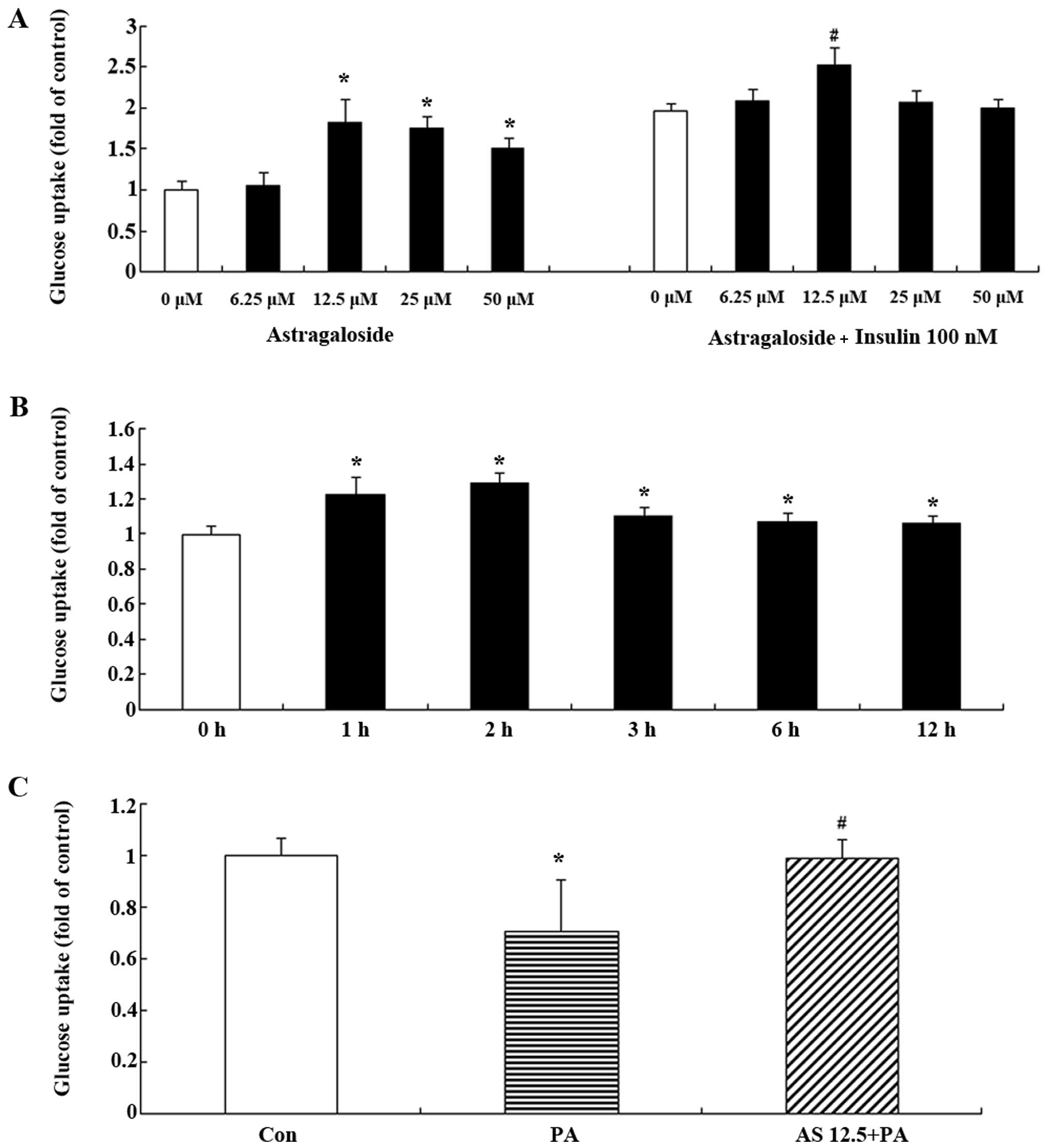
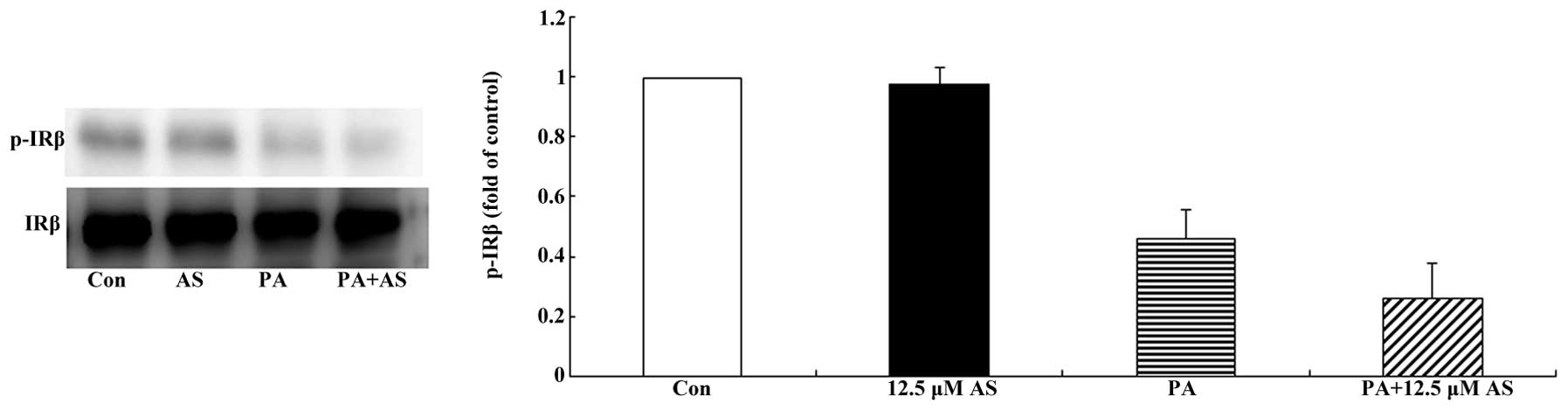
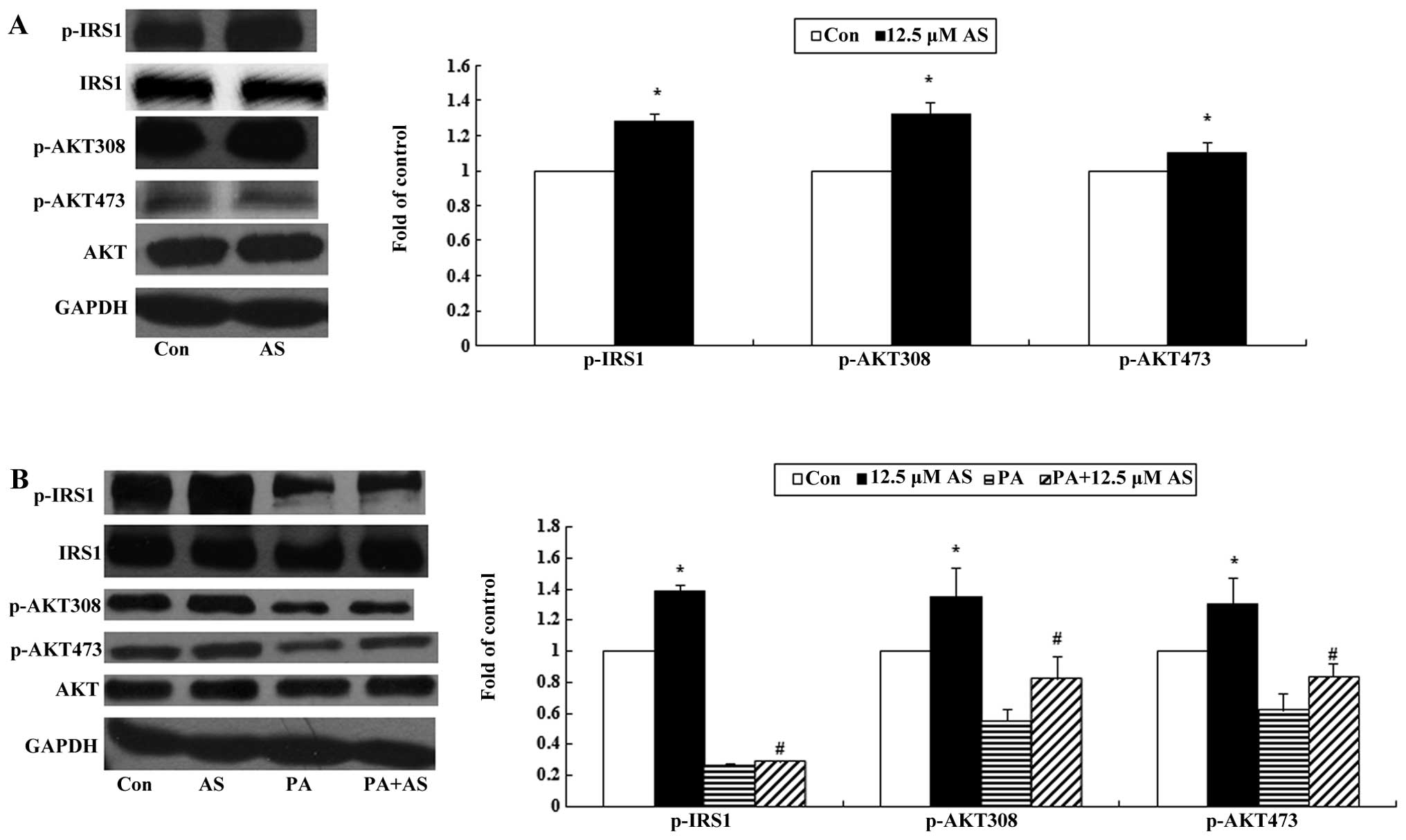
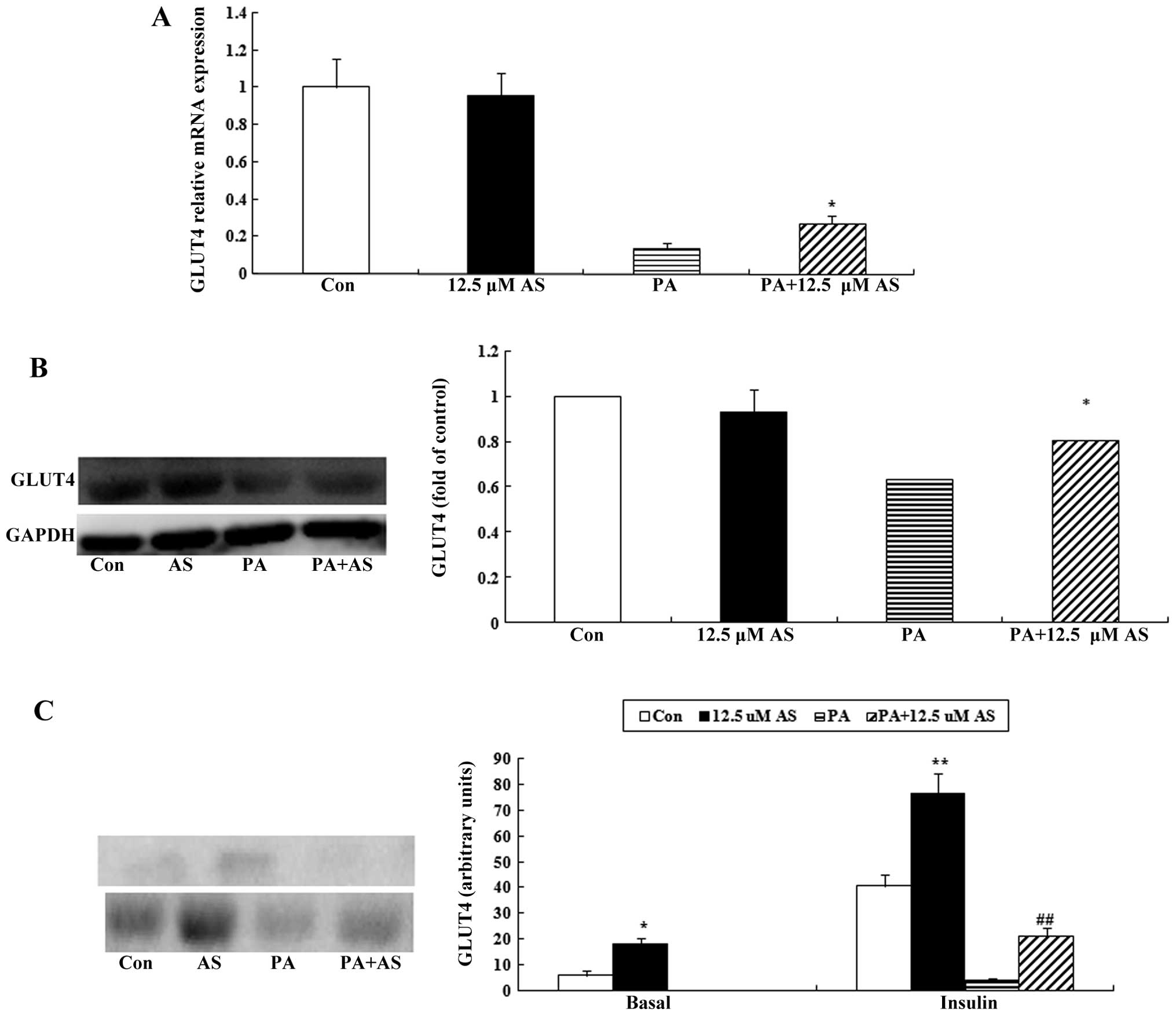
|
1
|
DeFronzo RA, Gunnarsson R, Björkman O,
Olsson M and Wahren J: Effects of insulin on peripheral and
splanchnic glucose metabolism in noninsulin-dependent (type II)
diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 76:149–155. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kiens B, Roemen TH and van der Vusse GJ:
Muscular long-chain fatty acid content during graded exercise in
humans. Am J Physiol. 276:E352–E357. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pirola L, Bonnafous S, Johnston AM,
Chaussade C, Portis F and Van Obberghen E: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase-mediated reduction of Insulin receptor substrate-1/2
protein expression via different mechanisms contributes to the
insulin-induced desensitization of its signaling pathways in L6
muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 278:15641–15651. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boden G: Fatty acid-induced inflammation
and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and liver. Curr Diab Rep.
6:177–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdul-Ghani MA, Muller FL, Liu Y, Chavez
AO, Balas B, Zuo P, Chang Z, Tripathy D, Jani R, Molina-Carrion M,
et al: Deleterious action of FA metabolites on ATP synthesis:
possible link between lipotoxicity, mitochondrial dysfunction, and
insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 295:E678–E685.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Itani SI, Zhou Q, Pories WJ, MacDonald KG
and Dohm GL: Involvement of protein kinase C in human skeletal
muscle insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes. 49:1353–1358.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koistinen HA, Galuska D, Chibalin AV, Yang
J, Zierath JR, Holman GD and Wallberg-Henriksson H:
5-amino-imidazole carboxamide riboside increases glucose transport
and cell-surface GLUT4 content in skeletal muscle from subjects
with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 52:1066–1072. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu W, Tang S, Shi J, Yin W, Cao S, Bu R,
Zhu D and Bi Y: Metformin attenuates palmitic acid-induced insulin
resistance in L6 cells through the AMP-activated protein
kinase/sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 35:1734–1740. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karlsson HK, Hällsten K, Björnholm M,
Tsuchida H, Chibalin AV, Virtanen KA, Heinonen OJ, Lönnqvist F,
Nuutila P and Zierath JR: Effects of metformin and rosiglitazone
treatment on insulin signaling and glucose uptake in patients with
newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled study.
Diabetes. 54:1459–1467. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meshkani R, Sadeghi A, Taheripak G,
Zarghooni M, Gerayesh-Nejad S and Bakhtiyari S: Rosiglitazone, a
PPARγ agonist, ameliorates palmitate-induced insulin resistance and
apoptosis in skeletal muscle cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 32:683–691.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steinberg GR, Watt MJ, Ernst M, Birnbaum
MJ, Kemp BE and Jørgensen SB: Ciliary neurotrophic factor
stimulates muscle glucose uptake by a PI3-kinase-dependent pathway
that is impaired with obesity. Diabetes. 58:829–839. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lv L, Wu SY, Wang GF, Zhang JJ, Pang JX,
Liu ZQ, Xu W, Wu SG and Rao JJ: Effect of astragaloside IV on
hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in diabetic mice induced by a
high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Phytother Res. 24:219–224.
2010.
|
|
13
|
Jiang B, Yang Y, Jin H, Shang W, Zhou L,
Qian L and Chen M: Astragaloside IV attenuates lipolysis and
improves insulin resistance induced by TNFalpha in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Phytother Res. 22:1434–1439. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang N, Wang XH, Mao SL and Zhao F:
Astragaloside IV improves metabolic syndrome and endothelium
dysfunction in fructose-fed rats. Molecules. 16:3896–3907. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li HB, Ge YK, Zhang L and Zheng XX:
Astragaloside IV improved barrier dysfunction induced by acute high
glucose in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Life Sci.
79:1186–1193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li ZP and Cao Q: Effects of astragaloside
IV on myocardial calcium transport and cardiac function in ischemic
rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:898–904. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Tang F, Yang Y, Lu M, Luan A,
Zhang J, Yang J and Wang H: Astragaloside IV protects against
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by regulating
NF-κB/PGC-1α signaling mediated energy biosynthesis. PLoS One.
10:e01187592015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lu M, Tang F, Zhang J, Luan A, Mei M, Xu
C, Zhang S, Wang H and Maslov LN: Astragaloside IV attenuates
injury caused by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats via
regulation of Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway. Phytother Res. 29:599–606. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen J, Gui D, Chen Y, Mou L, Liu Y and
Huang J: Astragaloside IV improves high glucose-induced podocyte
adhesion dysfunction via alpha3beta1 integrin upregulation and
integrin-linked kinase inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 76:796–804.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ai P, Yong G, Dingkun G, Qiuyu Z, Kaiyuan
Z and Shanyan L: Aqueous extract of Astragali Radix induces human
natriuresis through enhancement of renal response to atrial
natriuretic peptide. J Ethnopharmacol. 116:413–421. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang ZS, Xiong F, Xie XH, Chen D, Pan JH
and Cheng L: Astragaloside IV attenuates proteinuria in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy via the inhibition of
endoplasmic reticulum stress. BMC Nephrol. 16:442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu WS, Li S, Guo WW, Chen LL and Li YS:
Effects of Astragaloside IV on diabetic nephropathy in rats. Genet
Mol Res. 14:5427–5434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu J, Zhang Y, Sun S, Shen J, Qiu J, Yin
X, Yin H and Jiang S: Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on
diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
84:579–587. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang WJ, Hufnagl P, Binder BR and Wojta
J: Antiinflammatory activity of Astragaloside IV is mediated by
inhibition of NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule
expression. Thromb Haemost. 90:904–914. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao P, Wang Y, Zeng S, Lu J, Jiang TM and
Li YM: Protective effect of astragaloside IV on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction via downregulation
of inflammatory signaling in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
37:428–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang WJ and Frei B: Astragaloside IV
inhibits NF-κB activation and inflammatory gene expression in
LPS-treated mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:2743142015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xu A, Wang H, Hoo RL, Sweeney G, Vanhoutte
PM, Wang Y, Wu D, Chu W, Qin G and Lam KS: Selective elevation of
adiponectin production by the natural compounds derived from a
medicinal herb alleviates insulin resistance and glucose
intolerance in obese mice. Endocrinology. 150:625–633. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Perrini S, Natalicchio A, Laviola L,
Belsanti G, Montrone C, Cignarelli A, Minielli V, Grano M, De
Pergola G, Giorgino R and Giorgino F: Dehydroepiandrosterone
stimulates glucose uptake in human and murine adipocytes by
inducing GLUT1 and GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane.
Diabetes. 53:41–52. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tortorella LL and Pilch PF: C2C12 myocytes
lack an insulin-responsive vesicular compartment despite
dexamethasone-induced GLUT4 expression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 283:E514–E524. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jové M, Planavila A, Sánchez RM, Merlos M,
Laguna JC and Vázquez-Carrera M: Palmitate induces tumor necrosis
factor-alpha expression in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells by a
mechanism involving protein kinase C and nuclear factor-kappaB
activation. Endocrinology. 147:552–561. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Griffin ME, Marcucci MJ, Cline GW, Bell K,
Barucci N, Lee D, Goodyear LJ, Kraegen EW, White MF and Shulman GI:
Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with
activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin
signaling cascade. Diabetes. 48:1270–1274. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tabandeh MR, Jafari H, Hosseini SA and
Hashemitabar M: Ginsenoside Rb1 stimulates adiponectin signaling in
C2C12 muscle cells through up-regulation of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2
proteins. Pharm Biol. 53:125–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bryant NJ, Govers R and James DE:
Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 3:267–277. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O'Gorman DJ, Karlsson HK, McQuaid S,
Yousif O, Rahman Y, Gasparro D, Glund S, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR
and Nolan JJ: Exercise training increases insulin-stimulated
glucose disposal and GLUT4 (SLC2A4) protein content in patients
with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 49:2983–2992. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leonard BL, Watson RN, Loomes KM, Phillips
AR and Cooper GJ: Insulin resistance in the Zucker diabetic fatty
rat: a metabolic characterisation of obese and lean phenotypes.
Acta Diabetol. 42:162–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN and
Newsholme EA: The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin
sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus.
Lancet. 1:785–789. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McGarry JD: Banting lecture 2001:
dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 51:7–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Krook A, Björnholm M, Galuska D, Jiang XJ,
Fahlman R, Myers MG Jr, Wallberg-Henriksson H and Zierath JR:
Characterization of signal transduction and glucose transport in
skeletal muscle from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes.
49:284–292. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dohm GL, Tapscott EB, Pories WJ, Dabbs DJ,
Flickinger EG, Meelheim D, Fushiki T, Atkinson SM, Elton CW and
Caro JF: An in vitro human muscle preparation suitable for
metabolic studies. Decreased insulin stimulation of glucose
transport in muscle from morbidly obese and diabetic subjects. J
Clin Invest. 82:486–494. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ryder JW, Yang J, Galuska D, Rincón J,
Björnholm M, Krook A, Lund S, Pedersen O, Wallberg-Henriksson H,
Zierath JR and Holman GD: Use of a novel impermeable biotinylated
photo-labeling reagent to assess insulin- and hypoxia-stimulated
cell surface GLUT4 content in skeletal muscle from type 2 diabetic
patients. Diabetes. 49:647–654. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Festa A, D'Agostino R Jr, Tracy RP and
Haffner SM; Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study: Elevated
levels of acute-phase proteins and plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 predict the development of type 2 diabetes: the insulin
resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes. 51:1131–1137. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest.
112:1796–1808. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D,
Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA and Chen H:
Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development
of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest.
112:1821–1830. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K,
Hiasa K, Kitazawa R, Kitazawa S, Miyachi H, Maeda S, Egashira K and
Kasuga M: MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose
tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J
Clin Invest. 116:1494–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sinha S, Perdomo G, Brown NF and O'Doherty
RM: Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in L6 myotubes is
prevented by inhibition of activation and nuclear localization of
nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem. 279:41294–41301. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wada J and Makino H: Innate immunity in
diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 12:13–26. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yuan M, Konstantopoulos N, Lee J, Hansen
L, Li ZW, Karin M and Shoelson SE: Reversal of obesity- and
diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted
disruption of Ikkbeta. Science. 293:1673–1677. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shi H, Kokoeva MV, Inouye K, Tzameli I,
Yin H and Flier JS: TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty
acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 116:3015–3025.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hwang D: Modulation of the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 by fatty acids mediated through toll-like receptor
4-derived signaling pathways. FASEB J. 15:2556–2564. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sriwijitkamol A, Christ-Roberts C, Berria
R, Eagan P, Pratipanawatr T, DeFronzo RA, Mandarino LJ and Musi N:
Reduced skeletal muscle inhibitor of kappaB beta content is
associated with insulin resistance in subjects with type 2
diabetes: Reversal by exercise training. Diabetes. 55:760–767.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Reyna SM, Ghosh S, Tantiwong P, Meka CS,
Eagan P, Jenkinson CP, Cersosimo E, Defronzo RA, Coletta DK,
Sriwijitkamol A and Musi N: Elevated toll-like receptor 4
expression and signaling in muscle from insulin-resistant subjects.
Diabetes. 57:2595–2602. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Radin MS, Sinha S, Bhatt BA, Dedousis N
and O'Doherty RM: Inhibition or deletion of the lipopolysaccharide
receptor Toll-like receptor-4 confers partial protection against
lipid-induced insulin resistance in rodent skeletal muscle.
Diabetologia. 51:336–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Tsukumo DM, Carvalho-Filho MA, Carvalheira
JB, Prada PO, Hirabara SM, Schenka AA, Araújo EP, Vassallo J, Curi
R, Velloso LA and Saad MJ: Loss-of-function mutation in Toll-like
receptor 4 prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance.
Diabetes. 56:1986–1998. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L and
Ranganathan G: Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and
interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 280:E745–E751. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD and Burt
D: NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of
acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X.
Diabetologia. 40:1286–1292. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sell H, Dietze-Schroeder D, Kaiser U and
Eckel J: Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 is a potential player in
the negative cross-talk between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle.
Endocrinology. 147:2458–2467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|