|
1
|
O'Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui
LC, Kennedy JL, Shi X, Petronis A, George SR and Nguyen T: A human
gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin
receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene. 136:355–360. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R,
Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, et
al: Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide
ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:471–476. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie F, Lv D and Chen L: ELABELA: A novel
hormone in cardiac development acting as a new endogenous ligand
for the APJ receptor. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
46:620–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee DK, Cheng R, Nguyen T, Fan T,
Kariyawasam AP, Liu Y, Osmond DH, George SR and O'Dowd BF:
Characterization of apelin, the ligand for the APJ receptor. J
Neurochem. 74:34–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saavedra JM, Correa FM, Seltzer A, Pinto
JE, Viglione P and Tsutsumi K: Enhanced angiotensin converting
enzyme binding in arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J
Hypertens. 10:1353–1359. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choe W, Albright A, Sulcove J, Jaffer S,
Hesselgesser J, Lavi E, Crino P and Kolson DL: Functional
expression of the seven-transmembrane HIV-1 co-receptor APJ in
neural cells. J Neurovirol. 6(Suppl 1): S61–S69. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Habata Y, Fujii R, Hosoya M, Fukusumi S,
Kawamata Y, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Nishizawa N, Murosaki S, Kurokawa
T, et al: Apelin, the natural ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, is
abundantly secreted in the colostrum. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1452:25–35. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pope GR, Roberts EM, Lolait SJ and
O'Carroll AM: Central and peripheral apelin receptor distribution
in the mouse: species differences with rat. Peptides. 33:139–148.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Medhurst AD, Jennings CA, Robbins MJ,
Davis RP, Ellis C, Winborn KY, Lawrie KW, Hervieu G, Riley G,
Bolaky JE, et al: Pharmacological and immunohistochemical
characterization of the APJ receptor and its endogenous ligand
apelin. J Neurochem. 84:1162–1172. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y,
Nishiwaki S, Iguchi T, Harada S, Sugaya T, Matsuzaki H, Yamamoto R,
Shiota N, et al: Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane
receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure
in vivo. J Biol Chem. 279:26274–26279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szokodi I, Tavi P, Földes G,
Voutilainen-Myllylä S, Ilves M, Tokola H, Pikkarainen S, Piuhola J,
Rysä J, Tóth M and Ruskoaho H: Apelin, the novel endogenous ligand
of the orphan receptor APJ, regulates cardiac contractility. Circ
Res. 91:434–440. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang G, Anini Y, Wei W, Qi X, OCarroll AM,
Mochizuki T, Wang HQ, Hellmich MR, Englander EW and Greeley GH Jr:
Apelin, a new enteric peptide: localization in the gastrointestinal
tract, ontogeny, and stimulation of gastric cell proliferation and
of cholecystokinin secretion. Endocrinology. 145:1342–1348. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Castan-Laurell I, Dray C, Attane C, Duparc
T, Knauf C and Valet P: Apelin, diabetes, and obesity. Endocrine.
40:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lv D, Li L, Lu Q, Li Y, Xie F, Li H, Cao
J, Liu M, Wu D, He L and Chen LX: PAK1-cofilin phosphorylation
mediates human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration induced by
apelin-13. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. In Press.
|
|
15
|
Tiani C, Garcia-Pras E, Mejias M, de
Gottardi A, Berzigotti A, Bosch J and Fernandez M: Apelin signaling
modulates splanchnic angiogenesis and portosystemic collateral
vessel formation in rats with portal hypertension. J Hepatol.
50:296–305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Adam F, Khatib AM, Lopez JJ, Vatier C,
Turpin S, Muscat A, Soulet F, Aries A, Jardin I, Bobe R, et al:
Apelin: an antithrombotic factor that inhibits platelet function.
Blood. 127:908–920. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Than A, Zhang X, Leow MK, Poh CL, Chong SK
and Chen P: Apelin attenuates oxidative stress in human adipocytes.
J Biol Chem. 289:3763–3774. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Foussal C, Lairez O, Calise D, Pathak A,
Guilbeau-Frugier C, Valet P, Parini A and Kunduzova O: Activation
of catalase by apelin prevents oxidative stress-linked cardiac
hypertrophy. FEBS Lett. 584:2363–2370. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li L, Li F, Li F, Mao X, Yang L, Huang H,
Guo Y, Chen L and Li J: NOX4-derived reactive oxygen species drive
apelin-13-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via the
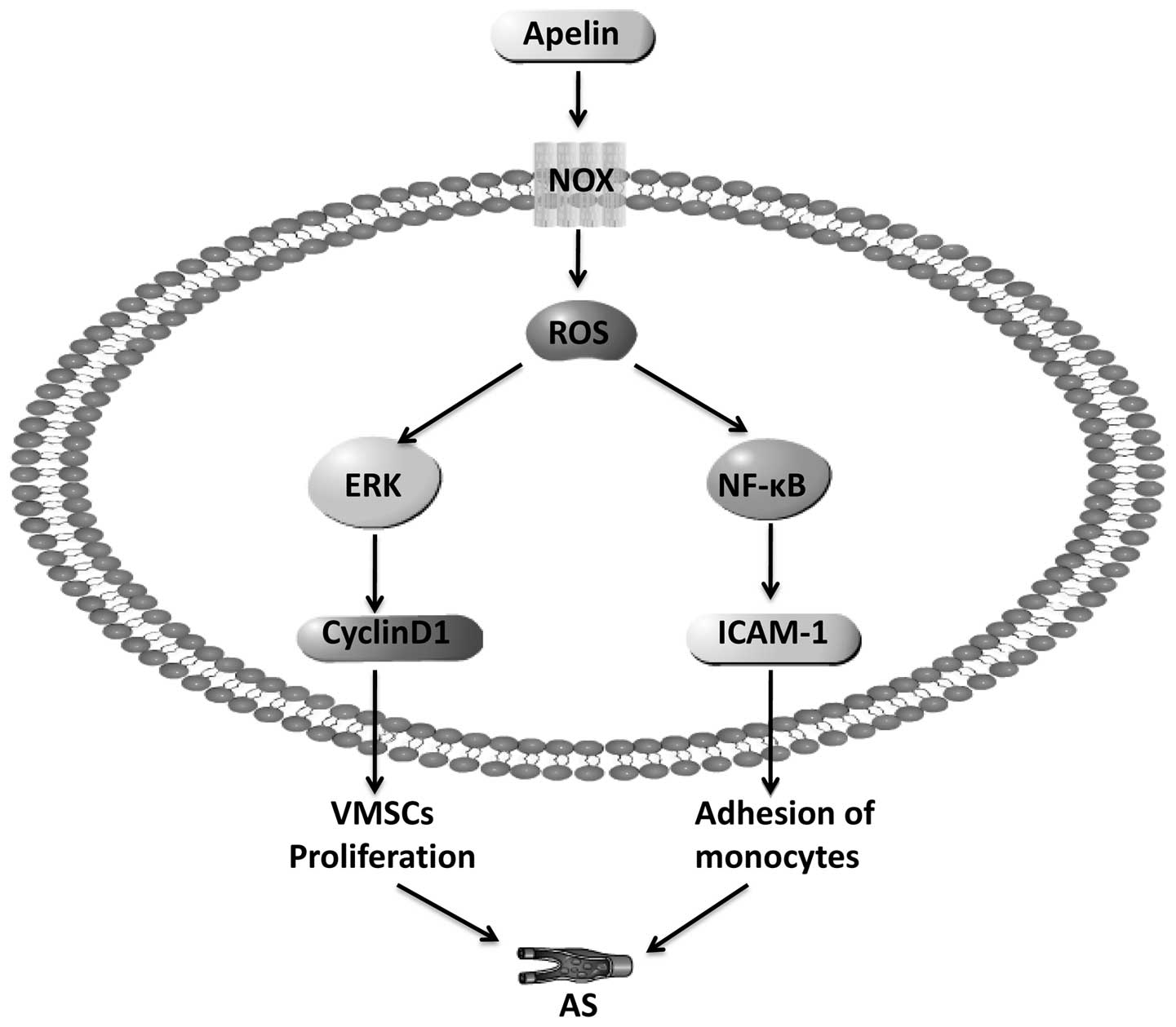
ERK pathway. Int J Pept Res Ther. 17:307–315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Katugampola SD, Maguire JJ, Matthewson SR
and Davenport AP: [(125)I]-(Pyr(1))Apelin-13 is a novel radioligand
for localizing the APJ orphan receptor in human and rat tissues
with evidence for a vasoconstrictor role in man. Br J Pharmacol.
132:1255–1260. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Falco M, De Luca L, Onori N, Cavallotti
I, Artigiano F, Esposito V, De Luca B, Laforgia V, Groeger AM and
De Luca A: Apelin expression in normal human tissues. In Vivo.
16:333–336. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kleinz MJ and Davenport AP:
Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous vasoactive
peptide apelin to human vascular and endocardial endothelial cells.
Regul Pept. 118:119–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li F, Li L, Qin X, Pan W, Feng F, Chen F,
Zhu B, Liao D, Tanowitz H, Albanese C and Chen L: Apelin-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation: the regulation of cyclin
D1. Front Biosci. 13:3786–3792. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu C, Su T, Li F, Li L, Qin X, Pan W,
Feng F, Chen F, Liao D and Chen L: PI3K/Akt signaling transduction
pathway is involved in rat vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation induced by apelin-13. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 42:396–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mao XH, Tao S, Zhang XHui, Li F, Qin XP,
Liao DF, Li LF and Chen LX: Apelin-13 promotes monocyte adhesion to
human umbilical vein endothelial cell mediated by
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Prog Biochem
Biophys. 38:1162–1170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu Y, Zhu X, Liang GX, Cui RR, Liu Y, Wu
SS, Liang QH, Liu GY, Jiang Y, Liao XB, et al: Apelin-APJ induces
ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and MCP-1 expression via NF-κB/JNK signal pathway in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Amino Acids. 43:2125–2136.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lassègue B and Clempus RE: Vascular
NAD(P)H oxidases: Specific features, expression, and regulation. Am
J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 285:R277–R297. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Potdar S and Kavdia M: NO/peroxynitrite
dynamics of high glucose-exposed HUVECs: Chemiluminescent
measurement and computational model. Microvasc Res. 78:191–198.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cohen RA and Tong X: Vascular oxidative
stress: The common link in hypertensive and diabetic vascular
disease. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 55:308–316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang JH, Li YN, Qi JS and Jia XX:
Peroxynitrite-induced protein nitration is responsible for renal
mitochondrial damage in diabetic rat. J Endocrinol Invest.
33:140–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li L, Li L, Xie F, Zhang Z, Guo Y, Tang G,
Lv D, Lu Q, Chen L and Li J: Jagged-1/Notch3 signaling transduction
pathway is involved in apelin-13-induced vascular smooth muscle
cells proliferation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
45:875–881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hashimoto T, Kihara M, Imai N, Yoshida S,
Shimoyamada H, Yasuzaki H, Ishida J, Toya Y, Kiuchi Y, Hirawa N, et
al: Requirement of apelin-apelin receptor system for oxidative
stress-linked atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 171:1705–1712. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Leeper NJ, Tedesco MM, Kojima Y, Schultz
GM, Kundu RK, Ashley EA, Tsao PS, Dalman RL and Quertermous T:
Apelin prevents aortic aneurysm formation by inhibiting macrophage
inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H1329–H1335.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lv D, Li H and Chen L: Apelin and APJ, a
novel critical factor and therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:527–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee DK, Saldivia VR, Nguyen T, Cheng R,
George SR and O'Dowd BF: Modification of the terminal residue of
apelin-13 antagonizes its hypotensive action. Endocrinology.
146:231–236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tatemoto K, Takayama K, Zou MX, Kumaki I,
Zhang W, Kumano K and Fujimiya M: The novel peptide apelin lowers
blood pressure via a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Regul Pept.
99:87–92. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Japp AG, Cruden NL, Barnes G, van Gemeren
N, Mathews J, Adamson J, Johnston NR, Denvir MA, Megson IL, Flapan
AD and Newby DE: Acute cardiovascular effects of apelin in humans:
Potential role in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation.
121:1818–1827. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dikalova AE, Góngora MC, Harrison DG,
Lambeth JD, Dikalov S and Griendling KK: Upregulation of Nox1 in
vascular smooth muscle leads to impaired endothelium-dependent
relaxation via eNOS uncoupling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H673–H679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ghiadoni L, Taddei S and Virdis A:
Hypertension and endothelial dysfunction: Therapeutic approach.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 10:42–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Siddiquee K, Hampton J, Khan S, Zadory D,
Gleaves L, Vaughan DE and Smith LH: Apelin protects against
angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular fibrosis and decreases
plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 production. J Hypertens.
29:724–731. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sun X, Iida S, Yoshikawa A, Senbonmatsu R,
Imanaka K, Maruyama K, Nishimura S, Inagami T and Senbonmatsu T:
Non-activated APJ suppresses the angiotensin II type 1 receptor,
whereas apelin-activated APJ acts conversely. Hypertens Res.
34:701–706. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ryu S, Ornoy A, Samuni A, Zangen S and
Kohen R: Oxidative stress in Cohen diabetic rat model by
high-sucrose, low-copper diet: Inducing pancreatic damage and
diabetes. Metabolism. 57:1253–1261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kitada M, Kume S, Imaizumi N and Koya D:
Resveratrol improves oxidative stress and protects against diabetic
nephropathy through normalization of Mn-SOD dysfunction in
AMPK/SIRT1-independent pathway. Diabetes. 60:634–643. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SH, Nam BY, Kang EW, Han SH, Li JJ,
Kim H, Kim SH, Kwak SJ, Park JT, Chang TI, et al: Effects of an
oral adsorbent on oxidative stress and fibronectin expression in
experimental diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
25:2134–2141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ha H, Yu MR, Choi YJ, Kitamura M and Lee
HB: Role of high glucose-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation
in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by mesangial
cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:894–902. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Shimotomai T,
Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M and Ito S: Association of
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with renal tubular damage in
diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 17:11–15. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Day RT, Cavaglieri RC and Feliers D:
Apelin retards the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J
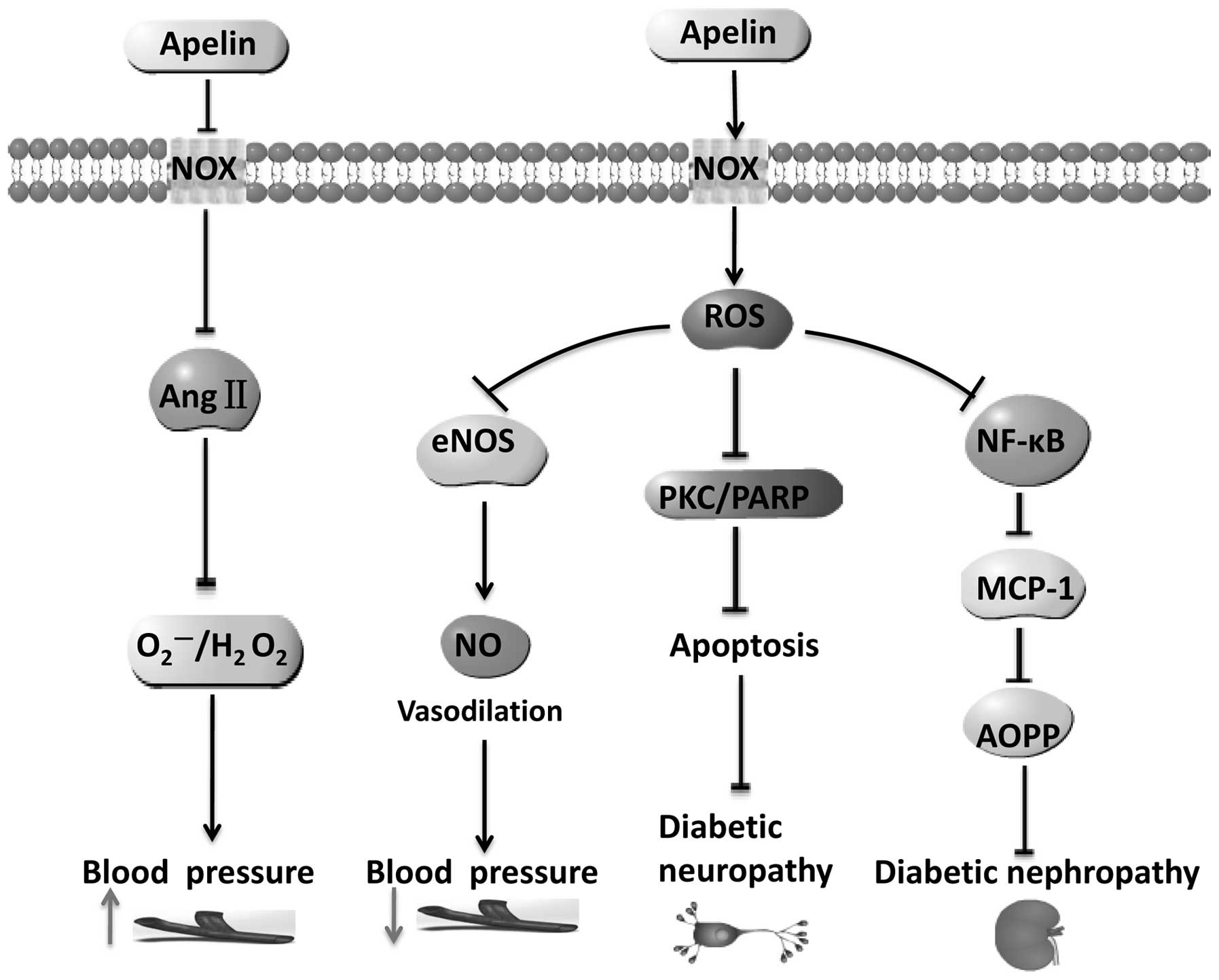
Physiol Renal Physiol. 304:F788–F800. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nishida M, Okumura Y, Oka T, Toiyama K,
Ozawa S, Itoi T and Hamaoka K: The role of apelin on the
alleviative effect of Angiotensin receptor blocker in unilateral
ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis. Nephron Extra.
2:39–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cameron NE and Cotter MA: Pro-inflammatory
mechanisms in diabetic neuropathy: Focus on the nuclear factor
kappa B pathway. Curr Drug Targets. 9:60–67. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ganesh Yerra V, Negi G, Sharma SS and
Kumar A: Potential therapeutic effects of the simultaneous
targeting of the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways in diabetic neuropathy.
Redox Biol. 1:394–397. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zeng XJ, Yu SP, Zhang L and Wei L:
Neuroprotective effect of the endogenous neural peptide apelin in
cultured mouse cortical neurons. Exp Cell Res. 316:1773–1783. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Simó R, Carrasco E, García-Ramírez M and
Hernández C: Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2:71–98. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tao Y, Lu Q, Jiang YR, Qian J, Wang JY,
Gao L and Jonas JB: Apelin in plasma and vitreous and in
fibrovascular retinal membranes of patients with proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:4237–4242.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lu Q, Feng J and Jiang YR: The role of
apelin in the retina of diabetic rats. PLoS One. 8:e697032013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Saint-Geniez M, Masri B, Malecaze F,
Knibiehler B and Audigier Y: Expression of the murine msr/apj
receptor and its ligand apelin is upregulated during formation of
the retinal vessels. Mech Dev. 110:183–186. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Cain K, Bratton SB and Cohen GM: The
Apaf-1 apoptosome: A large caspase-activating complex. Biochimie.
84:203–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Matsushita H, Morishita R, Nata T, Aoki M,
Nakagami H, Taniyama Y, Yamamoto K, Higaki J, Yasufumi K and
Ogihara T: Hypoxia-induced endothelial apoptosis through nuclear
factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated bcl-2 suppression: In vivo
evidence of the importance of NF-kappaB in endothelial cell
regulation. Circ Res. 86:974–981. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Di Stilo A, Chegaev K, Lazzarato L,
Fruttero R, Gasco A, Rastaldo R and Cappello S: Effects of nitric
oxide donor antioxidants containing the phenol vitamin E
substructure and a furoxan moiety on ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Arzneimittelforschung. 59:111–116. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rastaldo R, Cappello S, Folino A, Di Stilo
A, Chegaev K, Tritto I, Pagliaro P and Losano G: Low concentrations
of an nitric oxide-donor combined with a liposoluble antioxidant
compound enhance protection against reperfusion injury in isolated
rat hearts. J Physiol Pharmacol. 61:21–27. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen Z, Li T and Zhang B: Morphine
postconditioning protects against reperfusion injury in the
isolated rat hearts. J Surg Res. 145:287–294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zeng XJ, Zhang LK, Wang HX, Lu LQ, Ma LQ
and Tang CS: Apelin protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion
injury in rat. Peptides. 30:1144–1152. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Simpkin JC, Yellon DM, Davidson SM, Lim
SY, Wynne AM and Smith CC: Apelin-13 and apelin-36 exhibit direct
cardioprotective activity against ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Basic Res Cardiol. 102:518–528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sorli SC, Le Gonidec S, Knibiehler B and
Audigier Y: Apelin is a potent activator of tumour neoangiogenesis.
Oncogene. 26:7692–7699. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Han S, Wang G, Qi X, Lee HM, Englander EW
and Greeley GH Jr: A possible role for hypoxia-induced apelin
expression in enteric cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 294:R1832–R1839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu J and Wang Z: Increased oxidative
stress as a selective anticancer therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015:2943032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sawicka E, Lisowska A, Kowal P and Długosz
A: The role of oxidative stress in bladder cancer. Postepy Hig Med
Dosw (Online). 69:744–752. 2015.In Polish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Raina K, Tyagi A, Kumar D, Agarwal R and
Agarwal C: Role of oxidative stress in cytotoxicity of grape seed
extract in human bladder cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
61:187–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Tong L, Chuang CC, Wu S and Zuo L:
Reactive oxygen species in redox cancer therapy. Cancer Lett.
367:18–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shipitsin M and Polyak K: The cancer stem
cell hypothesis: In search of definitions, markers, and relevance.
Lab Invest. 88:459–463. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Shi X, Zhang Y, Zheng J and Pan J:
Reactive oxygen species in cancer stem cells. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 16:1215–1228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gu Q, Zhai L, Feng X, Chen J, Miao Z, Ren
L, Qian X, Yu J, Li Y, Xu X, et al: Apelin-36, a potent peptide,
protects against ischemic brain injury by activating the PI3K/Akt
pathway. Neurochem Int. 63:535–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Silva A, Yunes JA, Cardoso BA, Martins LR,
Jotta PY, Abecasis M, Nowill AE, Leslie NR, Cardoso AA and Barata
JT: PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the
PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability. J Clin
Invest. 3762–3774. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Min KJ, Lee JT, Joe EH and Kwon TK: An
IκBα phosphorylation inhibitor induces heme oxygenase-1(HO-1)
expression through the activation of reactive oxygen species
(ROS)-Nrf2-ARE signaling and ROS-PI3K/Akt signaling in an
NF-κB-independent mechanism. Cell Signal. 23:1505–1513. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Khaksari M, Aboutaleb N, Nasirinezhad F,
Vakili A and Madjd Z: Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemic
reperfusion injury and cerebral edema in a transient model of focal
cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 48:201–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bao HJ, Zhang L, Han WC and Dai DK:
Apelin-13 attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced damage by
suppressing autophagy. Neurochem Res. 40:89–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kasai A, Kinjo T, Ishihara R, Sakai I,
Ishimaru Y, Yoshioka Y, Yamamuro A, Ishige K, Ito Y and Maeda S:
Apelin deficiency accelerates the progression of amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis. PLoS One. 6:e239682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kidoya H, Ueno M, Yamada Y, Mochizuki N,
Nakata M, Yano T, Fujii R and Takakura N: Spatial and temporal role
of the apelin/APJ system in the caliber size regulation of blood
vessels during angiogenesis. EMBO J. 27:522–534. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Inuzuka H, Nishizawa H, Inagaki A, Suzuki
M, Ota S, Miyamura H, Miyazaki J, Sekiya T, Kurahashi H and Udagawa
Y: Decreased expression of apelin in placentas from severe
pre-eclampsia patients. Hypertens Pregnancy. 32:410–421. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bortoff KD, Qiu C, Runyon S, Williams MA
and Maitra R: Decreased maternal plasma apelin concentrations in
preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy. 31:398–404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Furuya M, Okuda M, Usui H, Takenouchi T,
Kami D, Nozawa A, Shozu M, Umezawa A, Takahashi T and Aoki I:
Expression of angiotensin II receptor-like 1 in the placentas of
pregnancy-induced hypertension. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 31:227–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Vatish M, Randeva HS and Grammatopoulos
DK: Hormonal regulation of placental nitric oxide and pathogenesis
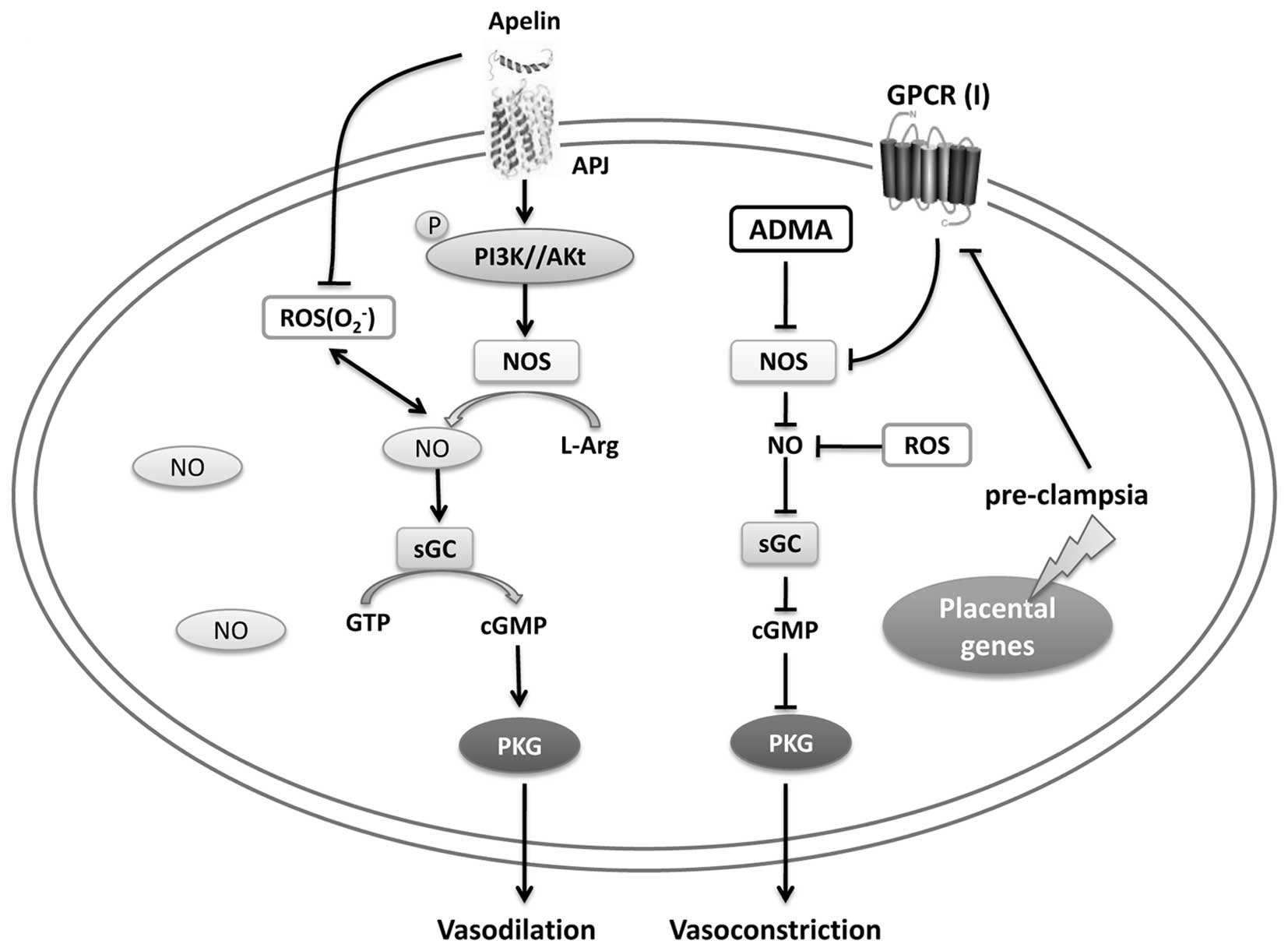
of pre-eclampsia. Trends Mol Med. 12:223–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Han S, Wang G, Qi X, Englander EW and
Greeley GH Jr: Involvement of a Stat3 binding site in
inflammation-induced enteric apelin expression. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 295:G1068–G1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cai X, Chen X, Wang X, Xu C, Guo Q, Zhu L,
Zhu S and Xu J: Pre-protective effect of lipoic acid on injury
induced by H2O2 in IPEC-J2 cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 378:73–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Baregamian N, Song J, Jeschke MG, Evers BM
and Chung DH: IGF-1 protects intestinal epithelial cells from
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Surg Res. 136:31–37. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gad GI, Ismail RI, El-Masry SA and Gouda
HR: Serum apelin in early-onset neonatal sepsis: Is it diagnostic?
J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 7:207–212. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lesur O, Roussy JF, Chagnon F, Gallo-Payet
N, Dumaine R, Sarret P, Chraibi A, Chouinard L and Hogue B: Proven
infection-related sepsis induces a differential stress response
early after ICU admission. Crit Care. 14:R1312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pan CS, Teng X, Zhang J, Cai Y, Zhao J, Wu
W, Wang X, Tang CS and Qi YF: Apelin antagonizes myocardial
impairment in sepsis. J Card Fail. 16:609–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mertens K, Lowes DA, Webster NR, Talib J,
Hall L, Davies MJ, Beattie JH and Galley HF: Low zinc and selenium
concentrations in sepsis are associated with oxidative damage and
inflammation. Br J Anaesth. 114:990–999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Bar-Or D, Carrick MM, Mains CW, Rael LT,
Slone D and Brody EN: Sepsis, oxidative stress, and hypoxia: Are
there clues to better treatment? Redox Rep. 20:193–197. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Rastaldo R, Cappello S, Folino A and
Losano G: Effect of apelin-apelin receptor system in postischaemic
myocardial protection: a pharmacological postconditioning tool?
Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:909–922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Azizi Y, Faghihi M, Imani A, Roghani M and
Nazari A: Post-infarct treatment with [Pyr1]-apelin-13 reduces
myocardial damage through reduction of oxidative injury and nitric
oxide enhancement in the rat model of myocardial infarction.
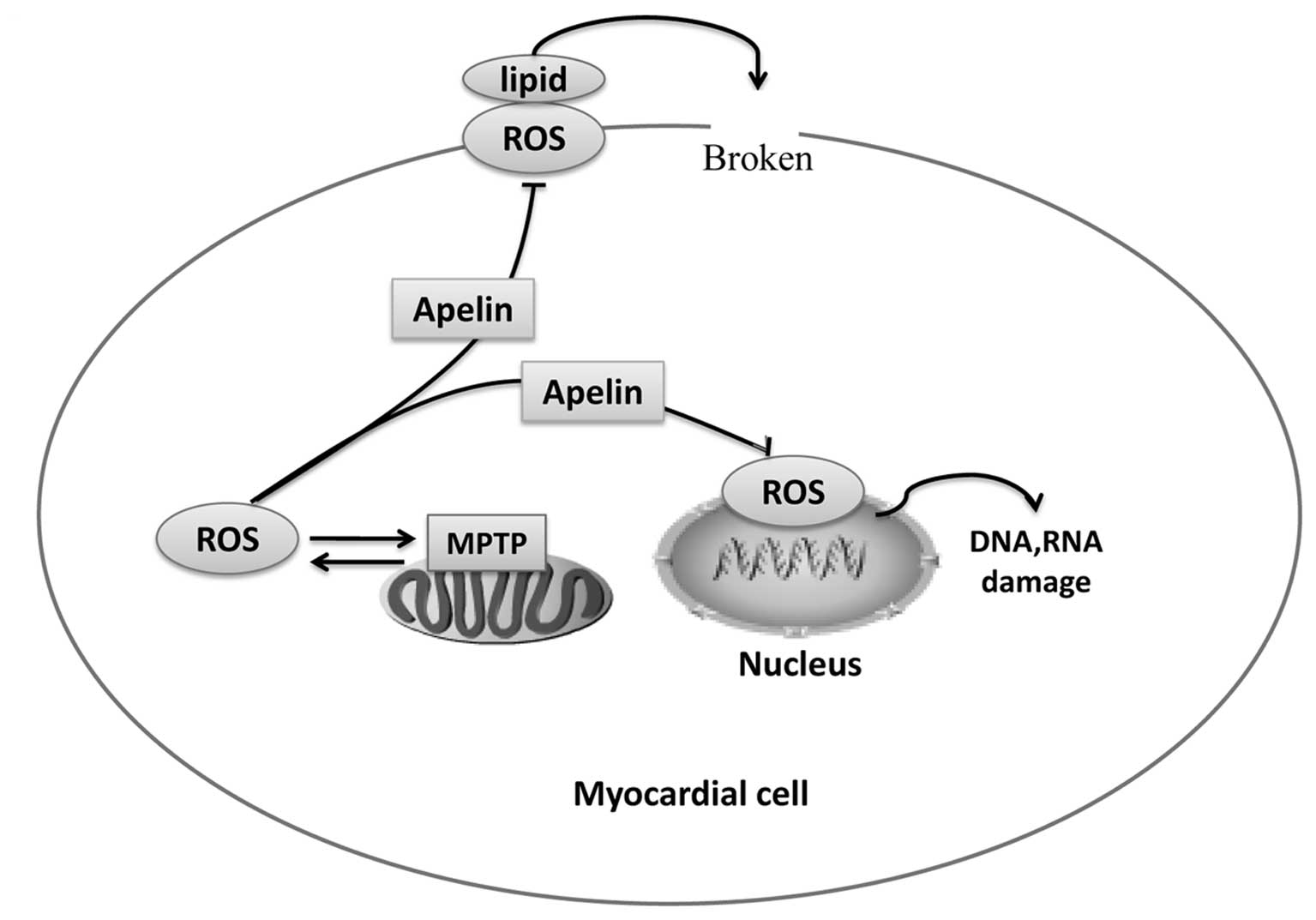
Peptides. 46:76–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Chen XY, Liu XM, Feng LL and Tang CS:
Changes and clinical significance of serum Apelin in patients with
severe sepsis and septic shock. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue
Bao. 30:131–135. 2008.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Cao J, Li H and Chen L: Targeting drugs to
APJ receptor: The prospect of treatment of hypertension and other
cardiovascular diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 16:148–155. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Iturrioz X, Alvear-Perez R, De Mota N,
Franchet C, Guillier F, Leroux V, Dabire H, Le Jouan M, Chabane H,
Gerbier R, et al: Identification and pharmacological properties of
E339-3D6, the first nonpeptidic apelin receptor agonist. FASEB J.
24:1506–1517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Khan P, Maloney PR, Hedrick M, Gosalia P,
Milewski M, Li L, Roth GP, Sergienko E, Suyama E, Sugarman E, et
al: Functional Agonists of the Apelin (APJ) Receptor. Probe Reports
from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Last Update.
Dec 12–2011
|
|
97
|
Mendez M: Renin release: Role of SNAREs.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 307:R484–R486. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Maloney PR, Khan P, Hedrick M, Gosalia P,
Milewski M, Li L, Roth GP, Sergienko E, Suyama E, Sugarman E, et
al: Discovery of 4-oxo-6-((pyrimidin-2-ylthio)methyl)-4H-pyran-3-yl
4-nitro-benzoate (ML221) as a functional antagonist of the apelin
(APJ) receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:6656–6660. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhou N, Fang J, Acheampong E, Mukhtar M
and Pomerantz RJ: Binding of ALX40-4C to APJ, a CNS-based receptor,
inhibits its utilization as a co-receptor by HIV-1. Virology.
312:196–203. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhang Y, Maitra R, Harris DL, Dhungana S,
Snyder R and Runyon SP: Identifying structural determinants of
potency for analogs of apelin-13: Integration of C-terminal
truncation with structure-activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 22:2992–2997.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Jin G, Yang P, Gong Y, Fan X, Tang J and
Lin J: Effects of puerarin on expression of apelin and its receptor
of 2K1C renal hypertension rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
34:3263–3267. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
102
|
Wu D, He L and Chen L: Apelin/APJ system:
A promising therapy target for hypertension. Mol Biol Rep.
41:6691–6703. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
El Messari S, Iturrioz X, Fassot C, De
Mota N, Roesch D and Llorens-Cortes C: Functional dissociation of
apelin receptor signaling and endocytosis: Implications for the
effects of apelin on arterial blood pressure. J Neurochem.
90:1290–1301. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhang BH, Wang W, Wang H, Yin J and Zeng
XJ: Promoting effects of the adipokine, apelin, on diabetic
nephropathy. PLoS One. 8:e604572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen H, Wan D, Wang L, Peng A, Xiao H,
Petersen RB, Liu C, Zheng L and Huang K: Apelin protects against
acute renal injury by inhibiting TGF-β1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1278–1287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yang Y, Zhang X, Cui H, Zhang C, Zhu C and
Li L: Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemia/reperfusion
injury through activating PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Neurosci Lett. 568:44–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Xin Q, Cheng B, Pan Y, Liu H, Yang C, Chen
J and Bai B: Neuroprotective effects of apelin-13 on experimental
ischemic stroke through suppression of inflammation. Peptides.
63:55–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|