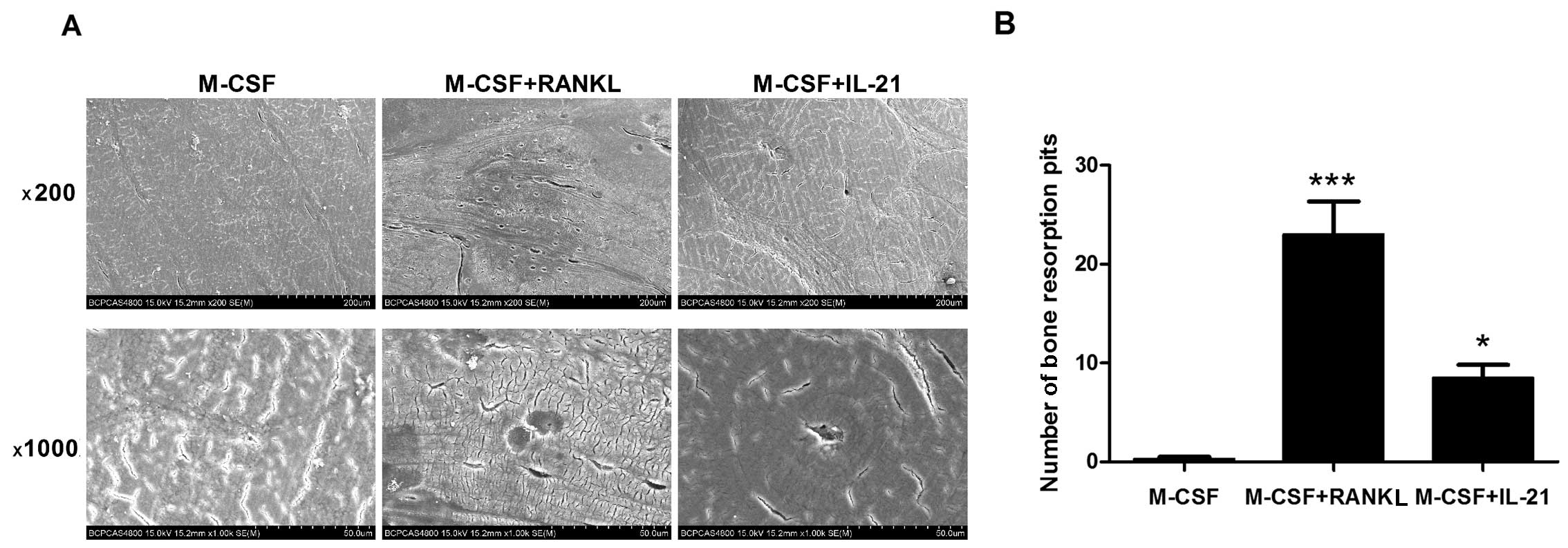
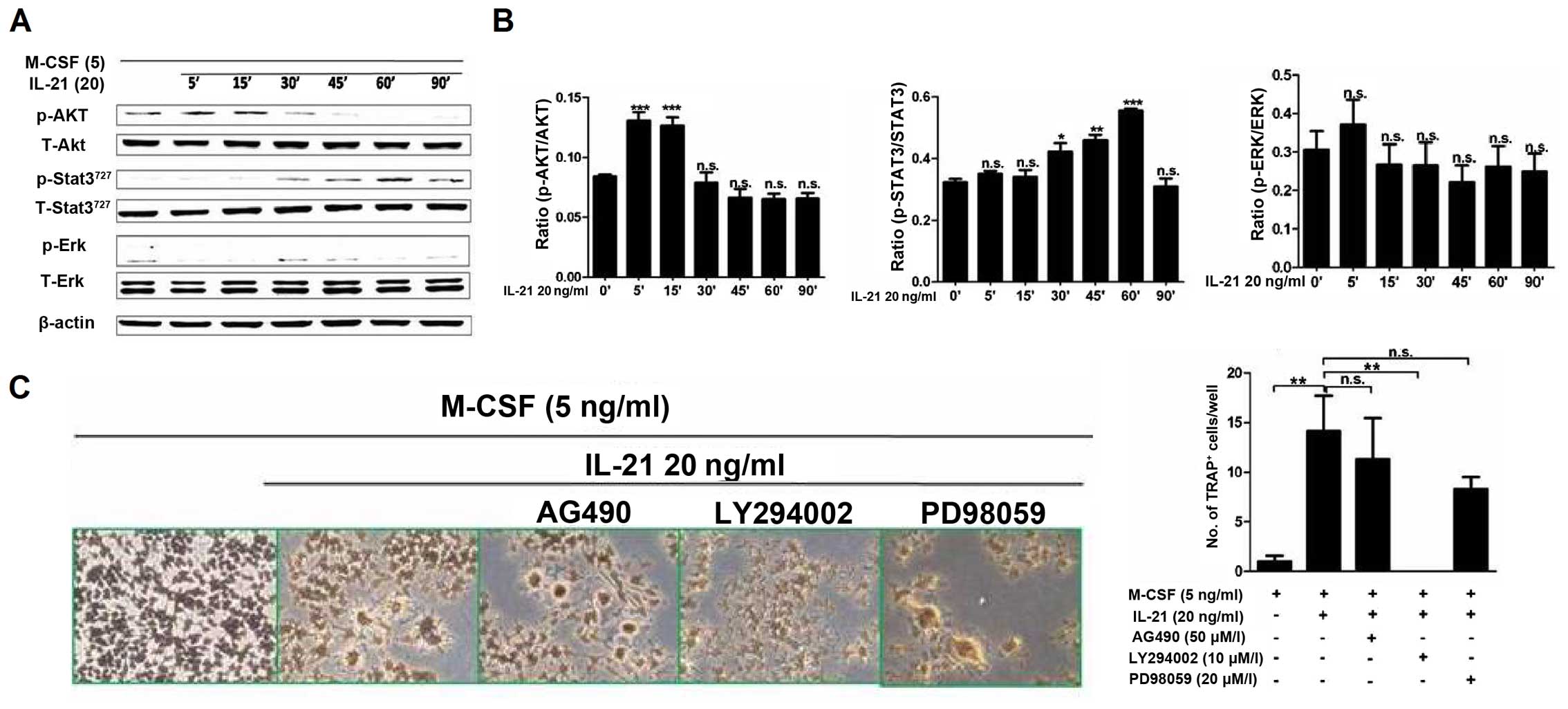
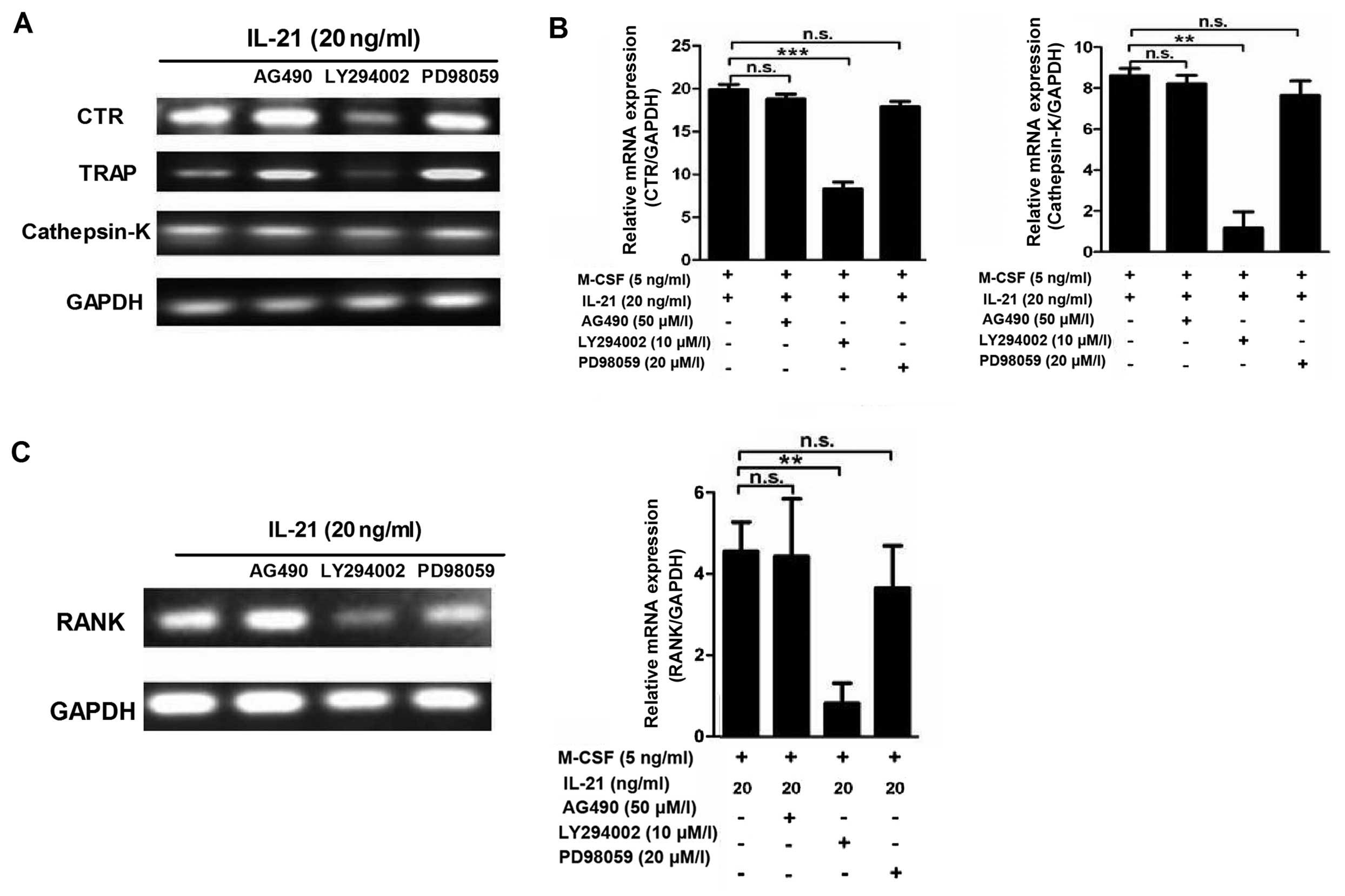
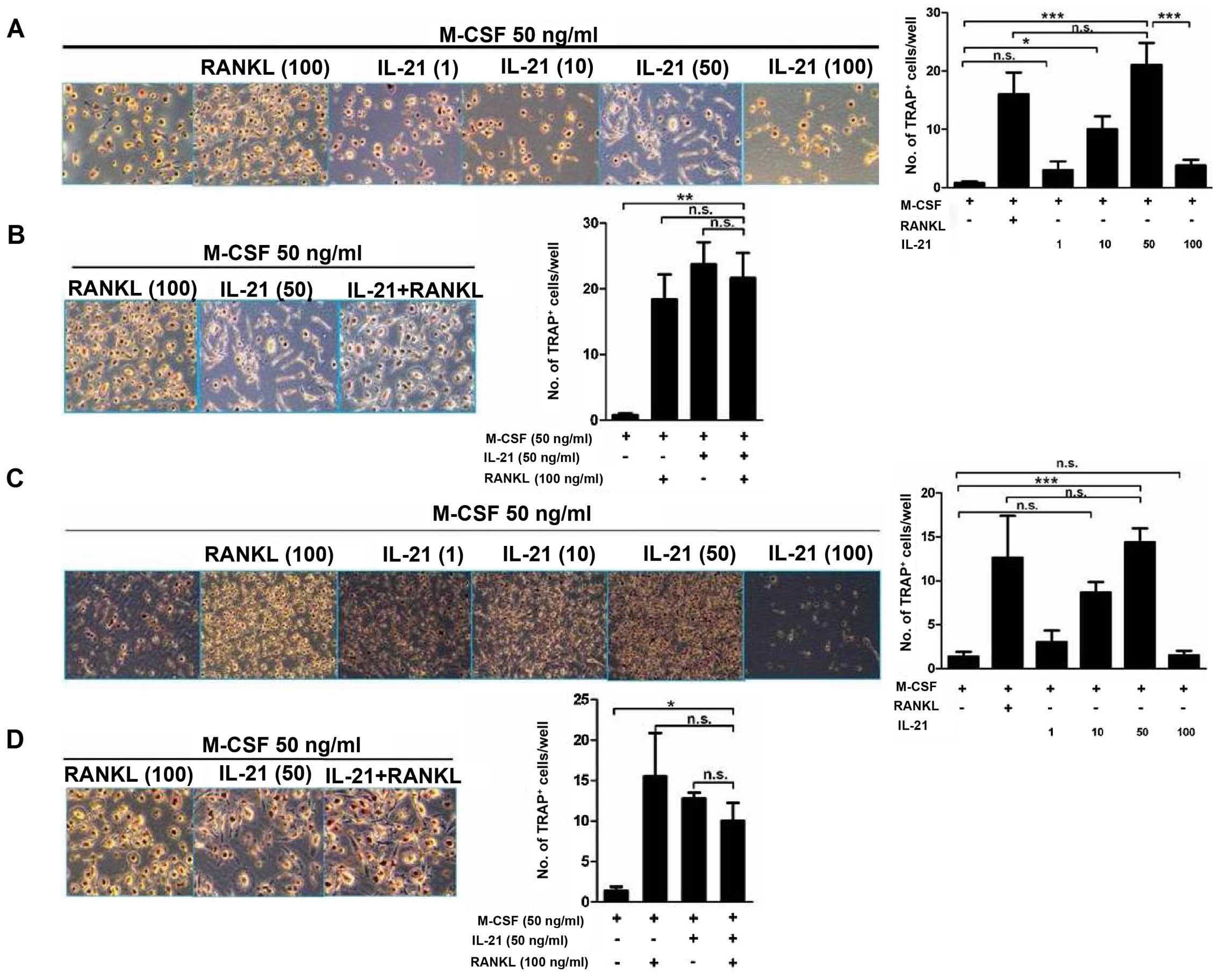
|
1
|
Maruotti N, Grano M, Colucci S, d'Onofrio
F and Cantatore FP: Osteoclastogenesis and arthritis. Clin Exp Med.
11:137–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Branimir A and Miroslav M: Pathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatizam. 61:19–23. 2014.In Croatian.
|
|
3
|
Kawai VK, Stein CM, Perrien DS and Griffin
MR: Effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor α agents on bone. Curr
Opin Rheumatol. 24:576–585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bloemen V, Schoenmaker T, de Vries TJ and
Everts V: IL-1β favors osteoclastogenesis via supporting human
periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 112:1890–1897.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A,
Hammond A, Sprecher C, Gross JA, Johnston J, Madden K, Xu W, West
J, et al: Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell
expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 408:57–63.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leonard WJ and Spolski R: Interleukin-21:
a modulator of lymphoid proliferation, apoptosis and
differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:688–698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Fusco D, Izzo R, Figliuzzi MM, Pallone
F and Monteleone G: IL-21 as a therapeutic target in inflammatory
disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:1329–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Shen W, Kong K and Liu Z:
Interleukin-21 induces T-cell activation and proinflammatory
cytokine secretion in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol.
64:515–522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Spolski R and Leonard WJ: Interleukin-21:
A double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 13:379–395. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Monteleone G, Caruso R, Fina D, Peluso I,
Gioia V, Stolfi C, Fantini MC, Caprioli F, Tersigni R, Alessandroni
L, et al: Control of matrix metalloproteinase production in human
intestinal fibroblasts by interleukin 21. Gut. 55:1774–1780. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rasmussen TK, Andersen T, Hvid M, Hetland
ML, Hørslev-Petersen K, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Holm CK and Deleuran
B: Increased interleukin 21 (IL-21) and IL-23 are associated with
increased disease activity and with radiographic status in patients
with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 37:2014–2020. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Young DA, Hegen M, Ma HL, Whitters MJ,
Albert LM, Lowe L, Senices M, Wu PW, Sibley B, Leathurby Y, et al:
Blockade of the interleukin-21/interleukin-21 receptor pathway
ameliorates disease in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 56:1152–1163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kwok SK, Cho ML, Park MK, Oh HJ, Park JS,
Her YM, Lee SY, Youn J, Ju JH, Park KS, et al: Interleukin-21
promotes osteoclastogenesis in humans with rheumatoid arthritis and
in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
64:740–751. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL,
Timms E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Van G,
Itie A, et al: OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis,
lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature.
397:315–323. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parrish-Novak J, Foster DC, Holly RD and
Clegg CH: Interleukin-21 and the IL-21 receptor: novel effectors of
NK and T cell responses. J Leukoc Biol. 72:856–863. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Spolski R and Leonard WJ: The Yin and Yang
of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr Opin
Immunol. 20:295–301. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeng R, Spolski R, Casas E, Zhu W, Levy DE
and Leonard WJ: The molecular basis of IL-21-mediated
proliferation. Blood. 109:4135–4142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ryu JG, Lee J, Kim EK, Seo HB, Park JS,
Lee SY, Moon YM, Yoo SH, Park YW, Park SH, et al: Treatment of
IL-21R-Fc control autoimmune arthritis via suppression of STAT3
signal pathway mediated regulation of the Th17/Treg balance and
plasma B cells. Immunol Lett. 163:143–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Marijnissen RJ, Roeleveld DM, Young D,
Nickerson-Nutter C, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Garcia de Aquino S, van de
Loo FA, van Spriel AB, Boots AM, van den Berg WB and Koenders MI:
Interleukin-21 receptor deficiency increases the initial toll-like
receptor 2 response but protects against joint pathology by
reducing Th1 and Th17 cells during streptococcal cell wall
arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:886–895. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|