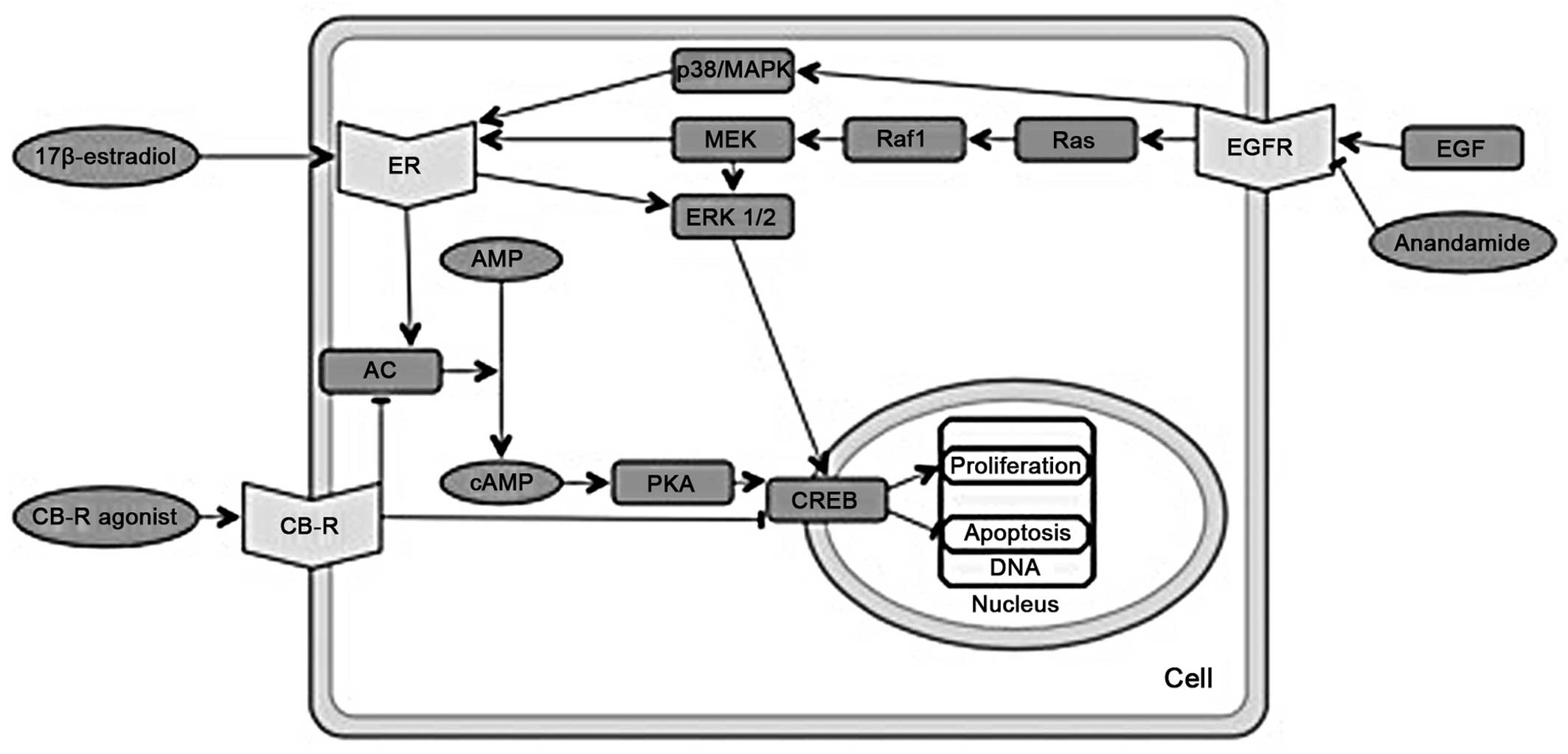
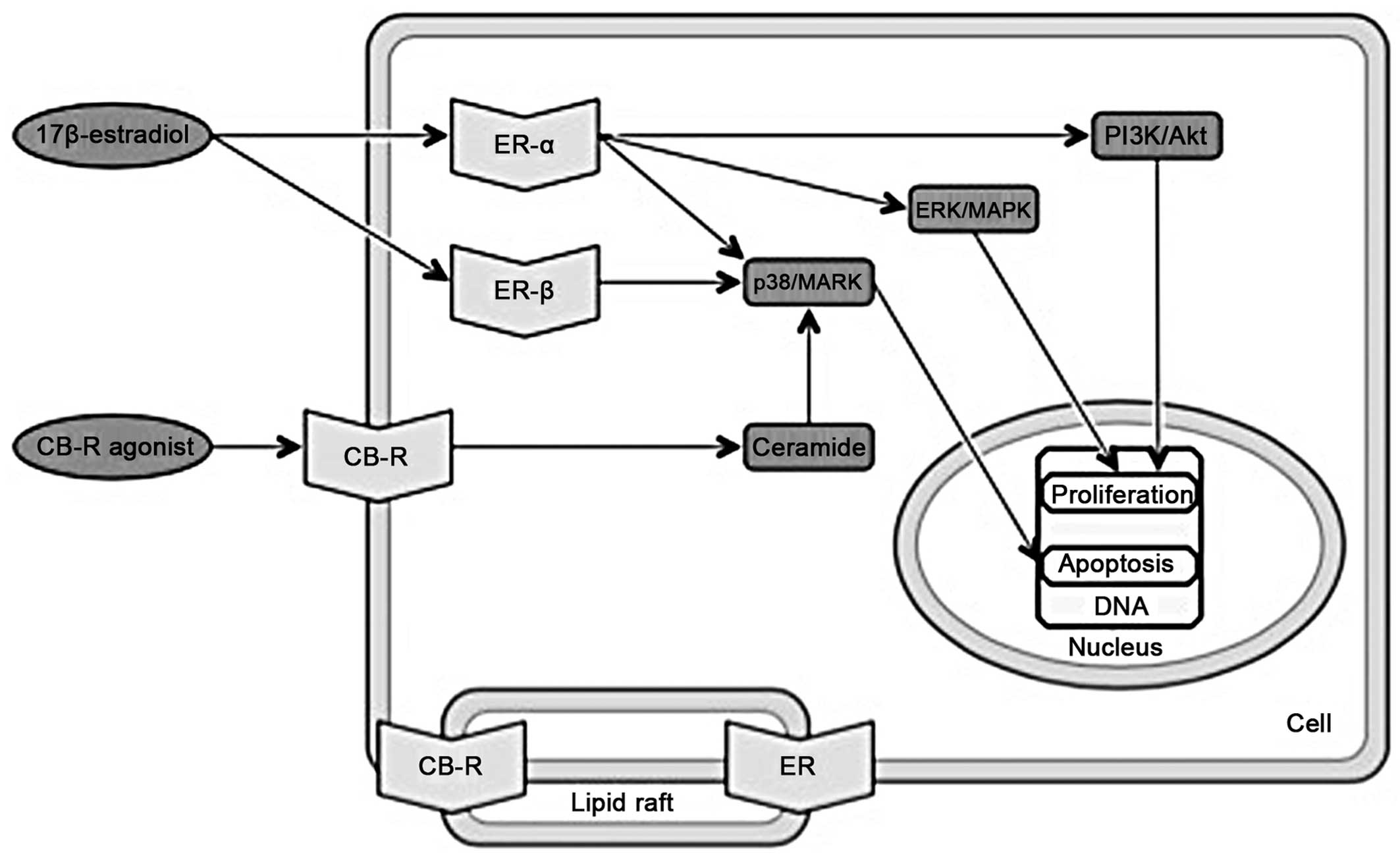
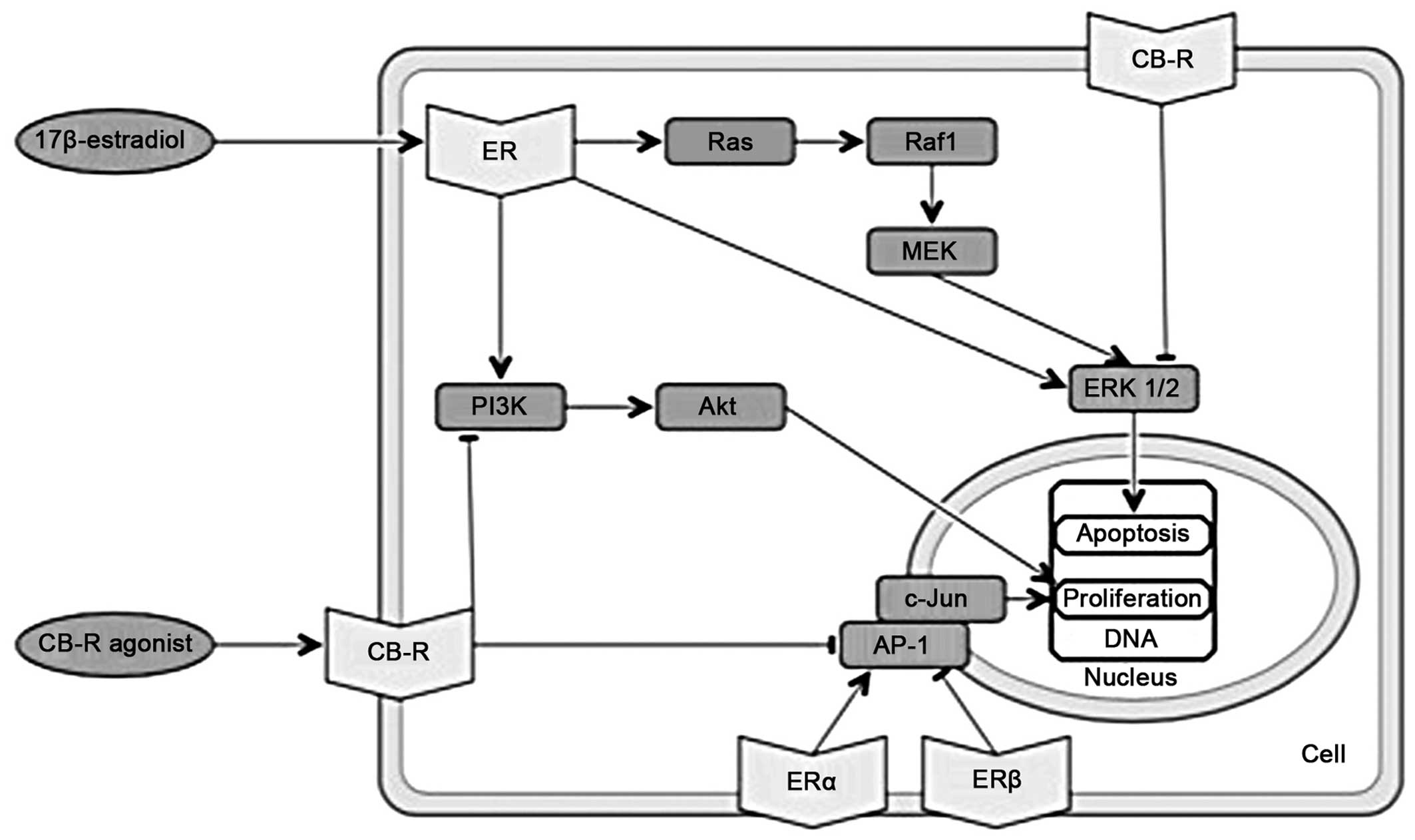
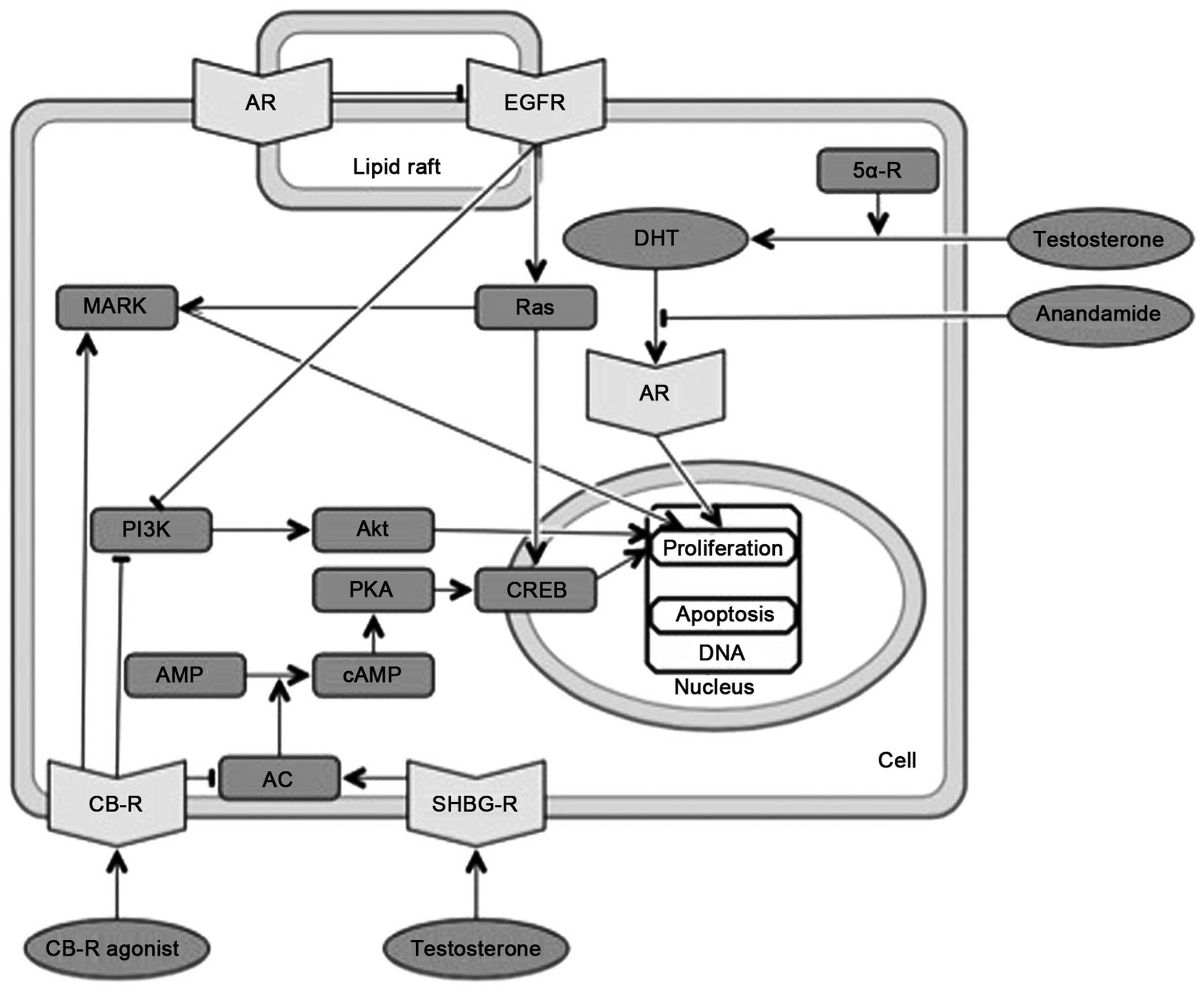
|
1
|
Han S, Thatte J, Buzard DJ and Jones RM:
Therapeutic utility of cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB(2))
selective agonists. J Med Chem. 56:8224–8256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ryberg E, Larsson N, Sjögren S, Hjorth S,
Hermansson NO, Leonova J, Elebring T, Nilsson K, Drmota T and
Greasley PJ: The orphan receptor GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid
receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 152:1092–1101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McHugh D, Hu SS, Rimmerman N, Juknat A,
Vogel Z, Walker JM and Bradshaw HB: N-arachidonoyl glycine, an
abundant endogenous lipid, potently drives directed cellular
migration through GPR18, the putative abnormal cannabidiol
receptor. BMC Neurosci. 11:442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown AJ: Novel cannabinoid receptors. Br
J Pharmacol. 152:567–575. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Starowicz K, Nigam S and Di Marzo V:
Biochemistry and pharmacology of endovanilloids. Pharmacol Ther.
114:13–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL, Scanlan
TS, Shiau AK, Uht RM and Webb P: Estrogen receptor pathways to
AP-1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 74:311–317. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hammes SR and Levin ER: Minireview: Recent
advances in extranuclear steroid receptor actions. Endocrinology.
152:4489–4495. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coleman KM and Smith CL: Intracellular
signaling pathways: Nongenomic actions of estrogens and
ligand-independent activation of estrogen receptors. Front Biosci.
6:D1379–D1391. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB and Sklar LA:
GPR30: A G protein-coupled receptor for estrogen. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 265–266:138–142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Paterni I, Granchi C, Katzenellenbogen JA
and Minutolo F: Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ):
Subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids.
90:13–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
John E: Hall: Guyton and Hall Textbook of
Medical Physiology. 12th edition. Saunders; pp. 991–992. 2010
|
|
12
|
Tyrey L: delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol
suppression of episodic luteinizing hormone secretion in the
ovariectomized rat. Endocrinology. 102:1808–1814. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tyrey L: delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: A
potent inhibitor of episodic luteinizing hormone secretion. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 213:306–308. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kumar MS and Chen CL: Effect of an acute
dose of delta 9-THC on hypothalamic luteinizing hormone releasing
hormone and met-enkephalin content and serum levels of testosterone
and corticosterone in rats. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse. 4:37–43.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scorticati C, Fernández-Solari J, De
Laurentiis A, Mohn C, Prestifilippo JP, Lasaga M, Seilicovich A,
Billi S, Franchi A, McCann SM, et al: The inhibitory effect of
anandamide on luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone secretion is
reversed by estrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11891–11896.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gammon CM, Freeman GM Jr, Xie W, Petersen
SL and Wetsel WC: Regulation of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
secretion by cannabinoids. Endocrinology. 146:4491–4499. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cravatt BF, Giang DK, Mayfield SP, Boger
DL, Lerner RA and Gilula NB: Molecular characterization of an
enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nature.
384:83–87. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
MacCarrone M, De Felici M, Bari M, Klinger
F, Siracusa G and Finazzi-Agrò A: Downregulation of anandamide
hydrolase in mouse uterus by sex hormones. Eur J Biochem.
267:2991–2997. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El-Talatini MR, Taylor AH and Konje JC:
The relationship between plasma levels of the endocannabinoid,
anandamide, sex steroids, and gonadotrophins during the menstrual
cycle. Fertil Steril. 93:1989–1996. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gorzalka BB and Dang SS: Minireview:
Endocannabinoids and gonadal hormones: bidirectional interactions
in physiology and behavior. Endocrinology. 153:1016–1024. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rossi F, Bellini G, Luongo L, Mancusi S,
Torella M, Tortora C, Manzo I, Guida F, Nobili B, de Novellis V and
Maione S: The 17-β-oestradiol inhibits osteoclast activity by
increasing the cannabinoid CB2 receptor expression. Pharmacol Res.
68:7–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Notarnicola M, Messa C, Orlando A, Bifulco
M, Laezza C, Gazzerro P and Caruso MG: Estrogenic induction of
cannabinoid CB1 receptor in human colon cancer cell lines. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 43:66–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Riebe CJ, Hill MN, Lee TT, Hillard CJ and
Gorzalka BB: Estrogenic regulation of limbic cannabinoid receptor
binding. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 35:1265–1269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar P and Song ZH: CB2 cannabinoid
receptor is a novel target for third-generation selective estrogen
receptor modulators bazedoxifene and lasofoxifene. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 443:144–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Prather PL, FrancisDevaraj F, Dates CR,
Greer AK, Bratton SM, Ford BM, Franks LN and Radominska-Pandya A:
CB1 and CB2 receptors are novel molecular targets for Tamoxifen and
4OH-Tamoxifen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:339–343. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Melck D, Rueda D, Galve-Roperh I, De
Petrocellis L, Guzmán M and Di Marzo V: Involvement of the
cAMP/protein kinase A pathway and of mitogen-activated protein
kinase in the anti-proliferative effects of anandamide in human
breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 463:235–240. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gu Q and Moss RL: 17 beta-Estradiol
potentiates kainate-induced currents via activation of the cAMP
cascade. J Neurosci. 16:3620–3629. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Picotto G, Massheimer V and Boland R:
Acute stimulation of intestinal cell calcium influx induced by 17
beta-estradiol via the cAMP messenger system. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
119:129–134. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Watters JJ and Dorsa DM: Transcriptional
effects of estrogen on neuronal neurotensin gene expression involve
cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent signaling mechanisms. J Neurosci.
18:6672–6680. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szego CM and Davis JS: Adenosine
3′,5′-monophosphate in rat uterus: Acute elevation by estrogen.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 58:1711–1718. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mimeault M, Pommery N, Wattez N, Bailly C
and Hénichart JP: Anti-fn of epidermal growth factor receptor
downregulation and ceramide production. Prostate. 56:1–12. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Preet A, Qamri Z, Nasser MW, Prasad A,
Shilo K, Zou X, Groopman JE and Ganju RK: Cannabinoid receptors,
CB1 and CB2, as novel targets for inhibition of non-small cell lung
cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:65–75.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Driggers PH and Segars JH: Estrogen action
and cytoplasmic signaling pathways. Part II: The role of growth
factors and phosphorylation in estrogen signaling. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 13:422–427. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O'Lone R, Frith MC, Karlsson EK and Hansen
U: Genomic targets of nuclear estrogen receptors. Mol Endocrinol.
18:1859–1875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marino M, Galluzzo P and Ascenzi P:
Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription.
Curr Genomics. 7:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bosier B, Hermans E and Lambert D:
Differential modulation of AP-1- and CRE-driven transcription by
cannabinoid agonists emphasizes functional selectivity at the CB1
receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 155:24–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Melck D, De Petrocellis L, Orlando P,
Bisogno T, Laezza C, Bifulco M and Di Marzo V: Suppression of nerve
growth factor Trk receptors and prolactin receptors by
endocannabinoids leads to inhibition of human breast and prostate
cancer cell proliferation. Endocrinology. 141:118–126. 2000.
|
|
38
|
Watters JJ, Chun TY, Kim YN, Bertics PJ
and Gorski J: Estrogen modulation of prolactin gene expression
requires an intact mitogen-activated protein kinase signal
transduction pathway in cultured rat pituitary cells. Mol
Endocrinol. 14:1872–1881. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Portella G, Laezza C, Laccetti P, De
Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V and Bifulco M: Inhibitory effects of
cannabinoid CB1 receptor stimulation on tumor growth and metastatic
spreading: Actions on signals involved in angiogenesis and
metastasis. FASEB J. 17:1771–1773. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blázquez C, González-Feria L, Alvarez L,
Haro A, Casanova ML and Guzmán M: Cannabinoids inhibit the vascular
endothelial growth factor pathway in gliomas. Cancer Res.
64:5617–5623. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mueller MD, Vigne JL, Minchenko A, Lebovic
DI, Leitman DC and Taylor RN: Regulation of vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) gene transcription by estrogen receptors alpha
and beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:10972–10977. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stoner M, Wang F, Wormke M, Nguyen T,
Samudio I, Vyhlidal C, Marme D, Finkenzeller G and Safe S:
Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
HEC1A endometrial cancer cells through interactions of estrogen
receptor alpha and Sp3 proteins. J Biol Chem. 275:22769–22779.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Galve-Roperh I, Sánchez C, Cortés ML,
Gómez del Pulgar T, Izquierdo M and Guzmán M: Anti-tumoral action
of cannabinoids: Involvement of sustained ceramide accumulation and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Nat Med.
6:313–319. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Klinge CM, Blankenship KA, Risinger KE,
Bhatnagar S, Noisin EL, Sumanasekera WK, Zhao L, Brey DM and
Keynton RS: Resveratrol and estradiol rapidly activate MAPK
signaling through estrogen receptors alpha and beta in endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 280:7460–7468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Acconcia F, Totta P, Ogawa S, Cardillo I,
Inoue S, Leone S, Trentalance A, Muramatsu M and Marino M: Survival
versus apoptotic 17beta-estradiol effect: Role of ER alpha and ER
beta activated non-genomic signaling. J Cell Physiol. 203:193–201.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kahlert S, Nuedling S, van Eickels M,
Vetter H, Meyer R and Grohe C: Estrogen receptor alpha rapidly
activates the IGF-1 receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 275:18447–18453.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pertwee RG, Howlett AC, Abood ME,
Alexander SP, Di Marzo V, Elphick MR, Greasley PJ, Hansen HS, Kunos
G, Mackie K, et al: International Union of Basic and Clinical
Pharmacology. LXXIX Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond
CB1 and CB2. Pharmacol Rev. 62:588–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ramer R, Weinzierl U, Schwind B, Brune K
and Hinz B: Ceramide is involved in r(+)-methanandamide-induced
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human neuroglioma cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 64:1189–1198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pisanti S, Picardi P, D'Alessandro A,
Laezza C and Bifulco M: The endocannabinoid signaling system in
cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 34:273–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ellert-Miklaszewska A, Kaminska B and
Konarska L: Cannabinoids downregulate PI3K/Akt and Erk signalling
pathways and activate proapoptotic function of Bad protein. Cell
Signal. 17:25–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Haynes MP, Li L, Sinha D, Russell KS,
Hisamoto K, Baron R, Collinge M, Sessa WC and Bender JR: Src kinase
mediates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent rapid
endothelial nitric-oxide synthase activation by estrogen. J Biol
Chem. 278:2118–2123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Marino M, Acconcia F and Trentalance A:
Biphasic estradiol-induced AKT phosphorylation is modulated by PTEN
via MAP kinase in HepG2 cells. Mol Biol Cell. 14:2583–2591. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gaub MP, Bellard M, Scheuer I, Chambon P
and Sassone-Corsi P: Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the
estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell. 63:1267–1276.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Paech K, Webb P, Kuiper GG, Nilsson S,
Gustafsson J, Kushner PJ and Scanlan TS: Differential ligand
activation of estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta at AP1 sites.
Science. 277:1508–1510. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kousteni S, Han L, Chen JR, Almeida M,
Plotkin LI, Bellido T and Manolagas SC: Kinase-mediated regulation
of common transcription factors accounts for the bone-protective
effects of sex steroids. J Clin Invest. 111:1651–1664. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sarfaraz S, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Malik A and
Mukhtar H: Cannabinoid receptor agonist-induced apoptosis of human
prostate cancer cells LNCaP proceeds through sustained activation
of ERK1/2 leading to G1 cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem.
281:39480–39491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cianchi F, Papucci L, Schiavone N, Lulli
M, Magnelli L, Vinci MC, Messerini L, Manera C, Ronconi E,
Romagnani P, et al: Cannabinoid receptor activation induces
apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated ceramide de
novo synthesis in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:7691–7700. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Guo Y, Wang H, Okamoto Y, Ueda N, Kingsley
PJ, Marnett LJ, Schmid HH, Das SK and Dey SK:
N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D is an
important determinant of uterine anandamide levels during
implantation. J Biol Chem. 280:23429–23432. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tsuboi K, Okamoto Y, Ikematsu N, Inoue M,
Shimizu Y, Uyama T, Wang J, Deutsch DG, Burns MP, Ulloa NM, et al:
Enzymatic formation of N-acylethanolamines from N-acylethanolamine
plasmalogen through N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing
phospholipase D-dependent and -independent pathways. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1811:565–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Urquhart P, Nicolaou A and Woodward DF:
Endocannabinoids and their oxygenation by cyclo-oxygenases,
lipoxygenases and other oxygenases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1851:366–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Tamura M, Deb S, Sebastian S, Okamura K
and Bulun SE: Estrogen up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 via estrogen
receptor in human uterine microvascular endothelial cells. Fertil
Steril. 81:1351–1356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Higa GM and Fell RG: Sex hormone receptor
repertoire in breast cancer. Int J Breast Cancer. 2013:2840362013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Caffarel MM, Sarrió D, Palacios J, Guzmán
M and Sánchez C: Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits cell cycle
progression in human breast cancer cells through Cdc2 regulation.
Cancer Res. 66:6615–6621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shrivastava A, Kuzontkoski PM, Groopman JE
and Prasad A: Cannabidiol induces programmed cell death in breast
cancer cells by coordinating the cross-talk between apoptosis and
autophagy. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1161–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Murase R, Kawamura R, Singer E, Pakdel A,
Sarma P, Judkins J, Elwakeel E, Dayal S, Martinez-Martinez E, Amere
M, et al: Targeting multiple cannabinoid anti-tumour pathways with
a resorcinol derivative leads to inhibition of advanced stages of
breast cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 171:4464–4477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Qamri Z, Preet A, Nasser MW, Bass CE,
Leone G, Barsky SH and Ganju RK: Synthetic cannabinoid receptor
agonists inhibit tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 8:3117–3129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
McKallip RJ, Nagarkatti M and Nagarkatti
PS: Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances breast cancer growth and
metastasis by suppression of the antitumor immune response. J
Immunol. 174:3281–3289. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
SGO Clinical Practice Endometrial Cancer
Working Group; Burke WM, Orr J, Leitao M, Salom E, Gehrig P,
Olawaiye AB, Brewer M, Boruta D, Villella J, Herzog T and Abu
Shahin F; Society of Gynecologic Oncology Clinical Practice
Committee: Endometrial cancer: A review and current management
strategies: part I. Gynecol Oncol. 134:385–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tangen IL, Werner HM, Berg A, Halle MK,
Kusonmano K, Trovik J, Hoivik EA, Mills GB, Krakstad C and Salvesen
HB: Loss of progesterone receptor links to high proliferation and
increases from primary to metastatic endometrial cancer lesions.
Eur J Cancer. 50:3003–3010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ayakannu A, Taylor AH, Marczylo TH,
Willets JM, Brown L, Davies Q, Moss E and Konje JC: Association of
cannabinoid receptor expression with anandamide concentrations in
endometrial cancer. Lancet Volume. 383:S232014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Guida M, Ligresti A, De Filippis D,
D'Amico A, Petrosino S, Cipriano M, Bifulco G, Simonetti S, Orlando
P, Insabato L, et al: The levels of the endocannabinoid receptor
CB2 and its ligand 2-arachidonoylglycerol are elevated in
endometrial carcinoma. Endocrinology. 151:921–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Raisz LG: Pathogenesis of osteoporosis:
Concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 115:3318–3325.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Centrella M and McCarthy TL: Estrogen
receptor dependent gene expression by osteoblasts - direct,
indirect, circumspect, and speculative effects. Steroids.
77:174–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Bilezikian JP, Raisz LG and Martin TJ:
Principles of Bone Biology. 3rd edition. Elsevier; Amsterdam: pp.
855–885. 2008
|
|
76
|
Bradford PG, Gerace KV, Roland RL and
Chrzan BG: Estrogen regulation of apoptosis in osteoblasts. Physiol
Behav. 99:181–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
77
|
Ofek O, Karsak M, Leclerc N, Fogel M,
Frenkel B, Wright K, Tam J, Attar-Namdar M, Kram V, Shohami E, et
al: Peripheral cannabinoid receptor, CB2, regulates bone mass. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:696–701. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hanus L, Breuer A, Tchilibon S, Shiloah S,
Goldenberg D, Horowitz M, Pertwee RG, Ross RA, Mechoulam R and
Fride E: HU-308: A specific agonist for CB(2), a peripheral
cannabinoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:14228–14233. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hojnik M, Dobovišek L, Knez Ž and Ferk P:
A synergistic interaction of 17-β-estradiol with specific
cannabinoid receptor type 2 antagonist/inverse agonist on
proliferation activity in primary human osteoblasts. Biomed Rep.
3:554–558. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Steffens S, Veillard NR, Arnaud C, Pelli
G, Burger F, Staub C, Karsak M, Zimmer A, Frossard JL and Mach F:
Low dose oral cannabinoid therapy reduces progression of
atherosclerosis in mice. Nature. 434:782–786. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Paganini-Hill A, Dworsky R and Krauss RM:
Hormone replacement therapy, hormone levels, and lipoprotein
cholesterol concentrations in elderly women. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
174:897–902. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Boosani CS and Sudhakar YA:
Proteolytically derived endogenous angioinhibitors originating from
the extracellular matrix. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 4:1551–1577.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Deroo BJ and Korach KS: Estrogen receptors
and human disease. J Clin Invest. 116:561–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Murphy E: Estrogen signaling and
cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 109:687–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Dol-Gleizes F, Paumelle R, Visentin V,
Marés AM, Desitter P, Hennuyer N, Gilde A, Staels B, Schaeffer P
and Bono F: Rimonabant, a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor
antagonist, inhibits atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:12–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Pacher P: Cannabinoid CB1 receptor
antagonists for atherosclerosis and cardiometabolic disorders: New
hopes, old concerns? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:7–9. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
87
|
Mach F, Montecucco F and Steffens S:
Cannabinoid receptors in acute and chronic complications of
atherosclerosis. Br J Pharmacol. 153:290–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Chiurchiù V, Lanuti M, Catanzaro G, Fezza
F, Rapino C and Maccarrone M: Detailed characterization of the
endocannabinoid system in human macrophages and foam cells, and
anti-inflammatory role of type-2 cannabinoid receptor.
Atherosclerosis. 233:55–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Collot-Teixeira S, Martin J, McDermott-Roe
C, Poston R and McGregor JL: CD36 and macrophages in
atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res. 75:468–477. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Heinlein CA and Chang C: The roles of
androgen receptors and androgen-binding proteins in nongenomic
androgen actions. Mol Endocrinol. 16:2181–2187. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Michels G and Hoppe UC: Rapid actions of
androgens. Front Neuroendocrinol. 29:182–198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Cohen S: The 94-day cannabis study. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 282:211–220. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Block RI, Farinpour R and Schlechte JA:
Effects of chronic marijuana use on testosterone, luteinizing
hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, prolactin and cortisol in
men and women. Drug Alcohol Depend. 28:121–128. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Dalterio S, Bartke A and Burstein S:
Cannabinoids inhibit testosterone secretion by mouse testes in
vitro. Science. 196:1472–1473. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dixit VP, Sharma VN and Lohiya NK: The
effect of chronically administered cannabis extract on the
testicular function of mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 26:111–114. 1974.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Ghosh SP, Chatterjee TK and Ghosh JJ:
Antiandrogenic effect of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in adult
castrated rats. J Reprod Fertil. 62:513–517. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Dixit VP, Gupta CL and Agrawal M:
Testicular degeneration and necrosis induced by chronic
administration of cannabis extract in dogs. Endokrinologie.
69:299–305. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M,
de Falco A, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Barone MV, Ametrano D, Zannini
MS, Abbondanza C and Auricchio F: Steroid-induced androgen
receptor-oestradiol receptor beta-Src complex triggers prostate
cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 19:5406–5417. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Unni E, Sun S, Nan B, McPhaul MJ, Cheskis
B, Mancini MA and Marcelli M: Changes in androgen receptor
nongenotropic signaling correlate with transition of LNCaP cells to
androgen independence. Cancer Res. 64:7156–7168. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Li J and Al-Azzawi F: Mechanism of
androgen receptor action. Maturitas. 63:142–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Taichman RS, Loberg RD, Mehra R and Pienta
KJ: The evolving biology and treatment of prostate cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:2351–2361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bonaccorsi L, Nosi D, Quercioli F,
Formigli L, Zecchi S, Maggi M, Forti G and Baldi E: Prostate
cancer: A model of integration of genomic and non-genomic effects
of the androgen receptor in cell lines model. Steroids.
73:1030–1037. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bonaccorsi L, Nosi D, Muratori M, Formigli
L, Forti G and Baldi E: Altered endocytosis of epidermal growth
factor receptor in androgen receptor positive prostate cancer cell
lines. J Mol Endocrinol. 38:51–66. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Purohit V, Ahluwahlia BS and Vigersky RA:
Marihuana inhibits dihydrotestosterone binding to the androgen
receptor. Endocrinology. 107:848–850. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Grech A, Breck J and Heidelbaugh J:
Adverse effects of testosterone replacement therapy: An update on
the evidence and controversy. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 5:190–200. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ahmed A, Ali S and Sarkar FH: Advances in
androgen receptor targeted therapy for prostate cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 229:271–276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Morales P, Vara D, Goméz-Cañas M, Zúñiga
MC, Olea-Azar C, Goya P, Fernández-Ruiz J, Díaz-Laviada I and
Jagerovic N: Synthetic cannabinoid quinones: Preparation, in vitro
antiproliferative effects and in vivo prostate antitumor activity.
Eur J Med Chem. 70:111–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
De Petrocellis L, Ligresti A, Schiano
Moriello A, Iappelli M, Verde R, Stott CG, Cristino L, Orlando P
and Di Marzo V: Non-THC cannabinoids inhibit prostate carcinoma
growth in vitro and in vivo: Pro-apoptotic effects and underlying
mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 168:79–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|