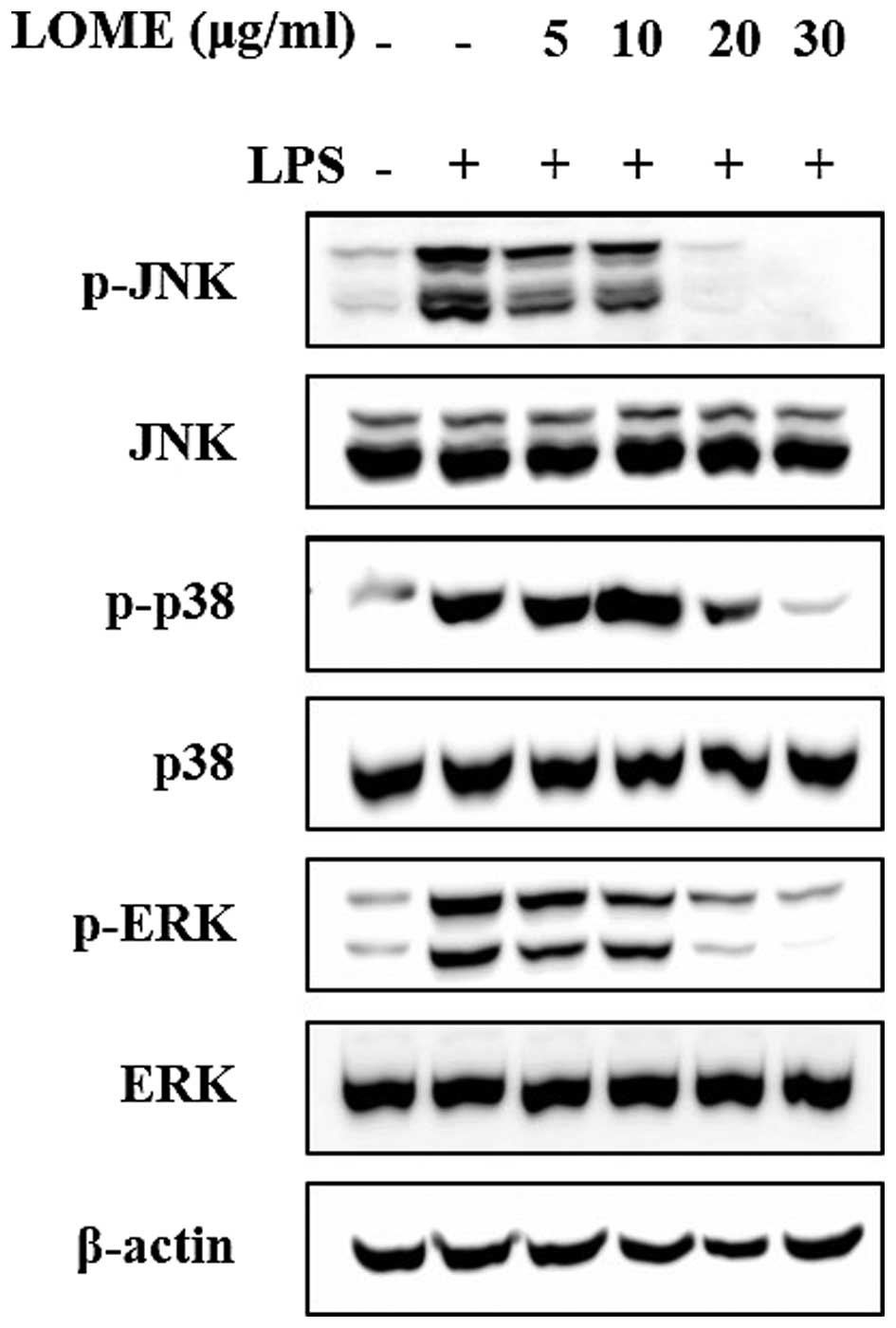
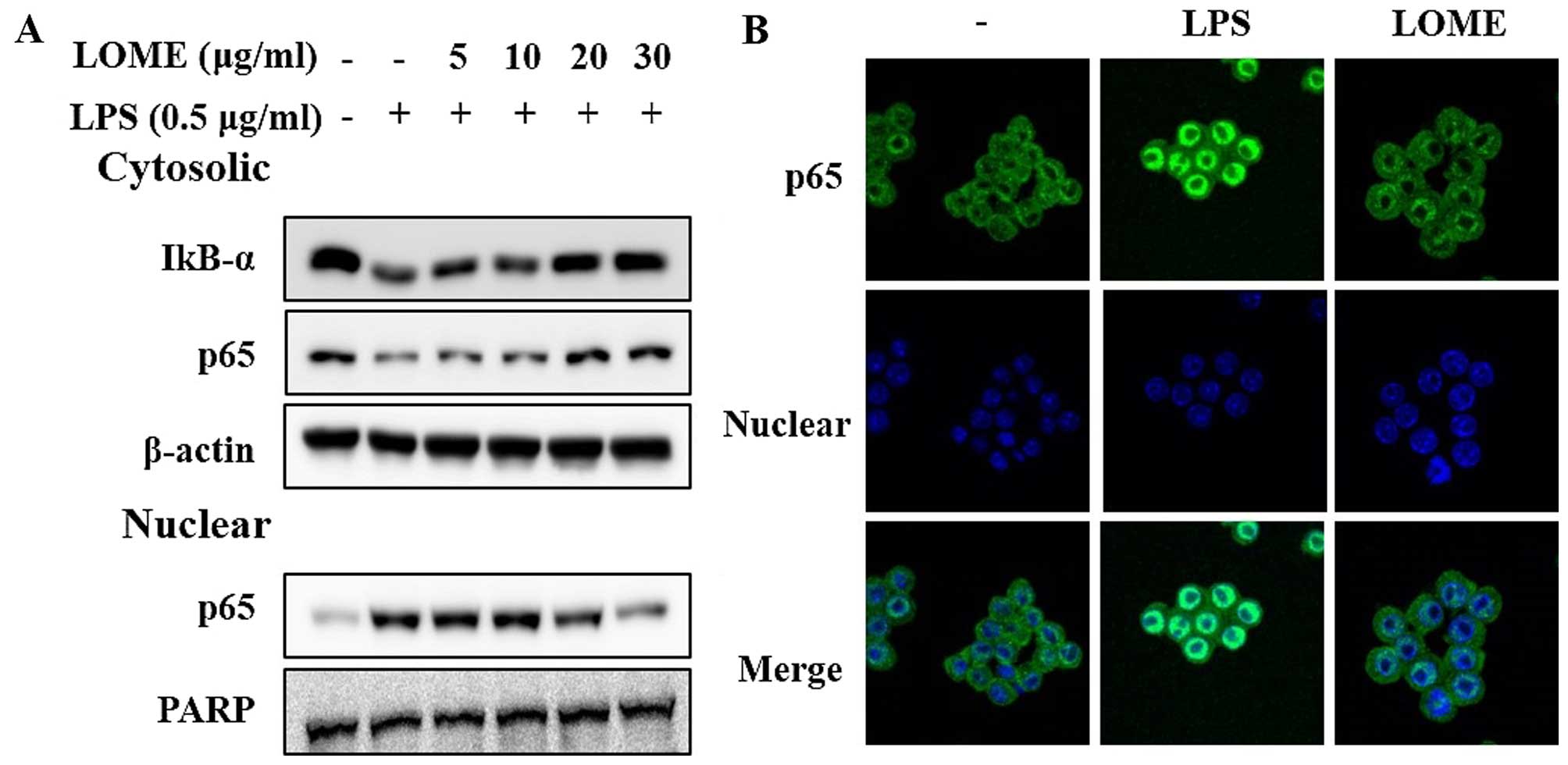
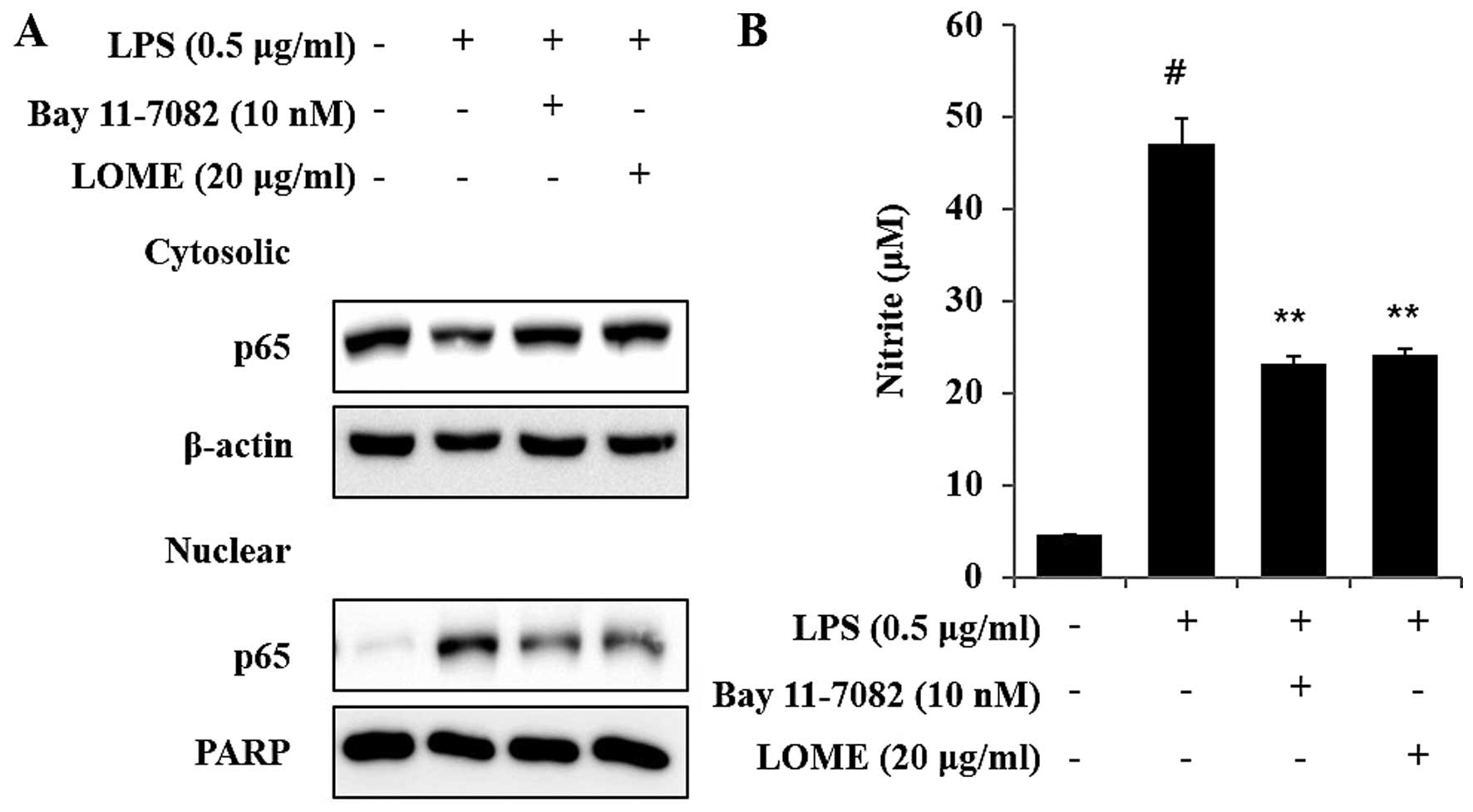
|
1
|
Lee AK, Sung SH, Kim YC and Kim SG:
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase,
TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on
I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br J
Pharmacol. 139:11–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Curran AD: The role of nitric oxide in the
development of asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 111:1–4. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ketteler M, Cetto C, Kirdorf M, Jeschke
GS, Schafer JH and Distler A: Nitric oxide in sepsis-syndrome:
Potential treatment of septic shock by nitric oxide synthase
antagonists. Kidney Int Suppl. 64:S27–S30. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heo SJ, Yoon WJ, Kim KN, Ahn GN, Kang SM,
Kang DH, Affan A, Oh C, Jung WK and Jeon YJ: Evaluation of
anti-inflammatory effect of fucoxanthin isolated from brown algae
in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem
Toxicol. 48:2045–2051. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu Y, Suh SJ, Kwak CH, Kwon KM, Seo CS, Li
Y, Jin Y, Li X, Hwang SL, Kwon O, et al: Saucerneol F, a new
lignan, inhibits iNOS expression via MAPKs, NF-kappaB and AP-1
inactivation in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
12:175–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mordan LJ, Burnett TS, Zhang LX, Tom J and
Cooney RV: Inhibitors of endogenous nitrogen oxide formation block
the promotion of neoplastic transformation in C3H 10T1/2
fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 14:1555–1559. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ochoa JB, Udekwu AO, Billiar TR, Curran
RD, Cerra FB, Simmons RL and Peitzman AB: Nitrogen oxide levels in
patients after trauma and during sepsis. Ann Surg. 214:621–626.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hunt J and Gaston B: Airway nitrogen oxide
measurements in asthma and other pediatric respiratory diseases. J
Pediatr. 137:14–20. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Giuliano F and Warner TD: Origins of
prostaglandin E2: involvements of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1
and COX-2 in human and rat systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
303:1001–1006. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Graham A, Nowicke JW, Skvarla JJ, Graham
SA, Patel V and Lee S: Palynology and systematics of the
Lythraceae. II. Genera Haitia through Peplis. Am J Bot. 74:829–850.
1987. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
de Wilde WJJO and Duyfjes BEE:
Lagerstroemia (Lythraceae) in Malesia. Blumea - Biodiversity,
Evolution and Biogeography of Plants. 59:113–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Priyadi H, Takao G, Rahmawati I,
Supriyanto B, Ikbal Nursal W and Rahman I: Five hundred plant
species in Gunung Halimun Salak National Park, West Java: a
checklist including Sundanese names, distribution and use. Cifor.
p182010.
|
|
13
|
Burkill IH: A Dictionary of the Economic
Products of the Malay Peninsula. II. Crown Agents; London: pp.
p13001935
|
|
14
|
Su YW, Chiou WF, Chao SH, Lee MH, Chen CC
and Tsai YC: Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in
RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and
down-regulating the MAPK, NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways.
Int Immunopharmacol. 11:1166–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park JW, Kwon OK, Kim JH, Oh SR, Kim JH,
Paik JH, Marwoto B, Widjhati R, Juniarti F, Irawan D and Ahn KS:
Rhododendron album Blume inhibits iNOS and COX-2 expression in
LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells through the downregulation of NF-κB
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 35:987–994. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cirino G, Distrutti E and Wallace JL:
Nitric oxide and inflammation. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets.
5:115–119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guha M and Mackman N: LPS induction of
gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 13:85–94. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lawrence T, Willoughby DA and Gilroy DW:
Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution
of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:787–795. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keller SA, Hernandez-Hopkins D, Vider J,
Ponomarev V, Hyjek E, Schattner EJ and Cesarman E: NF-kappaB is
essential for the progression of KSHV- and EBV-infected lymphomas
in vivo. Blood. 107:3295–3302. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zheng X, Chang RL, Cui XX, Avila G, Huang
MT, Liu Y, Kong AN, Rabson AB and Conney AH: Inhibition of NF-κB by
(E)3-[(4-methylphenyl)-sulfonyl]-2-propenenitrile (BAY11-7082; BAY)
is associated with enhanced
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced growth suppression and
apoptosis in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Int J Oncol.
32:257–264. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y,
Tsukasaki K, Tanaka Y, Tomonaga M, Yamamoto N and Fujii M: Bay
11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces
apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell
leukemia cells. Blood. 100:1828–1834. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schroder K, Zhou R and Tschopp J: The
NLRP3 inflammasome: a sensor for metabolic danger? Science.
327:296–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM,
Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nunez G, Schnurr
M, et al: NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and
activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 464:1357–1361. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A,
Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL, Ravussin E, Stephens JM and Dixit
VD: The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation
and insulin resistance. Nat Med. 17:179–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart
CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E, Moore KJ and
Golenbock DT: The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate
immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol. 9:857–865. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel
A and Tschopp J: Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the
NALP3 inflammasome. Nature. 440:237–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsai PY, Ka SM, Chang JM, Chen HC, Shui
HA, Li CY, Hua KF, Chang WL, Huang JJ, Yang SS and Chen A:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents lupus nephritis development in
mice via enhancing the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and inhibiting
NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:744–754.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goldring MB and Berenbaum F: The
regulation of chondrocyte function by proinflammatory mediators:
prostaglandins and nitric oxide. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
427:S37–S46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim HS, Park JW, Kwon OK, Kim JH, Oh SR,
Lee HK, Bach TT, Quang BH and Ahn KS: Anti-inflammatory activity of
a methanol extract from Ardisia tinctoria on mouse macrophages and
paw edema. Mol Med Rep. 9:1388–1394. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sautebin L: Prostaglandins and nitric
oxide as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy.
Fitoterapia. 71(Suppl 1): S48–S57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi T and Narumiya S: Prostanoids in
health and disease; lessons from receptor-knockout mice. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 507:593–597. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim JY, Kim HJ, Kim SM, Park KR, Jang HJ,
Lee EH, Jung SH and Ahn KS: Methylene chloride fraction of the
leaves of Thuja orientalis inhibits in vitro inflammatory
biomarkers by blocking NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK signaling and
protects mice from lethal endotoxemia. J Ethnopharmacol.
133:687–695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ji LL, Gomez-Cabrera MC and Vina J: Role
of nuclear factor kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling in exercise-induced antioxidant enzyme adaptation. Appl
Physiol Nutr Metab. 32:930–935. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park JW, Kwon OK, Jang HY, Jeong H, Oh SR,
Lee HK, Han SB and Ahn KS: A leaf methanolic extract of Wercklea
insignis attenuates the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
response by blocking the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in RAW 264.7
macrophages. Inflammation. 35:321–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|