|
1
|
Sheskin J: Thalidomide in the treatment of
lepra reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 6:303–306. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
D'Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E and
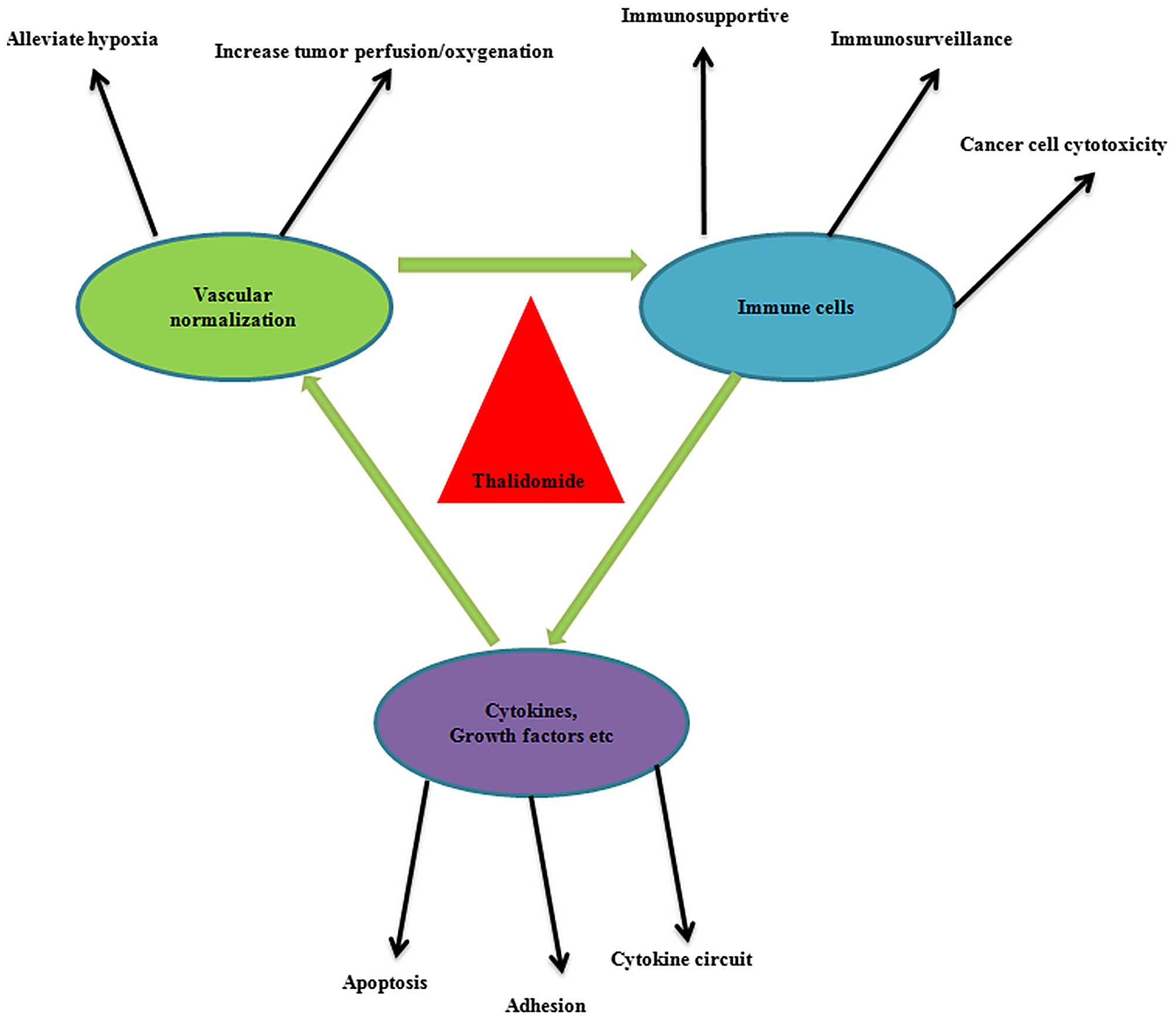
Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:4082–4085. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singhal S, Mehta J, Desikan R, Ayers D,
Roberson P, Eddlemon P, Munshi N, Anaissie E, Wilson C, Dhodapkar
M, et al: Antitumor activity of thalidomide in refractory multiple
myeloma. N Engl J Med. 341:1565–1571. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Drake MJ, Robson W, Mehta P, Schofield I,
Neal DE and Leung HY: An open-label phase II study of low-dose
thalidomide in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
88:822–827. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marx GM, Pavlakis N, McCowatt S, Boyle FM,
Levi JA, Bell DR, Cook R, Biggs M, Little N and Wheeler HR: Phase
II study of thalidomide in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma
multiforme. J Neurooncol. 54:31–38. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Figg WD, Dahut W, Duray P, Hamilton M,
Tompkins A, Steinberg SM, Jones E, Premkumar A, Linehan WM, Floeter
MK, et al: A randomized phase II trial of thalidomide, an
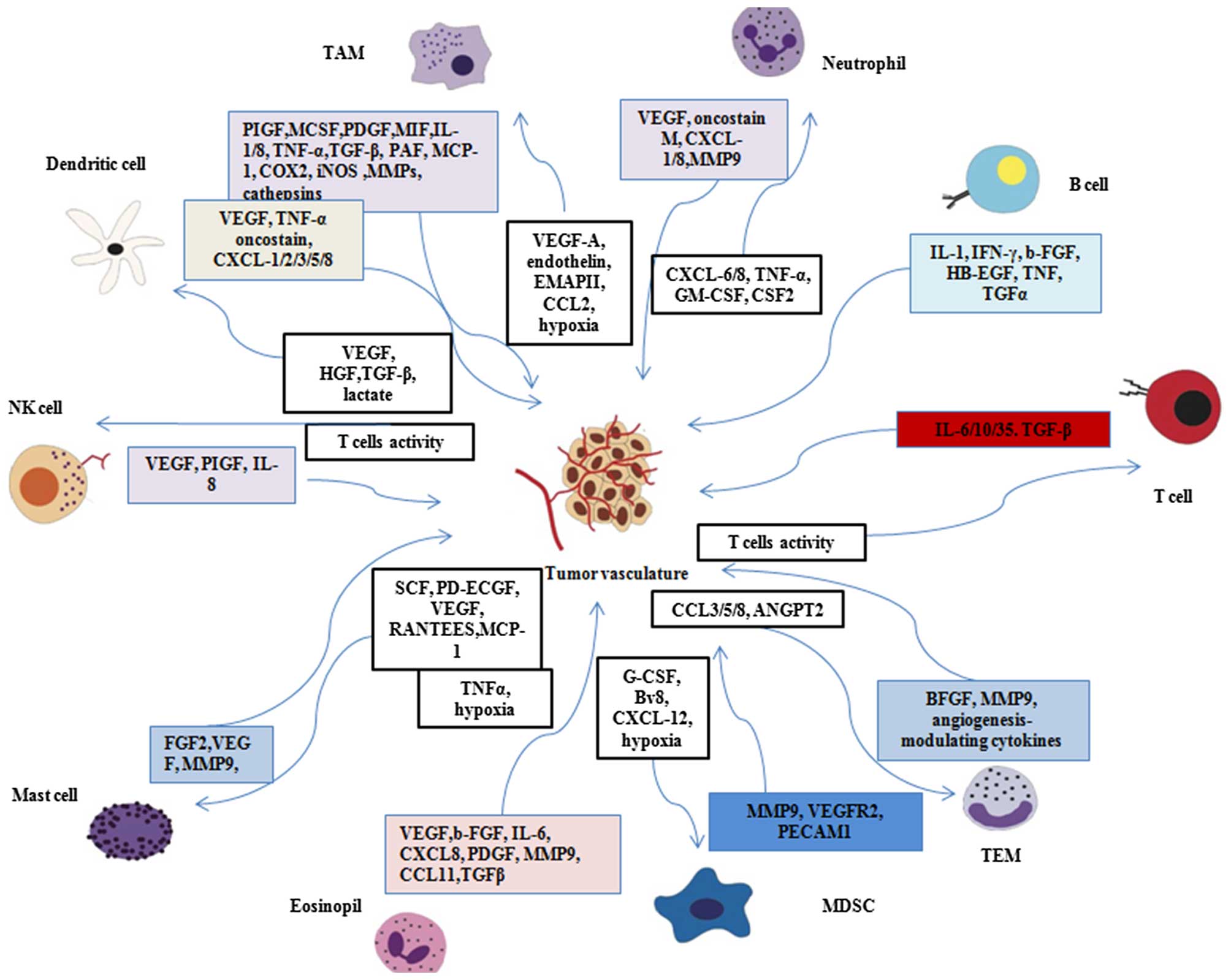
angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with androgen-independent
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1888–1893. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou V, Bamias A and
Dimopoulos MA: Thalidomide in cancer medicine. Ann Oncol.
8:1151–1160. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kesari S, Schiff D, Henson JW, Muzikansky
A, Gigas DC, Doherty L, Batchelor TT, Longtine JA, Ligon KL, Weaver
S, et al: Phase II study of temozolomide, thalidomide, and
celecoxib for newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults. Neuro Oncol.
10:300–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
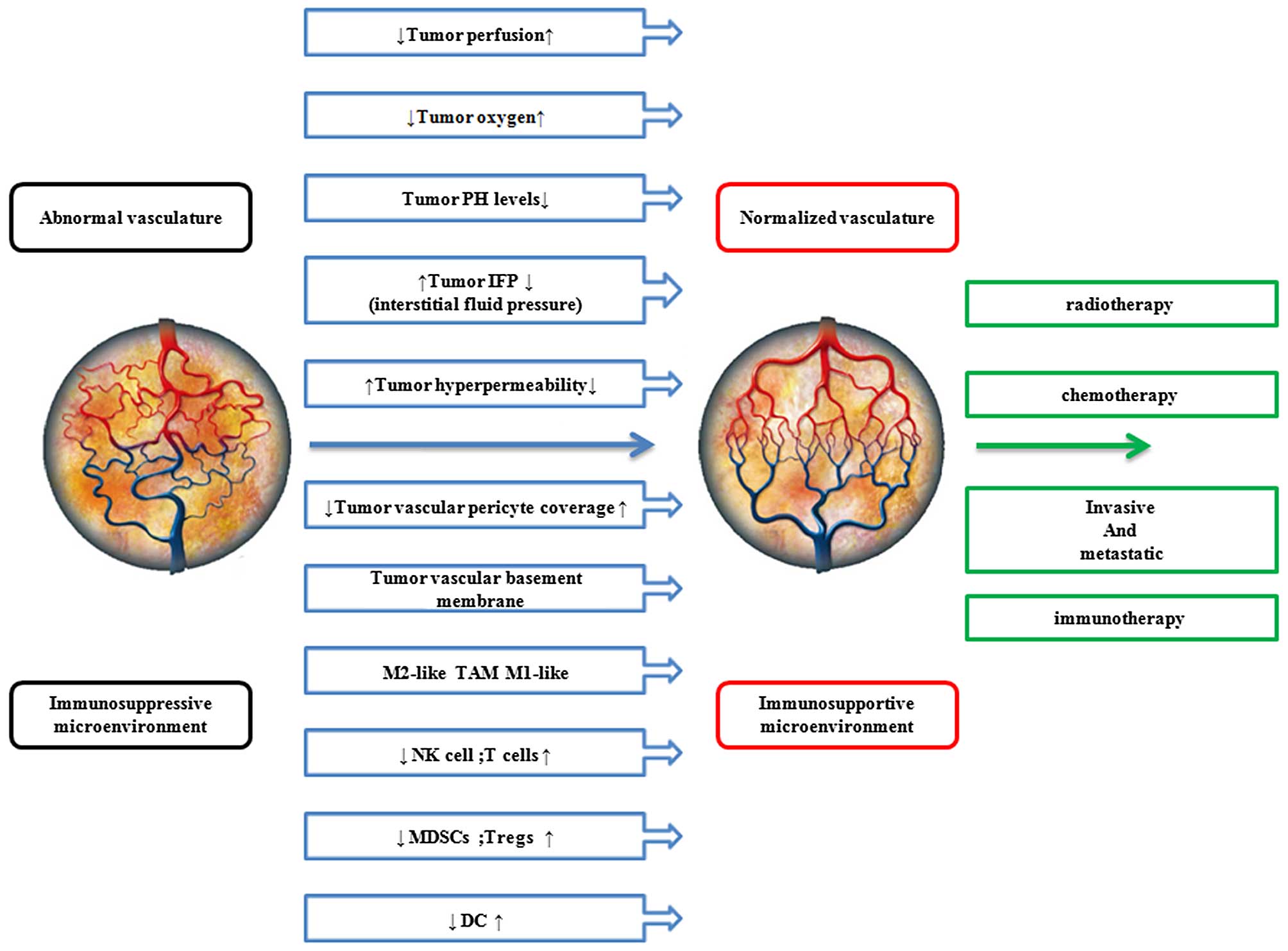
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ansiaux R, Baudelet C, Jordan BF, Beghein
N, Sonveaux P, De Wever J, Martinive P, Grégoire V, Feron O and
Gallez B: Thalidomide radiosensitizes tumors through early changes
in the tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 11:743–750.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
El-Aarag BY, Kasai T, Zahran MA, Zakhary
NI, Shigehiro T, Sekhar SC, Agwa HS, Mizutani A, Murakami H, Kakuta
H and Seno M: In vitro anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic
activities of thalidomide dithiocarbamate analogs. Int
Immunopharmacol. 21:283–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T, Lentzsch
S, Young G, Tai YT, Lin B, Podar K, Gupta D, Chauhan D, et al:
Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer
cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood. 98:210–216. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kawamata A, Ito D, Odani T, Isobe T, Iwase
M, Hatori M and Nagumo M: Thalidomide suppresses melanoma growth by
activating natural killer cells in mice. Oncol Rep. 16:1231–1236.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
von Moos R, Stolz R, Cerny T and Gillessen
S: Thalidomide: from tragedy to promise. Swiss Med Wkly. 133:77–87.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Corral LG, Haslett PA, Muller GW, Chen R,
Wong LM, Ocampo CJ, Patterson RT, Stirling DI and Kaplan G:
Differential cytokine modulation and T cell activation by two
distinct classes of thalidomide analogues that are potent
inhibitors of TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 163:380–386. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Corral LG and Kaplan G: Immunomodulation
by thalidomide and thalidomide analogues. Ann Rheum Dis. 58(Suppl
1): I107–I113. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haslett PA, Klausner JD, Makonkawkeyoon S,
Moreira A, Metatratip P, Boyle B, Kunachiwa W, Maneekarn N,
Vongchan P, Corral LG, et al: Thalidomide stimulates T cell
responses and interleukin 12 production in HIV-infected patients.
AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 15:1169–1179. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muller GW, Chen R, Huang SY, Corral LG,
Wong LM, Patterson RT, Chen Y, Kaplan G and Stirling DI:
Amino-substituted thalidomide analogs: potent inhibitors of
TNF-alpha production. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 9:1625–1630. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Joussen AM, Germann T and Kirchhof B:
Effect of thalidomide and structurally related compounds on corneal
angiogenesis is comparable to their teratological potency. Graefes
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 237:952–961. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Therapontos C, Erskine L, Gardner ER, Figg
WD and Vargesson N: Thalidomide induces limb defects by preventing
angiogenic outgrowth during early limb formation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:8573–8578. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ito T, Ando H, Suzuki T, Ogura T, Hotta K,
Imamura Y, Yamaguchi Y and Handa H: Identification of a primary
target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science. 327:1345–1350. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yabu T, Tomimoto H, Taguchi Y, Yamaoka S,
Igarashi Y and Okazaki T: Thalidomide-induced antiangiogenic action
is mediated by ceramide through depletion of VEGF receptors, and is
antagonized by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Blood. 106:125–134. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Verheul HM, Panigrahy D, Yuan J and
D'Amato RJ: Combination oral antiangiogenic therapy with
thalidomide and sulindac inhibits tumour growth in rabbits. Br J
Cancer. 79:114–118. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bertolini F, Mingrone W, Alietti A,
Ferrucci PF, Cocorocchio E, Peccatori F, Cinieri S, Mancuso P,
Corsini C, et al: Thalidomide in multiple myeloma, myelodysplastic
syndromes and histiocytosis. Analysis of clinical results and of
surrogate angiogenesis markers. Ann Oncol. 12:987–990. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Liu X, Wang J, Wang Z, Jiang W, Reed
E, Zhang Y, Liu Y and Li QQ: Effects of thalidomide on the
expression of angiogenesis growth factors in human A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 11:785–790. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vasvari GP, Dyckhoff G, Kashfi F, Lemke B,
Lohr J, Helmke BM, Schirrmacher V, Plinkert PK, Beckhove P and
Herold-Mende CC: Combination of thalidomide and cisplatin in an
head and neck squamous cell carcinomas model results in an enhanced
antiangiogenic activity in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer.
121:1697–1704. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stephens TD, Bunde CJ and Fillmore BJ:
Mechanism of action in thalidomide teratogenesis. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:1489–1499. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stephens TD and Fillmore BJ: Hypothesis:
thalidomide embryopathy-proposed mechanism of action. Teratology.
61:189–195. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fujita J, Mestre JR, Zeldis JB,
Subbaramaiah K and Dannenberg AJ: Thalidomide and its analogues
inhibit lipopolysaccharide-mediated linduction of cyclooxygenase-2.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:3349–3355. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang SH, Liu CH, Conway R, Han DK,
Nithipatikom K, Trifan OC, Lane TF and Hla T: Role of prostaglandin
E2-dependent angiogenic switch in cyclooxygenase 2-induced breast
cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:591–596. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Yamada M, Kawai M, Kawai Y and Mashima Y:
The effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor on corneal
angiogenesis in the rat. Curr Eye Res. 19:300–304. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vargesson N: Thalidomide-induced limb
defects: resolving a 50-year-old puzzle. BioEssays. 31:1327–1336.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vargesson N: Thalidomide embryopathy: An
enigmatic challenge. ISRN Dev Biol. 241016:2013 View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Feng Q, Tan HH, Ge ZZ, Gao YJ, Chen HM and
Xiao SD: Thalidomide-induced angiopoietin 2, Notch1 and Dll4
downregulation under hypoxic condition in tissues with
gastrointestinal vascular malformation and human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. J Dig Dis. 15:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Fu S, Chen H, Feng Q, Gao Y, Xue H,
Ge Z, Fang J and Xiao S: Inhibition of endothelial Slit2/Robo1
signaling by thalidomide restrains angiogenesis by blocking the
PI3K/Akt pathway. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2958–2966. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Segers J, Di Fazio V, Ansiaux R, Martinive
P, Feron O, Wallemacq P and Gallez B: Potentiation of
cyclophosphamide chemotherapy using the anti-angiogenic drug
thalidomide: importance of optimal scheduling to exploit the
'normalization' window of the tumor vasculature. Cancer Lett.
244:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lebrin F, Srun S, Raymond K, Martin S, van
den Brink S, Freitas C, Bréant C, Mathivet T, Larrivée B, Thomas
JL, et al: Thalidomide stimulates vessel maturation and reduces
epistaxis in individuals with hereditary hemorrhagic
telangiectasia. Nat Med. 16:420–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y,
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Normalization of the vasculature for
treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev. 91:1071–1121.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Floros T and Tarhini AA: Anticancer
cytokines: biology and clinical effects of Interferon-α2,
Interleukin (IL)-2, IL-15, IL-21, and IL-12. Semin Oncol.
42:539–548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V,
Chauhan D, Richardson PG, Hideshima T, Munshi NC, Treon SP and
Anderson KC: Apoptotic signaling induced by immunomodulatory
thalidomide analogs in human multiple myeloma cells: therapeutic
implications. Blood. 99:4525–4530. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marriott JB, Clarke IA, Czajka A, Dredge
K, Childs K, Man HW, Schafer P, Govinda S, Muller GW, Stirling DI
and Dalgleish AG: A novel subclass of thalidomide analogue with
anti-solid tumor activity in which caspase-dependent apoptosis is
associated with altered expression of bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer
Res. 63:593–599. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schuster SR, Kortuem KM, Zhu YX, Braggio
E, Shi CX, Bruins LA, Schmidt JE, Ahmann G, Kumar S, Rajkumar SV,
et al: The clinical significance of cereblon expression in multiple
myeloma. Leuk Res. 38:23–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Chung AS, Lee J and Ferrara N: Targeting
the tumour vasculature: insights from physiological angiogenesis.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:505–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sitkovsky MV, Kjaergaard J, Lukashev D and
Ohta A: Hypoxia-adenosinergic immunosuppression: tumor protection
by T regulatory cells and cancerous tissue hypoxia. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:5947–5952. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Palazon A, Aragones J, Morales-Kastresana
A, de Landazuri MO and Melero I: Molecular pathways: hypoxia
response in immune cells fighting or promoting cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:1207–1213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Huang Y, Goel S, Duda DG, Fukumura D and
Jain RK: Vascular normalization as an emerging strategy to enhance
cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 73:2943–2948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hamzah J, Jugold M, Kiessling F, Rigby P,
Manzur M, Marti HH, Rabie T, Kaden S, Gröne HJ, Hämmerling GJ, et
al: Vascular normalization in Rgs5-deficient tumours promotes
immune destruction. Nature. 453:410–414. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rolny C, Mazzone M, Tugues S, Laoui D,
Johansson I, Coulon C, Squadrito ML, Segura I, Li X, Knevels E, et
al: HRG inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by inducing macrophage
polarization and vessel normalization through downregulation of
PlGF. Cancer Cell. 19:31–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X,
Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L,
Burow M, et al: Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in
ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced
survival. Nat Med. 10:942–949. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F,
Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagès C, Tosolini M, Camus M,
Berger A, Wind P, et al: Type, density, and location of immune
cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome.
Science. 313:1960–1964. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tan TT and Coussens LM: Humoral immunity,
inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol. 19:209–216. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Galustian C, Meyer B, Labarthe MC, Dredge
K, Klaschka D, Henry J, Todryk S, Chen R, Muller G, Stirling D, et
al: The anti-cancer agents lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibit
the proliferation and function of T regulatory cells. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 58:1033–1045. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
de Visser KE and Coussens LM: The
inflammatory tumor microenvironment and its impact on cancer
development. Contrib Microbiol. 13:118–137. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lin EY, Li JF, Gnatovskiy L, Deng Y, Zhu
L, Grzesik DA, Qian H, Xue XN and Pollard JW: Macrophages regulate
the angiogenic switch in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 66:11238–11246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Murdoch C, Giannoudis A and Lewis CE:
Mechanisms regulating the recruitment of macrophages into hypoxic
areas of tumors and other ischemic tissues. Blood. 104:2224–2234.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB and Lewis
CE: The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour
angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:618–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Burke B, Tang N, Corke KP, Tazzyman D,
Ameri K, Wells M and Lewis CE: Expression of HIF-1alpha by human
macrophages: implications for the use of macrophages in
hypoxia-regulated cancer gene therapy. J Pathol. 196:204–212. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lewis CE and Pollard JW: Distinct role of
macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res.
66:605–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Murdoch C and Lewis CE: Macrophage
migration and gene expression in response to tumor hypoxia. Int J
Cancer. 117:701–708. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee HS, Kwon HS, Park DE, Woo YD, Kim HY,
Kim HR, Cho SH, Min KU, Kang HR and Chang YS: Thalidomide inhibits
alternative activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro: a
potential mechanism of anti-asthmatic effect of thalidomide. PLoS
One. 10:e01230942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bruno A, Focaccetti C, Pagani A,
Imperatori AS, Spagnoletti M, Rotolo N, Cantelmo AR, Franzi F,
Capella C, Ferlazzo G, et al: The proangiogenic phenotype of
natural killer cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Neoplasia. 15:133–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Haslett PA, Corral LG, Albert M and Kaplan
G: Thalidomide costimulates primary human T lymphocytes,
preferentially inducing proliferation, cytokine production, and
cytotoxic responses in the CD8+ subset. J Exp Med. 187:1885–1892.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pober JS, Gimbrone MA Jr, Cotran RS, Reiss
CS, Burakoff SJ, Fiers W and Ault KA: Ia expression by vascular
endothelium is inducible by activated T cells and by human gamma
interferon. J Exp Med. 157:1339–1353. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pober JS, Gimbrone MA Jr, Lapierre LA,
Mendrick DL, Fiers W, Rothlein R and Springer TA: Overlapping
patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1,
tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol.
137:1893–1896. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Choi J, Enis DR, Koh KP, Shiao SL and
Pober JS: T lymphocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Annu Rev
Immunol. 22:683–709. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Trédan O, Lacroix-Triki M, Guiu S,
Mouret-Reynier MA, Barrière J, Bidard FC, Braccini AL, Mir O,
Villanueva C and Barthélémy P: Angiogenesis and tumor
microenvironment: bevacizumab in the breast cancer model. Target
Oncol. 10:189–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rivas-Fuentes S, Salgado-Aguayo A, Pertuz
Belloso S, Gorocica Rosete P, Alvarado-Vásquez N and Aquino-Jarquin
G: Role of chemokines in non-small cell lung cancer: angiogenesis
and inflammation. J Cancer. 6:938–952. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Dirkx AE, Oude Egbrink MG, Wagstaff J and
Griffioen AW: Monocyte/macrophage infiltration in tumors:
modulators of angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 80:1183–1196. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fischer C, Jonckx B, Mazzone M, Zacchigna
S, Loges S, Pattarini L, Chorianopoulos E, Liesenborghs L, Koch M,
De Mol M, et al: Anti-PlGF inhibits growth of
VEGF(R)-inhibitor-resistant tumors without affecting healthy
vessels. Cell. 131:463–475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nakayama T, Yao L and Tosato G: Mast
cell-derived angiopoietin-1 plays a critical role in the growth of
plasma cell tumors. J Clin Invest. 114:1317–1325. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Stockmann C, Schadendorf D, Klose R and
Helfrich I: The impact of the immune system on tumor: angiogenesis
and vascular remodeling. Front Oncol. 4:692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jain RK: Antiangiogenesis strategies
revisited: from starving tumors to alleviating hypoxia. Cancer
Cell. 26:605–622. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|