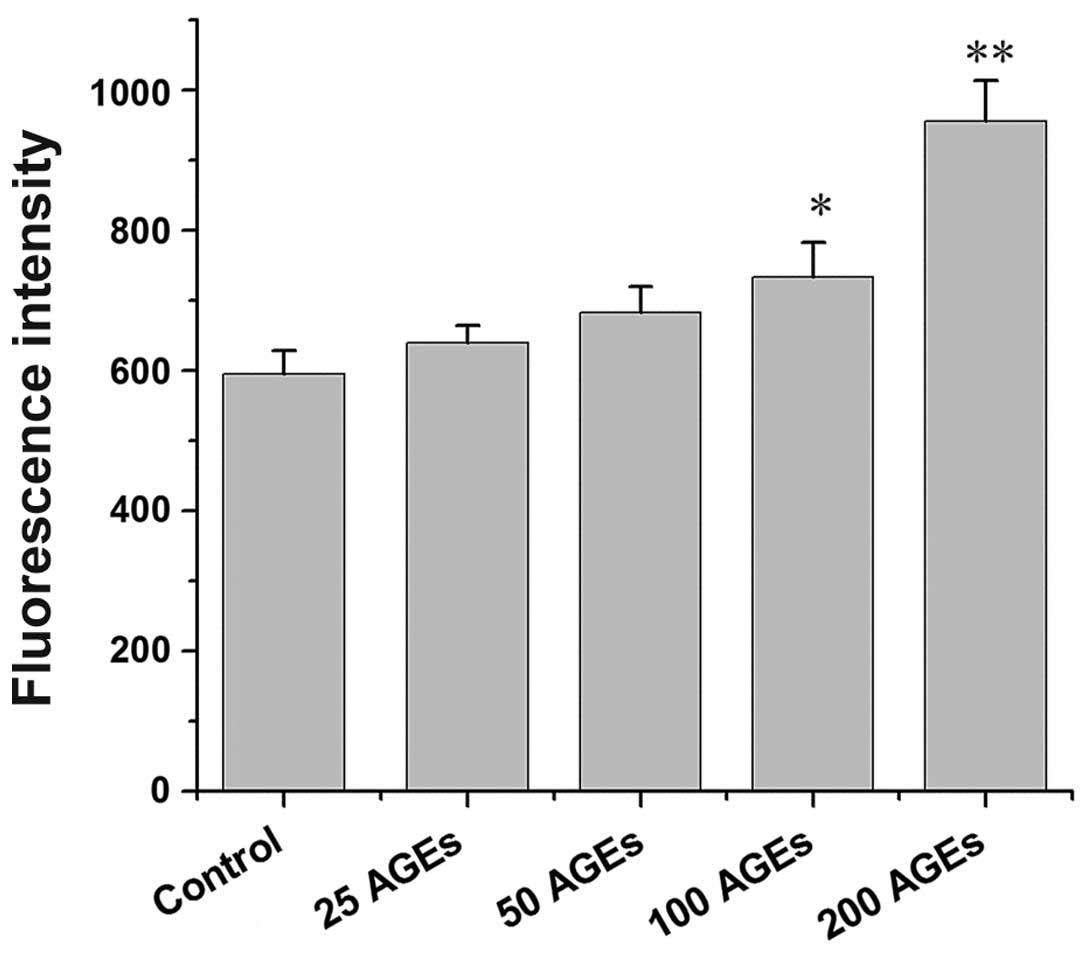
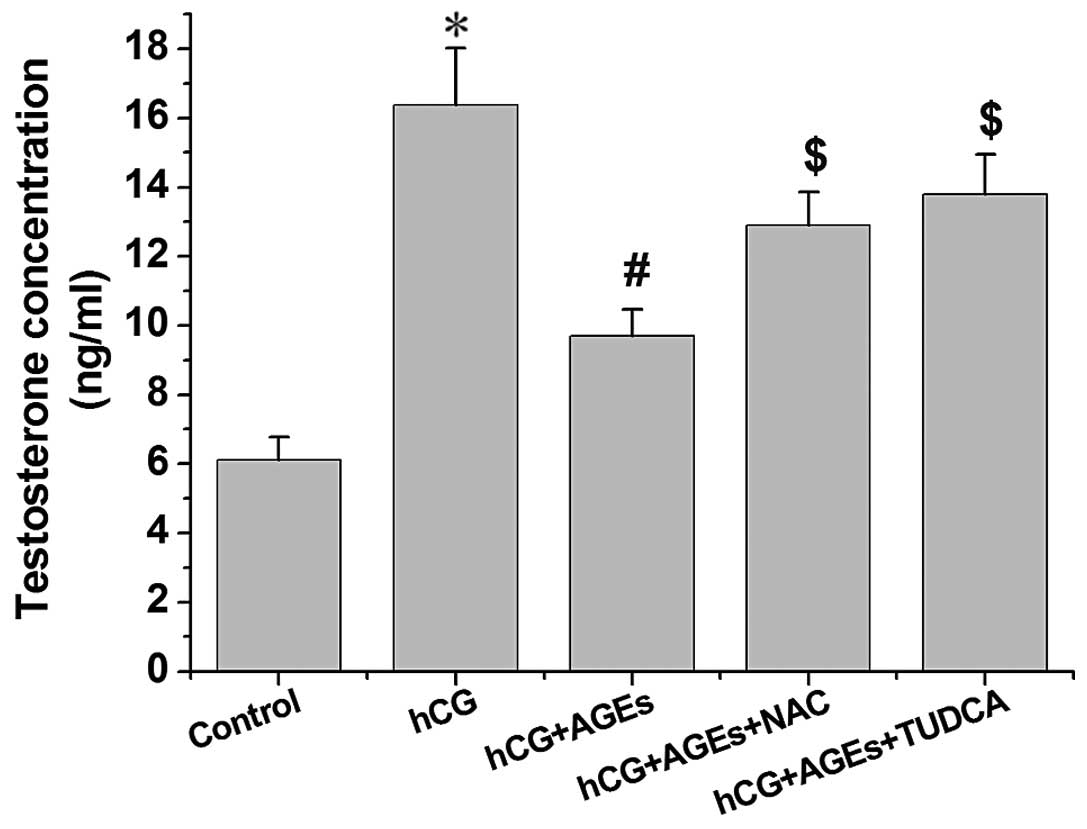
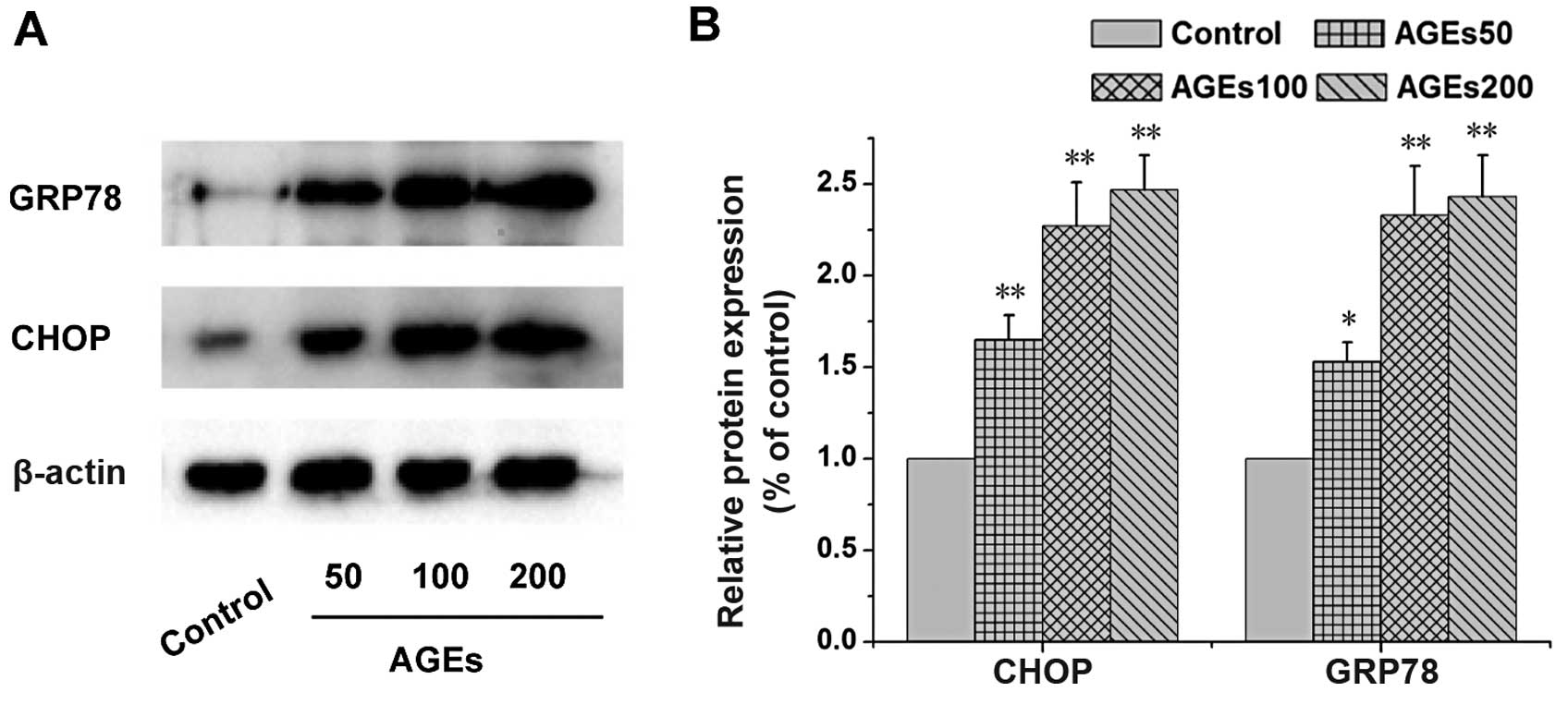
|
1
|
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I,
Beagley J, Linnenkamp U and Shaw JE: Global estimates of diabetes
prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin
Pract. 103:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Daniels SR,
Standiford D, Khoury PR and Zeitler P: Increased incidence of
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among adolescents. J
Pediatr. 128:608–615. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pinhas-Hamiel O and Zeitler P: The global
spread of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. J
Pediatr. 146:693–700. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nadeau K and Dabelea D: Epidemiology of
type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Endocr Res. 33:35–58.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Urakami T, Kubota S, Nitadori Y, Harada K,
Owada M and Kitagawa T: Annual incidence and clinical
characteristics of type 2 diabetes in children as detected by urine
glucose screening in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Diabetes Care.
28:1876–1881. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jangir RN and Jain GC: Diabetes mellitus
induced impairment of male reproductive functions: a review. Curr
Diabetes Rev. 10:147–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sexton WJ and Jarow JP: Effect of diabetes
mellitus upon male reproductive function. Urology. 49:508–513.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baccetti B, La Marca A, Piomboni P,
Capitani S, Bruni E, Petraglia F and De Leo V: Insulin-dependent
diabetes in men is associated with hypothalamo-pituitary
derangement and with impairment in semen quality. Hum Reprod.
17:2673–2677. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schoeller EL, Schon S and Moley KH: The
effects of type 1 diabetes on the hypothalamic, pituitary and
testes axis. Cell Tissue Res. 349:839–847. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scarano WR, Messias AG, Oliva SU,
Klinefelter GR and Kempinas WG: Sexual behaviour, sperm quantity
and quality after short-term streptozotocin-induced hyperglycaemia
in rats. Int J Androl. 29:482–488. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Agbaje IM, Rogers DA, McVicar CM, McClure
N, Atkinson AB, Mallidis C and Lewis SE: Insulin dependant diabetes
mellitus: implications for male reproductive function. Hum Reprod.
22:1871–1877. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ricci G, Catizone A, Esposito R, Pisanti
FA, Vietri MT and Galdieri M: Diabetic rat testes: morphological
and functional alterations. Andrologia. 41:361–368. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mallidis C, Agbaje I, McClure N and
Kliesch S: The influence of diabetes mellitus on male reproductive
function: a poorly investigated aspect of male infertility. Urologe
A. 50:33–37. 2011.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
La Vignera S, Condorelli R, Vicari E,
D'Agata R and Calogero AE: Diabetes mellitus and sperm parameters.
J Androl. 33:145–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Alves MG, Martins AD, Cavaco JE, Socorro S
and Oliveira PF: Diabetes, insulin-mediated glucose metabolism and
Sertoli/blood-testis barrier function. Tissue Barriers.
1:e239922013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vlassara H and Uribarri J: Advanced
glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: cause, effect, or both?
Curr Diab Rep. 14:4532014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Vlassara H and Striker GE: Advanced
glycation endproducts in diabetes and diabetic complications.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 42:697–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vlassara H and Striker GE: AGE restriction
in diabetes mellitus: a paradigm shift. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
7:526–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mallidis C, Agbaje I, Rogers D, Glenn J,
McCullough S, Atkinson AB, Steger K, Stitt A and McClure N:
Distribution of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in
the human male reproductive tract: prevalence in men with diabetes
mellitus. Hum Reprod. 22:2169–2177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moschonas DP, Piperi C, Korkolopoulou P,
Levidou G, Kavantzas N, Trigka EA, Vlachos I, Arapostathi C, Perrea
D, Mitropoulos D, et al: Impact of diet-induced obesity in male
mouse reproductive system: the role of advanced glycation end
product-receptor for advanced glycation end product axis. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 239:937–947. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mallidis C, Agbaje IM, Rogers DA, Glenn
JV, Pringle R, Atkinson AB, Steger K, Stitt AW and McClure N:
Advanced glycation end products accumulate in the reproductive
tract of men with diabetes. Int J Androl. 32:295–305. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
O'Neill J, Czerwiec A, Agbaje I, Glenn J,
Stitt A, McClure N and Mallidis C: Differences in mouse models of
diabetes mellitus in studies of male reproduction. Int J Androl.
33:709–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mallidis C, Czerwiec A, Filippi S, O'Neill
J, Maggi M and McClure N: Spermatogenic and sperm quality
differences in an experimental model of metabolic syndrome and
hypogonadal hypogonadism. Reproduction. 142:63–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karimi J, Goodarzi MT, Tavilani H,
Khodadadi I and Amiri I: Relationship between advanced glycation
end products and increased lipid peroxidation in semen of diabetic
men. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 91:61–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Karimi J, Goodarzi MT, Tavilani H,
Khodadadi I and Amiri I: Increased receptor for advanced glycation
end products in spermatozoa of diabetic men and its association
with sperm nuclear DNA fragmentation. Andrologia. 44(Suppl 1):
280–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheung KK, Luk AO, So WY, Ma RC, Kong AP,
Chow FC and Chan JC: Testosterone level in men with type 2 diabetes
mellitus and related metabolic effects: a review of current
evidence. J Diabetes Investig. 6:112–123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
El Baba K and Azar ST: Low testosterone
and diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 9:418–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iwashima Y, Eto M, Horiuchi S and Sano H:
Advanced glycation end product-induced peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma gene expression in the
cultured mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 264:441–448.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chemes H, Cigorraga S, Bergadá C,
Schteingart H, Rey R and Pellizzari E: Isolation of human Leydig
cell mesenchymal precursors from patients with the androgen
insensitivity syndrome: testosterone production and response to
human chorionic gonadotropin stimulation in culture. Biol Reprod.
46:793–801. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Klinefelter GR, Hall PF and Ewing LL:
Effect of luteinizing hormone deprivation in situ on
steroidogenesis of rat Leydig cells purified by a multistep
procedure. Biol Reprod. 36:769–783. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bose HS, Lingappa VR and Miller WL: The
steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, StAR, works only at the
outer mitochondrial membrane. Endocr Res. 28:295–308. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Payne AH and Hales DB: Overview of
steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active
steroid hormones. Endocr Rev. 25:947–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ott C, Jacobs K, Haucke E, Navarrete
Santos A, Grune T and Simm A: Role of advanced glycation end
products in cellular signaling. Redox Biol. 2:411–429. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jahan H and Choudhary MI: Glycation,
carbonyl stress and AGEs inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 25:1267–1284. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin X, Yao T, Zhou Z, Zhu J, Zhang S, Hu W
and Shen C: Advanced glycation end products enhance macrophages
polarization into M1 phenotype through activating RAGE/NF-κB
pathway. BioMed Res Int. 2015:7324502015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Amaral S, Oliveira PJ and Ramalho-Santos
J: Diabetes and the impairment of reproductive function: possible
role of mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. Curr Diabetes
Rev. 4:46–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wautier MP, Chappey O, Corda S, Stern DM,
Schmidt AM and Wautier JL: Activation of NADPH oxidase by AGE links
oxidant stress to altered gene expression via RAGE. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 280:E685–E694. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rong G, Tang X, Guo T, Duan N, Wang Y,
Yang L, Zhang J and Liang X: Advanced oxidation protein products
induce apoptosis in podocytes through induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. J Physiol Biochem. 71:455–470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Xiong M, Huang B and Chen H:
Advanced glycation end products upregulate the endoplasmic
reticulum stress in human periodontal ligament cells. J
Periodontol. 86:440–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wu L, Wang D, Xiao Y, Zhou X, Wang L, Chen
B, Li Q, Guo X and Huang Q: Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a
role in the advanced glycation end product-induced inflammatory
response in endothelial cells. Life Sci. 110:44–51. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Huang K, Cai GY, Chen XM, Yang JR,
Lin LR, Yang J, Huo BG, Zhan J and He YN: Receptor for advanced
glycation end-products promotes premature senescence of proximal
tubular epithelial cells via activation of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-dependent p21 signaling. Cell Signal. 26:110–121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Piperi C, Adamopoulos C, Dalagiorgou G,
Diamanti-Kandarakis E and Papavassiliou AG: Crosstalk between
advanced glycation and endoplasmic reticulum stress: emerging
therapeutic targeting for metabolic diseases. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 97:2231–2242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|