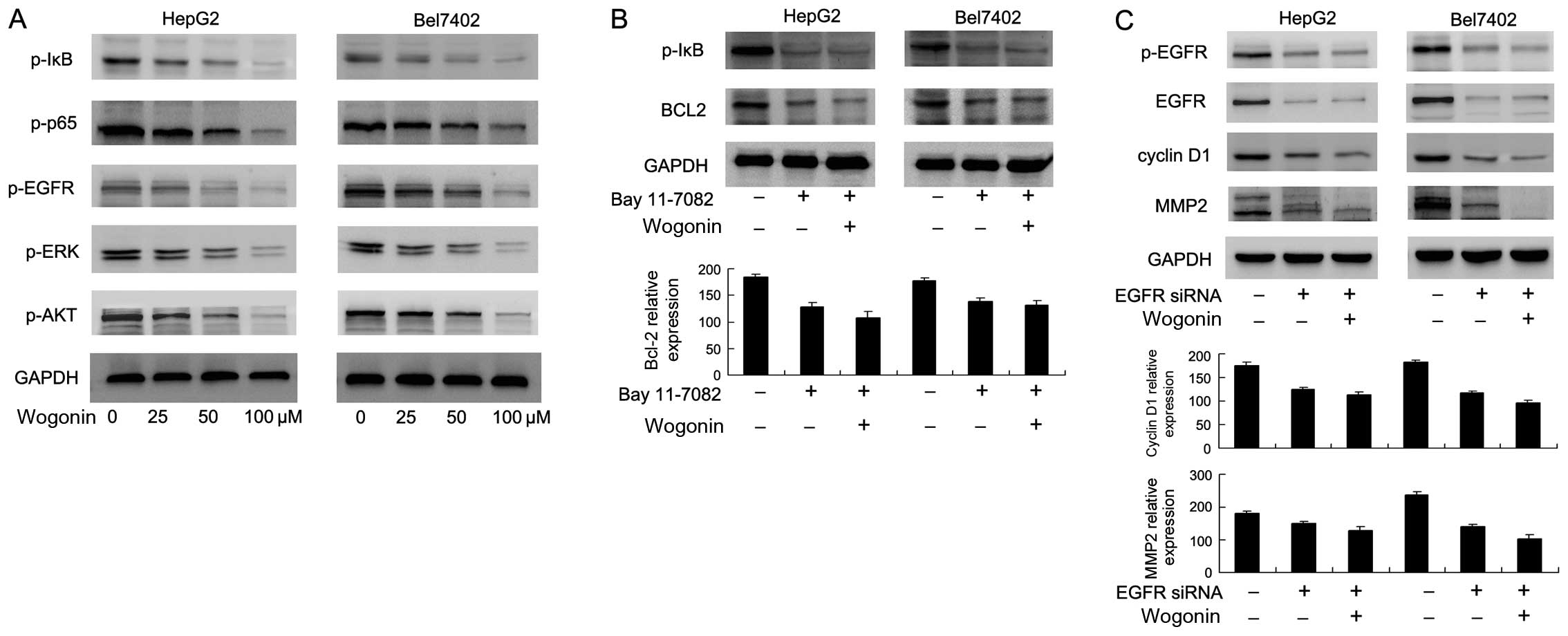
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ye H and Liu W: Connectivity-based risk
score for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Hepatology.
58:1191–1192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li H, Wu K, Tao K, Chen L, Zheng Q, Lu X,
Liu J, Shi L, Liu C, Wang G, et al: Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling
pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in
patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1342–1351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ke AW, Shi GM, Zhou J, Wu FZ, Ding ZB, Hu
MY, Xu Y, Song ZJ, Wang ZJ, Wu JC, et al: Role of overexpression of
CD151 and/or c-Met in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:491–503. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ueng YF, Shyu CC, Lin YL, Park SS, Liao JF
and Chen CF: Effects of baicalein and wogonin on drug-metabolizing
enzymes in C57BL/6J mice. Life Sci. 67:2189–2200. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wakabayashi I and Yasui K: Wogonin
inhibits inducible prostaglandin E(2) production in macrophages.
Eur J Pharmacol. 406:477–481. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin SJ, Tseng HH, Wen KC and Suen TT:
Determination of gentiopicroside, mangiferin, palmatine, berberine,
baicalin, wogonin and glycyrrhizin in the traditional Chinese
medicinal preparation sann-joong-kuey-jian-tang by high-performance
liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 730:17–23. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin CC and Shieh DE: The anti-inflammatory
activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active
components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am J Chin Med.
24:31–36. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen LG, Hung LY, Tsai KW, Pan YS, Tsai
YD, Li YZ and Liu YW: Wogonin, a bioactive flavonoid in herbal tea,
inhibits inflammatory cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human
lung epithelial cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:1349–1357.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee E, Enomoto R, Suzuki C, Ohno M, Ohashi
T, Miyauchi A, Tanimoto E, Maeda K, Hirano H, Yokoi T and Sugahara
C: Wogonin, a plant flavone, potentiates etoposide-induced
apoptosis in cancer cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1095:521–526. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Himeji M, Ohtsuki T, Fukazawa H, Tanaka M,
Yazaki S, Ui S, Nishio K, Yamamoto H, Tasaka K and Mimura A:
Difference of growth-inhibitory effect of Scutellaria
baicalensis-producing flavonoid wogonin among human cancer cells
and normal diploid cell. Cancer Lett. 245:269–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
He F, Wang Q, Zheng XL, Yan JQ, Yang L,
Sun H, Hu LN, Lin Y and Wang X: Wogonin potentiates
cisplatin-induced cancer cell apoptosis through accumulation of
intracellular reactive oxygen species. Oncol Rep. 28:601–605.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang KF, Zhang GD, Huang YQ and Diao Y:
Wogonin induces apoptosis and down-regulates survivin in human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:334–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
He L, Lu N, Dai Q, Zhao Y, Zhao L, Wang H,
Li Z, You Q and Guo Q: Wogonin induced G1 cell cycle arrest by
regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and inactivating CDK8 in
human colorectal cancer carcinoma cells. Toxicology. 312:36–47.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saif MW: Colorectal cancer in review: the
role of the EGFR pathway. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:357–369.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Navolanic PM, Steelman LS and McCubrey JA:
EGFR family signaling and its association with breast cancer
development and resistance to chemotherapy (Review). Int J Oncol.
22:237–252. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee DH, Szczepanski MJ and Lee YJ:
Magnolol induces apoptosis via inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
106:1113–1122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Raufman JP, Shant J, Guo CY, Roy S and
Cheng K: Deoxycholyltaurine rescues human colon cancer cells from
apoptosis by activating EGFR-dependent PI3K/Akt signaling. J Cell
Physiol. 215:538–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qian L, Liu Y, Xu Y, Ji W, Wu Q, Liu Y,
Gao Q and Su C: Matrine derivative WM130 inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma by suppressing EGFR/ERK/MMP-2 and PTEN/AKT signaling
pathways. Cancer Lett. 368:126–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao X, Ning Q, Sun X and Tian D: Pokemon
reduces Bcl-2 expression through NF-κ Bp65: A possible mechanism of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 4:492–497. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia XF, Li J, Zhao HB, Liu J and Liu JJ:
Correlation of EGFR gene amplification with invasion and metastasis
of non-small cell lung cancer. Genet Mol Res. 14:11006–11012. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mader CC, Oser M, Magalhaes MA,
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Condeelis J, Koleske AJ and Gil-Henn H: An
EGFR-Src-Arg-cortactin pathway mediates functional maturation of
invadopodia and breast cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res.
71:1730–1741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong C, Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang Y, Ma H, Wu
W, Cui J, Wang Y and Ren Z: Dynamin2 downregulation delays EGFR
endocytic trafficking and promotes EGFR signaling and invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 5:702–713.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YP, Huang LY, Sun WM, Zhang ZZ, Fang
JZ, Wei BF, Wu BH and Han ZG: Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase
substrate activates EGFR/ERK signalling pathway and promotes cell
proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 337:96–106.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alam S, Pal A, Kumar R, Dwivedi PD, Das M
and Ansari KM: EGFR-mediated Akt and MAPKs signal pathways play a
crucial role in patulin-induced cell proliferation in primary
murine keratinocytes via modulation of Cyclin D1 and COX-2
expression. Mol Carcinog. 53:988–998. 2014.
|
|
26
|
Fiano V, Ghimenti C, Imarisio S, Silengo L
and Schiffer D: PAkt, cyclin D1 and p27/Kip.1 in glioblastomas with
and without EGFR amplification and PTEN mutation. Anticancer Res.
24:2643–2647. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ezzoukhry Z, Louandre C, Trécherel E,
Godin C, Chauffert B, Dupont S, Diouf M, Barbare JC, Mazière JC and
Galmiche A: EGFR activation is a potential determinant of primary
resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Int J
Cancer. 131:2961–2969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kannangai R, Sahin F and Torbenson MS:
EGFR is phosphorylated at Ty845 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod
Pathol. 19:1456–1461. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bae GY, Choi SJ, Lee JS, Jo J, Lee J, Kim
J and Cha HJ: Loss of E-cadherin activates EGFR-MEK/ERK signaling,
which promotes invasion via the ZEB1/MMP2 axis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncotarget. 4:2512–2522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong QZ, Wang Y, Tang ZP, Fu L, Li QC,
Wang ED and Wang EH: Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell
lung cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion via EGFR-ERK-mediated
up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Am J Pathol. 182:954–964. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim H and Lim HY: Novel EGFR-TK inhibitor
EKB-569 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by AKT
and MAPK pathways. J Korean Med Sci. 26:1563–1568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ling Y, Yang X, Li W, Li Z, Yang L, Qiu T,
Guo L, Dong L, Li L, Ying J and Lin D: Overexpression of mutant
EGFR protein indicates a better survival benefit from EGFR-TKI
therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. July
13–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shan L, Wang Z, Guo L, Sun H, Qiu T, Ling
Y, Li W, Li L, Liu X and Zheng B: Concurrence of EGFR amplification
and sensitizing mutations indicate a better survival benefit from
EGFR-TKI therapy in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer.
89:337–342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nose N, Uramoto H, Iwata T, Hanagiri T and
Yasumoto K: Expression of estrogen receptor beta predicts a
clinical response and longer progression-free survival after
treatment with EGFR-TKI for adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung
Cancer. 71:350–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen GG, Liang NC, Lee JF, Chan UP, Wang
SH, Leung BC and Leung KL: Over-expression of Bcl-2 against Pteris
semipinnata L-induced apoptosis of human colon cancer cells via a
NF-kappa B-related pathway. Apoptosis. 9:619–627. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kurland JF, Voehringer DW and Meyn RE: The
MEK/ERK pathway acts upstream of NF kappa B1 (p50) homodimer
activity and Bcl-2 expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma cell
line. MEK inhibition restores radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 278:32465–32470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Herrmann JL, Beham AW, Sarkiss M, Chiao
PJ, Rands MT, Bruckheimer EM, Brisbay S and McDonnell TJ: Bcl-2
suppresses apoptosis resulting from disruption of the NF-kappa B
survival pathway. Exp Cell Res. 237:101–109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cheng JC, Chou CH, Kuo ML and Hsieh CY:
Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with
MMP-9 expression through PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction
pathway. Oncogene. 25:7009–7018. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiang T, Grabiner B, Zhu Y, Jiang C, Li H,
You Y, Lang J, Hung MC and Lin X: CARMA3 is crucial for
EGFR-Induced activation of NF-kappaB and tumor progression. Cancer
Res. 71:2183–2192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|