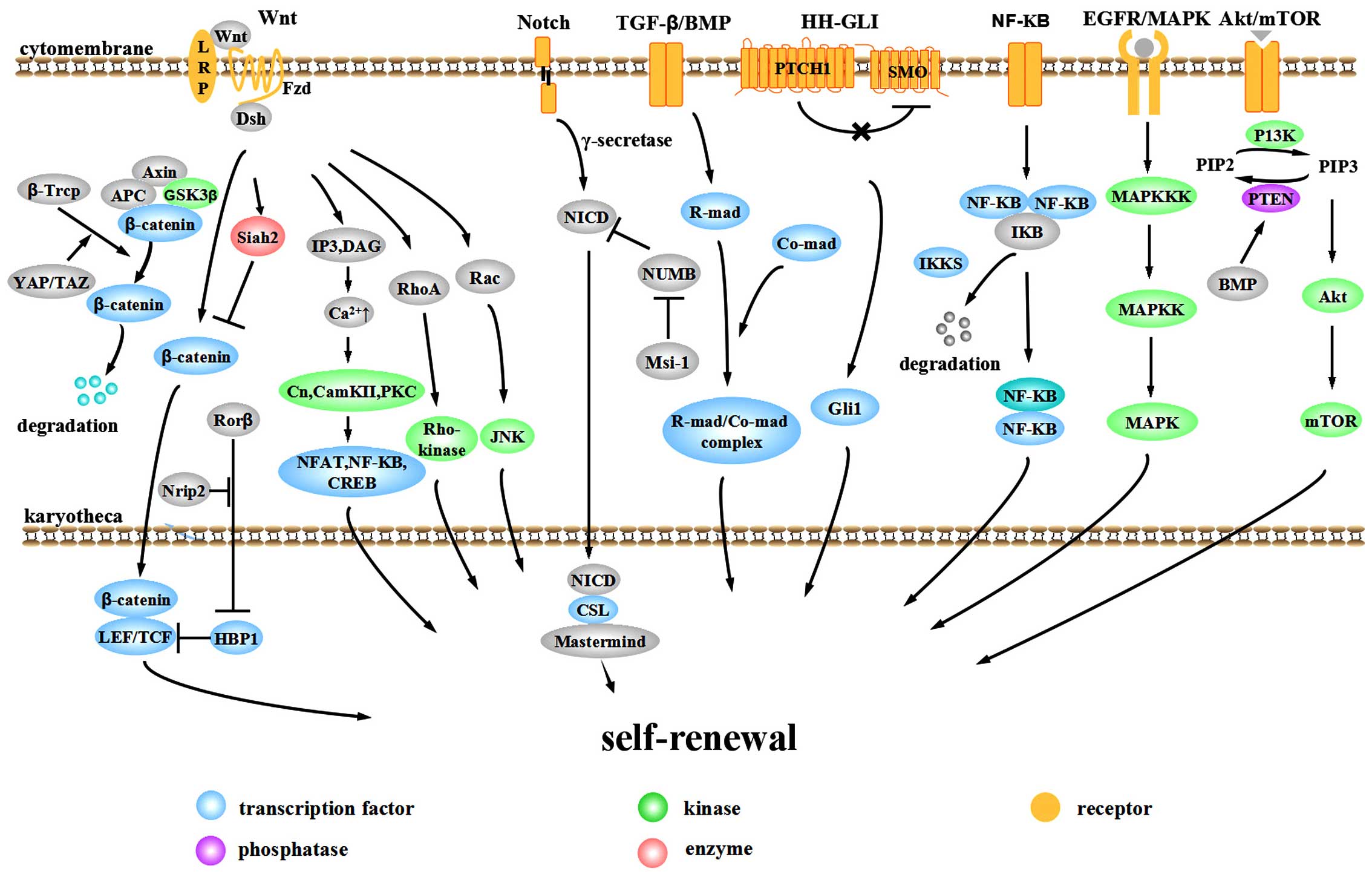
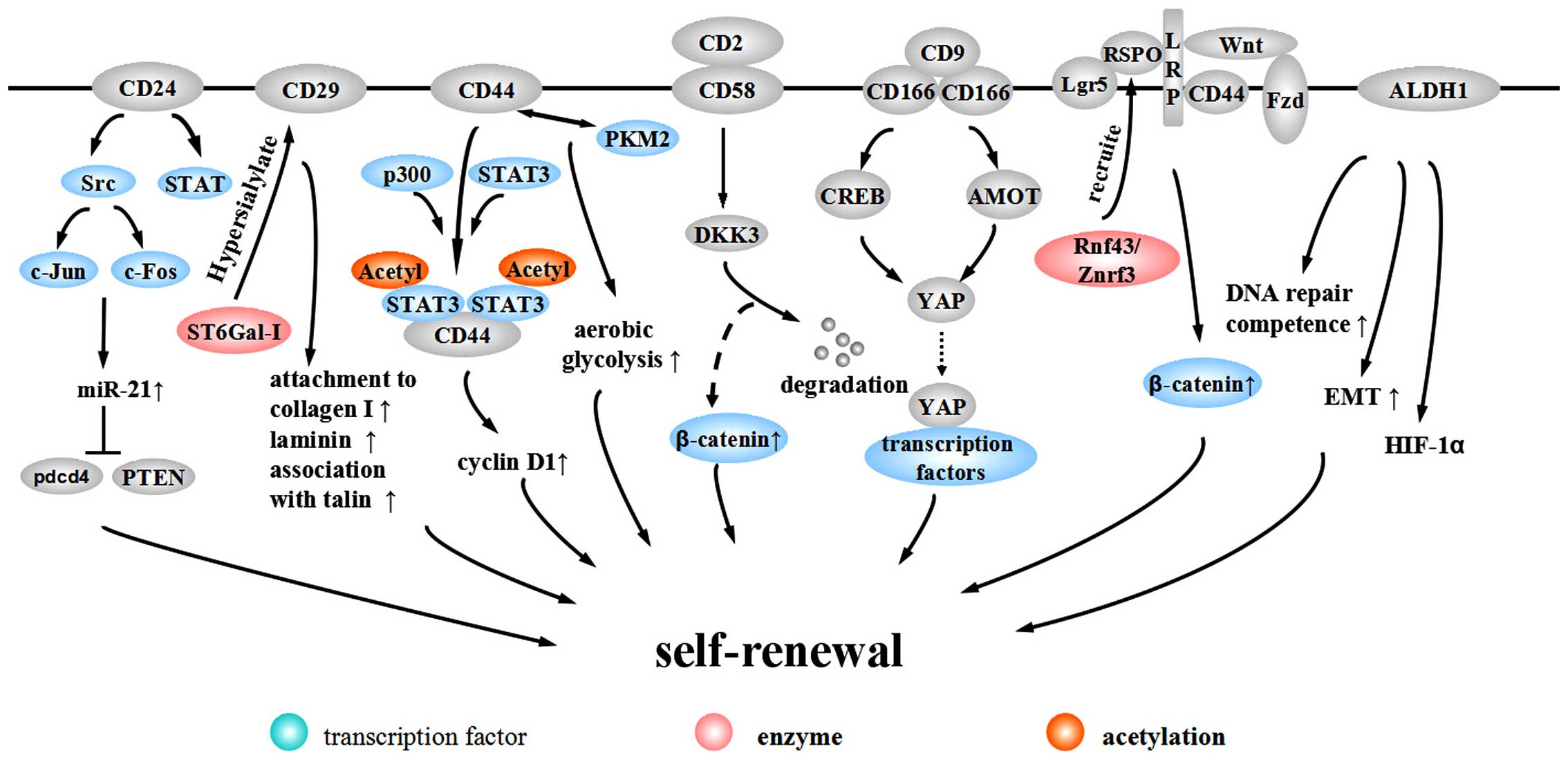
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
De Sousa E, Melo F, Vermeulen L, Fessler E
and Medema JP: Cancer heterogeneity - a multifaceted view. EMBO
Rep. 14:686–695. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zeuner A, Todaro M, Stassi G and De Maria
R: Colorectal cancer stem cells: From the crypt to the clinic. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:692–705. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaiopoulos AG, Kostakis ID, Koutsilieris M
and Papavassiliou AG: Colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem Cells.
30:363–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pardal R, Clarke MF and Morrison SJ:
Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:895–902. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de
Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR,
Sansom OJ and Clevers H: Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of
intestinal cancer. Nature. 457:608–611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schepers AG, Snippert HJ, Stange DE, van
den Born M, van Es JH, van de Wetering M and Clevers H: Lineage
tracing reveals Lgr5+ stem cell activity in mouse
intestinal adenomas. Science. 337:730–735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang J, Papadopoulos N, McKinley AJ,
Farrington SM, Curtis LJ, Wyllie AH, Zheng S, Willson JK, Markowitz
SD, Morin P, et al: APC mutations in colorectal tumors with
mismatch repair deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:9049–9054.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Castets M, Broutier L, Molin Y, Brevet M,
Chazot G, Gadot N, Paquet A, Mazelin L, Jarrosson-Wuilleme L,
Scoazec JY, et al: DCC constrains tumour progression via its
dependence receptor activity. Nature. 482:534–537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schwitalla S, Fingerle AA, Cammareri P,
Nebelsiek T, Göktuna SI, Ziegler PK, Canli O, Heijmans J, Huels DJ,
Moreaux G, et al: Intestinal tumorigenesis initiated by
dedifferentiation and acquisition of stem-cell-like properties.
Cell. 152:25–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Scheel C, Eaton EN, Li SH, Chaffer CL,
Reinhardt F, Kah KJ, Bell G, Guo W, Rubin J, Richardson AL, et al:
Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain mesenchymal and
stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 145:926–940. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chaffer CL, Brueckmann I, Scheel C,
Kaestli AJ, Wiggins PA, Rodrigues LO, Brooks M, Reinhardt F, Su Y,
Polyak K, et al: Normal and neoplastic nonstem cells can
spontaneously convert to a stem-like state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:7950–7955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yan KS, Chia LA, Li X, Ootani A, Su J, Lee
JY, Su N, Luo Y, Heilshorn SC, Amieva MR, et al: The intestinal
stem cell markers Bmi1 and Lgr5 identify two functionally distinct
populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:466–471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Yeung TM, Chia LA, Kosinski CM and Kuo CJ:
Regulation of self-renewal and differentiation by the intestinal
stem cell niche. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:2513–2523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yeung TM, Gandhi SC, Wilding JL, Muschel R
and Bodmer WF: Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived
cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:3722–3727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu S, Wen Z, Jiang Q, Zhu L, Feng S, Zhao
Y, Wu J, Dong Q, Mao J and Zhu Y: CD58, a novel surface marker,
promotes self-renewal of tumor-initiating cells in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 34:1520–1531. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Horst D, Kriegl L, Engel J, Kirchner T and
Jung A: Prognostic significance of the cancer stem cell markers
CD133, CD44, and CD166 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Invest.
27:844–850. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dalerba P, Dylla SJ, Park IK, Liu R, Wang
X, Cho RW, Hoey T, Gurney A, Huang EH, Simeone DM, et al:
Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10158–10163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang EH, Hynes MJ, Zhang T, Ginestier C,
Dontu G, Appelman H, Fields JZ, Wicha MS and Boman BM: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1 is a marker for normal and malignant human colonic
stem cells (SC) and tracks SC overpopulation during colon
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 69:3382–3389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miranda-Lorenzo I, Dorado J, Lonardo E,
Alcala S, Serrano AG, Clausell-Tormos J, Cioffi M, Megias D,
Zagorac S, Balic A, et al: Intracellular autofluorescence: A
biomarker for epithelial cancer stem cells. Nat Methods.
11:1161–1169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dotse E and Bian Y: Isolation of
colorectal cancer stem-like cells. Cytotechnology. 68:609–619.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fevr T, Robine S, Louvard D and Huelsken
J: Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and
maintenance of intestinal stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 27:7551–7559.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao C, Chen G, Romero G, Moschos S, Xu X
and Hu J: Induction of Gsk3β-β-TrCP interaction is required for
late phase stabilization of β-catenin in canonical Wnt signaling. J
Biol Chem. 289:7099–7108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A
and Kemler R: beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. EMBO J. 16:3797–3804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of beta-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sebio A, Kahn M and Lenz HJ: The potential
of targeting Wnt/β-catenin in colon cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 18:611–615. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Krausova M and Korinek V: Wnt signaling in
adult intestinal stem cells and cancer. Cell Signal. 26:570–579.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
van de Wetering M, Sancho E, Verweij C, de
Lau W, Oving I, Hurlstone A, van der Horn K, Batlle E, Coudreuse D,
Haramis AP, et al: The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt
progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell. 111:241–250.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Muncan V, Sansom OJ, Tertoolen L, Phesse
TJ, Begthel H, Sancho E, Cole AM, Gregorieff A, de Alboran IM,
Clevers H, et al: Rapid loss of intestinal crypts upon conditional
deletion of the Wnt/Tcf-4 target gene c-Myc. Mol Cell Biol.
26:8418–8426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E,
Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V,
et al: YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex
orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell. 158:157–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho JH, Dimri M and Dimri GP: A positive
feedback loop regulates the expression of polycomb group protein
BMI1 via WNT signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 288:3406–3418. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Ciznadija D, Tothill R, Waterman ML, Zhao
L, Huynh D, Yu RM, Ernst M, Ishii S, Mantamadiotis T, Gonda TJ, et
al: Intestinal adenoma formation and MYC activation are regulated
by cooperation between MYB and Wnt signaling. Cell Death Differ.
16:1530–1538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vermeulen L, De Sousa E, Melo F, van der
Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M,
Merz C, Rodermond H, et al: Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem
cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol.
12:468–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De A: Wnt/Ca2+ signaling
pathway: A brief overview. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
43:745–756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
MacLeod RJ, Hayes M and Pacheco I: Wnt5a
secretion stimulated by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor
inhibits defective Wnt signaling in colon cancer cells. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G403–G411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gwak J, Cho M, Gong SJ, Won J, Kim DE, Kim
EY, Lee SS, Kim M, Kim TK, Shin JG, et al:
Protein-kinase-C-mediated beta-catenin phosphorylation negatively
regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Sci. 119:4702–4709.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hernández-Maqueda JG, Luna-Ulloa LB,
Santoyo-Ramos P, Castañeda-Patlán MC and Robles-Flores M: Protein
kinase C delta negatively modulates canonical Wnt pathway and cell
proliferation in colon tumor cell lines. PLoS One. 8:e585402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JM, Kim IS, Kim H, Lee JS, Kim K, Yim
HY, Jeong J, Kim JH, Kim JY, Lee H, et al: RORalpha attenuates
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by PKCalpha-dependent phosphorylation in
colon cancer. Mol Cell. 37:183–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno
N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J and
Matsumoto K: The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade
functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:131–139. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Katoh M: WNT/PCP signaling pathway and
human cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 14:1583–1588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Piazzi G, Selgrad M, Garcia M, Ceccarelli
C, Fini L, Bianchi P, Laghi L, D'Angelo L, Paterini P,
Malfertheiner P, et al: Van-Gogh-like 2 antagonises the canonical
WNT pathway and is methylated in colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer.
108:1750–1756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sancho R, Nateri AS, de Vinuesa AG,
Aguilera C, Nye E, Spencer-Dene B and Behrens A: JNK signalling
modulates intestinal homeostasis and tumourigenesis in mice. EMBO
J. 28:1843–1854. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Notch signaling in
gastrointestinal tract (Review). Int J Oncol. 30:247–251. 2007.
|
|
49
|
Couturier L, Mazouni K and Schweisguth F:
Inhibition of Notch recycling by Numb: Relevance and mechanism(s).
Cell Cycle. 12:1647–1648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Giebel B and Wodarz A: Notch signaling:
Numb makes the difference. Curr Biol. 22:R133–R135. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pastò A, Serafin V, Pilotto G, Lago C,
Bellio C, Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Hoey T, Plateroti M, Esposito G,
et al: NOTCH3 signaling regulates MUSASHI-1 expression in
metastatic colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 74:2106–2118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sikandar SS, Pate KT, Anderson S, Dizon D,
Edwards RA, Waterman ML and Lipkin SM: NOTCH signaling is required
for formation and self-renewal of tumor-initiating cells and for
repression of secretory cell differentiation in colon cancer.
Cancer Res. 70:1469–1478. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Meng RD, Shelton CC, Li YM, Qin LX,
Notterman D, Paty PB and Schwartz GK: gamma-Secretase inhibitors
abrogate oxaliplatin-induced activation of the Notch-1 signaling
pathway in colon cancer cells resulting in enhanced
chemosensitivity. Cancer Res. 69:573–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gao F, Zhang Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Zheng L,
Yang J, Huang W, Ye Y, Luo W and Xiao D: Hes1 is involved in the
self-renewal and tumourigenicity of stem-like cancer cells in colon
cancer. Sci Rep. 4:39632014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ghaleb AM, Aggarwal G, Bialkowska AB,
Nandan MO and Yang VW: Notch inhibits expression of the
Krüppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal
epithelium. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1920–1927. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mishra L, Derynck R and Mishra B:
Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in stem cells and cancer.
Science. 310:68–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kamato D, Burch ML, Piva TJ, Rezaei HB,
Rostam MA, Xu S, Zheng W, Little PJ and Osman N: Transforming
growth factor-β signalling: Role and consequences of Smad linker
region phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 25:2017–2024. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu M, Trobridge P, Wang Y, Kanngurn S,
Morris SM, Knoblaugh S and Grady WM: Inactivation of TGF-β
signaling and loss of PTEN cooperate to induce colon cancer in
vivo. Oncogene. 33:1538–1547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Villanueva A, García C, Paules AB, Vicente
M, Megías M, Reyes G, de Villalonga P, Agell N, Lluís F, Bachs O,
et al: Disruption of the antiproliferative TGF-beta signaling
pathways in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 17:1969–1978.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Xu X, Brodie SG, Yang X, Im YH, Parks WT,
Chen L, Zhou YX, Weinstein M, Kim SJ and Deng CX: Haploid loss of
the tumor suppressor Smad4/Dpc4 initiates gastric polyposis and
cancer in mice. Oncogene. 19:1868–1874. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Grady WM, Myeroff LL, Swinler SE, Rajput
A, Thiagalingam S, Lutterbaugh JD, Neumann A, Brattain MG, Chang J,
Kim SJ, et al: Mutational inactivation of transforming growth
factor beta receptor type II in microsatellite stable colon
cancers. Cancer Res. 59:320–324. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Woodford-Richens KL, Rowan AJ, Gorman P,
Halford S, Bicknell DC, Wasan HS, Roylance RR, Bodmer WF and
Tomlinson IP: SMAD4 mutations in colorectal cancer probably occur
before chromosomal instability, but after divergence of the
microsatellite instability pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:9719–9723. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zubeldia IG, Bleau AM, Redrado M, Serrano
D, Agliano A, Gil-Puig C, Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Lecanda J and Calvo
A: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell
phenotypes leading to liver metastasis are abrogated by the novel
TGFβ1-targeting peptides P17 and P144. Exp Cell Res. 319:12–22.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Signaling
networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during
embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 98:1512–1520.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hwang WL, Yang MH, Tsai ML, Lan HY, Su SH,
Chang SC, Teng HW, Yang SH, Lan YT, Chiou SH, et al: SNAIL
regulates interleukin-8 expression, stem cell-like activity, and
tumorigenicity of human colorectal carcinoma cells.
Gastroenterology. 141:279–291. 2912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Karreth FA, Tay Y, Perna D, Ala U, Tan SM,
Rust AG, DeNicola G, Webster KA, Weiss D, Perez-Mancera PA, et al:
In vivo identification of tumor- suppressive PTEN ceRNAs in an
oncogenic BRAF-induced mouse model of melanoma. Cell. 147:382–395.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Loh K, Chia JA, Greco S, Cozzi SJ,
Buttenshaw RL, Bond CE, Simms LA, Pike T, Young JP, Jass JR, et al:
Bone morphogenic protein 3 inactivation is an early and frequent
event in colorectal cancer development. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
47:449–460. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lombardo Y, Scopelliti A, Cammareri P,
Todaro M, Iovino F, Ricci-Vitiani L, Gulotta G, Dieli F, de Maria R
and Stassi G: Bone morphogenetic protein 4 induces differentiation
of colorectal cancer stem cells and increases their response to
chemotherapy in mice. Gastroenterology. 140:297–309. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Garulli C, Kalogris C, Pietrella L,
Bartolacci C, Andreani C, Falconi M, Marchini C and Amici A:
Dorsomorphin reverses the mesenchymal phenotype of breast cancer
initiating cells by inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein
signaling. Cell Signal. 26:352–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Whissell G, Montagni E, Martinelli P,
Hernando-Momblona X, Sevillano M, Jung P, Cortina C, Calon A, Abuli
A, Castells A, et al: The transcription factor GATA6 enables
self-renewal of colon adenoma stem cells by repressing BMP gene
expression. Nat Cell Biol. 16:695–707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Varnat F, Duquet A, Malerba M, Zbinden M,
Mas C, Gervaz P and Ruiz i Altaba A: Human colon cancer epithelial
cells harbour active HEDGEHOG-GLI signalling that is essential for
tumour growth, recurrence, metastasis and stem cell survival and
expansion. EMBO Mol Med. 1:338–351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Akiyoshi T, Nakamura M, Koga K, Nakashima
H, Yao T, Tsuneyoshi M, Tanaka M and Katano M: Gli1, downregulated
in colorectal cancers, inhibits proliferation of colon cancer cells
involving Wnt signalling activation. Gut. 55:991–999. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Arimura S, Matsunaga A, Kitamura T, Aoki
K, Aoki M and Taketo MM: Reduced level of smoothened suppresses
intestinal tumorigenesis by downregulation of Wnt signaling.
Gastroenterology. 137:629–638. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sakamoto K and Maeda S: Targeting
NF-kappaB for colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:593–601. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Vlantis K, Wullaert A, Sasaki Y,
Schmidt-Supprian M, Rajewsky K, Roskams T and Pasparakis M:
Constitutive IKK2 activation in intestinal epithelial cells induces
intestinal tumors in mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2781–2793. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Feng Y, Dai X, Li X, Wang H, Liu J, Zhang
J, Du Y and Xia L: EGF signalling pathway regulates colon cancer
stem cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 45:413–419.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Al Moustafa AE, Achkhar A and Yasmeen A:
EGF-receptor signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human carcinomas. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 4:671–684. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Munshi A and Ramesh R: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases and their role in radiation response. Genes Cancer.
4:401–408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Moschetta M, Reale A, Marasco C, Vacca A
and Carratù MR: Therapeutic targeting of the mTOR-signalling
pathway in cancer: Benefits and limitations. Br J Pharmacol.
171:3801–3813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Vivanco I, Chen ZC, Tanos B, Oldrini B,
Hsieh WY, Yannuzzi N, Campos C and Mellinghoff IK: A
kinase-independent function of AKT promotes cancer cell survival.
eLife. 3:32014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Tian Q, He XC, Hood L and Li L: Bridging
the BMP and Wnt pathways by PI3 kinase/Akt and 14-3-3zeta. Cell
Cycle. 4:215–216. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lim SC: CD24 and human carcinoma: Tumor
biological aspects. Biomed Pharmacother. 59(Suppl 2): S351–S354.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Ke J, Wu X, Wu X, He X, Lian L, Zou Y, He
X, Wang H, Luo Y, Wang L, et al: A subpopulation of
CD24+ cells in colon cancer cell lines possess stem cell
characteristics. Neoplasma. 59:282–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Shulewitz M, Soloviev I, Wu T, Koeppen H,
Polakis P and Sakanaka C: Repressor roles for TCF-4 and Sfrp1 in
Wnt signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene. 25:4361–4369. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Muppala S, Mudduluru G, Leupold JH, Buergy
D, Sleeman JP and Allgayer H: CD24 induces expression of the
oncomir miR-21 via Src, and CD24 and Src are both
post-transcriptionally downregulated by the tumor suppressor
miR-34a. PLoS One. 8:e595632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang YC, Wang JL, Kong X, Sun TT, Chen HY,
Hong J and Fang JY: CD24 mediates gastric carcinogenesis and
promotes gastric cancer progression via STAT3 activation.
Apoptosis. 19:643–656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Seales EC, Jurado GA, Brunson BA,
Wakefield JK, Frost AR and Bellis SL: Hypersialylation of beta1
integrins, observed in colon adenocarcinoma, may contribute to
cancer progression by upregulating cell motility. Cancer Res.
65:4645–4652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fujita S, Watanabe M, Kubota T, Teramoto T
and Kitajima M: Alteration of expression in integrin beta 1-subunit
correlates with invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Lett. 91:145–149. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Song J, Zhang J, Wang J, Wang J, Guo X and
Dong W: β1 integrin mediates colorectal cancer cell proliferation
and migration through regulation of the Hedgehog pathway. Tumour
Biol. 36:2013–2021. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Marhaba R and Zöller M: CD44 in cancer
progression: Adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J Mol
Histol. 35:211–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Du L, Wang H, He L, Zhang J, Ni B, Wang X,
Jin H, Cahuzac N, Mehrpour M, Lu Y, et al: CD44 is of functional
importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:6751–6760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bánky B, Rásó-Barnett L, Barbai T, Tímár
J, Becságh P and Rásó E: Characteristics of CD44 alternative splice
pattern in the course of human colorectal adenocarcinoma
progression. Mol Cancer. 11:832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wielenga VJ, Smits R, Korinek V, Smit L,
Kielman M, Fodde R, Clevers H and Pals ST: Expression of CD44 in
Apc and Tcf mutant mice implies regulation by the WNT pathway. Am J
Pathol. 154:515–523. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang C, Xie J, Guo J, Manning HC, Gore JC
and Guo N: Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as cancer stem cell markers
for colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 28:1301–1308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Schmitt M, Metzger M, Gradl D, Davidson G
and Orian-Rousseau V: CD44 functions in Wnt signaling by regulating
LRP6 localization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 22:677–689.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
96
|
Lee JL, Wang MJ and Chen JY: Acetylation
and activation of STAT3 mediated by nuclear translocation of CD44.
J Cell Biol. 185:949–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Su YJ, Lai HM, Chang YW, Chen GY and Lee
JL: Direct reprogramming of stem cell properties in colon cancer
cells by CD44. EMBO J. 30:3186–3199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tamada M, Nagano O, Tateyama S, Ohmura M,
Yae T, Ishimoto T, Sugihara E, Onishi N, Yamamoto T, Yanagawa H, et
al: Modulation of glucose metabolism by CD44 contributes to
antioxidant status and drug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
72:1438–1448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kvale D, Krajci P and Brandtzaeg P:
Expression and regulation of adhesion molecules ICAM-1 (CD54) and
LFA-3 (CD58) in human intestinal epithelial cell lines. Scand J
Immunol. 35:669–676. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ebert EC, Panja A and Praveen R: Human
intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and epithelial cells
coinduce interleukin-8 production through the CD2-CD58 interaction.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G671–G677. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Levin TG, Powell AE, Davies PS, Silk AD,
Dismuke AD, Anderson EC, Swain JR and Wong MH: Characterization of
the intestinal cancer stem cell marker CD166 in the human and mouse
gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 139:2072–2082.e5. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Gilsanz A, Sánchez-Martín L,
Gutiérrez-López MD, Ovalle S, Machado-Pineda Y, Reyes R, Swart GW,
Figdor CG, Lafuente EM and Cabañas C: ALCAM/CD166 adhesive function
is regulated by the tetraspanin CD9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:475–493.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Hansen AG, Arnold SA, Jiang M, Palmer TD,
Ketova T, Merkel A, Pickup M, Samaras S, Shyr Y, Moses HL, et al:
ALCAM/CD166 is a TGF-β-responsive marker and functional regulator
of prostate cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Res. 74:1404–1415.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Wang J, Gu Z, Ni P, Qiao Y, Chen C, Liu X,
Lin J, Chen N and Fan Q: NF-kappaB P50/P65 hetero-dimer mediates
differential regulation of CD166/ALCAM expression via interaction
with micoRNA-9 after serum deprivation, providing evidence for a
novel negative auto-regulatory loop. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:6440–6455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ma L, Wang J, Lin J, Pan Q, Yu Y and Sun
F: Cluster of differentiation 166 (CD166) regulated by
phosphatidylinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling to exert its
anti-apoptotic role via yes-associated protein (YAP) in liver
cancer. J Biol Chem. 289:6921–6933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P,
van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H,
Peters PJ, et al: Identification of stem cells in small intestine
and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 449:1003–1007. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ritsma L, Ellenbroek SI, Zomer A, Snippert
HJ, de Sauvage FJ, Simons BD, Clevers H and van Rheenen J:
Intestinal crypt homeostasis revealed at single-stem-cell level by
in vivo live imaging. Nature. 507:362–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gerbe F, van Es JH, Makrini L, Brulin B,
Mellitzer G, Robine S, Romagnolo B, Shroyer NF, Bourgaux JF,
Pignodel C, et al: Distinct ATOH1 and Neurog3 requirements define
tuft cells as a new secretory cell type in the intestinal
epithelium. J Cell Biol. 192:767–780. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Schuijers J and Clevers H: Adult mammalian
stem cells: The role of Wnt, Lgr5 and R-spondins. EMBO J.
31:2685–2696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
de Lau W, Peng WC, Gros P and Clevers H:
The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: Regulator of Wnt signal strength.
Genes Dev. 28:305–316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Toll AD, Boman BM and Palazzo JP:
Dysplastic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease show increased
positivity for the stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase. Hum
Pathol. 43:238–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Cojoc M, Peitzsch C, Kurth I, Trautmann F,
Kunz-Schughart LA, Telegeev GD, Stakhovsky EA, Walker JR, Simin K,
Lyle S, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase is regulated by
Beta-catenin/TCF and promotes radioresistance in prostate cancer
progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 75:1482–1494. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chen S and Huang EH: The colon cancer stem
cell microenvironment holds keys to future cancer therapy. J
Gastrointest Surg. 18:1040–1048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P:
Cancer-associated-fibroblasts and tumour cells: A diabolic liaison
driving cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:195–208.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Calon A, Tauriello DV and Batlle E:
TGF-beta in CAF-mediated tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Cancer
Biol. 25:15–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S,
Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung
P, Zhang XH, et al: Dependency of colorectal cancer on a
TGF-β-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation.
Cancer Cell. 22:571–584. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
McIntyre A and Harris AL: Metabolic and
hypoxic adaptation to anti-angiogenic therapy: A target for induced
essentiality. EMBO Mol Med. 7:368–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Rebucci M and Michiels C: Molecular
aspects of cancer cell resistance to chemotherapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:1219–1226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Santoyo-Ramos P, Likhatcheva M,
García-Zepeda EA, Castañeda-Patlán MC and Robles-Flores M:
Hypoxia-inducible factors modulate the stemness and malignancy of
colon cancer cells by playing opposite roles in canonical Wnt
signaling. PLoS One. 9:e1125802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Newton IP, Kenneth NS, Appleton PL, Näthke
I and Rocha S: Adenomatous polyposis coli and hypoxia-inducible
factor-1{alpha} have an antagonistic connection. Mol Biol Cell.
21:3630–3638. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Shay JE, Imtiyaz HZ, Sivanand S, Durham
AC, Skuli N, Hsu S, Mucaj V, Eisinger-Mathason TS, Krock BL,
Giannoukos DN, et al: Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factors
limits tumor progression in a mouse model of colorectal cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1067–1077. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S and
Bronte V: Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat
Rev Immunol. 12:253–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Katoh H, Wang D, Daikoku T, Sun H, Dey SK
and Dubois RN: CXCR2-expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells
are essential to promote colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer
Cell. 24:631–644. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB and Lewis
CE: The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour
angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:618–631. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Motz GT and Coukos G: The parallel lives
of angiogenesis and immunosuppression: Cancer and other tales. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:702–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Cui TX, Kryczek I, Zhao L, Zhao E, Kuick
R, Roh MH, Vatan L, Szeliga W, Mao Y, Thomas DG, et al:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells enhance stemness of cancer cells
by inducing microRNA101 and suppressing the corepressor CtBP2.
Immunity. 39:611–621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin
C and Flavell RA: Inflammation-induced cancer: Crosstalk between
tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:759–771. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Suzuki H, Ogawa H, Miura K, Haneda S,
Watanabe K, Ohnuma S, Sasaki H, Sase T, Kimura S, Kajiwara T, et
al: IL-23 directly enhances the proliferative and invasive
activities of colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 4:199–204.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Zhang L, Li J, Li L, Zhang J, Wang X, Yang
C, Li Y, Lan F and Lin P: IL-23 selectively promotes the metastasis
of colorectal carcinoma cells with impaired Socs3 expression via
the STAT5 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 35:1330–1340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Grivennikov SI, Wang K, Mucida D, Stewart
CA, Schnabl B, Jauch D, Taniguchi K, Yu GY, Osterreicher CH, Hung
KE, et al: Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products
drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature. 491:254–258.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang K, Kim MK, Di Caro G, Wong J,
Shalapour S, Wan J, Zhang W, Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Wu LW, et
al: Interleukin-17 receptor a signaling in transformed enterocytes
promotes early colorectal tumorigenesis. Immunity. 41:1052–1063.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Waugh DJ and Wilson C: The interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Bellamkonda K, Sime W and Sjolander A: The
impact of inflammatory lipid mediators on colon cancer-initiating
cells. Mol Carcinog. 54:1315–1327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Taketo MM: Roles of stromal
microenvironment in colon cancer progression. J Biochem.
151:477–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Sun J: Enteric bacteria and cancer stem
cells. Cancers (Basel). 3:285–297. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Ischenko I, Seeliger H, Schaffer M, Jauch
KW and Bruns CJ: Cancer stem cells: How can we target them? Curr
Med Chem. 15:3171–3184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Fujimoto K, Beauchamp RD and Whitehead RH:
Identification and isolation of candidate human colonic clonogenic
cells based on cell surface integrin expression. Gastroenterology.
123:1941–1948. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
May R, Riehl TE, Hunt C, Sureban SM, Anant
S and Houchen CW: Identification of a novel putative
gastrointestinal stem cell and adenoma stem cell marker,
doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1, following radiation injury and
in adenomatous polyposis coli/multiple intestinal neoplasia mice.
Stem Cells. 26:630–637. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Li D, Peng X, Yan D, Tang H, Huang F, Yang
Y and Peng Z: Msi-1 is a predictor of survival and a novel
therapeutic target in colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2074–2083.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Yu T, Chen X, Zhang W, Colon D, Shi J,
Napier D, Rychahou P, Lu W, Lee EY, Weiss HL, et al: Regulation of
the potential marker for intestinal cells, Bmi1, by β-catenin and
the zinc finger protein KLF4: Implications for colon cancer. J Biol
Chem. 287:3760–3768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Sagiv E, Memeo L, Karin A, Kazanov D,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Mansukhani M, Rechavi G, Hibshoosh H and Arber N:
CD24 is a new oncogene, early at the multistep process of
colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 131:630–639.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Haraguchi N, Ishii H, Mimori K, Ohta K,
Uemura M, Nishimura J, Hata T, Takemasa I, Mizushima T, Yamamoto H,
et al: CD49f-positive cell population efficiently enriches colon
cancer-initiating cells. Int J Oncol. 43:425–430. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Gemei M, Mirabelli P, Di Noto R, Corbo C,
Iaccarino A, Zamboli A, Troncone G, Galizia G, Lieto E, Del Vecchio
L, et al: CD66c is a novel marker for colorectal cancer stem cell
isolation, and its silencing halts tumor growth in vivo. Cancer.
119:729–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Nakanishi Y, Seno H, Fukuoka A, Ueo T,
Yamaga Y, Maruno T, Nakanishi N, Kanda K, Komekado H, Kawada M, et
al: Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the
intestine. Nat Genet. 45:98–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
van der Flier LG, Haegebarth A, Stange DE,
van de Wetering M and Clevers H: OLFM4 is a robust marker for stem
cells in human intestine and marks a subset of colorectal cancer
cells. Gastroenterology. 137:15–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|