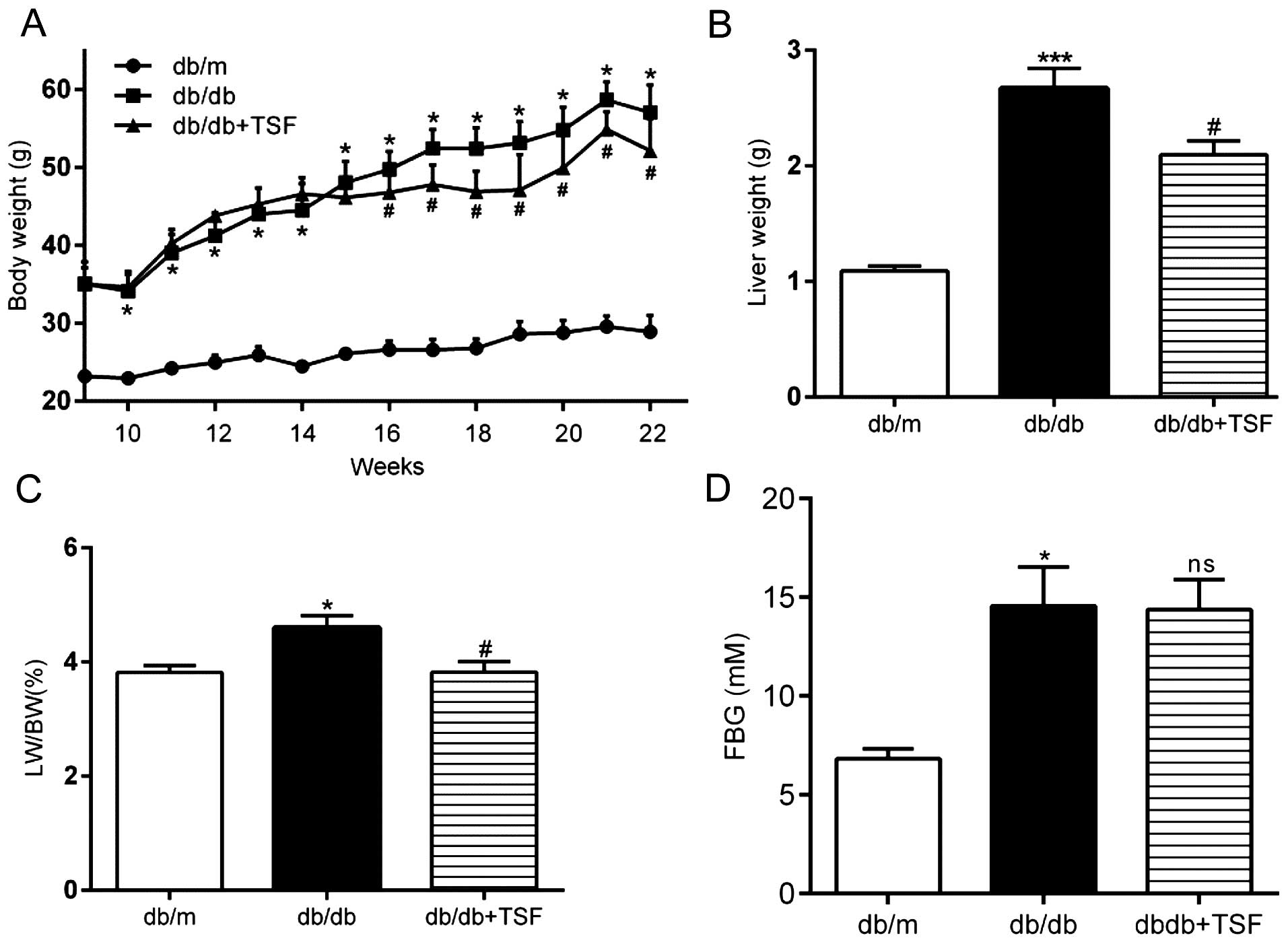
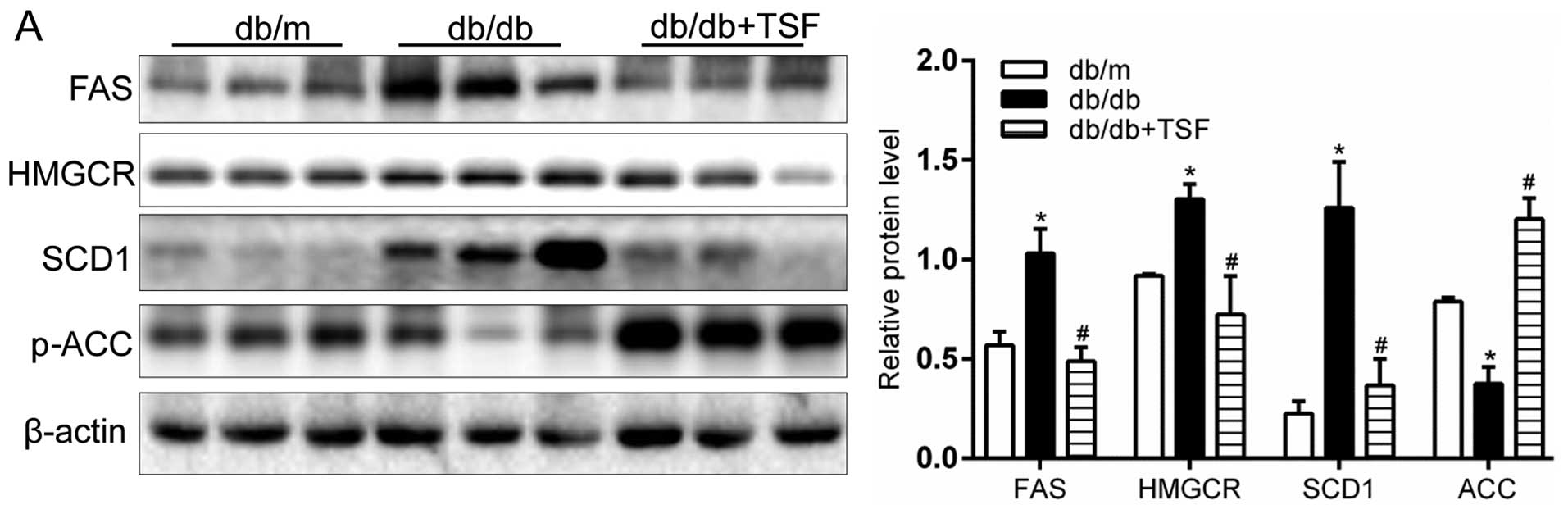
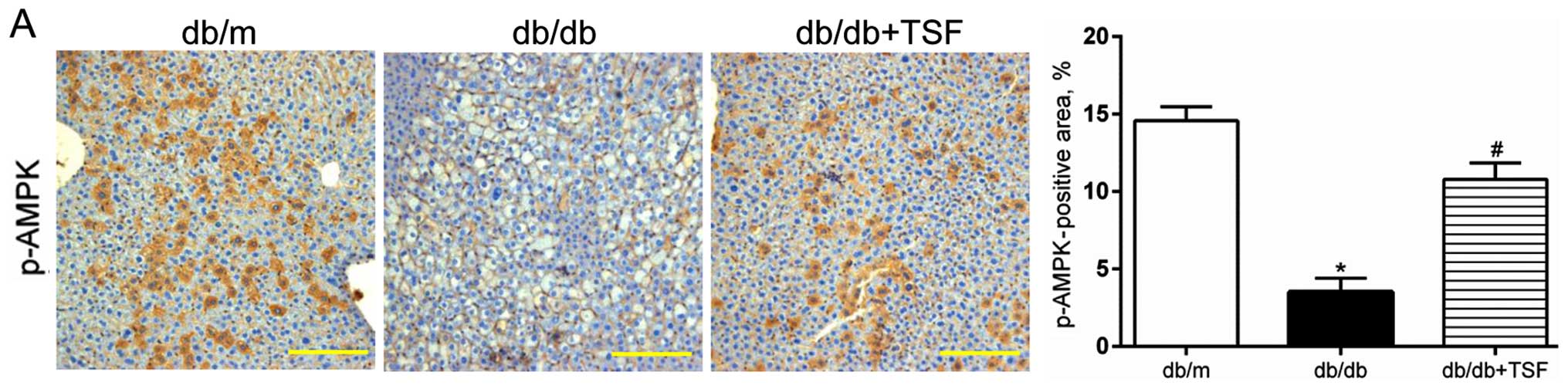
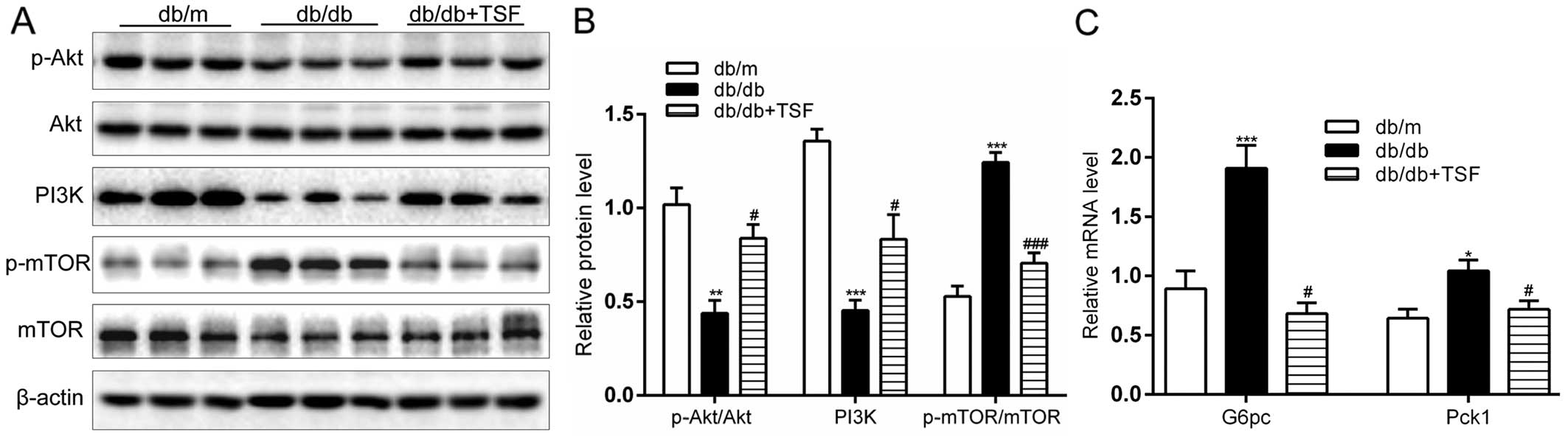
|
1
|
Smyth S and Heron A: Diabetes and obesity:
The twin epidemics. Nat Med. 12:75–80. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Loomba R and Sanyal AJ: The global NAFLD
epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:686–690. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ruderman NB, Carling D, Prentki M and
Cacicedo JM: AMPK, insulin resistance, and the metabolic syndrome.
J Clin Invest. 123:2764–2772. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fu L, Bruckbauer A, Li F, Cao Q, Cui X, Wu
R, Shi H, Zemel MB and Xue B: Interaction between metformin and
leucine in reducing hyperlipidemia and hepatic lipid accumulation
in diet-induced obese mice. Metabolism. 64:1426–1434. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lian Z, Li Y, Gao J, Qu K, Li J, Hao L, Wu
S and Zhu H: A novel AMPK activator, WS070117, improves lipid
metabolism discords in hamsters and HepG2 cells. Lipids Health Dis.
10:672011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JH, Jung JY, Jang EJ, Jegal KH, Moon
SY, Ku SK, Kang SH, Cho IJ, Park SJ, Lee JR, et al: Combination of
honokiol and magnolol inhibits hepatic steatosis through
AMPK-SREBP-1 c pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:508–518. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jeon TI and Osborne TF: SREBPs: Metabolic
integrators in physiology and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
23:65–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Han J, Li E, Chen L, Zhang Y, Wei F, Liu
J, Deng H and Wang Y: The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic
lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1. Nature. 524:243–246. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ponugoti B, Kim DH, Xiao Z, Smith Z, Miao
J, Zang M, Wu SY, Chiang CM, Veenstra TD and Kemper JK: SIRT1
deacetylates and inhibits SREBP-1C activity in regulation of
hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 285:33959–33970. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hou X, Xu S, Maitland-Toolan KA, Sato K,
Jiang B, Ido Y, Lan F, Walsh K, Wierzbicki M, Verbeuren TJ, et al:
SIRT1 regulates hepatocyte lipid metabolism through activating
AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 283:20015–20026. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Musso G, Gambino R and Cassader M:
Emerging molecular targets for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Annu Rev Med. 61:375–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Li P, Burczynski FJ, Gong Y, Choy
P, Sha H and Li J: Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy in Otsuka
Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats with a combination of
Chinese Herbs (Tangshen Formula). Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2011:6137372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang M, Z C, Liang QL, Li P, Li J, Wang
YM and Luo GA: Effect of Tangshen Formula on phospholipids
metabolism in diabetic nephropathy patients. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
46:780–786. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Tiniakos DG, Vos MB and Brunt EM:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathology and pathogenesis. Annu
Rev Pathol. 5:145–171. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li P, Chen Y, Liu J, Hong J, Deng Y, Yang
F, Jin X, Gao J, Li J, Fang H, et al: Efficacy and safety of
tangshen formula on patients with type 2 diabetic kidney disease: A
multicenter double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial.
PLoS One. 10:e01260272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M and Ahmad N: Dose
translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J.
22:659–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM,
Neuschwander-Tetri BA and Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A
proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:2467–2474. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun SF, Zhao TT, Zhang HJ, Huang XR, Zhang
WK, Zhang L, Yan MH, Dong X, Wang H, Wen YM, et al: Renoprotective
effect of berberine on type 2 diabetic nephropathy in rats. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 42:662–670. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Quan HY, Kim Y, Kim SJ, Jo HK, Kim GW and
Chung SH: Betulinic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver by
inhibiting SREBP1 activity via the AMPK-mTOR-SREBP signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1330–1340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Castaño D, Larequi E, Belza I, Astudillo
AM, Martínez-Ansó E, Balsinde J, Argemi J, Aragon T, Moreno-Aliaga
MJ, Muntane J, et al: Cardiotrophin-1 eliminates hepatic steatosis
in obese mice by mechanisms involving AMPK activation. J Hepatol.
60:1017–1025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jung EJ, Kwon SW, Jung BH, Oh SH and Lee
BH: Role of the AMPK/SREBP-1 pathway in the development of orotic
acid-induced fatty liver. J Lipid Res. 52:1617–1625. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X,
Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, et al: AMPK
phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic
steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant
mice. Cell Metab. 13:376–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Purushotham A, Schug TT, Xu Q, Surapureddi
S, Guo X and Li X: Hepatocyte-specific deletion of SIRT1 alters
fatty acid metabolism and results in hepatic steatosis and
inflammation. Cell Metab. 9:327–338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grefhorst A, Elzinga BM, Voshol PJ, Plösch
T, Kok T, Bloks VW, van der Sluijs FH, Havekes LM, Romijn JA,
Verkade HJ and Kuipers F: Stimulation of lipogenesis by
pharmacological activation of the liver X receptor leads to
production of large, triglyceride-rich very low density lipoprotein
particles. J Biol Chem. 277:34182–34190. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sim WC, Park S, Lee KY, Je YT, Yin HQ,
Choi YJ, Sung SH, Park SJ, Park HJ, Shin KJ and Lee BH: LXR-α
antagonist meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid attenuates high-fat
diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver. Biochem Pharmacol.
90:414–424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Foster DW: Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of
fatty acid synthesis and oxidation. J Clin Invest. 122:1958–1959.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Derdak Z, Villegas KA, Harb R, Wu AM,
Sousa A and Wands JR: Inhibition of p53 attenuates steatosis and
liver injury in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
J Hepatol. 58:785–791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Wang C, Hu L, Zhao L, Yang P, Moorhead JF,
Varghese Z, Chen Y and Ruan XZ: Inflammatory stress increases
hepatic CD36 translational efficiency via activation of the mTOR
signalling pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1030712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV,
Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro
JS, et al: SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial
effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab.
15:675–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Imai Y,
Shimozawa N, Hioki K, Uchida S, Ito Y, Takakuwa K, Matsui J, et al:
Globular adiponectin protected ob/ob mice from diabetes and
ApoE-deficient mice from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem.
278:2461–2468. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y,
Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, et al:
Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation
by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 8:1288–1295.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Pérez-Echarri N,
Marcos-Gómez B, Larequi E, Gil-Bea FJ, Viollet B, Gimenez I,
Martínez JA, Prieto J and Bustos M: Cardiotrophin-1 is a key
regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Cell Metab. 14:242–253.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McGarry JD, Mannaerts GP and Foster DW: A
possible role for malonyl-CoA in the regulation of hepatic fatty
acid oxidation and ketogenesis. J Clin Invest. 60:265–270. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang J, Zhang LN, Chen DM, Fu YY, Zhang
F, Yang LL, Xia CM, Jiang HW, Tang CL, Xie ZF, et al:
2-(3-Benzoylthioureido)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic
acid ameliorates metabolic disorders in high-fat diet-fed mice.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:483–496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lamming DW and Sabatini DM: A Central role
for mTOR in lipid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 18:465–469. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Soliman GA: The integral role of mTOR in
lipid metabolism. Cell Cycle. 10:861–862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yecies JL, Zhang HH, Menon S, Liu S,
Yecies D, Lipovsky AI, Gorgun C, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hotamisligil GS,
Lee CH and Manning BD: Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and
lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent
pathways. Cell Metab. 14:21–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Birkenfeld AL and Shulman GI: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease, hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2
diabetes. Hepatology. 59:713–723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ,
Jessurun J, Boldt MD and Parks EJ: Sources of fatty acids stored in
liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 115:1343–1351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koonen DP, Jacobs RL, Febbraio M, Young
ME, Soltys CL, Ong H, Vance DE and Dyck JR: Increased hepatic CD36
expression contributes to dyslipidemia associated with diet-induced
obesity. Diabetes. 56:2863–2871. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee GY, Kim NH, Zhao ZS, Cha BS and Kim
YS: Peroxisomal-proliferator-activated receptor alpha activates
transcription of the rat hepatic malonyl-CoA decarboxylase gene: A
key regulation of malonyl-CoA level. Biochem J. 378:983–990. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu LH, Wang A, Luo P, Wang X, Jiang DS,
Deng W, Zhang X, Wang T, Liu Y, Gao L, et al: Mindin/Spondin 2
inhibits hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and obesity via
interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α in
mice. J Hepatol. 60:1046–1054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|