines and factors. Am J Reprod Immunol. 67:1–8. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chau JF, Leong WF and Li B: Signaling
pathways governing osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and
function. Histol Histopathol. 24:1593–1606. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pountos I, Georgouli T, Henshaw K, Bird H,
Jones E and Giannoudis PV: The effect of bone morphogenetic
protein-2, bone morphogenetic protein-7, parathyroid hormone, and
platelet-derived growth factor on the proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from osteoporotic
bone. J Orthop Trauma. 24:552–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hughes FJ, Turner W, Belibasakis G and
Martuscelli G: Effects of growth factors and cytokines on
osteoblast differentiation. Periodontol. 2000 41:48–72. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yokota J, Chosa N, Sawada S, Okubo N,
Takahashi N, Hasegawa T, Kondo H and Ishisaki A: PDGF-induced
PI3K-mediated signaling enhances the TGF-β-induced osteogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a
TGF-β-activated MEK-dependent manner. Int J Mol Med. 33:534–542.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aomatsu E, Takahashi N, Sawada S, Okubo N,
Hasegawa T, Taira M, Miura H, Ishisaki A and Chosa N: Novel
SCRG1/BST1 axis regulates self-renewal, migration, and osteogenic
differentiation potential in mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep.
4(3652)2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ellis LM and Hicklin DJ: VEGF-targeted
therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:579–591. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dvorak HF: Vascular permeability
factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in
tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 20:4368–4380. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Orlandini M, Marconcini L, Ferruzzi R and
Oliviero S: Identification of a c-fos-induced gene that is related
to the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth
factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:11675–11680. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roche PA and Cresswell P: Proteolysis of
the class II-associated invariant chain generates a peptide binding
site in intracellular HLA-DR molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:3150–3154. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Olofsson B, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, von
Euler G, Joukov V, Saksela O, Orpana A, Pettersson RF, Alitalo K
and Eriksson U: Vascular endothelial growth factor B, a novel
growth factor for endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:2576–2581. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov
D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N and Alitalo K: A
novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for
the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases.
EMBO J. 15(1751)1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G
and Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor
cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial
growth factor. Cell. 92:735–745. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Migdal M, Huppertz B, Tessler S, Comforti
A, Shibuya M, Reich R, Baumann H and Neufeld G: Neuropilin-1 is a
placenta growth factor-2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 273:22272–22278.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neufeld G, Kessler O and Herzog Y: The
interaction of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase
receptors for VEGF. Adv Exp Med Biol. 515:81–90. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cao Y: Positive and negative modulation of
angiogenesis by VEGFR1 ligands. Sci Signal. 2:re12009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang F, Tang Z, Hou X, Lennartsson J, Li
Y, Koch AW, Scotney P, Lee C, Arjunan P, Dong L, et al: VEGF-B is
dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their
survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:6152–6157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hanrahan V, Currie MJ, Gunningham SP,
Morrin HR, Scott PA, Robinson BA and Fox SB: The angiogenic switch
for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C,
and VEGF-D in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence during colorectal
cancer progression. J Pathol. 200:183–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang TB, Chen ZG, Wei XQ, Wei B and Dong
WG: Serum vascular endothelial growth factor-C and
lymphoangiogenesis are associated with the lymph node metastasis
and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. ANZ J Surg.
81:694–699. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo
R, Janes L, Velasco P, Riccardi L, Alitalo K, Claffey K and Detmar
M: Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast
cancer metastasis. Nat Med. 7:192–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu QW, She HQ, Liang J, Huang YF, Yang QM,
Yang QL and Zhang ZM: Expression and clinical significance of
extracellular matrix protein 1 and vascular endothelial growth
factor-C in lymphatic metastasis of human breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 12(47)2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Karnezis T, Shayan R, Caesar C, Roufail S,
Harris NC, Ardipradja K, Zhang YF, Williams SP, Farnsworth RH, Chai
MG, et al: VEGF-D promotes tumor metastasis by regulating
prostaglandins produced by the collecting lymphatic endothelium.
Cancer Cell. 21:181–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stacker SA, Caesar C, Baldwin ME, Thornton
GE, Williams RA, Prevo R, Jackson DG, Nishikawa S, Kubo H and Achen
MG: VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the
lymphatics. Nat Med. 7:186–191. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y and Olsen BR: Distinct VEGF
functions during bone development and homeostasis. Arch Immunol
Ther Exp (Warsz). 62:363–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Deckers MM, Karperien M, van der Bent C,
Yamashita T, Papapoulos SE and Löwik CW: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factors and their receptors during osteoblast
differentiation. Endocrinology. 141:1667–1674. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zelzer E, McLean W, Ng YS, Fukai N,
Reginato AM, Lovejoy S, D'Amore PA and Olsen BR: Skeletal defects
in VEGF(120/120) mice reveal multiple roles for VEGF in
skeletogenesis. Development. 129:1893–1904. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alonso V, de Gortázar AR, Ardura JA,
Andrade-Zapata I, Alvarez-Arroyo MV and Esbrit P: Parathyroid
hormone-related protein (107-139) increases human osteoblastic cell
survival by activation of vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2. J Cell Physiol. 217:717–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sawada S, Chosa N, Takizawa N, Yokota J,
Igarashi Y, Tomoda K, Kondo H, Yaegashi T and Ishisaki A:
Establishment of mesenchymal stem cell lines derived from the bone
marrow of GFP-transgenic mice exhibiting diversity in intracellular
TGF-β and BMP signaling. Mol Med Rep. 13:2023–2031. 2016.
|
|
36
|
Tammela T and Alitalo K:
Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell.
140:460–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M,
Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ and Moore MW:
Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation
of the VEGF gene. Nature. 380:439–442. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Carmeliet P, Mackman N, Moons L, Luther T,
Gressens P, Van Vlaenderen I, Demunck H, Kasper M, Breier G, Evrard
P, et al: Role of tissue factor in embryonic blood vessel
development. Nature. 383:73–75. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP,
Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Breitman ML and Schuh AC: Failure of
blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice.
Nature. 376:62–66. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gille H, Kowalski J, Li B, LeCouter J,
Moffat B, Zioncheck TF, Pelletier N and Ferrara N: Analysis of
biological effects and signaling properties of Flt-1 (VEGFR-1) and
KDR (VEGFR-2). A reassessment using novel receptor-specific
vascular endothelial growth factor mutants. J Biol Chem.
276:3222–3230. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Takahashi T, Ueno H and Shibuya M: VEGF
activates protein kinase C-dependent, but Ras-independent
Raf-MEK-MAP kinase pathway for DNA synthesis in primary endothelial
cells. Oncogene. 18:2221–2230. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meadows KN, Bryant P and Pumiglia K:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induction of the angiogenic
phenotype requires Ras activation. J Biol Chem. 276:49289–49298.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang H, Bhat A, Woodnutt G and Lappe R:
Targeting the ANGPT-TIE2 pathway in malignancy. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:575–585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: αV integrins in
angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
1:a0064782011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dixelius J, Makinen T, Wirzenius M,
Karkkainen MJ, Wernstedt C, Alitalo K and Claesson-Welsh L:
Ligand-induced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3
(VEGFR-3) hetero-dimerization with VEGFR-2 in primary lymphatic
endothelial cells regulates tyrosine phosphorylation sites. J Biol
Chem. 278:40973–40979. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nilsson I, Bahram F, Li X, Gualandi L,
Koch S, Jarvius M, Söderberg O, Anisimov A, Kholová I, Pytowski B,
et al: VEGF receptor 2/-3 heterodimers detected in situ by
proximity ligation on angiogenic sprouts. EMBO J. 29:1377–1388.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dumont DJ, Jussila L, Taipale J,
Lymboussaki A, Mustonen T, Pajusola K, Breitman M and Alitalo K:
Cardiovascular failure in mouse embryos deficient in VEGF
receptor-3. Science. 282:946–949. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kaipainen A, Korhonen J, Mustonen T, van
Hinsbergh VW, Fang GH, Dumont D, Breitman M and Alitalo K:
Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 gene becomes
restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:3566–3570. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jussila L, Valtola R, Partanen TA, Salven
P, Heikkilä P, Matikainen MT, Renkonen R, Kaipainen A, Detmar M,
Tschachler E, et al: Lymphatic endothelium and Kaposi's sarcoma
spindle cells detected by antibodies against the vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-3. Cancer Res. 58:1599–1604.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Partanen TA, Arola J, Saaristo A, Jussila
L, Ora A, Miettinen M, Stacker SA, Achen MG and Alitalo K: VEGF-C
and VEGF-D expression in neuroendocrine cells and their receptor,
VEGFR-3, in fenestrated blood vessels in human tissues. FASEB J.
14:2087–2096. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Paavonen K, Puolakkainen P, Jussila L,
Jahkola T and Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-3 in lymphangio-genesis in wound healing. Am J Pathol.
156:1499–1504. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Valtola R, Salven P, Heikkilä P, Taipale
J, Joensuu H, Rehn M, Pihlajaniemi T, Weich H, deWaal R and Alitalo
K: VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis
in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 154:1381–1390. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Partanen TA, Alitalo K and Miettinen M:
Lack of lymphatic vascular specificity of vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 3 in 185 vascular tumors. Cancer.
86:2406–2412. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kubo H, Fujiwara T, Jussila L, Hashi H,
Ogawa M, Shimizu K, Awane M, Sakai Y, Takabayashi A, Alitalo K, et
al: Involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in
maintenance of integrity of endothelial cell lining during tumor
angiogenesis. Blood. 96:546–553. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rattigan Y, Hsu JM, Mishra PJ, Glod J and
Banerjee D: Interleukin 6 mediated recruitment of mesenchymal stem
cells to the hypoxic tumor milieu. Exp Cell Res. 316:3417–3424.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wei L, Liu Y, Chen G, Fang Y, Song X, Dong
P, Gao J, Liu R, Ding Z, Bi Y and Liu Z: Differentiation of
lymphatic endothelial cells from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
with VEGFs. Lymphology. 45:177–187. 2012.
|
|
57
|
Zhan J, Li Y, Yu J, Zhao Y, Cao W, Ma J,
Sun X, Sun L, Qian H, Zhu W and Xu W: Culture medium of bone
marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells effects lymphatic
endothelial cells and tumor lymph vessel formation. Oncol Lett.
9:1221–1226. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|