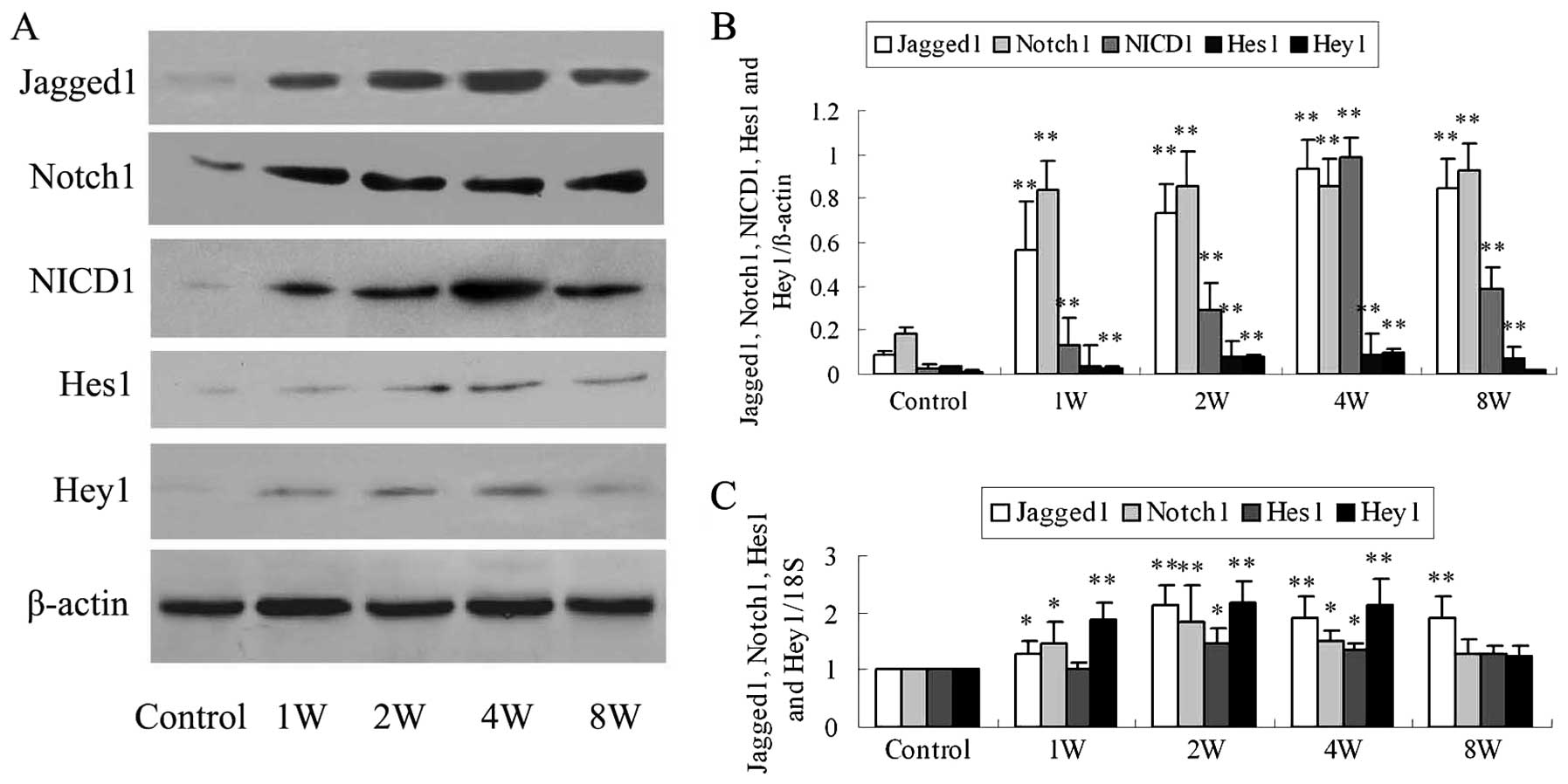
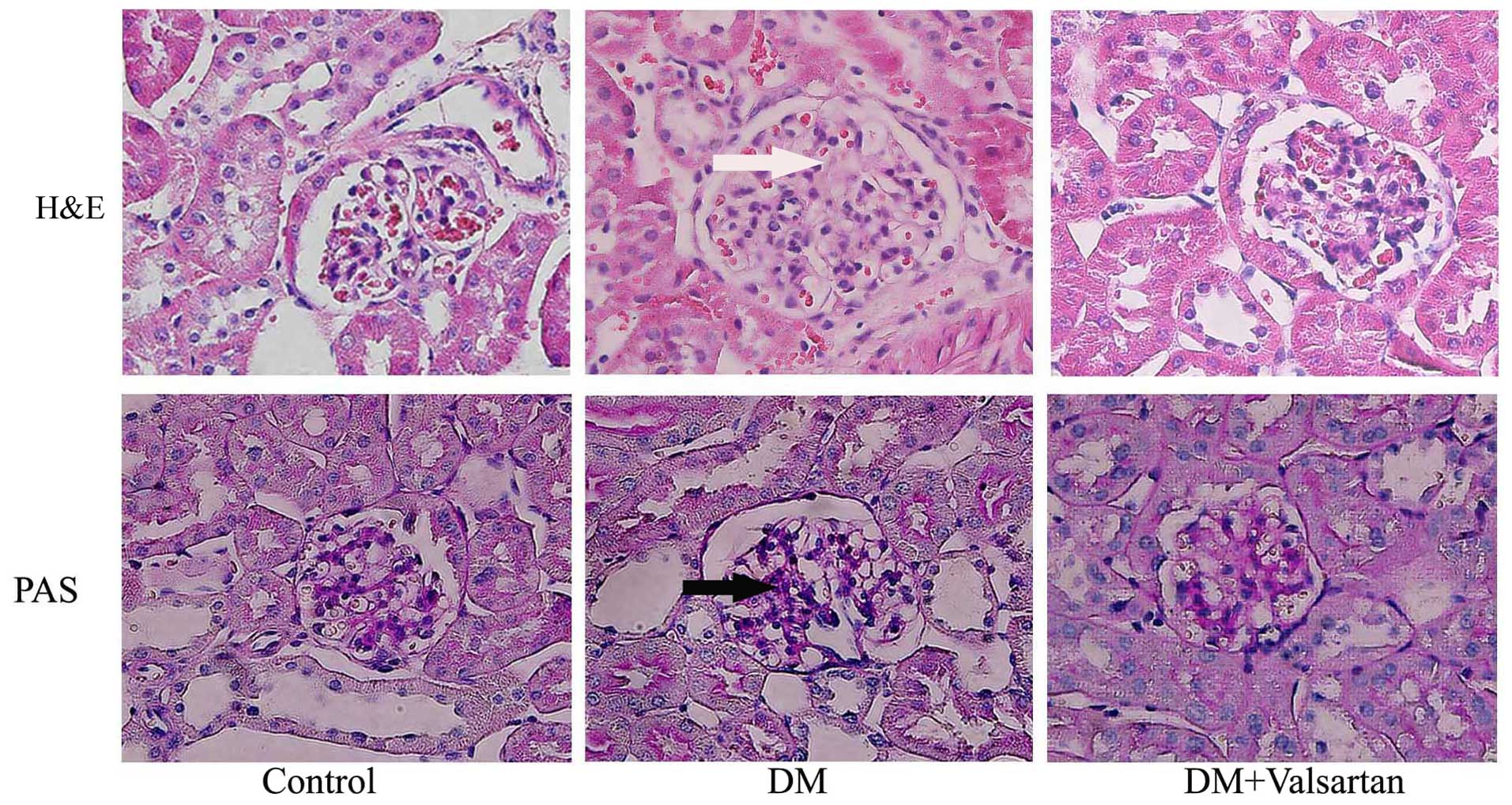
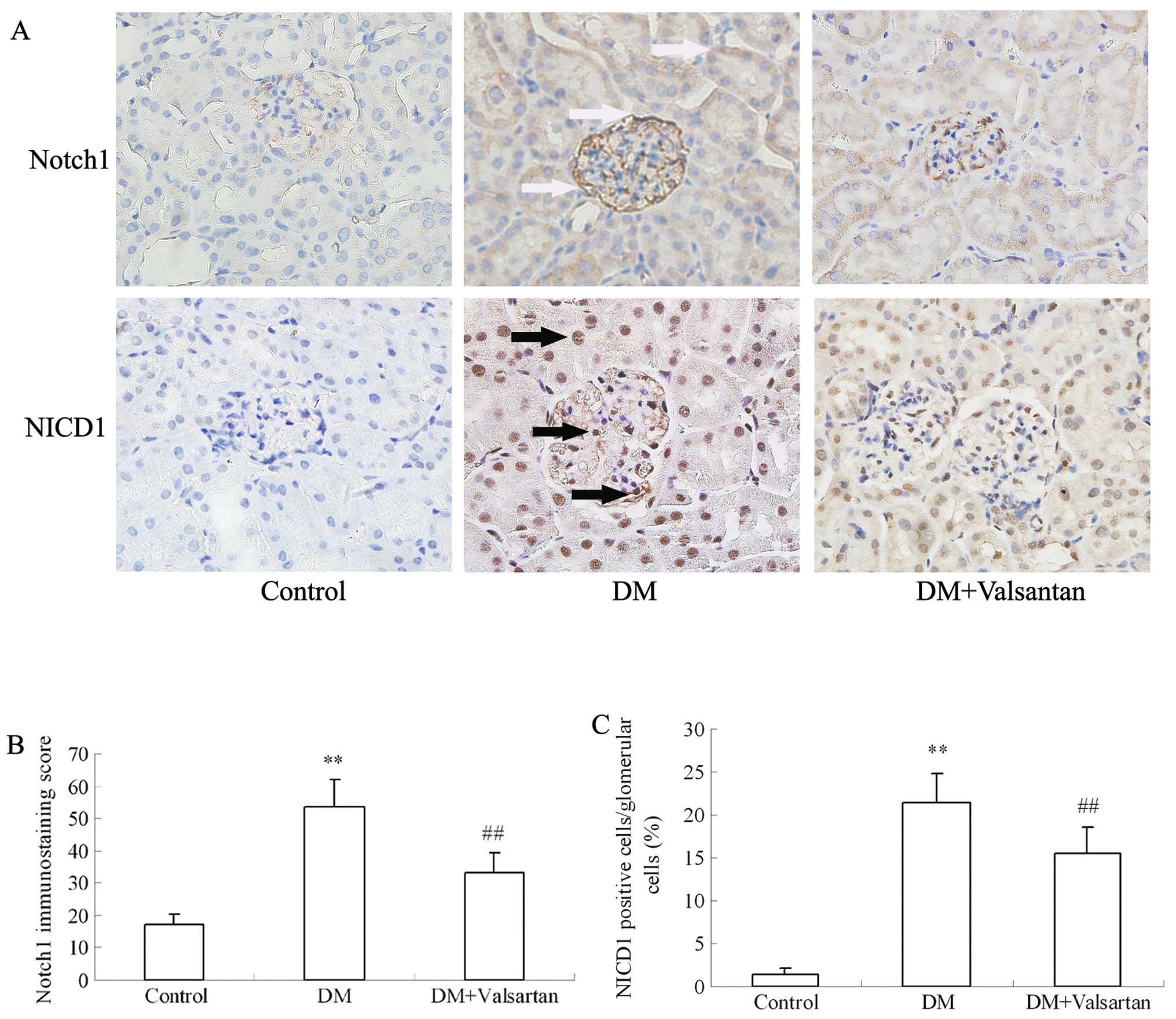
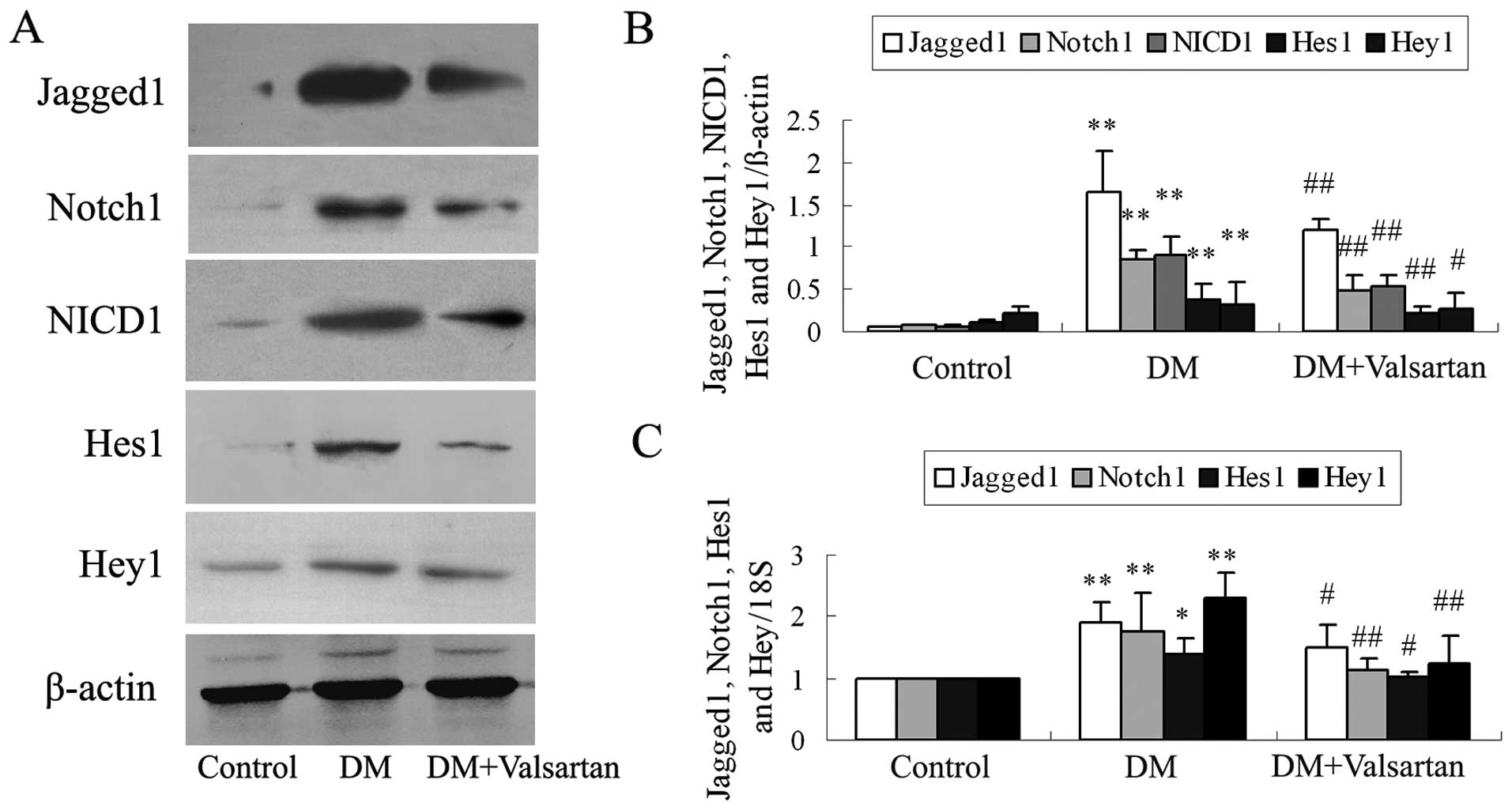
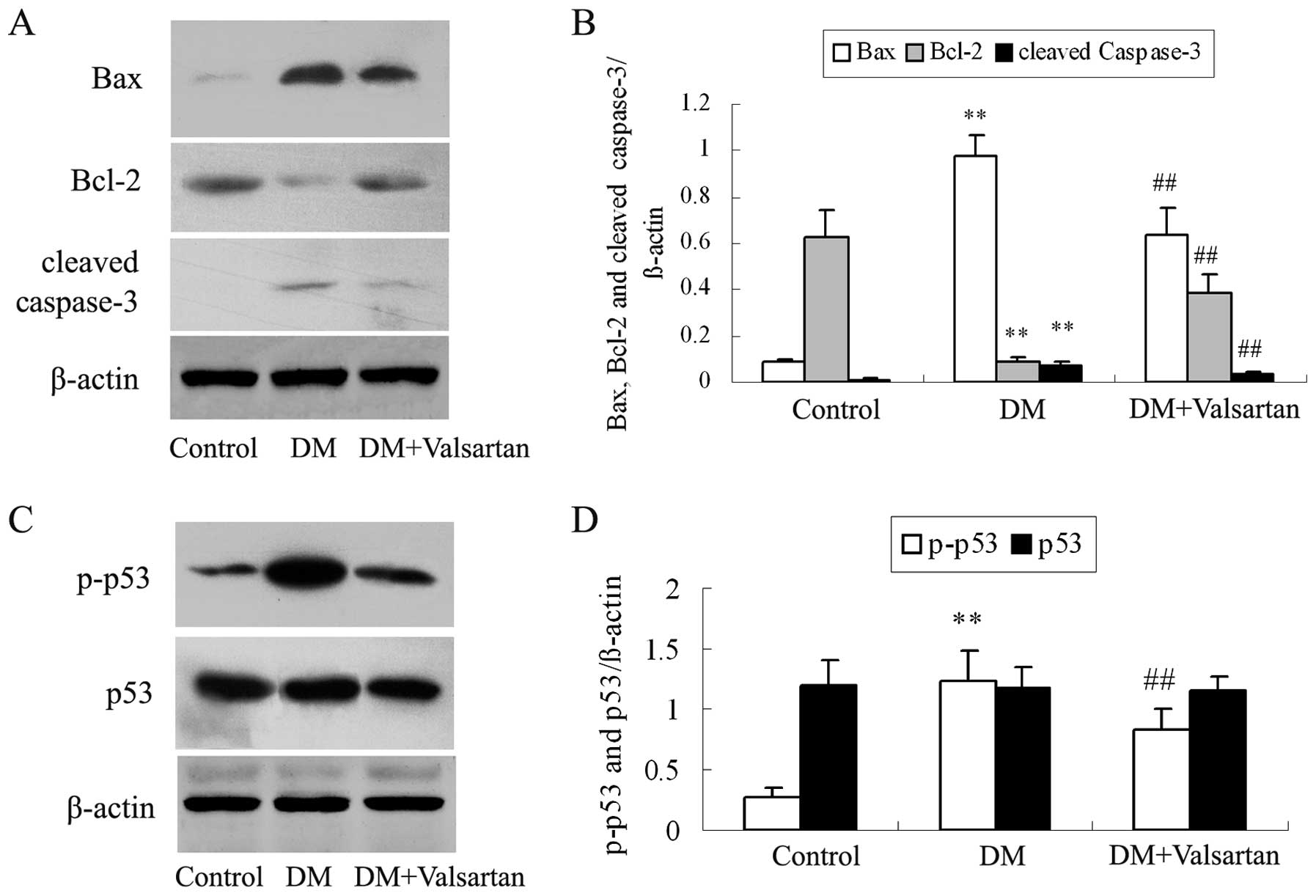
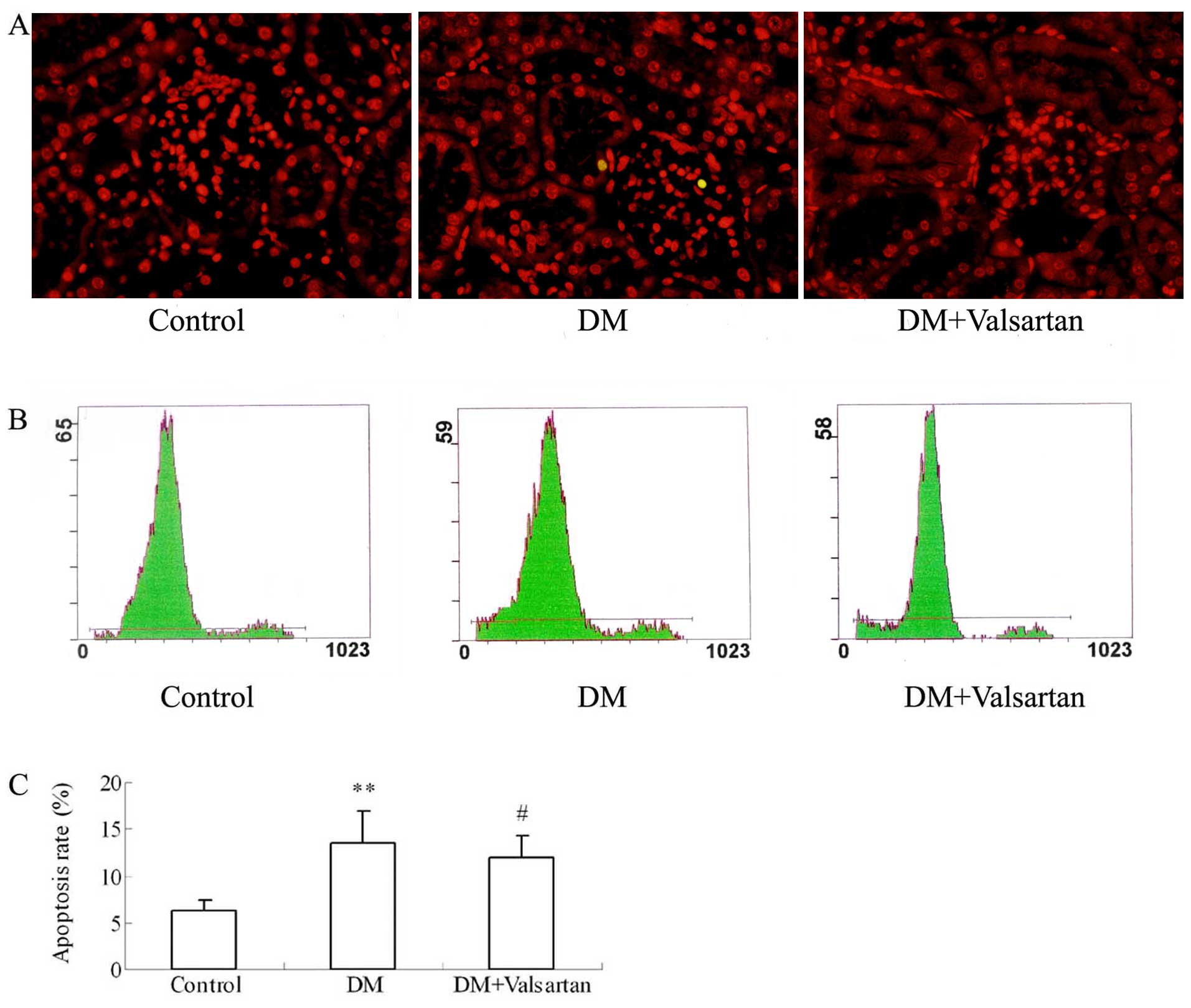
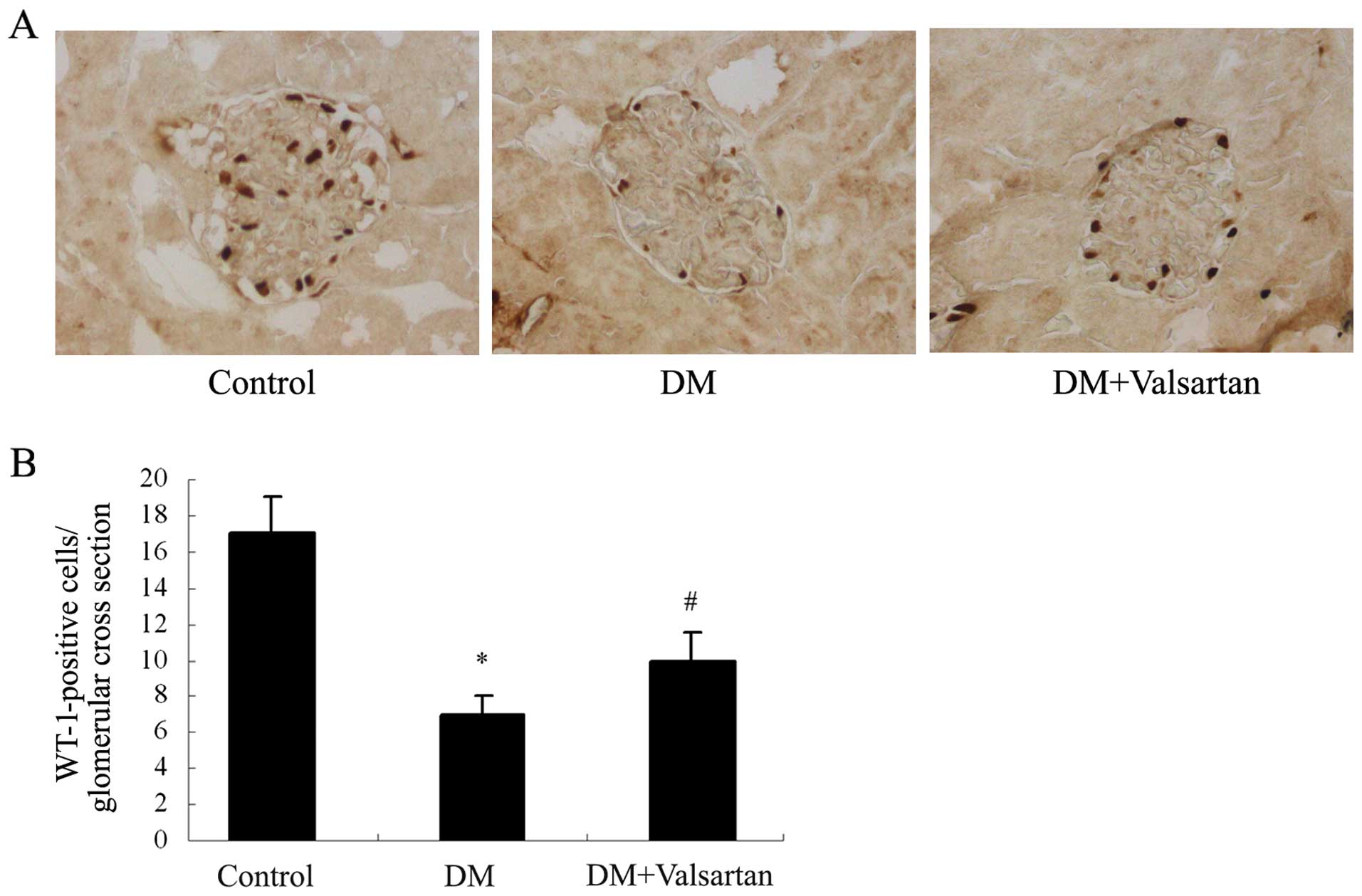
|
1
|
Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T and Susztak
K: Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest.
124:2333–2340. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Butt A and Riaz S: Study of protein
profiling of human urine in diabetic hypertensive nephropathy
versus normal healthy controls. Diabetes Technol Ther. 12:379–386.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Piwkowska A, Rogacka D, Audzeyenka I,
Jankowski M and Angielski S: High glucose concentration affects the
oxidant-antioxidant balance in cultured mouse podocytes. J Cell
Biochem. 112:1661–1672. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu W, Zhang Y, Liu S, Liu Q, Hao J, Shi
Y, Zhao S and Duan H: The expression of intermediate filament
protein nestin and its association with cyclin-dependent kinase 5
in the glomeruli of rats with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Med Sci.
345:470–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cao Y, Hao Y, Li H, Liu Q, Gao F, Liu W
and Duan H: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in apoptosis of
differentiated mouse podocytes induced by high glucose. Int J Mol
Med. 33:809–816. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li JJ, Kwak SJ, Jung DS, Kim JJ, Yoo TH,
Ryu DR, Han SH, Choi HY, Lee JE, Moon SJ, et al: Podocyte biology
in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl. 106:S36–S42. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Das R, Xu S, Quan X, Nguyen TT, Kong ID,
Chung CH, Lee EY, Cha SK and Park KS: Upregulation of mitochondrial
Nox4 mediates TGF-β-induced apoptosis in cultured mouse podocytes.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F155–F167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mertens PR, Raffetseder U and Rauen T:
Notch receptors: a new target in glomerular diseases. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 23:2743–2745. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cook KM and Figg WD: Angiogenesis
inhibitors: current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J
Clin. 60:222–243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ji X, Wang Z, Geamanu A, Sarkar FH and
Gupta SV: Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells by delta-tocotrienol is associated
with notch-1 down-regulation. J Cell Biochem. 112:2773–2783. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bonegio R and Susztak K: Notch signaling
in diabetic nephropathy. Exp Cell Res. 318:986–992. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Samon JB, Champhekar A, Minter LM, Telfer
JC, Miele L, Fauq A, Das P, Golde TE and Osborne BA: Notch1 and
TGFbeta1 cooperatively regulate Foxp3 expression and the
maintenance of peripheral regulatory T cells. Blood. 112:1813–1821.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ntziachristos P, Lim JS, Sage J and
Aifantis I: From fly wings to targeted cancer therapies: a
centennial for notch signaling. Cancer Cell. 25:318–334. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niranjan T, Bielesz B, Gruenwald A, Ponda
MP, Kopp JB, Thomas DB and Susztak K: The Notch pathway in
podocytes plays a role in the development of glomerular disease.
Nat Med. 14:290–298. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weil EJ, Lemley KV, Mason CC, Yee B, Jones
LI, Blouch K, Lovato T, Richardson M, Myers BD and Nelson RG:
Podocyte detachment and reduced glomerular capillary endothelial
fenestration promote kidney disease in type 2 diabetic nephropathy.
Kidney Int. 82:1010–1017. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mavrakanas TA, Gariani K and Martin PY:
Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade in addition to angiotensin
converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker
treatment: an emerging paradigm in diabetic nephropathy: a
systematic review. Eur J Intern Med. 25:173–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mansour MH, Al-Qattan K, Thomson M and Ali
M: Garlic (Allium sativum) down-regulates the expression of
angiotensin II AT(1) receptor in adrenal and renal tissues of
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Inflammopharmacology.
21:147–159. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ozasa Y, Akazawa H, Qin Y, Tateno K, Ito
K, Kudo-Sakamoto Y, Yano M, Yabumoto C, Naito AT, Oka T, et al:
Notch activation mediates angiotensin II-induced vascular
remodeling by promoting the proliferation and migration of vascular
smooth muscle cells. Hypertens Res. 36:859–865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johnson RJ, Garcia RL, Pritzl P and Alpers
CE: Platelets mediate glomerular cell proliferation in immune
complex nephritis induced by anti-mesangial cell antibodies in the
rat. Am J Pathol. 136:369–374. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng HT and Kopan R: The role of Notch
signaling in specification of podocyte and proximal tubules within
the developing mouse kidney. Kidney Int. 68:1951–1952. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Waters AM, Wu MY, Onay T, Scutaru J, Liu
J, Lobe CG, Quaggin SE and Piscione TD: Ectopic notch activation in
developing podocytes causes glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:1139–1157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Graziani I, Eliasz S, De Marco MA, Chen Y,
Pass HI, De May RM, Strack PR, Miele L and Bocchetta M: Opposite
effects of Notch-1 and Notch-2 on mesothelioma cell survival under
hypoxia are exerted through the Akt pathway. Cancer Res.
68:9678–9685. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kennard S, Liu H and Lilly B: Transforming
growth factor-β (TGF-1) down-regulates Notch3 in fibroblasts to
promote smooth muscle gene expression. J Biol Chem. 283:1324–1333.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Patrakka J and Tryggvason K: New insights
into the role of podocytes in proteinuria. Nat Rev Nephrol.
5:463–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lasagni L, Ballerini L, Angelotti ML,
Parente E, Sagrinati C, Mazzinghi B, Peired A, Ronconi E,
Becherucci F, Bani D, et al: Notch activation differentially
regulates renal progenitors proliferation and differentiation
toward the podocyte lineage in glomerular disorders. Stem Cells.
28:1674–1685. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ueno T, Kobayashi N, Nakayama M, Takashima
Y, Ohse T, Pastan I, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ, Uesugi N, Matsusaka T
and Nagata M: Aberrant Notch1-dependent effects on glomerular
parietal epithelial cells promotes collapsing focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis with progressive podocyte loss. Kidney Int.
83:1065–1075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brosius FC and Coward RJ: Podocytes,
signaling pathways, and vascular factors in diabetic kidney
disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 21:304–310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wharram BL, Goyal M, Wiggins JE, Sanden
SK, Hussain S, Filipiak WE, Saunders TL, Dysko RC, Kohno K, Holzman
LB and Wiggins RC: Podocyte depletion causes glomerulosclerosis:
Diphtheria toxin-induced podocyte depletion in rats expressing
human diphtheria toxin receptor transgene. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:2941–2952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao F, Yao M, Shi Y, Hao J, Ren Y, Liu Q,
Wang X and Duan H: Notch pathway is involved in high
glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes via Bcl-2 and p53 pathways.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1029–1038. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lai KN, Leung JC and Tang SC: The
renin-angiotensin system. Contrib Nephrol. 170:135–144. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kintscher U, Foryst-Ludwig A and Unger T:
Inhibiting angiotensin type 1 receptors as a target for diabetes.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:1257–1263. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fujisawa T, Ikegami H, Ono M, Nishino M,
Noso S, Kawabata Y and Ogihara T: Combination of half doses of
angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist and angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitor in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Hypertens. 18:13–17.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Das J and Sil PC: Taurine ameliorates
alloxan-induced diabetic renal injury, oxidative stress-related
signaling pathways and apoptosis in rats. Amino Acids.
43:1509–1523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lau GJ, Godin N, Maachi H, Lo CS, Wu SJ,
Zhu JX, Brezniceanu ML, Chénier I, Fragasso-Marquis J, Lattouf JB,
et al: Bcl-2-modifying factor induces renal proximal tubular cell
apoptosis in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 61:474–484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng J, Li X, Zhang D, Chen JK, Su Y,
Smith SB and Dong Z: Hyperglycemia, p53, and mitochondrial pathway
of apoptosis are involved in the susceptibility of diabetic models
to ischemic acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 87:137–150. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Huang J, Tang XH, Ikejima T, Sun XJ, Wang
XB, Xi RG and Wu LJ: A new triterpenoid from Panax ginseng exhibits
cytotoxicity through p53 and the caspase signaling pathway in the
HepG2 cell line. Arch Pharm Res. 31:323–329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Niimi H, Pardali K, Vanlandewijck M,
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Notch signaling is necessary for
epithelial growth arrest by TGF-β. J Cell Biol. 176:695–707. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Purow BW, Sundaresan TK, Burdick MJ, Kefas
BA, Comeau LD, Hawkinson MP, Su Q, Kotliarov Y, Lee J, Zhang W and
Fine HA: Notch-1 regulates transcription of the epidermal growth
factor receptor through p53. Carcinogenesis. 29:918–925. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|