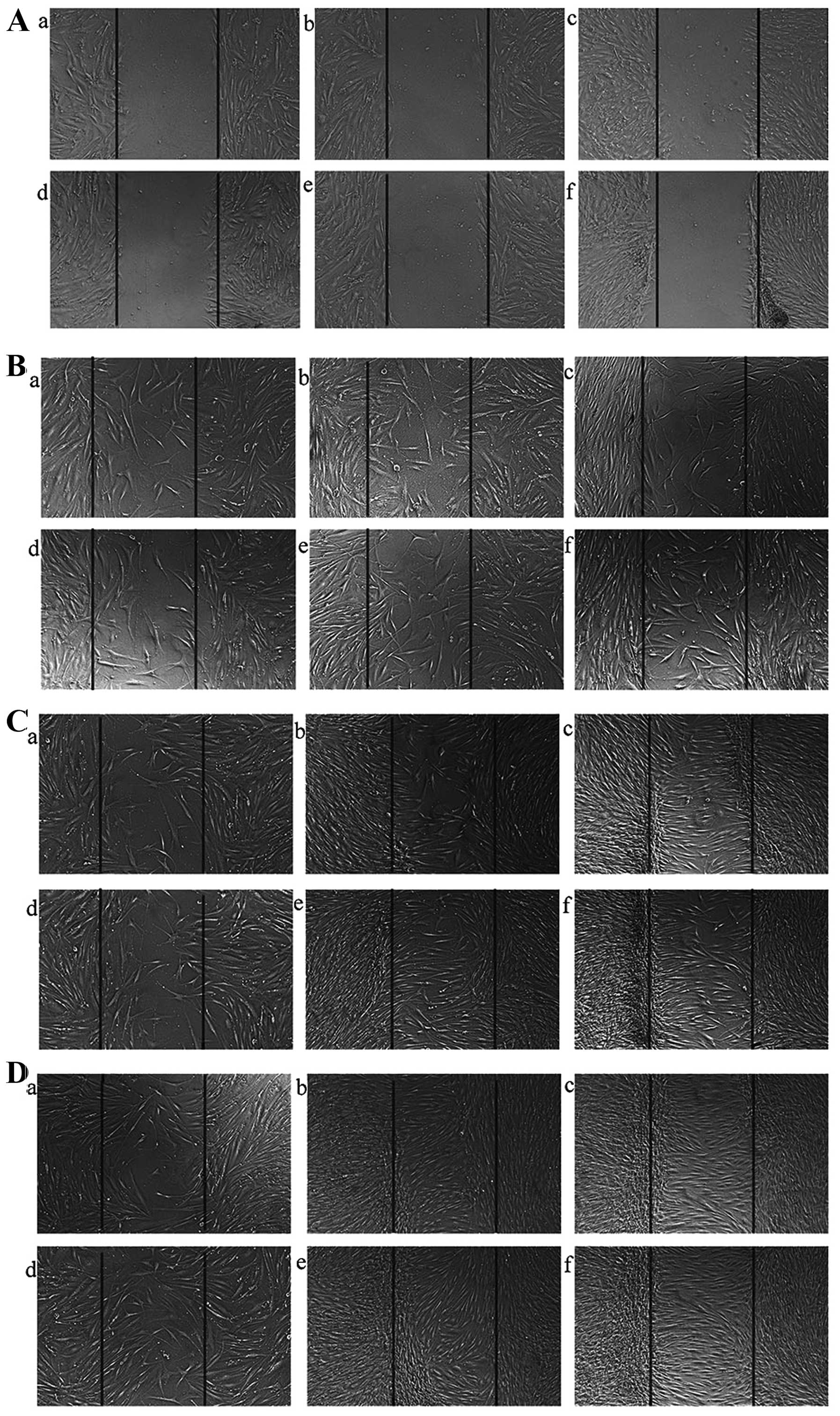
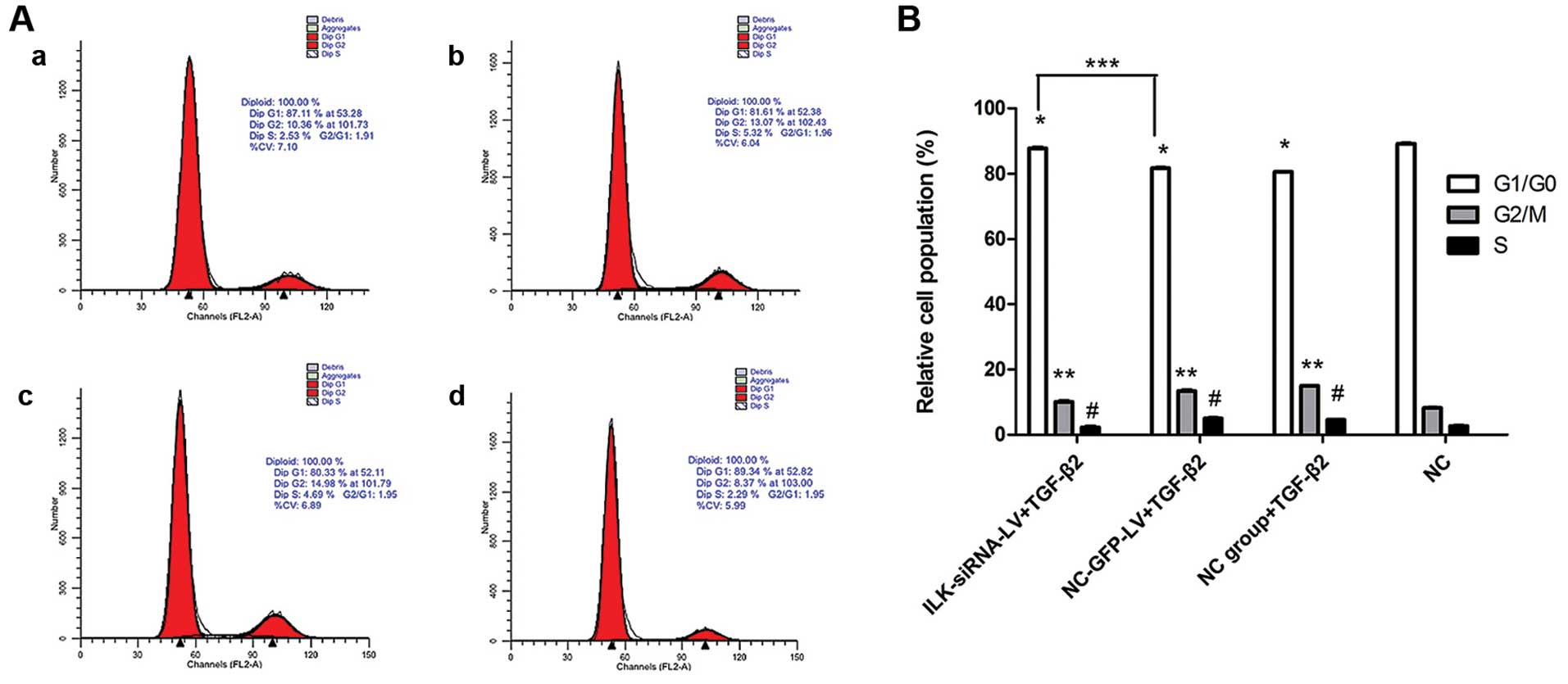
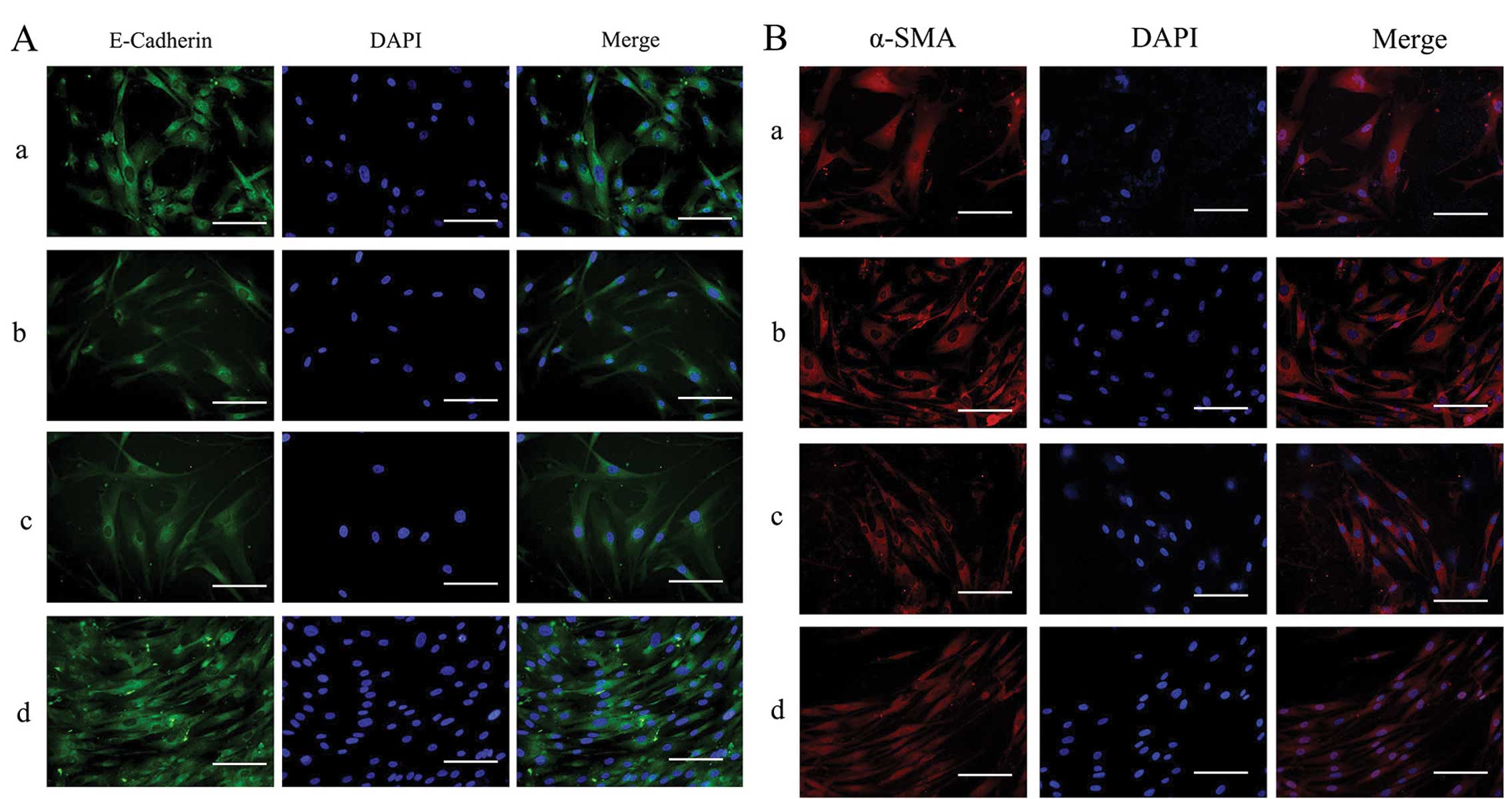
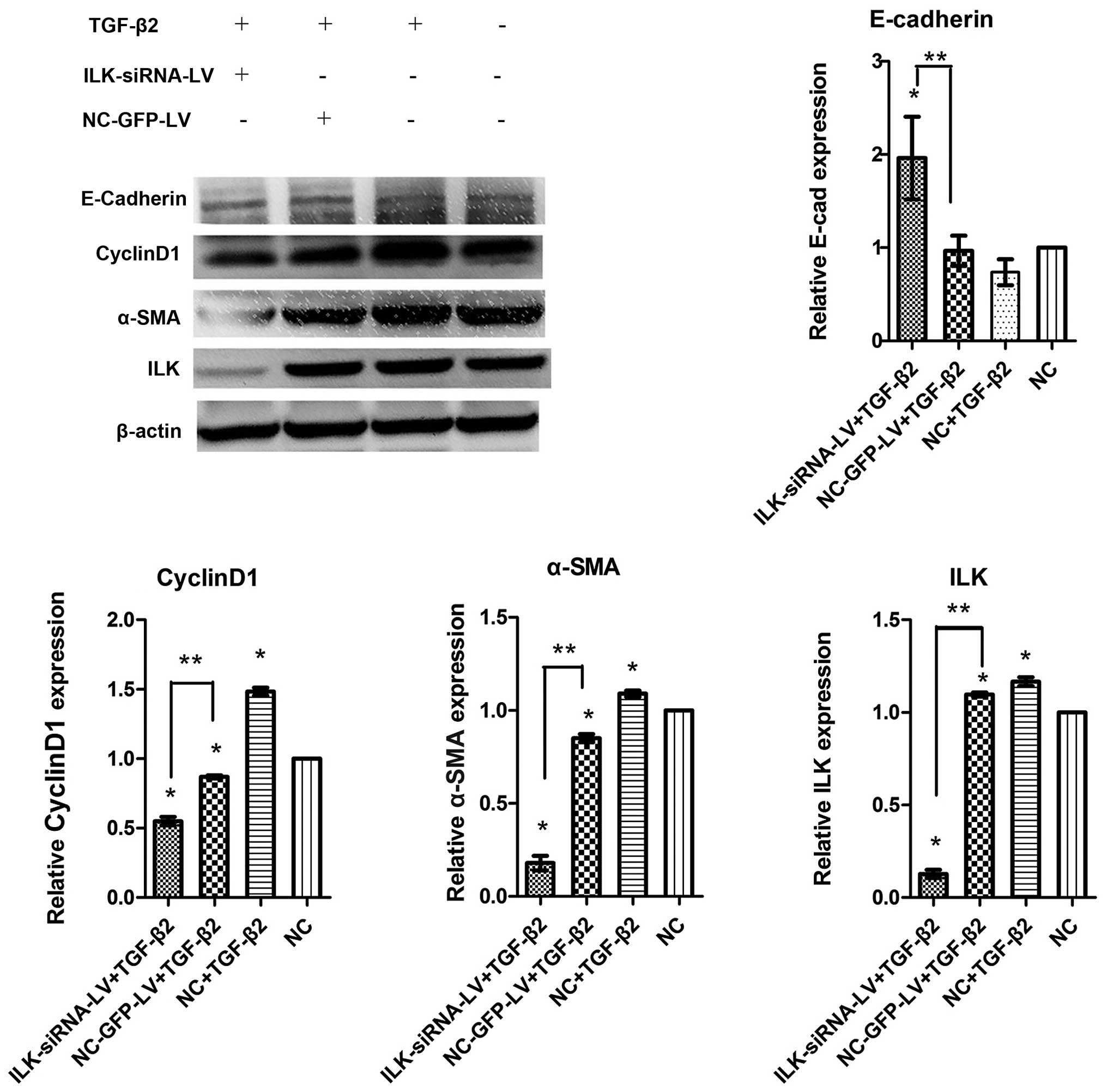
|
1
|
Quigley HA and Broman AT: The number of
people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020. Br J Ophthalmol.
90:262–267. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grisanti S, Szurman P, Warga M, Kaczmarek
R, Ziemssen F, Tatar O and Bartz-Schmidt KU: Decorin modulates
wound healing in experimental glaucoma filtration surgery: a pilot
study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:191–196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ashaye AO and Komolafe OO: Post-operative
complication of trabeculectomy in Ibadan, Nigeria: outcome of
1-year follow-up. Eye (Lond). 23:448–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cordeiro MF: Role of transforming growth
factor beta in conjunctival scarring. Clin Sci (Lond). 104:181–187.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Denk PO, Hoppe J, Hoppe V and Knorr M:
Effect of growth factors on the activation of human Tenon's capsule
fibroblasts. Curr Eye Res. 27:35–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyer-Ter-Vehn T, Katzenberger B, Han H,
Grehn F and Schlunck G: Lovastatin inhibits TGF-beta-induced
myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human tenon fibroblasts.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:3955–3960. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyazono K: TGF-beta signaling by Smad
proteins. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11:15–22. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Piek E, Ju WJ, Heyer J, Escalante-Alcalde
D, Stewart CL, Weinstein M, Deng C, Kucherlapati R, Bottinger EP
and Roberts AB: Functional characterization of transforming growth
factor beta signaling in Smad2- and Smad3-deficient fibroblasts. J
Biol Chem. 276:19945–19953. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grotendorst GR, Rahmanie H and Duncan MR:
Combinatorial signaling pathways determine fibroblast proliferation
and myofibroblast differentiation. FASEB J. 18:469–479. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schiller M, Javelaud D and Mauviel A:
TGF-beta-induced SMAD signaling and gene regulation: consequences
for extracellular matrix remodeling and wound healing. J Dermatol
Sci. 35:83–92. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu C and Dedhar S: Integrin-linked kinase
(ILK) and its inter-actors: a new paradigm for the coupling of
extracellular matrix to actin cytoskeleton and signaling complexes.
J Cell Biol. 155:505–510. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Yang ZL, Ren X, Zou Q, Yuan Y, Liang
L, Chen M and Chen S: ILK and PRDX1 are prognostic markers in
squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinomas and adenocarcinoma of
gallbladder. Tumour Biol. 34:359–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Yang J, Dai C, Wu C and Liu Y: Role
for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 112:503–516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vi L, de Lasa C, DiGuglielmo GM and
Dagnino L: Integrin-linked kinase is required for TGF-β1 induction
of dermal myofibroblast differentiation. J Invest Dermatol.
131:586–593. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bravou V, Klironomos G, Papadaki E,
Taraviras S and Varakis J: ILK over-expression in human colon
cancer progression correlates with activation of beta-catenin,
down-regulation of E-cadherin and activation of the Akt-FKHR
pathway. J Pathol. 208:91–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liang F, Zhang S, Wang B, Qiu J and Wang
Y: Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) promotes glioma
cell invasion and migration and down-regulates E-cadherin via the
NF-κB pathway. J Mol Histol. 45:141–151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Delcommenne
M, Troussard A, Sanghera J and Dedhar S: Inhibition of
integrin-linked kinase (ILK) suppresses activation of protein
kinase B/Akt and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of
PTEN-mutant prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
97:3207–12. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Verreault M and Bally MB: siRNA-mediated
integrin-linked kinase suppression: nonspecific effects of
siRNA/cationic liposome complexes trigger changes in the expression
of phosphorylated-AKT and mTOR independently of ILK silencing.
Oligonucleotides. 19:129–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu DY, Morgan WH, Sun X, Su EN, Cringle
SJ, Yu PK, House P, Guo W and Yu X: The critical role of the
conjunctiva in glaucoma filtration surgery. Prog Retin Eye Res.
28:303–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holló G: Wound healing and glaucoma
surgery: modulating the scarring process with conventional
antimetabolites and new molecules. Dev Ophthalmol. 50:79–89. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan ZC, Bai YJ, Tian Z, Hu HY, You XH, Lin
JX, Liu SR, Zhuo YH and Luo RJ: Anti-proliferation effects of
Sirolimus sustained delivery film in rabbit glaucoma filtration
surgery. Mol Vis. 17:2495–2506. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Falco E, Scafetta G, Napoletano C, Puca
R, Vingolo EM, Ragona G, Iorio O and Frati G: A standardized
laboratory and surgical method for in vitro culture isolation and
expansion of primary human Tenon's fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Bank.
14:277–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Stahnke T, Löbler M, Kastner C, Stachs O,
Wree A, Sternberg K, Schmitz KP and Guthoff R: Different fibroblast
subpopulations of the eye: a therapeutic target to prevent
postoperative fibrosis in glaucoma therapy. Exp Eye Res. 100:88–97.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Horbelt D, Denkis A and Knaus P: A
portrait of transforming growth factor β superfamily signalling:
background matters. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:469–474. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karoń P, Olejek A and Olszak-Wasik K:
TGF-β expression in vulvar cancer. Ginekol Pol. 85:847–851. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bentley-Hewitt KL, De Guzman CE, Ansell J,
Mandimika T, Narbad A and Lund EK: Polyunsaturated fatty acids
modify expression of TGF-β in a co-culture model ultilising human
colorectal cells and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
exposed to Lactobacillus gasseri, Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. 116:505–513. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhu X, Li L, Zou L, Zhu X, Xian G, Li H,
Tan Y and Xie L: A novel aptamer targeting TGF-β receptor II
inhibits transdifferentiation of human tenon's fibroblasts into
myofibroblast. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:6897–6903. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mietz H, Chévez-Barrios P and Lieberman
MW: A mouse model to study the wound healing response following
filtration surgery. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 236:467–475.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kavvadas P, Kypreou KP, Protopapadakis E,
Prodromidi E, Sideras P and Charonis AS: Integrin-linked kinase
(ILK) in pulmonary fibrosis. Virchows Archiv. 457:563–75. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo L, Liu H, Dong Z, Sun L, Peng Y and
Liu F: Small interfering RNA targeting ILK inhibits EMT in human
peritoneal mesothelial cells through phosphorylation of GSK 3β. Mol
Med Rep. 10:137–144. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li R, Liu B, Yin H, Sun W, Yin J and Su Q:
Overexpression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is associated with
tumor progression and an unfavorable prognosis in patients with
colorectal cancer. J Mol Histol. 44:183–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Serrano I, McDonald PC, Lock FE and Dedhar
S: Role of the integrin-linked kinase (ILK)/Rictor complex in
TGFβ-1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Oncogene.
32:50–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yao X, Li D, Xiong DM, Li L, Jiang R and
Chen JX: A novel role of ribonuclease inhibitor in regulation of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and ILK signaling pathway in
bladder cancer cells. Cell Tissue Res. 353:409–423. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li L, Pan XY, Shu J, Jiang R, Zhou YJ and
Chen JX: Ribonuclease inhibitor up-regulation inhibits the growth
and induces apoptosis in murine melanoma cells through repression
of angiogenin and ILK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biochimie.
103:89–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xing Y, Qi J, Deng S, Wang C, Zhang L and
Chen J: Small interfering RNA targeting ILK inhibits metastasis in
human tongue cancer cells through repression of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp Cell Res. 319:2058–2072.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang AH, Pan SH, Chang WH, Hong QS, Chen
JJ and Yu SL: PARVA promotes metastasis by modulating ILK
signalling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01185302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Teo ZL, McQueen-Miscamble L, Turner K,
Martinez G, Madakashira B, Dedhar S, Robinson ML and de Iongh RU:
Integrin linked kinase (ILK) is required for lens epithelial cell
survival, proliferation and differentiation. Exp Eye Res.
121:130–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai J, Matsui T, Abel ED, Dedhar S,
Gerszten RE, Seidman CE, Seidman JG and Rosenzweig A: Deep sequence
analysis of gene expression identifies osteopontin as a downstream
effector of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in cardiac-specific ILK
knockout mice. Circ Heart Fail. 7:184–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Buntrock P: Ultrastructural
characteristics of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and fibroclasts in
the process of wound healing (author's transl). Zentralbl Allg
Pathol. 124:48–59. 1980.In German.
|
|
40
|
Ohtani H and Sasano N: Stromal cell
changes in human colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. An
ultrastructural study of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and smooth
muscle cells. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 401:209–222.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Desmoulière A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F and
Gabbiani G: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth
muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in
quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol.
122:103–111. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oka H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Inoue M,
Tahara H, Kobayashi T, Takatsuka Y, Matsuyoshi N, Hirano S,
Takeichi M, et al: Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion molecules
in human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to metastasis.
Cancer Res. 53:1696–16701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jankowski J, Newham P, Kandemir O, Hirano
S, Takeichi M and Pignatelli M: Differential expression of
e-cadherin in normal, metaplastic and dysplastic esophageal mucosa
- a putative biomarker. Int J Oncol. 4:441–448. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Suzuki SC and Takeichi M: Cadherins in
neuronal morphogenesis and function. Dev Growth Differ. 50(Suppl
1): S119–S130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|