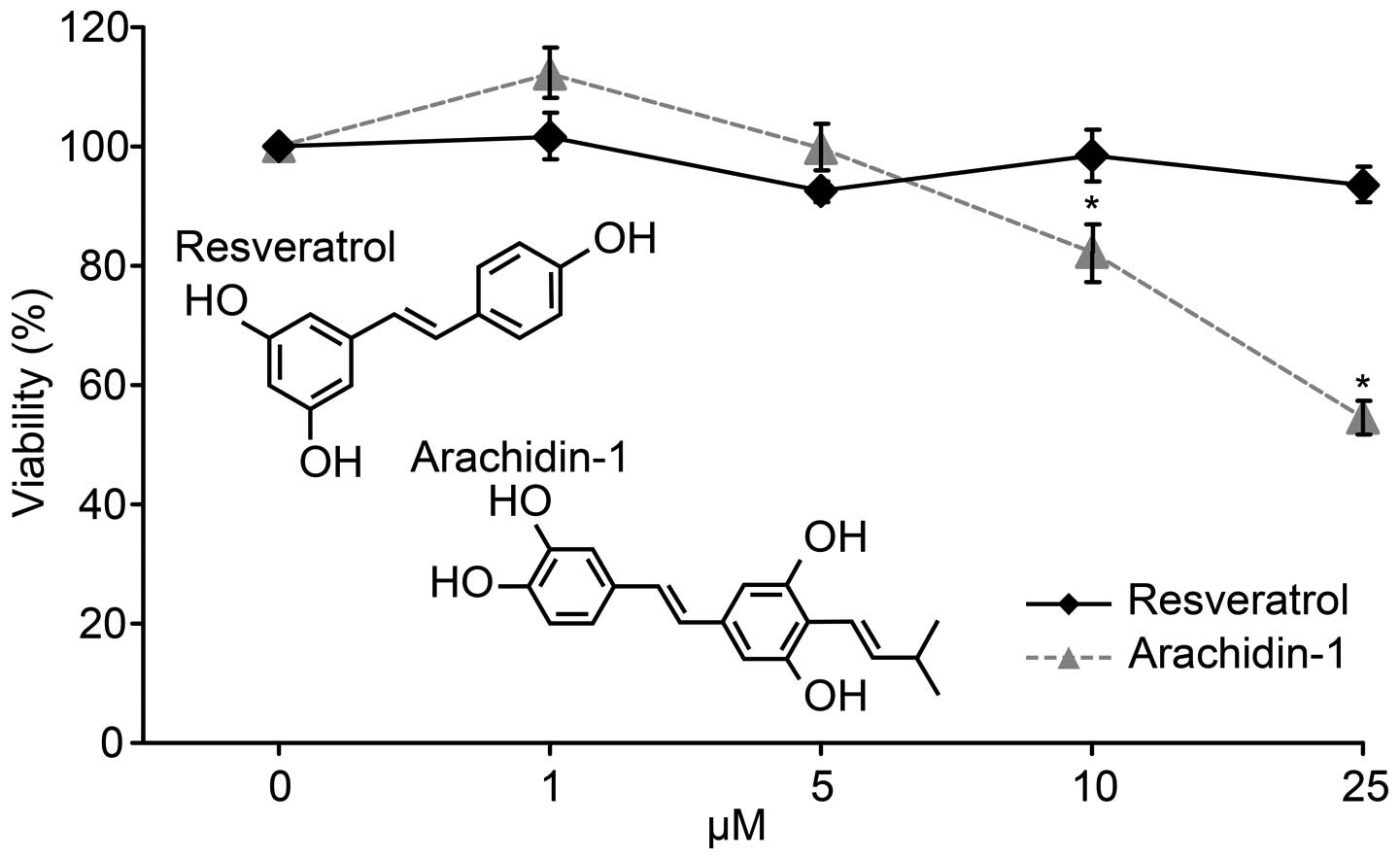
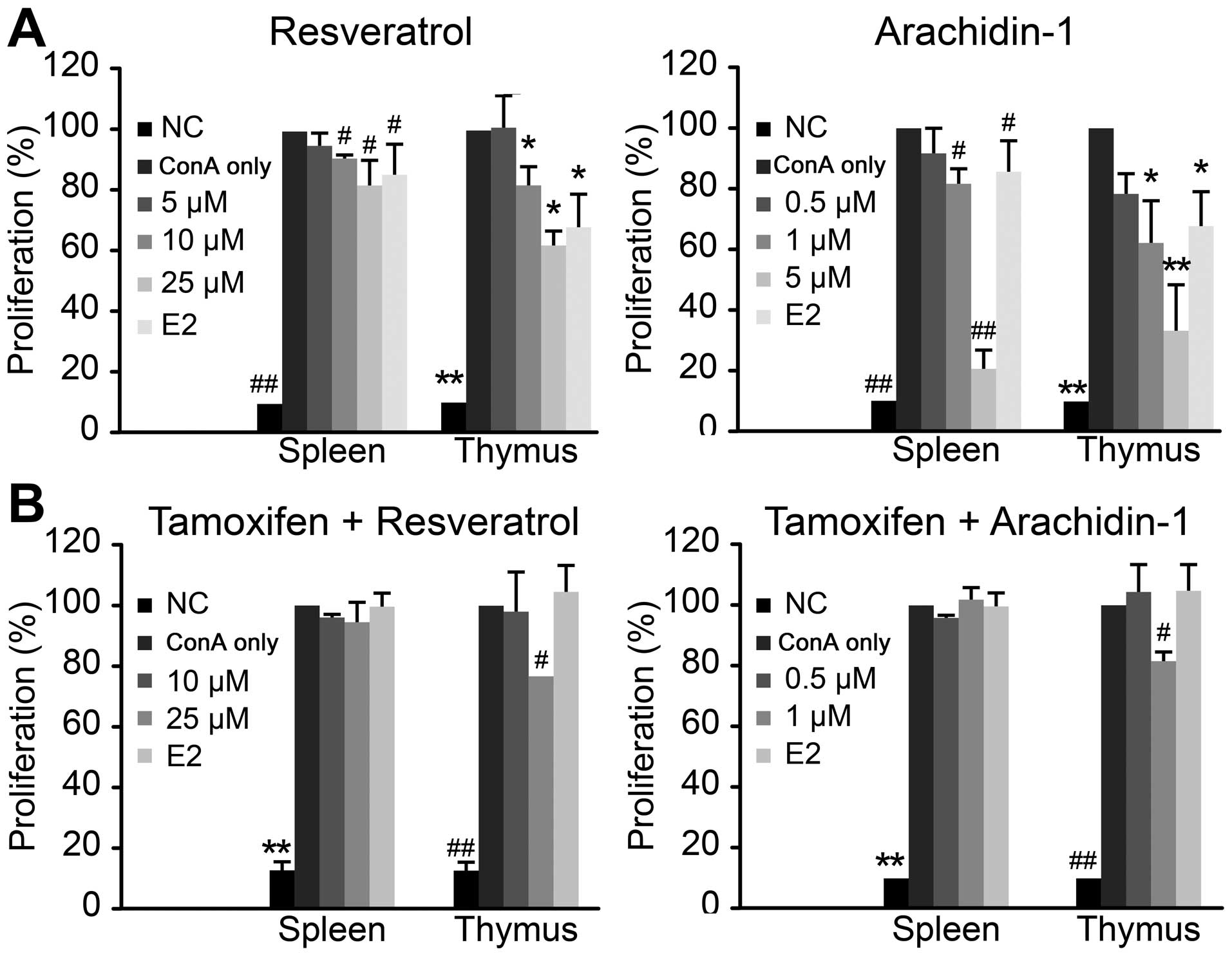
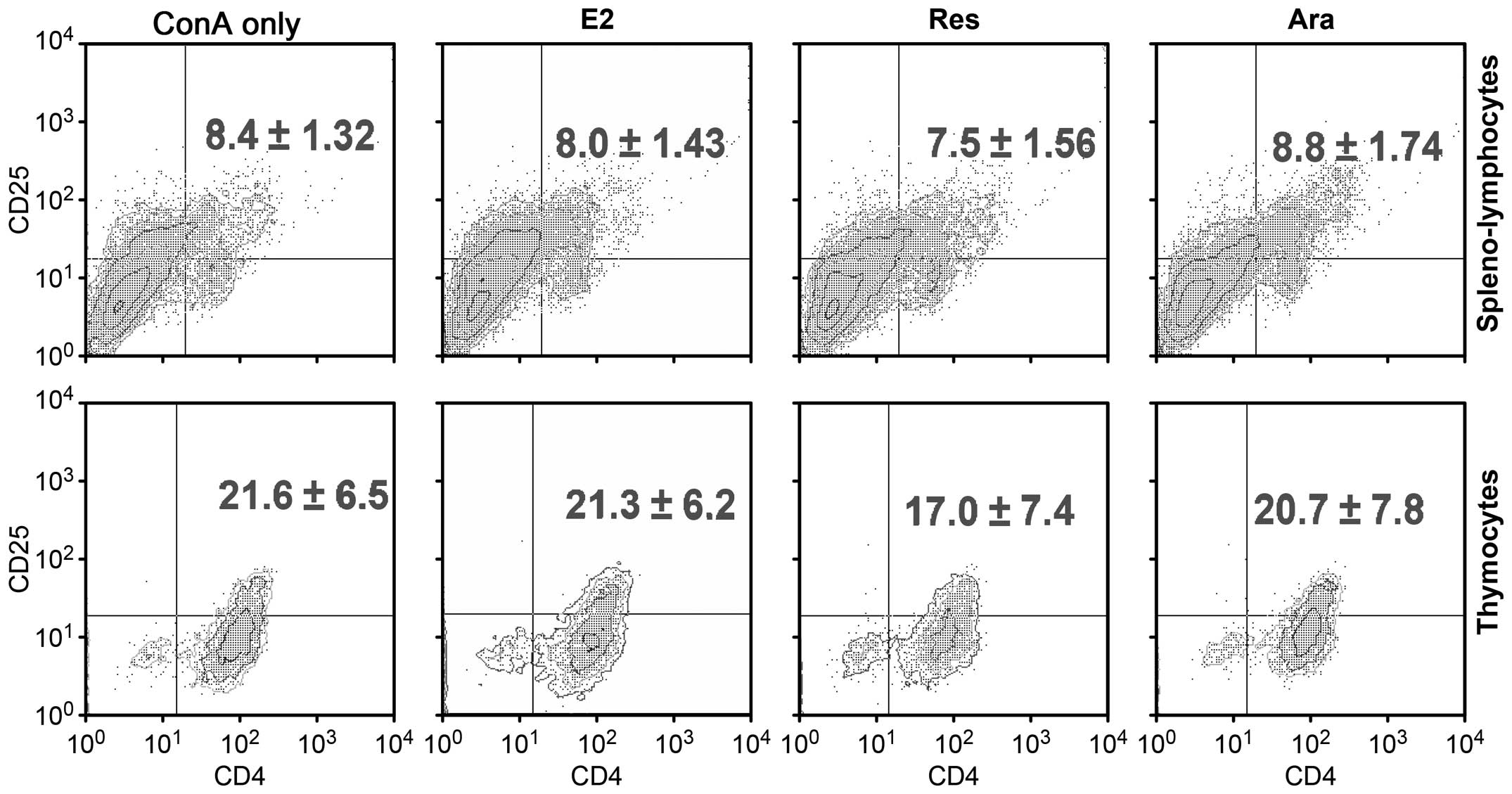
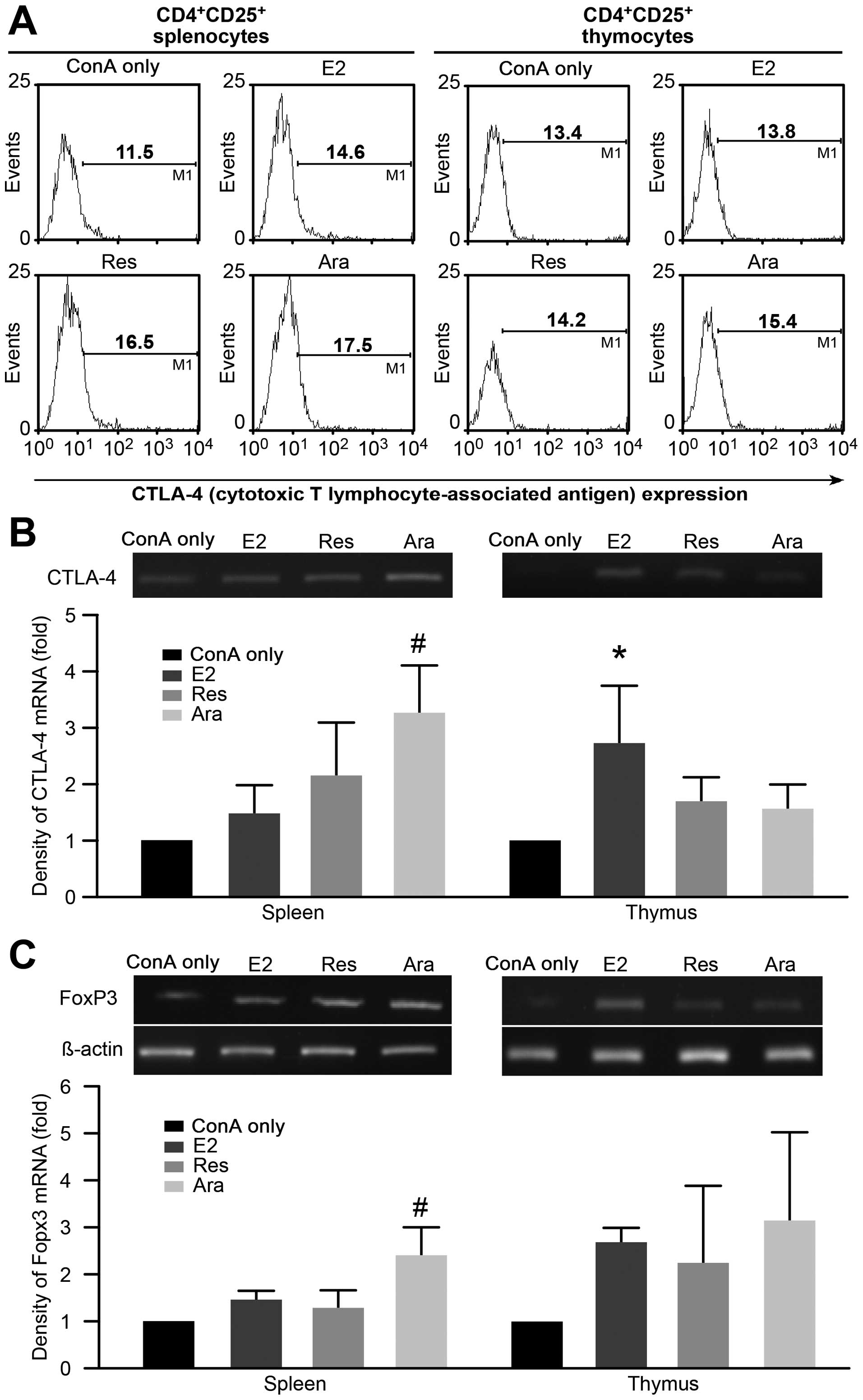
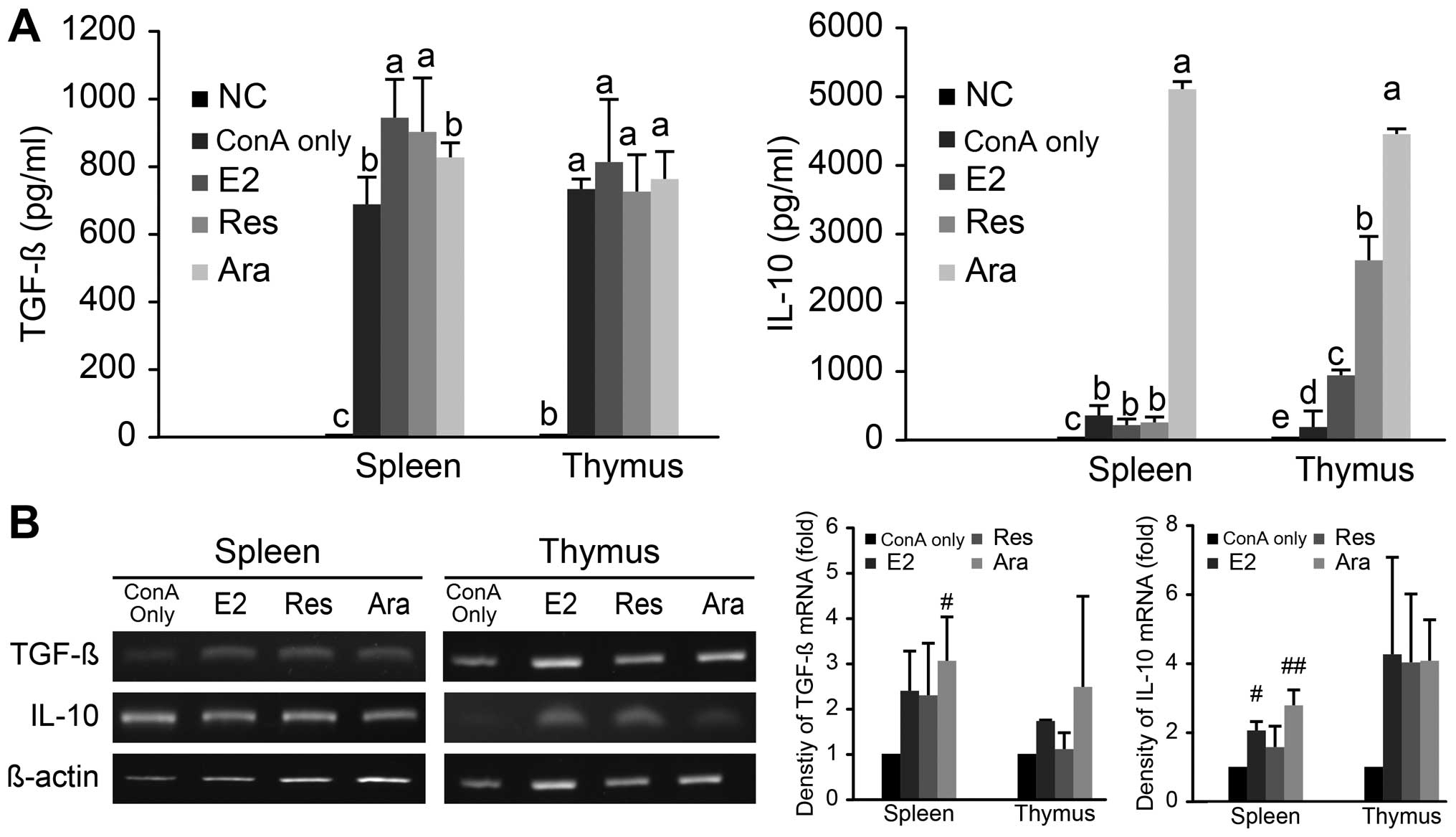
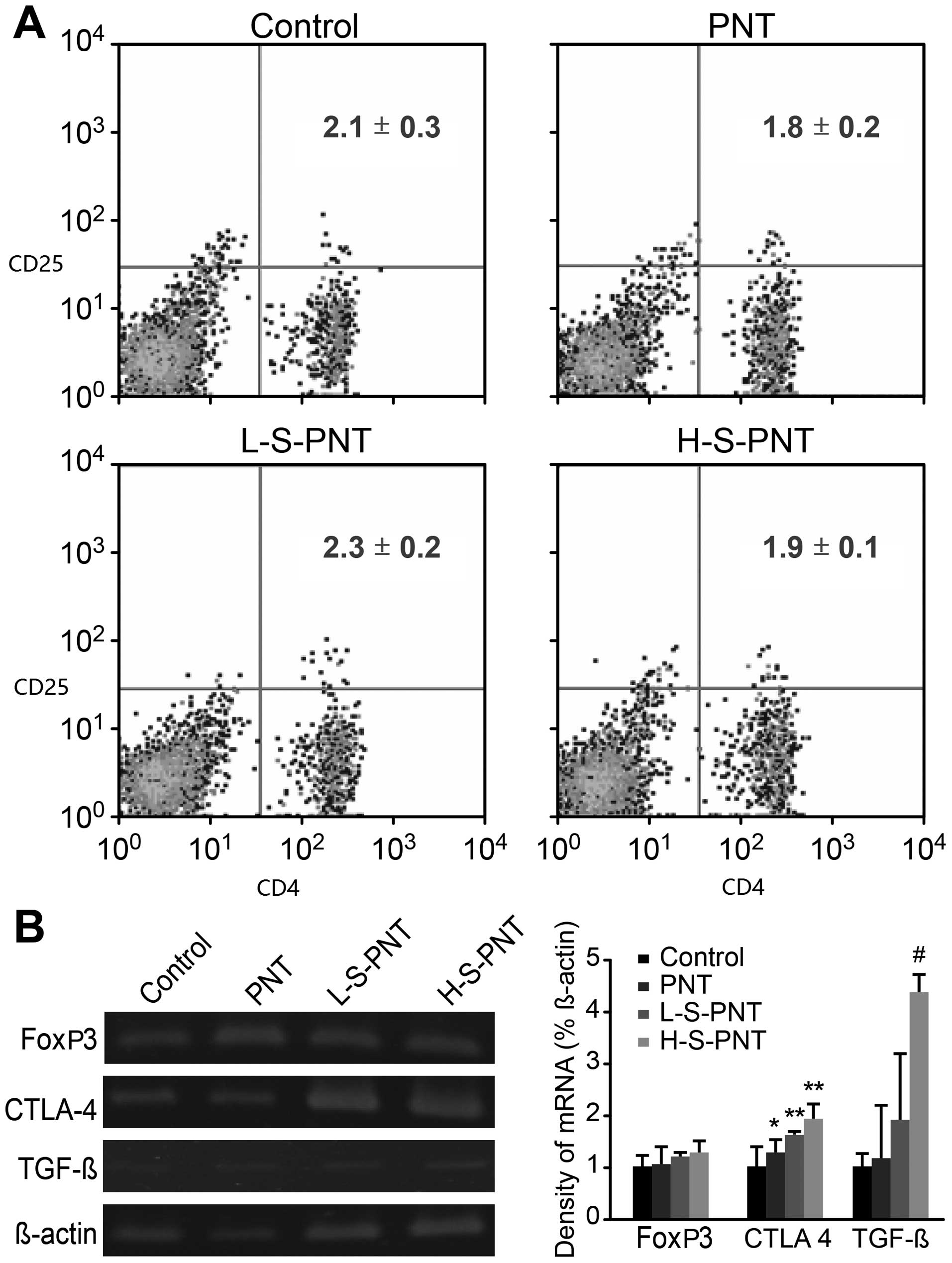
|
1
|
Gregg R, Smith CM, Clark FJ, Dunnion D,
Khan N, Chakraverty R, Nayak L and Moss PA: The number of human
peripheral blood CD4+ CD25high regulatory T
cells increases with age. Clin Exp Immunol. 140:540–546. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao L, Sun L, Wang H, Ma H, Liu G and
Zhao Y: Changes of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells in aged Balb/c mice. J Leukoc Biol.
81:1386–1394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma S, Dominguez AL and Lustgarten J:
High accumulation of T regulatory cells prevents the activation of
immune responses in aged animals. J Immunol. 177:8348–8355. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakaguchi S: Naturally arising
CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance
and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol.
22:531–562. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miyara M and Sakaguchi S: Natural
regulatory T cells: Mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol Med.
13:108–116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wan YY and Flavell RA: The roles for
cytokines in the generation and maintenance of regulatory T cells.
Immunol Rev. 212:114–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dario AA: Vignali, Lauren W. Collision,
and Creg J. Workman: How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:523–532. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hunt JS, Miller L, Roby KF, Huang J, Platt
JS and DeBrot BL: Female steroid hormones regulate production of
pro-inflammatory molecules in uterine leukocytes. J Reprod Immunol.
35:87–99. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lengi AJ, Phillips RA, Karpuzoglu E and
Ahmed SA: Estrogen selectively regulates chemokines in murine
splenocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 81:1065–1074. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pacifici R: Estrogen deficiency, T cells
and bone loss. Cell Immunol. 252:68–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cunningham M and Gilkeson G: Estrogen
receptors in immunity and autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol.
40:66–73. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bowers JL, Tyulmenkov VV, Jernigan SC and
Klinge CM: Resveratrol acts as a mixed agonist/antagonist for
estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Endocrinology. 141:3657–3667.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roupe KA, Remsberg CM, Yáñez JA and Davies
NM: Pharmacometrics of stilbenes: Seguing towards the clinic. Curr
Clin Pharmacol. 1:81–101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Michel T, Halabalaki M and Skaltsounis AL:
New concepts, experimental approaches, and dereplication strategies
for the discovery of novel phytoestrogens from natural sources.
Planta Med. 79:514–532. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiou RY: Review: Resveratrol, a promising
phytochemical in grapes, grape juices, wines and peanuts. Food Sci
Agric Chem. 4:8–14. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Wotton HR and Strange RN: Increased
susceptibility and reduced phytoalexin accumulation in
drought-stressed peanut kernels challenged with Aspergillus flavus.
Appl Environ Microbiol. 53:270–273. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang JC, Lai YH, Djoko B, Wu PL, Liu CD,
Liu YW and Chiou RY: Biosynthesis enhancement and antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory activities of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.)
arachidin-1, arachidin-3, and isopentadienylresveratrol. J Agric
Food Chem. 54:10281–10287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gehm BD, McAndrews JM, Chien PY and
Jameson JL: Resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound found in grapes
and wine, is an agonist for the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:14138–14143. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pozo-Guisado E, Lorenzo-Benayas MJ and
Fernández-Salguero PM: Resveratrol modulates the phosphoinositide
3-kinase pathway through an estrogen receptor alpha-dependent
mechanism: Relevance in cell proliferation. Int J Cancer.
109:167–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Djoko B, Chiou RYY, Shee JJ and Liu YW:
Characterization of immunological activities of peanut stilbenoids,
arachidin-1, piceatannol, and resveratrol on
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation of RAW 264.7 macrophages. J
Agric Food Chem. 55:2376–2383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao X, Xu YX, Janakiraman N, Chapman RA
and Gautam SC: Immunomodulatory activity of resveratrol:
Suppression of lymphocyte proliferation, development of
cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and cytokine production. Biochem
Pharmacol. 62:1299–1308. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weng BB, Lin YC, Hu CW, Kao MY, Wang SH,
Lo DY, Lai TY, Kan LS and Chiou RYY: Toxicological and
immunomodulatory assessments of botryosphaeran (β-glucan) produced
by Botryosphaeria rhodina RCYU 30101. Food Chem Toxicol.
49:910–916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lin BS, Lien TF, Chao MR, Lai YH, Chang
JC, Chou SJ, Liao HF and Chiou RYY: Toxicological and nutraceutical
assessments of peanut sprouts as daily supplments to feed
Sprague-Dawley rats for 18 weeks. J Sci Food Agric. 88:2201–2207.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Huang CP, Au LC, Chiou RYY, Chung PC, Chen
SY, Tang WC, Chang CL, Fang WH and Lin SB: Arachidin-1, a peanut
stilbenoid, induces programmed cell death in human leukemia HL-60
cells. J Agric Food Chem. 58:12123–12129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pfeifer RW and Patterson RM: Modulation of
lectin-stimulated lymphocyte agglutination and mitogenesis by
estrogen metabolites: Effects on early events of lymphocyte
activation. Arch Toxicol. 58:157–164. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brown N, Nagarkatti M and Nagarkatti PS:
Diethylstilbestrol alters positive and negative selection of T
cells in the thymus and modulates T-cell repertoire in the
periphery. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 212:119–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L,
Kushner PJ, Agard DA and Greene GL: The structural basis of
estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of
this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 95:927–937. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Brandenberger AW, Tee MK, Lee JY, Chao V
and Jaffe RB: Tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha
(ER-alpha) and beta (ER-beta) mRNA in the midgestational human
fetus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:3509–3512. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Adori M, Kiss E, Barad Z, Barabás K,
Kiszely E, Schneider A, Kövesdi D, Sziksz E, Abrahám IM, Matkó J,
et al: Estrogen augments the T cell-dependent but not the
T-independent immune response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1661–1674.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arruvito L, Sanz M, Banham AH and Fainboim
L: Expansion of CD4+CD25+and
FOXP3+ regulatory T cells during the follicular phase of
the menstrual cycle: Implications for human reproduction. J
Immunol. 178:2572–2578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Walker LS: CD4+
CD25+ Treg: Divide and rule? Immunology. 111:129–137.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matejuk A, Dwyer J, Zamora A, Vandenbark
AA and Offner H: Evaluation of the effects of 17beta-estradiol
(17beta-e2) on gene expression in experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis using DNA microarray. Endocrinology. 143:313–319.
2002.
|
|
33
|
Mjösberg J, Svensson J, Johansson E,
Hellström L, Casas R, Jenmalm MC, Boij R, Matthiesen L, Jönsson JI,
Berg G and Ernerudh J: Systemic reduction of functionally
suppressive CD4dimCD25highFoxp3+
Tregs in human second trimester pregnancy is induced by
progesterone and 17beta-estradiol. J Immunol. 183:759–769. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sharma S, Chopra K, Kulkarni SK and
Agrewala JN: Resveratrol and curcumin suppress immune response
through CD28/CTLA-4 and CD80 co-stimulatory pathway. Clin Exp
Immunol. 147:155–163. 2007.
|
|
35
|
Polanczyk MJ, Carson BD, Subramanian S,
Afentoulis M, Vandenbark AA, Ziegler SF and Offner H: Cutting edge:
Estrogen drives expansion of the CD4+CD25+
regulatory T cell compartment. J Immunol. 173:2227–2230. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tai P, Wang J, Jin H, Song X, Yan J, Kang
Y, Zhao L, An X, Du X, Chen X, et al: Induction of regulatory T
cells by physiological level estrogen. J Cell Physiol. 214:456–464.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vignali DAA, Collison LW and Workman CJ:
How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:523–532. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mellor AL and Munn DH: IDO expression by
dendritic cells: Tolerance and tryptophan catabolism. Nat Rev
Immunol. 4:762–774. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baeza I, Alvarado C, Alvarez P, Salazar V,
Castillo C, Ariznavarreta C, Fdez-Tresguerres JA and De la Fuente
M: Improvement of leucocyte functions in ovariectomised aged rats
after treatment with growth hormone, melatonin, oestrogens or
phyto-oestrogens. J Reprod Immunol. 80:70–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang B, Sun J, Li X, Zhou Q, Bai J, Shi Y
and Le G: Resveratrol prevents suppression of regulatory T-cell
production, oxidative stress, and inflammation of mice prone or
resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity. Nutr Res. 33:971–981.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson
HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K,
et al: Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a
high-calorie diet. Nature. 444:337–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Austad S: Recent advances in vertebrate
aging research 2009. Aging Cell. 9:297–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|