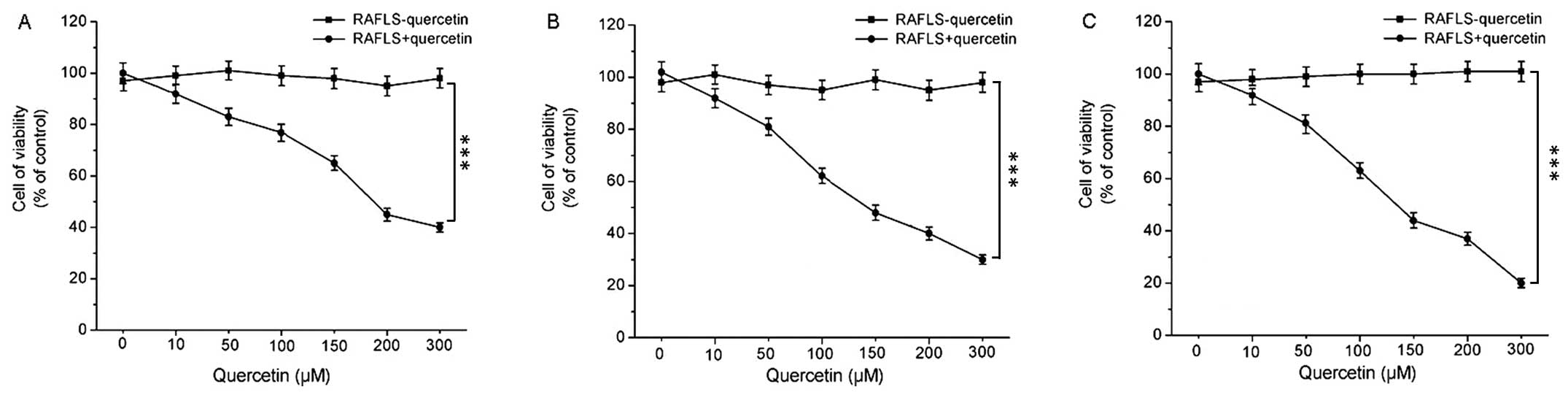
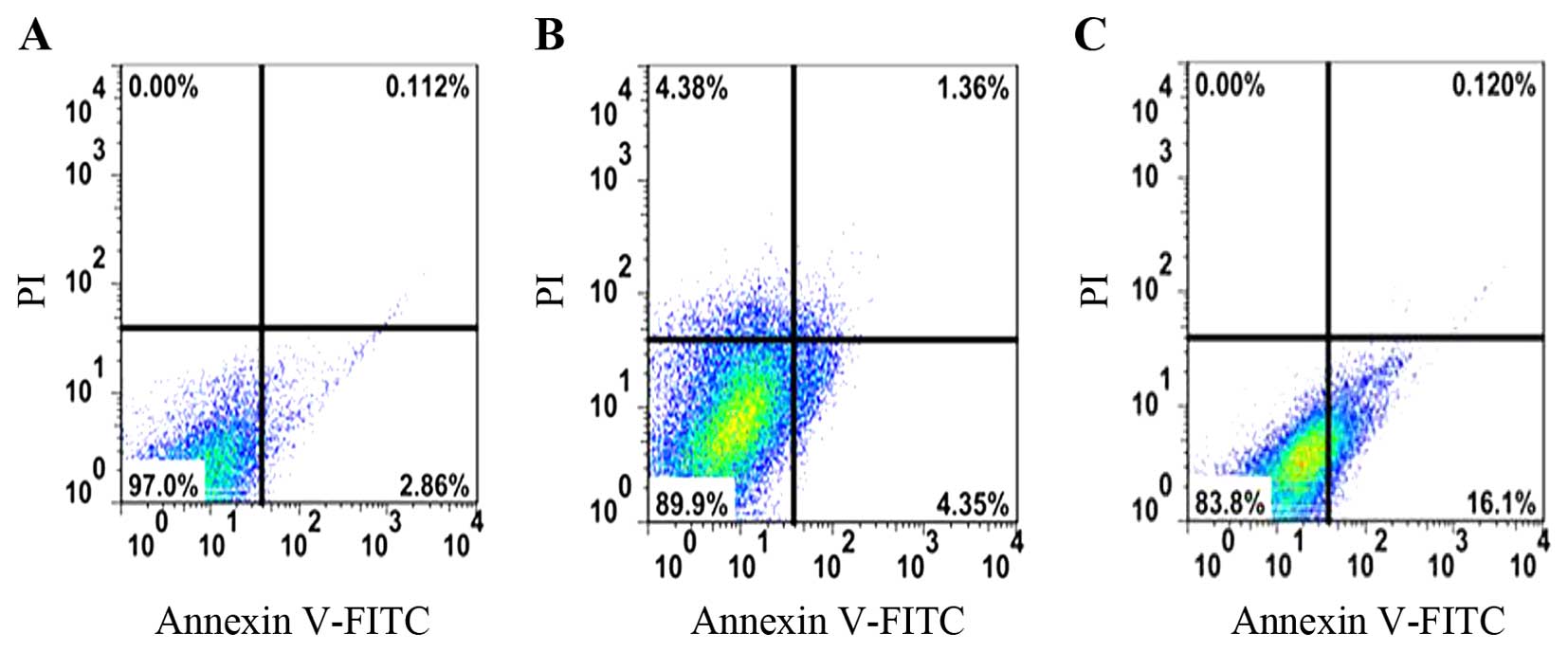
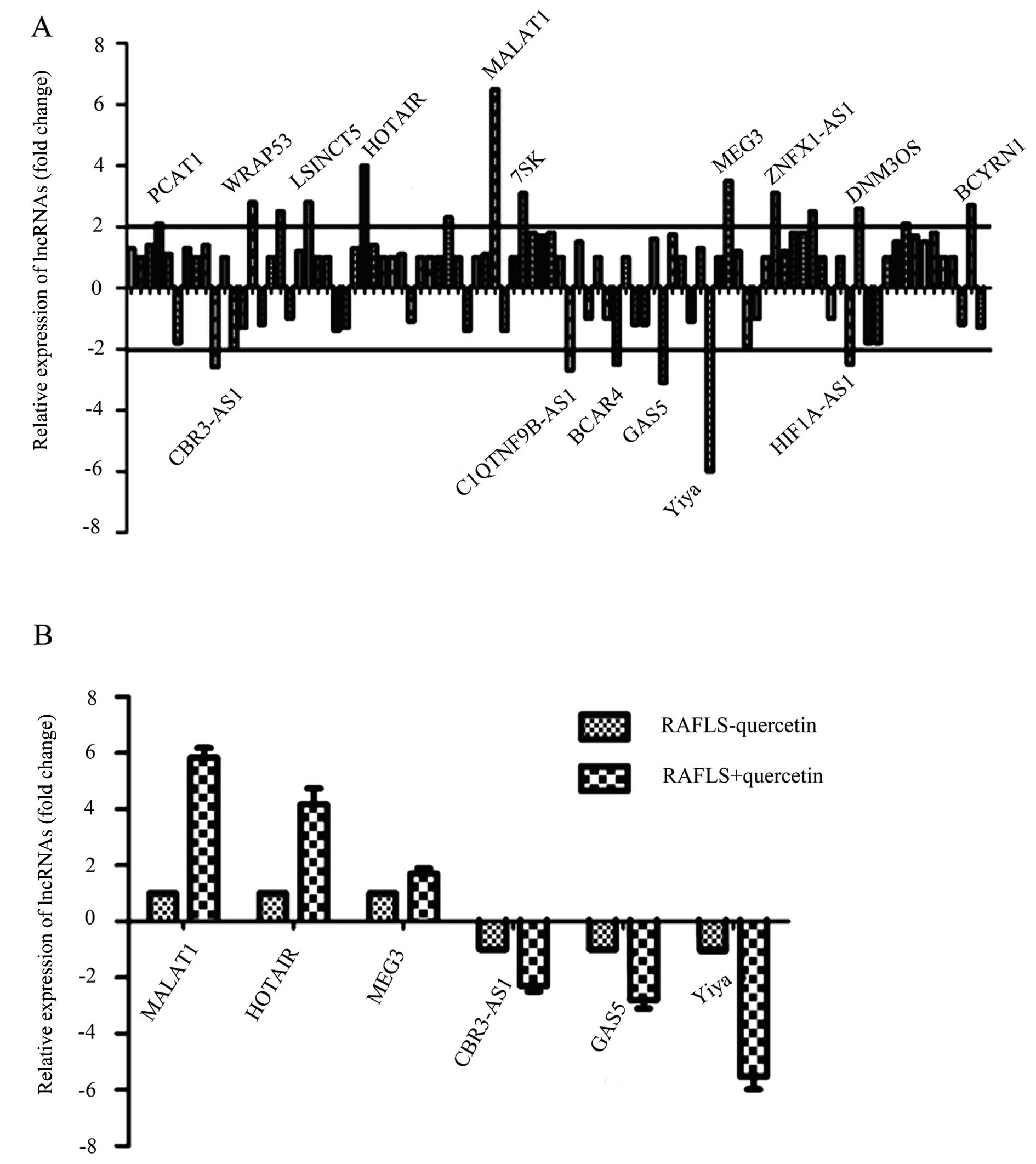
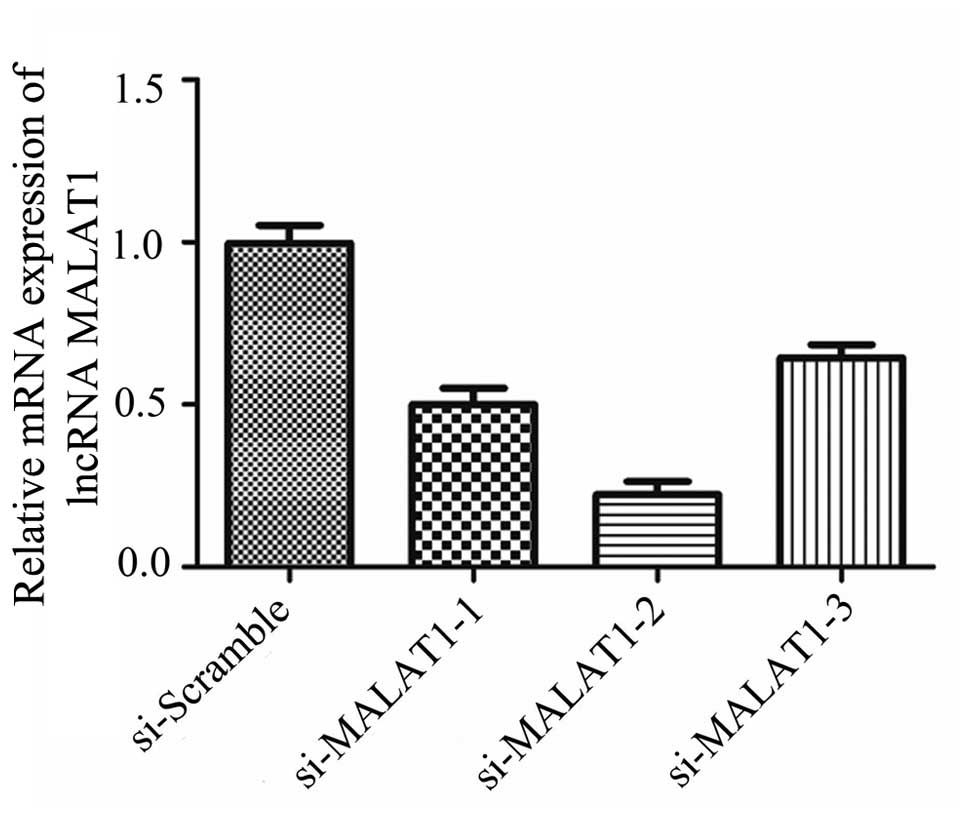
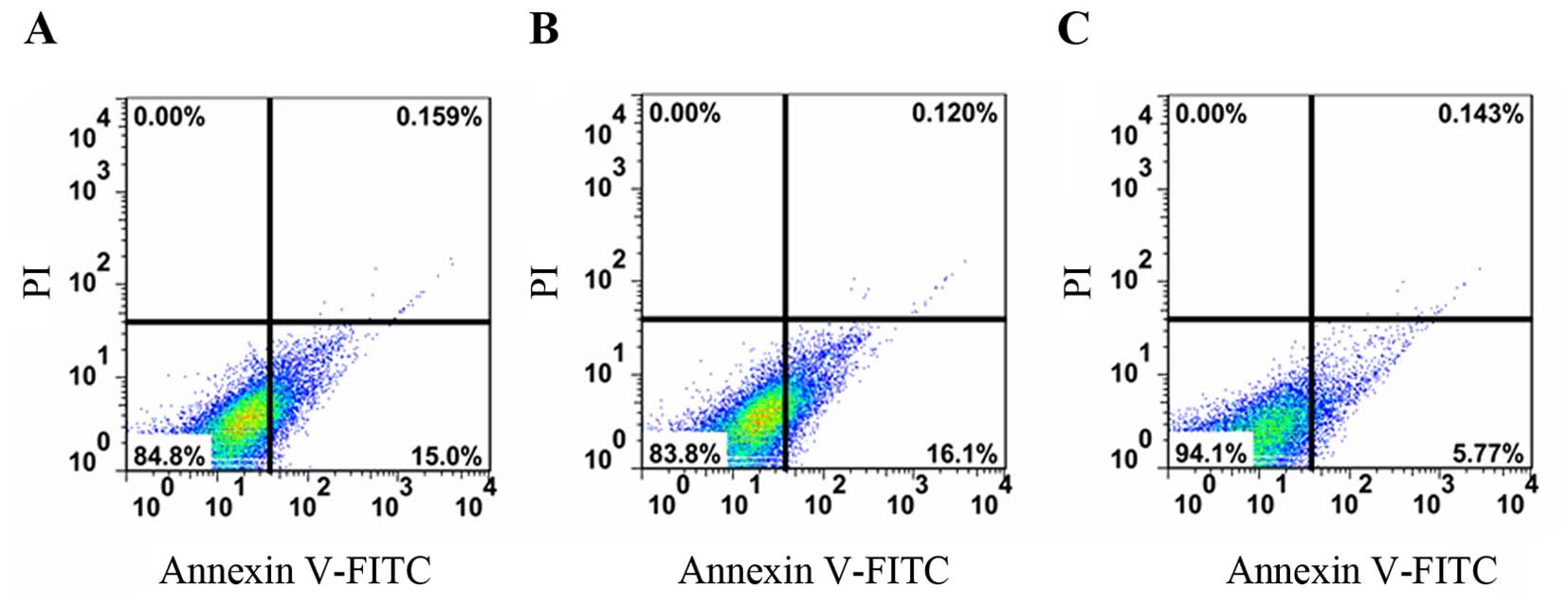
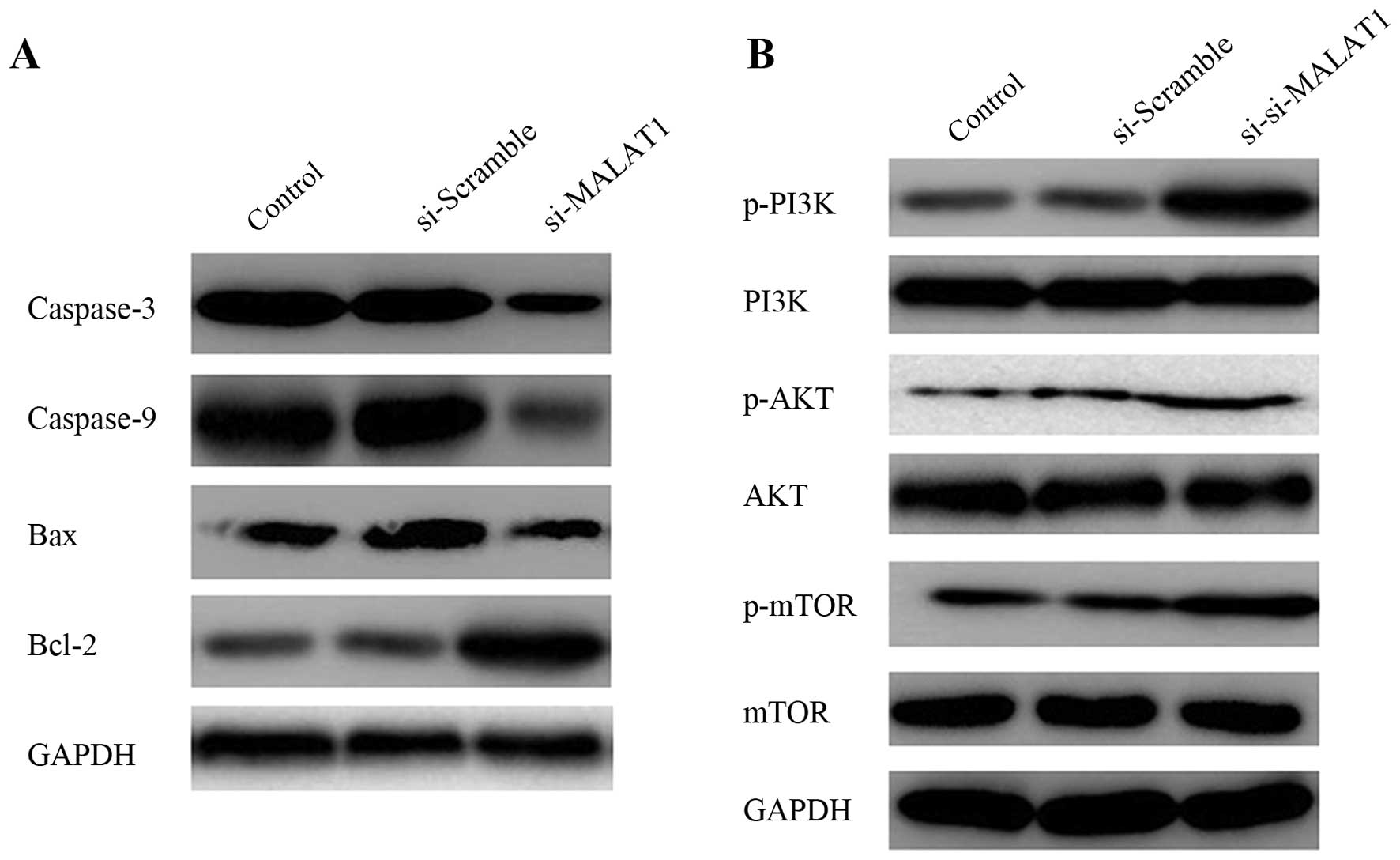
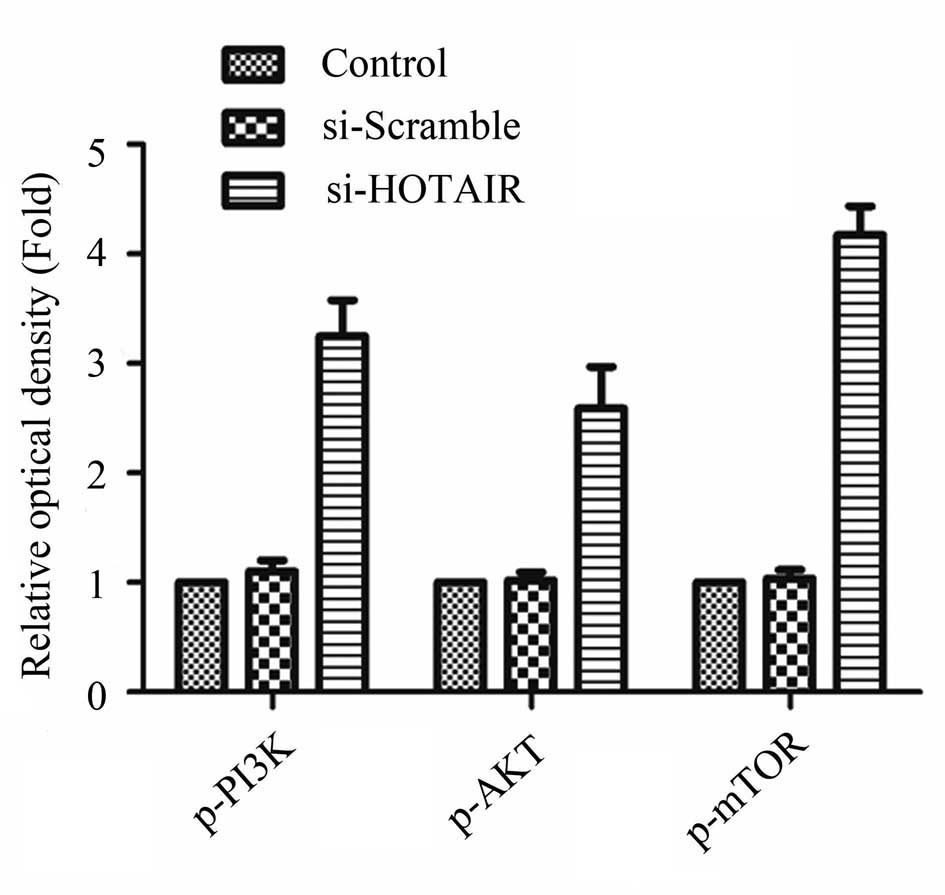
|
1
|
Nanki T, Nagasaka K, Hayashida K, Saita Y
and Miyasaka N: Chemokines regulate IL-6 and IL-8 production by
fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. J Immunol. 167:5381–5385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gabriel SE and Michaud K: Epidemiological
studies in incidence, prevalence, mortality, and comorbidity of the
rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:2292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurowska M, Rudnicka W, Kontny E, Janicka
I, Chorazy M, Kowalczewski J, Ziółkowska M, Ferrari-Lacraz S, Strom
TB and Maśliński W: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid
arthritis patients express functional IL-15 receptor complex:
endogenous IL-15 in autocrine fashion enhances cell proliferation
and expression of Bcl-x(L) and Bcl-2. J Immunol. 169:1760–1767.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen S, Yang Y, Feng H, Wang H, Zhao R and
Liu H: Baicalein inhibits interleukin-1β-induced proliferation of
human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Inflammation. 37:163–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu H and Pope RM: The role of apoptosis
in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 3:317–322. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pope RM: Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool
in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:527–535. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baier A, Meineckel I, Gay S and Pap T:
Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 15:274–279.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gloss BS and Dinger ME: The specificity of
long noncoding RNA expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1859:16–22.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pedram Fatemi R, Salah-Uddin S, Modarresi
F, Khoury N, Wahlestedt C and Faghihi MA: Screening for
small-molecule modulators of long noncoding RNA-protein
interactions using AlphaScreen. J Biomol Screen. 20:1132–1141.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weber DG, Johnen G, Casjens S, Bryk O,
Pesch B, Jöckel KH, Kollmeier J and Brüning T: Evaluation of long
noncoding RNA MALAT1 as a candidate blood-based biomarker for the
diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Res Notes. 6:5182013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jalali S, Bhartiya D, Lalwani MK,
Sivasubbu S and Scaria V: Systematic transcriptome wide analysis of
lncRNA-miRNA interactions. PLoS One. 8:e538232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu C, Yang M, Tian J, Wang X and Li Z:
MALAT-1: A long non-coding RNA and its important 3′ end functional
motif in colorectal cancer metastasis. Int J Oncol. 39:169–175.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lai MC, Yang Z, Zhou L, Zhu QQ, Xie HY,
Zhang F, Wu LM, Chen LM and Zheng SS: Long non-coding RNA MALAT-1
over-expression predicts tumor recurrence of hepatocellular
carcinoma after liver transplantation. Med Oncol. 29:1810–1816.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ying L, Chen Q, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Huang Y
and Qiu F: Upregulated MALAT-1 contributes to bladder cancer cell
migration by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol
Biosyst. 8:2289–2294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tripathi V, Shen Z, Chakraborty A, Giri S,
Freier SM, Wu X, Zhang Y, Gorospe M, Prasanth SG, Lal A and
Prasanth KV: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 controls cell cycle
progression by regulating the expression of oncogenic transcription
factor B-MYB. PLoS Genet. 9:e10033682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong Y, Liang G, Yuan B, Yang C, Gao R and
Zhou X: MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:1477–1486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bjelogrlić S, Srdić T and Radulović S:
Mammalian target of rapamycin is a promising target for novel
therapeutic strategy against cancer. J BUON. 11:267–276. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Gauthier A and Ho M: Role of sorafenib in
the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: an update.
Hepatol Res. 43:147–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lamson DW and Brignall MS: Antioxidants
and cancer, part 3: quercetin. Altern Med Rev. 5:196–208.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hollman PC, vd Gaag M, Mengelers MJ, van
Trijp JM, de Vries JH and Katan MB: Absorption and disposition
kinetics of the dietary antioxidant quercetin in man. Free Radic
Biol Med. 21:703–707. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi JA, Kim JY, Lee JY, Kang CM, Kwon HJ,
Yoo YD, Kim TW, Lee YS and Lee SJ: Induction of cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by quercetin. Int J
Oncol. 19:837–844. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coskun O, Kanter M, Korkmaz A and Oter S:
Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects
streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and β-cell damage in rat
pancreas. Pharmacol Res. 51:117–123. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Natarajan V, Krithica N, Madhan B and
Sehgal PK: Formulation and evaluation of quercetin polycaprolactone
microspheres for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharm
Sci. 100:195–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mamani-Matsuda M, Kauss T, Al-Kharrat A,
Rambert J, Fawaz F, Thiolat D, Moynet D, Coves S, Malvy D and
Mossalayi MD: Therapeutic and preventive properties of quercetin in
experimental arthritis correlate with decreased macrophage
inflammatory mediators. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1304–1310. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Loof A, Vandersmissen T, Marchal E and
Schoofs L: Initiation of metamorphosis and control of ecdysteroid
biosynthesis in insects: The interplay of absence of Juvenile
hormone, PTTH, and Ca(2+)-homeostasis. Peptides. 68:120–129. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Korb A, Pavenstädt H and Pap T: Cell death
in rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis. 14:447–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brunelle JK and Letai A: Control of
mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci.
122:437–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Sun S, Chen J, Ren P, Hu Y, Cao
Z, Sun H and Ding Y: Oxymatrine induces mitochondria dependent
apoptosis in human osteosarcoma MNNG/HOS cells through inhibition
of PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol. 35:1619–1625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hong SK, Yoon S, Moelling C, Arthan D and
Park JI: Noncatalytic function of ERK1/2 can promote
Raf/MEK/ERK-mediated growth arrest signaling. J Biol Chem.
284:33006–33018. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Firestein GS: Evolving concepts of
rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 423:356–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McInnes IB, al-Mughales J, Field M, Leung
BP, Huang FP, Dixon R, Sturrock RD, Wilkinson PC and Liew FY: The
role of interleukin-15 in T-cell migration and activation in
rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2:175–182. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, Cannuscio
CC, Mandl LA, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ and Curhan GC: Cardiovascular
morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid
arthritis. Circulation. 107:1303–1307. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feldmann M and Maini RN: Anti-TNF α
therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev
Immunol. 19:163–196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Noss EH and Brenner MB: The role and
therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 223:252–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tolboom TC, van der Helm-Van Mil AH,
Nelissen RG, Breedveld FC, Toes RE and Huizinga TW: Invasiveness of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes is an individual patient
characteristic associated with the rate of joint destruction in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 52:1999–2002.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Q, Wu J, Cao Q, Xiao L, Wang L, He
D, Ouyang G, Lin J, Shen B, Shi Y, et al: A critical role of Cyr61
in interleukin-17-dependent proliferation of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
60:3602–3612. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boots AW, Haenen GR and Bast A: Health
effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur J
Pharmacol. 585:325–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase
activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt
and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr.
136:2715–2721. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sato M, Miyazaki T, Kambe F, Maeda K and
Seo H: Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, inhibits the induction of
interleukin 8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression by
tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cultured human synovial cells. J
Rheumatol. 24:1680–1684. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sung MS, Lee EG, Jeon HS, Chae HJ, Park
SJ, Lee YC and Yoo WH: Quercetin inhibits IL-1β-induced
proliferation and production of MMPs, COX-2, and PGE2 by rheumatoid
synovial fibroblast. Inflammation. 35:1585–1594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang KC, Yang YW, Liu B, Sanyal A,
Corces-Zimmerman R, Chen Y, Lajoie BR, Protacio A, Flynn RA, Gupta
RA, et al: A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to
coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature. 472:120–124. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wapinski O and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 21:354–361. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N,
Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E and Chang HY: Long noncoding RNA as
modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science.
329:689–693. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schmidt LH, Spieker T, Koschmieder S,
Schäffers S, Humberg J, Jungen D, Bulk E, Hascher A, Wittmer D,
Marra A, et al: The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and
tumor growth. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1984–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Eißmann M, Gutschner T, Hämmerle M,
Günther S, Caudron-Herger M, Groß M, Schirmacher P, Rippe K, Braun
T, Zörnig M and Diederichs S: Loss of the abundant nuclear
non-coding RNA MALAT1 is compatible with life and development. RNA
Biol. 9:1076–1087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Devarajan E, Sahin AA, Chen JS,
Krishnamurthy RR, Aggarwal N, Brun AM, Sapino A, Zhang F, Sharma D,
Yang XH, et al: Down-regulation of caspase 3 in breast cancer: a
possible mechanism for chemoresistance. Oncogene. 21:8843–8851.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Du J, Wang X, Miereles C, Bailey JL,
Debigare R, Zheng B, Price SR and Mitch WE: Activation of caspase-3
is an initial step triggering accelerated muscle proteolysis in
catabolic conditions. J Clin Invest. 113:115–123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kuida K: Caspase-9. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 32:121–124. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fujita E, Jinbo A, Matuzaki H, Konishi H,
Kikkawa U and Momoi T: Akt phosphorylation site found in human
caspase-9 is absent in mouse caspase-9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
264:550–555. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Ellerby LM,
Welsh K, Xie Z, Deveraux QL, Salvesen GS, Bredesen DE, Rosenthal
RE, Fiskum G and Reed JC: Release of caspase-9 from mitochondria
during neuronal apoptosis and cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 96:5752–5757. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong WX,
Rathmell JC, Shiels HA, Ulrich E, Waymire KG, Mahar P, Frauwirth K,
et al: The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members
bak and bax are essential for normal development of multiple
tissues. Mol Cell. 6:1389–1399. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J,
Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N: Noxa, a
BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of
p53-induced apoptosis. Science. 288:1053–1058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
LeBlanc H, Lawrence D, Varfolomeev E,
Totpal K, Morlan J, Schow P, Fong S, Schwall R, Sinicropi D and
Ashkenazi A: Tumor-cell resistance to death receptor-induced
apoptosis through mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2
homolog Bax. Nat Med. 8:274–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fulda S, Meyer E and Debatin K-M:
Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression.
Oncogene. 21:2283–2294. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: How do BCL-2
proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
Trends Cell Biol. 18:157–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Saxena A, Viswanathan S, Moshynska O,
Tandon P, Sankaran K and Sheridan DP: Mcl-1 and Bcl-2/Bax ratio are
associated with treatment response but not with Rai stage in B-cell
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 75:22–33. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman
LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA and McCubrey JA:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O,
Link W and Leal JF: The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer,
therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:187–198.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|