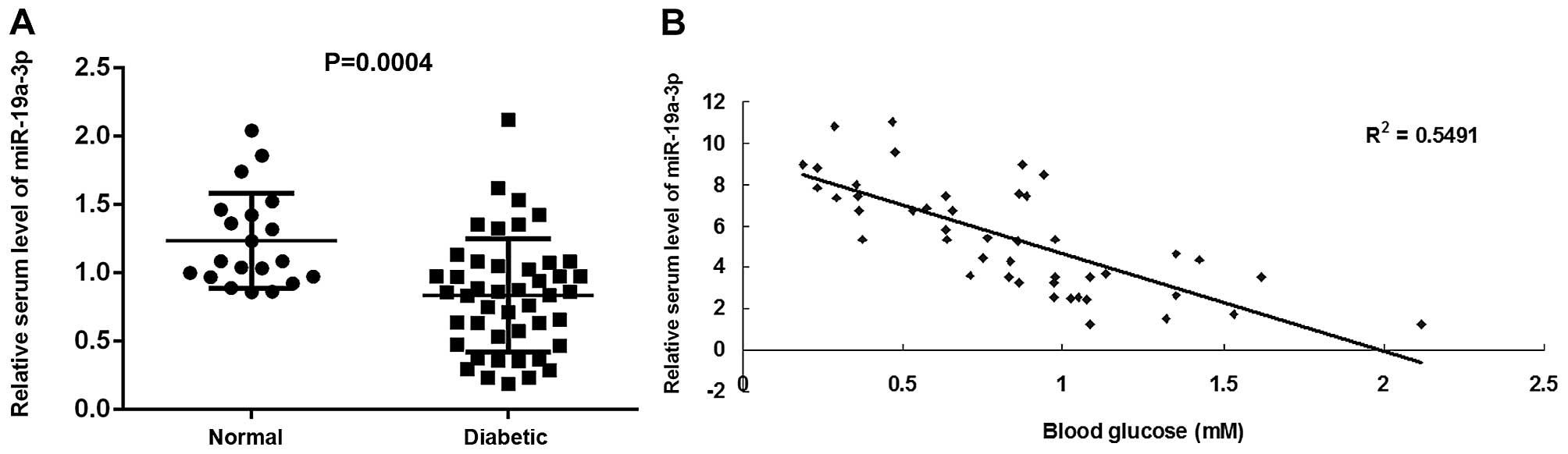
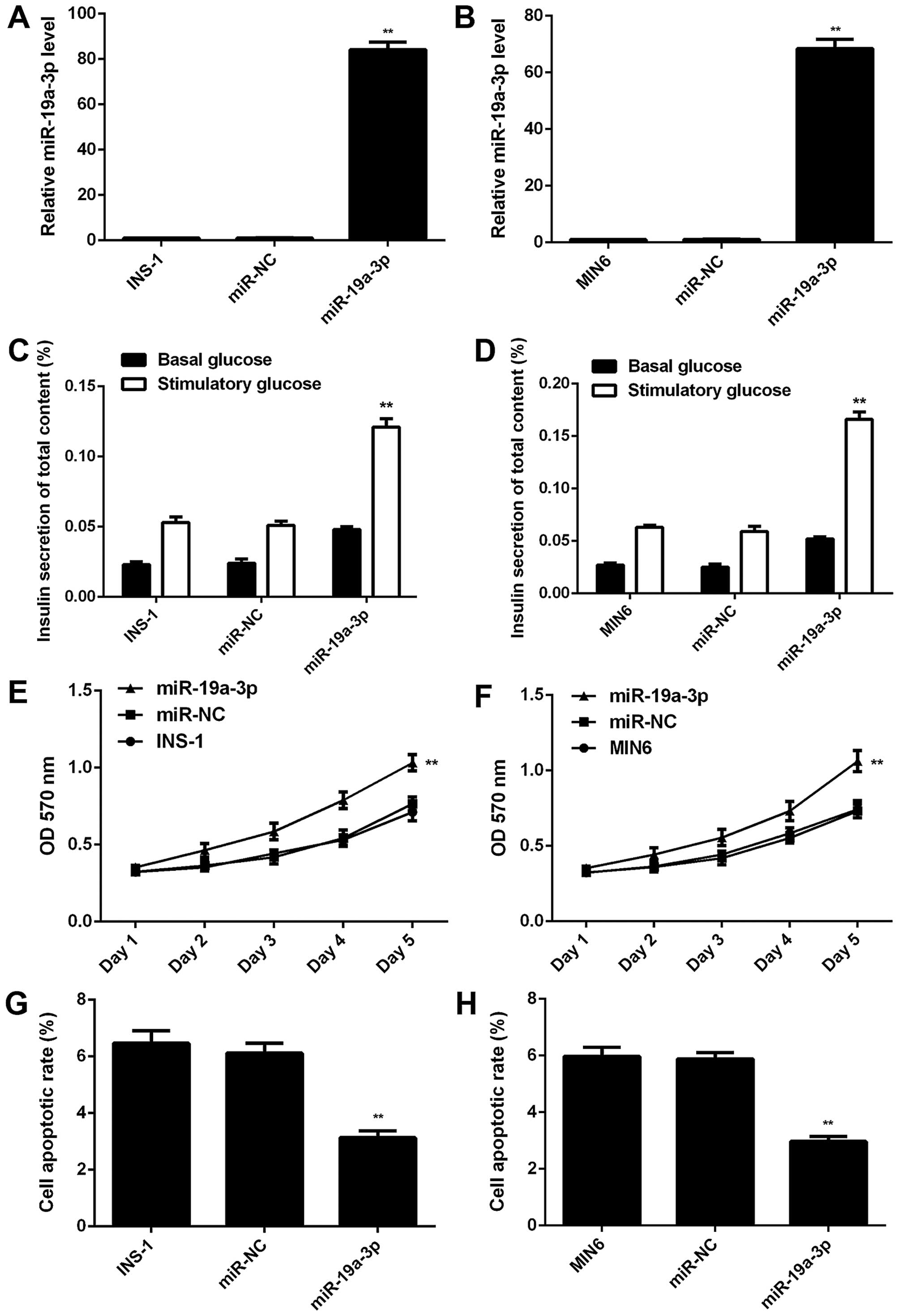
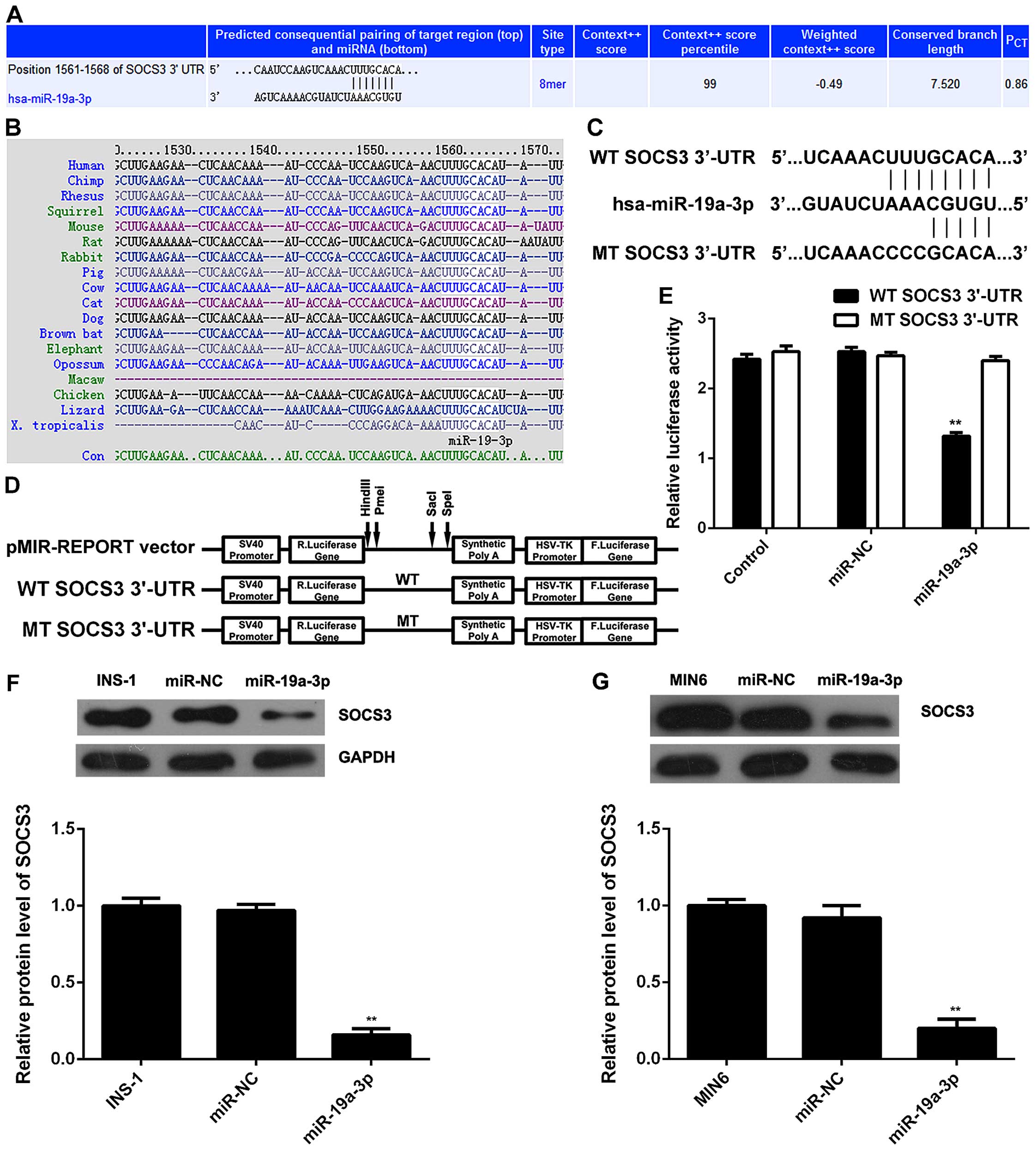
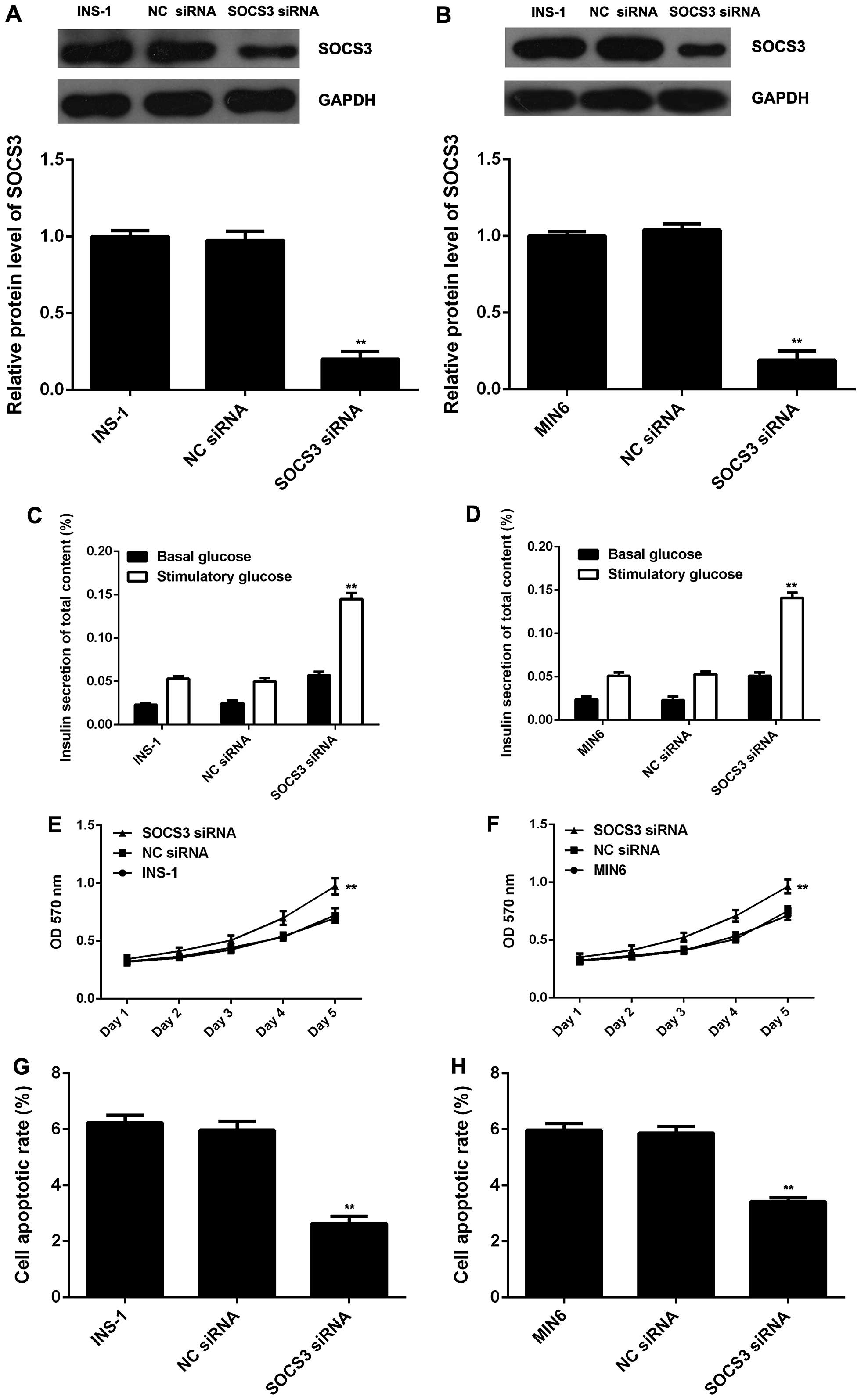
|
1
|
Kaul K, Apostolopoulou M and Roden M:
Insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism.
64:1629–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chatterjee S and Davies MJ: Current
management of diabetes mellitus and future directions in care.
Postgrad Med J. 91:612–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Keane KN, Cruzat VF, Carlessi R, de
Bittencourt PI Jr and Newsholme P: Molecular events linking
oxidative stress and inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell
dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:1816432015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Berge LI and Riise T: Comorbidity between
type 2 diabetes and depression in the adult population: Directions
of the association and its possible pathophysiological mechanisms.
Int J Endocrinol. 2015:1647602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhatia P, Raina S, Chugh J and Sharma S:
miRNAs: early prognostic biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Biomark Med. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Libânio D, Dinis-Ribeiro M and
Pimentel-Nunes P: Helicobacter pylori and microRNAs: Relation with
innate immunity and progression of preneoplastic conditions. World
J Clin Oncol. 6:111–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinez-Sanchez A, Nguyen-Tu MS and
Rutter GA: DICER inactivation identifies oancreatic β-cell
'Disallowed' genes targeted by MicroRNAs. Mol Endocrinol.
29:1067–1079. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Latreille M, Herrmanns K, Renwick N,
Tuschl T, Malecki MT, McCarthy MI, Owen KR, Rülicke T and Stoffel
M: miR-375 gene dosage in pancreatic β cells: Implications for
regulation of β cell mass and biomarker development. J Mol Med
Berl. 93:1159–1169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jacovetti C, Matkovich SJ, Rodriguez-Trejo
A, Guay C and Regazzi R: Postnatal β cell maturation is associated
with islet-specific microRNA changes induced by nutrient shifts at
weaning. Nat Commun. 6:80842015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al-Mahroos G, Alsayed NA,
Hasan ZA, Nawaz S and Bakhiet M: Peripheral blood microRNA-15a is a
potential biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes.
Mol Med Rep. 12:7485–7490. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Busch S, Auth E, Scholl F, Huenecke S,
Koehl U, Suess B and Steinhilber D: 5-Lipoxygenase is a direct
target of miR-19a-3p and miR-125b-5p. J Immunol. 194:1646–1653.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Zhang Z, Chen C, Liu Y, Si Q,
Chuang TH, Li N, Gomez-Cabrero A, Reisfeld RA, Xiang R and Luo Y:
MicroRNA-19a-3p inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis
by inducing macrophage polarization through downregulated
expression of Fra-1 proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 33:3014–3023. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhi F, Shao N, Wang R, Deng D, Xue L, Wang
Q, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Xia X, Wang S, et al: Identification of 9 serum
microRNAs as potential noninvasive biomarkers of human astrocytoma.
Neuro Oncol. 17:383–391. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Ibarrola-Villava M, Llorca-Cardeñosa MJ,
Tarazona N, Mongort C, Fleitas T, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Roselló S,
Navarro S, Ribas G and Cervantes A: Deregulation of ARID1A, CDH1,
cMET and PIK3CA and target-related microRNA expression in gastric
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:26935–26945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Balci S, Ayaz L, Gorur A, Yildirim Yaroglu
H, Akbayir S, Dogruer Unal N, Bulut B, Tursen U and Tamer L:
microRNA profiling for early detection of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Clin Exp Dermatol. 41:346–351. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zheng G, Du L, Yang X, Zhang X, Wang L,
Yang Y, Li J and Wang C: Serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for
early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer.
111:1985–1992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Tian F, Li H, Zhou Y, Lu J and Ge
Q: Profiling maternal plasma microRNA expression in early pregnancy
to predict gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Gynaecol Obstet.
130:49–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dou L, Meng X, Sui X, Wang S, Shen T,
Huang X, Guo J, Fang W, Man Y, Xi J and Li J: miR-19a regulates
PTEN expression to mediate glycogen synthesis in hepatocytes. Sci
Rep. 5:116022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chakraborty C, George Priya Doss C and
Bandyopadhyay S: miRNAs in insulin resistance and
diabetes-associated pancreatic cancer: The 'minute and miracle'
molecule moving as a monitor in the 'genomic galaxy'. Curr Drug
Targets. 14:1110–1117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Wang L, Mo Q, Jia A, Dong Y and
Wang G: A positive feedback loop of p53/miR-19/TP53INP1 modulates
pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol Rep.
35:518–523. 2016.
|
|
24
|
Tan Y, Yin H, Zhang H, Fang J, Zheng W, Li
D, Li Y, Cao W, Sun C, Liang Y, et al: Sp1-driven up-regulation of
miR-19a decreases RHOB and promotes pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
6:17391–17403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Tu Y, Shen H, Dai Z, Lin
J and Zhou Z: miR-101a and miR-30b contribute to inflammatory
cytokine- mediated β cell dysfunction. Lab Invest. 95:1387–1397.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leung CM, Chen TW, Li SC, Ho MR, Hu LY,
Liu WS, Wu TT, Hsu PC, Chang HT and Tsai KW: MicroRNA expression
profiles in human breast cancer cells after multifraction and
single-dose radiation treatment. Oncol Rep. 31:2147–2156.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang WL, Zhang YF, Xia QQ, Zhu J, Yu X,
Fan T and Wang F: MicroRNA-19a regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced
endothelial cell apoptosis through modulation of apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1 expression. BMC Mol Biol. 16:112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim MH, Kim MS, Kim W, Kang MA, Cacalano
NA, Kang SB, Shin YJ and Jeong JH: Suppressor of cytokine signaling
(SOCS) genes are silenced by DNA hypermethylation and histone
deacetylation and regulate response to radiotherapy in cervical
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01231332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wunderlich CM, Hövelmeyer N and Wunderlich
FT: Mechanisms of chronic JAK-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling in obesity.
JAKSTAT. 2:e238782013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krebs DL and Hilton DJ: A new role for
SOCS in insulin action. Suppressor of cytokine signaling. Sci STKE.
2003:PE62003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang Z, Hulver M, McMillan RP, Cai L,
Kershaw EE, Yu L, Xue B and Shi H: Regulation of insulin and leptin
signaling by muscle suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3).
PLoS One. 7:e474932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Zhou H, Han Y, Liu X, Wang M, Wang
X, Yin G, Li X and Xiang M: SOCS3 methylation in synergy with Reg3A
over-expression promotes cell growth in pancreatic cancer. J Mol
Med Berl. 92:1257–1269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|