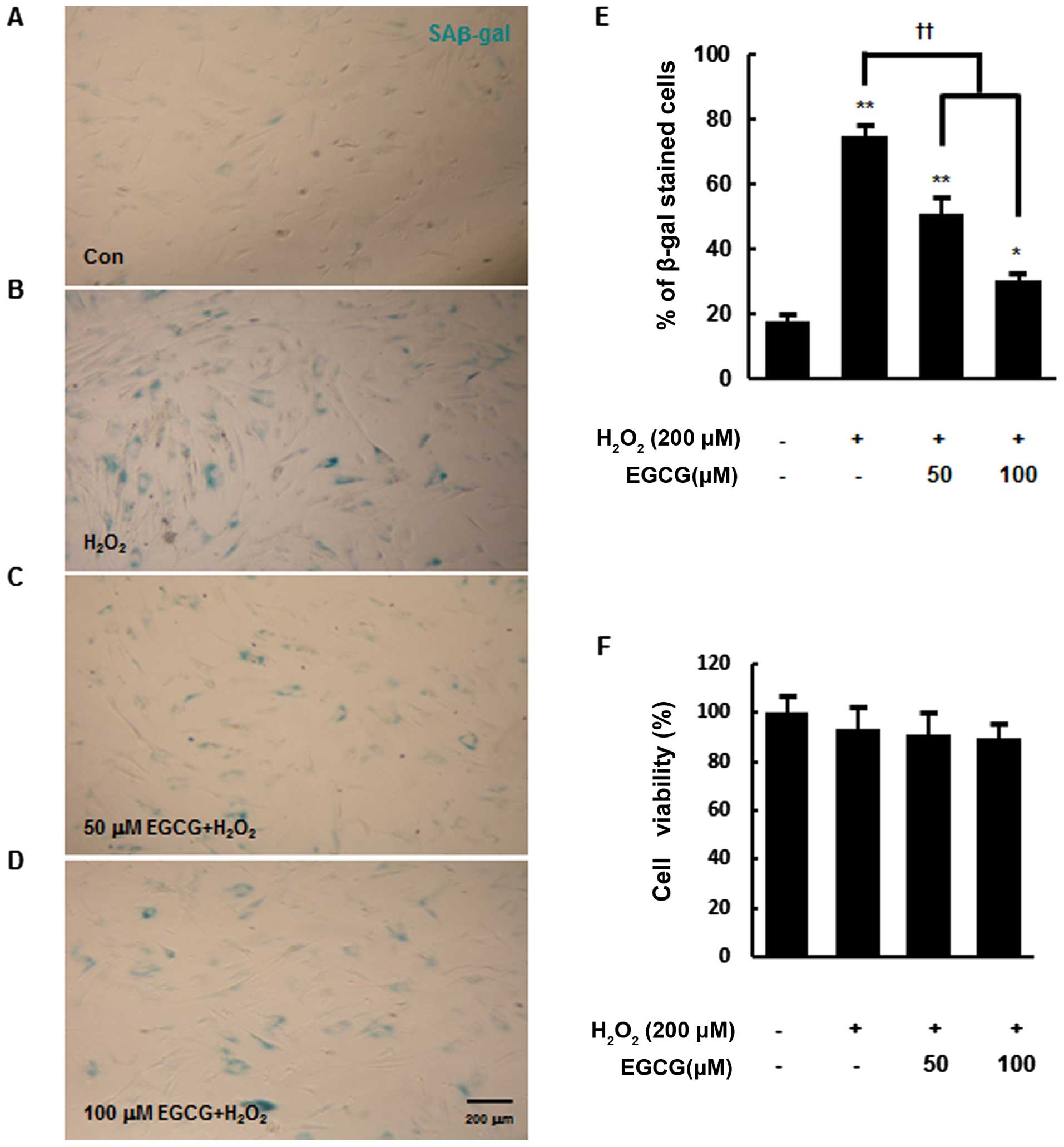
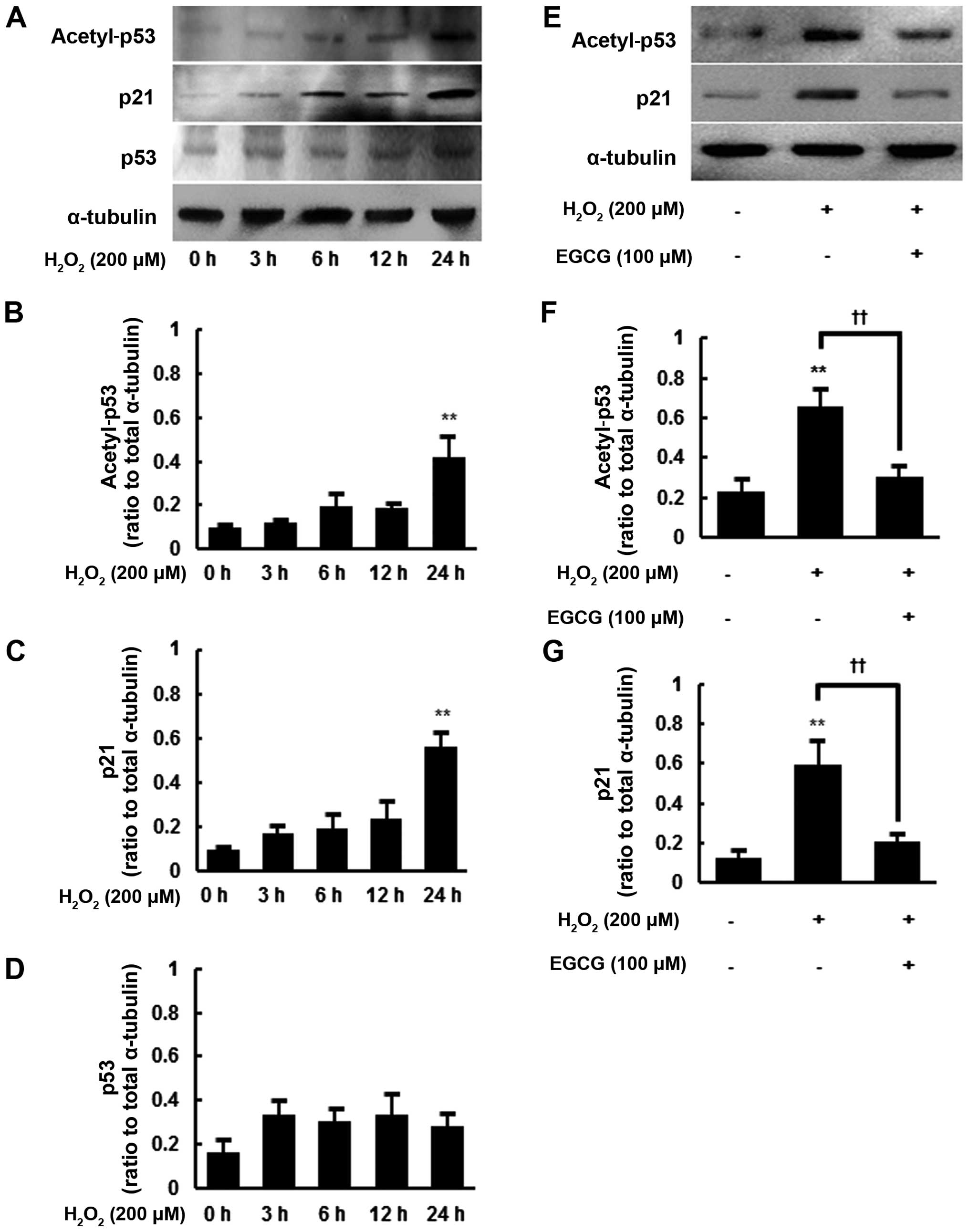
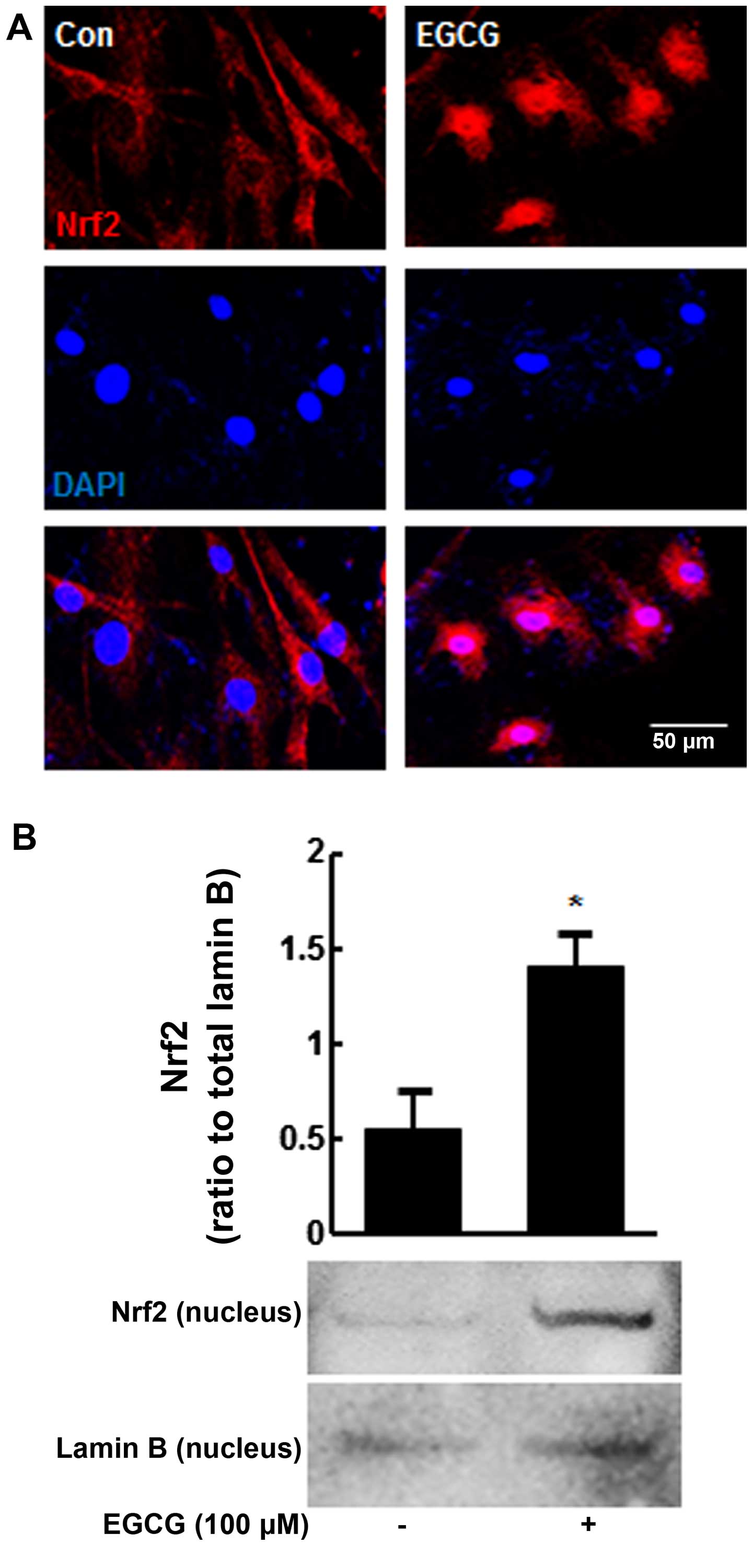
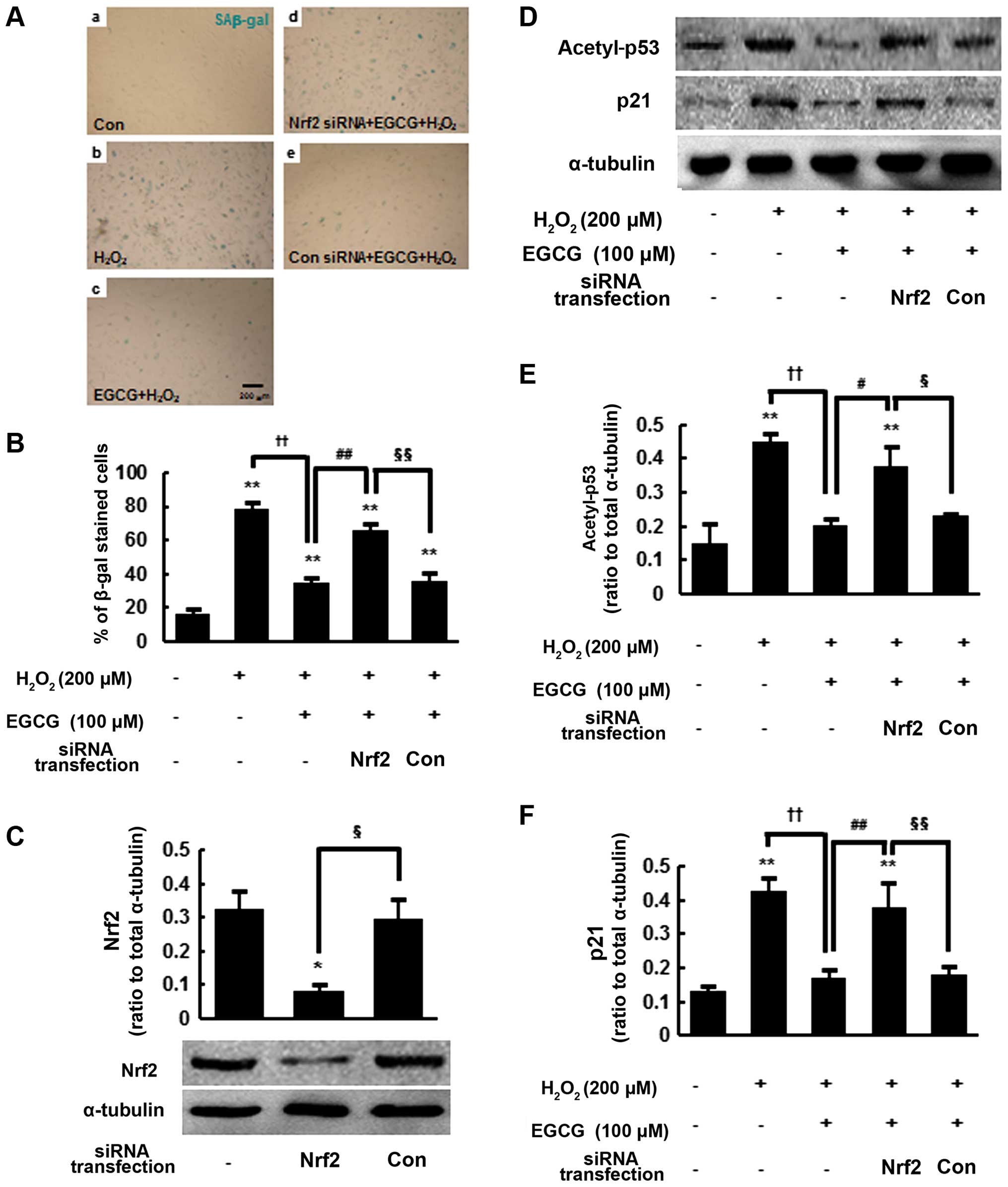
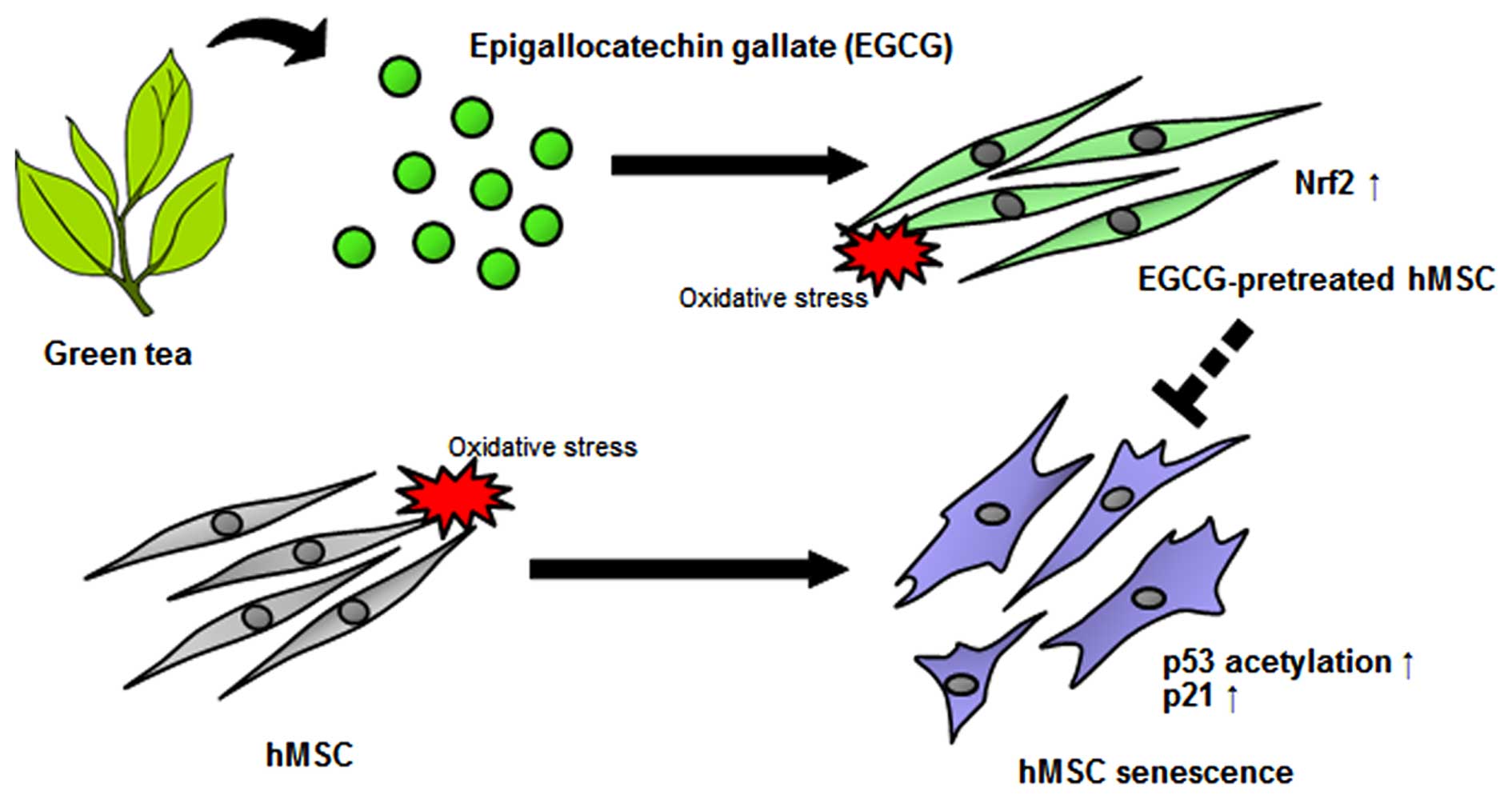
|
1
|
Pittenger MF1, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sherman LS, Munoz J, Patel SA, Dave MA,
Paige I and Rameshwar P: Moving from the laboratory bench to
patients' bedside: considerations for effective therapy with stem
cells. Clin Transl Sci. 4:380–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ and
Peeper DS: The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 24:2463–2479.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L,
Serrano M and Kroemer G: The hallmarks of aging. Cell.
153:1194–1217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oh J, Lee YD and Wagers AJ: Stem cell
aging: mechanisms, regulators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat
Med. 20:870–880. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brandl A, Meyer M, Bechmann V, Nerlich M
and Angele P: Oxidative stress induces senescence in human
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 317:1541–1547. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Campisi J and d'Adda di Fagagna F:
Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 8:729–740. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kume S, Haneda M, Kanasaki K, Sugimoto T,
Araki S, Isono M, Isshiki K, Uzu T, Kashiwagi A and Koya D: Silent
information regulator 2 (SIRT1) attenuates oxidative stress-induced
mesangial cell apoptosis via p53 deacetylation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 40:2175–2182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Langley E, Pearson M, Faretta M, Bauer UM,
Frye RA, Minucci S, Pelicci PG and Kouzarides T: Human SIR2
deacetylates p53 and antagonizes PML/p53-induced cellular
senescence. EMBO J. 21:2383–2396. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo J, Nikolaev AY, Imai S, Chen D, Su F,
Shiloh A, Guarente L and Gu W: Negative control of p53 by Sir2α
promotes cell survival under stress. Cell. 107:137–148. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E, Imai SI,
Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L and Weinberg RA: hSIR2(SIRT1)
functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell. 107:149–159.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han DW, Lee MH, Kim B, Lee JJ, Hyon SH and
Park JC: Preventive effects of epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate against
replicative senescence associated with p53 acetylation in human
dermal fibroblasts. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:8506842012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anderson RF, Fisher LJ, Hara Y, Harris T,
Mak WB, Melton LD and Packer JE: Green tea catechins partially
protect DNA from (.)OH radical-induced strand breaks and base
damage through fast chemical repair of DNA radicals.
Carcinogenesis. 22:1189–1193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chow HH, Cai Y, Alberts DS, Hakim I, Dorr
R, Shahi F, Crowell JA, Yang CS and Hara Y: Phase I pharmacokinetic
study of tea polyphenols following single-dose administration of
epigallocatechin gallate and polyphenon E. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 10:53–58. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Higdon JV and Frei B: Tea catechins and
polyphenols: health effects, metabolism, and antioxidant functions.
Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 43:89–143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yagi H, Tan J and Tuan RS: Polyphenols
suppress hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human
bone-marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
114:1163–1173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Surh YJ, Kundu JK, Na HK and Lee JS:
Redox-sensitive transcription factors as prime targets for
chemoprevention with anti-inflammatory and antioxidative
phytochemicals. J Nutr. 135(Suppl 12): 2993S–3001S. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayes JD and McMahon M: NRF2 and KEAP1
mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer.
Trends Biochem Sci. 34:176–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T,
Igarashi K, Engel JD and Yamamoto M: Keap1 represses nuclear
activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through
binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 13:76–86.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen T, Nioi P and Pickett CB: The
Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its
activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 284:13291–13295. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Burova E, Borodkina A, Shatrova A and
Nikolsky N: Sublethal oxidative stress induces the premature
senescence of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from
endometrium. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:4749312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD and
Wakabayashi N: Keap1, the sensor for electrophiles and oxidants
that regulates the phase 2 response, is a zinc metalloprotein.
Biochemistry. 44:6889–6899. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bond J, Haughton M, Blaydes J, Gire V,
Wynford-Thomas D and Wyllie F: Evidence that transcriptional
activation by p53 plays a direct role in the induction of cellular
senescence. Oncogene. 13:2097–2104. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo J, Li M, Tang Y, Laszkowska M, Roeder
RG and Gu W: Acetylation of p53 augments its site-specific DNA
binding both in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2259–2264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy
DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression.
Cell. 75:817–825. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K
and Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brown JP, Wei W and Sedivy JM: Bypass of
senescence after disruption of p21CIP1/WAF1 gene in normal diploid
human fibroblasts. Science. 277:831–834. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Herbig U, Wei W, Dutriaux A, Jobling WA
and Sedivy JM: Real-time imaging of transcriptional activation in
live cells reveals rapid up-regulation of the cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitor gene CDKN1A in replicative cellular senescence.
Aging Cell. 2:295–304. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Volonte D, Liu Z, Musille PM, Stoppani E,
Wakabayashi N, Di YP, Lisanti MP, Kensler TW and Galbiati F:
Inhibition of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) by
caveolin-1 promotes stress-induced premature senescence. Mol Biol
Cell. 24:1852–1862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
You A, Nam CW, Wakabayashi N, Yamamoto M,
Kensler TW and Kwak MK: Transcription factor Nrf2 maintains the
basal expression of Mdm2: an implication of the regulation of p53
signaling by Nrf2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 507:356–364. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|