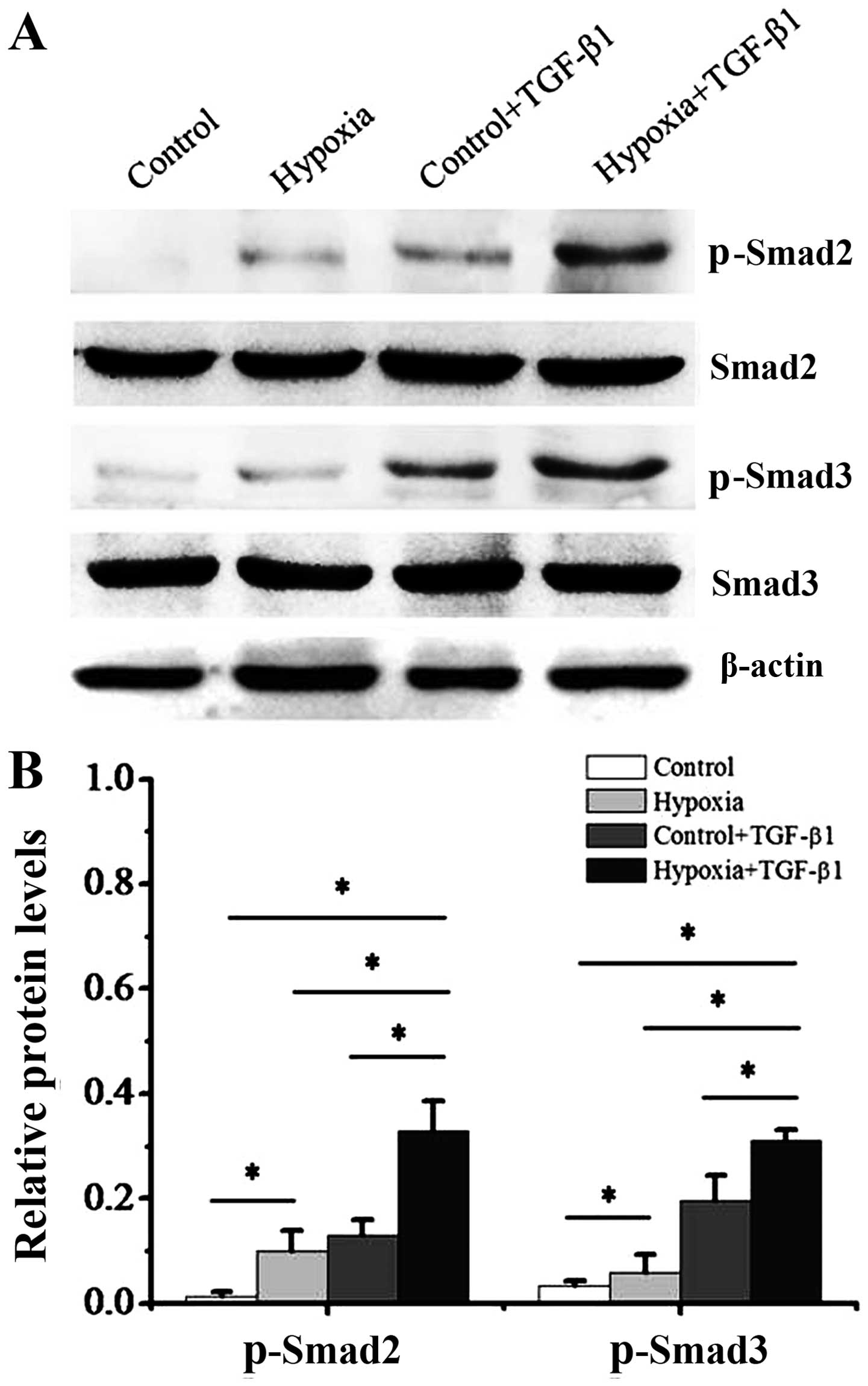
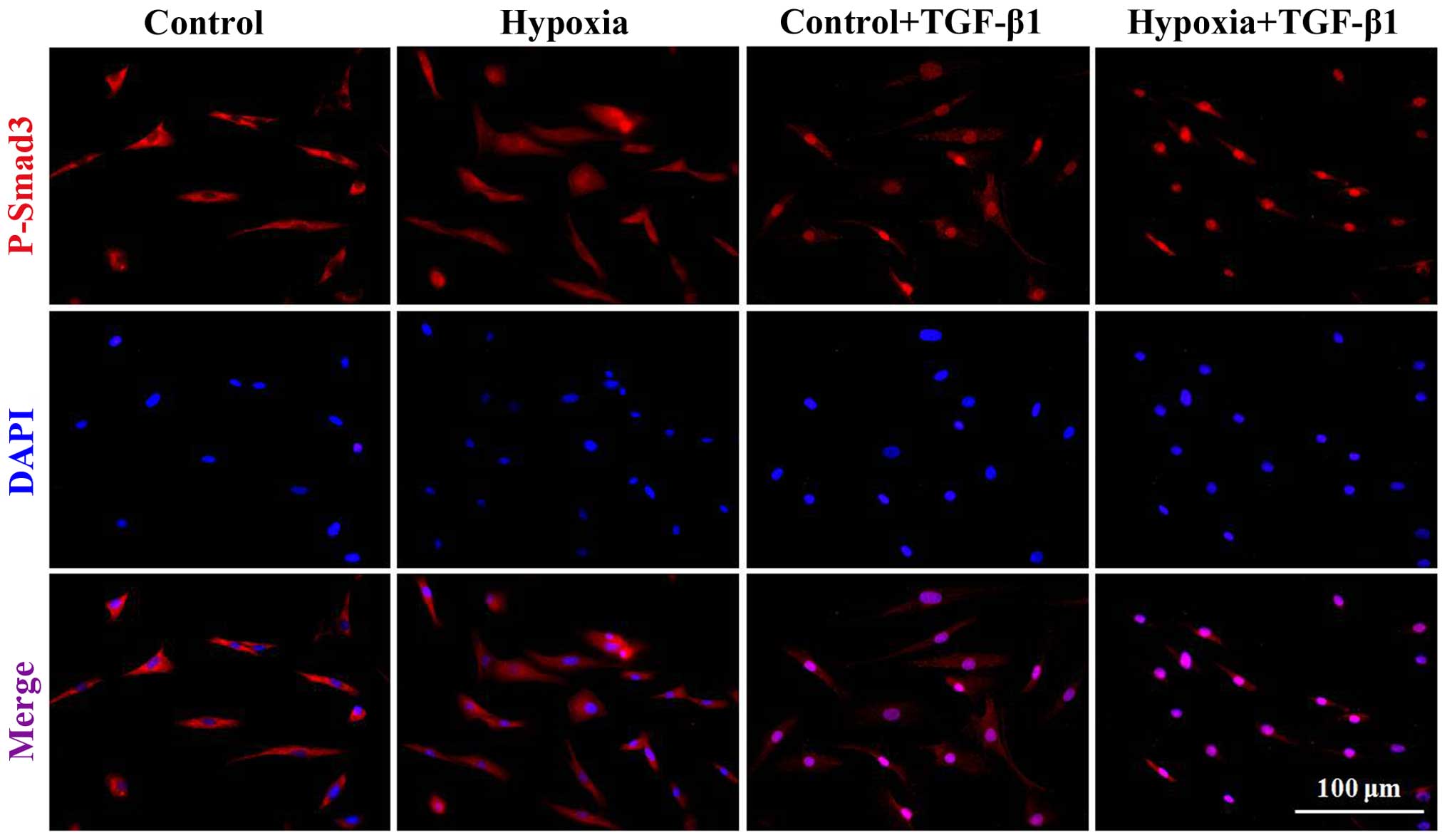
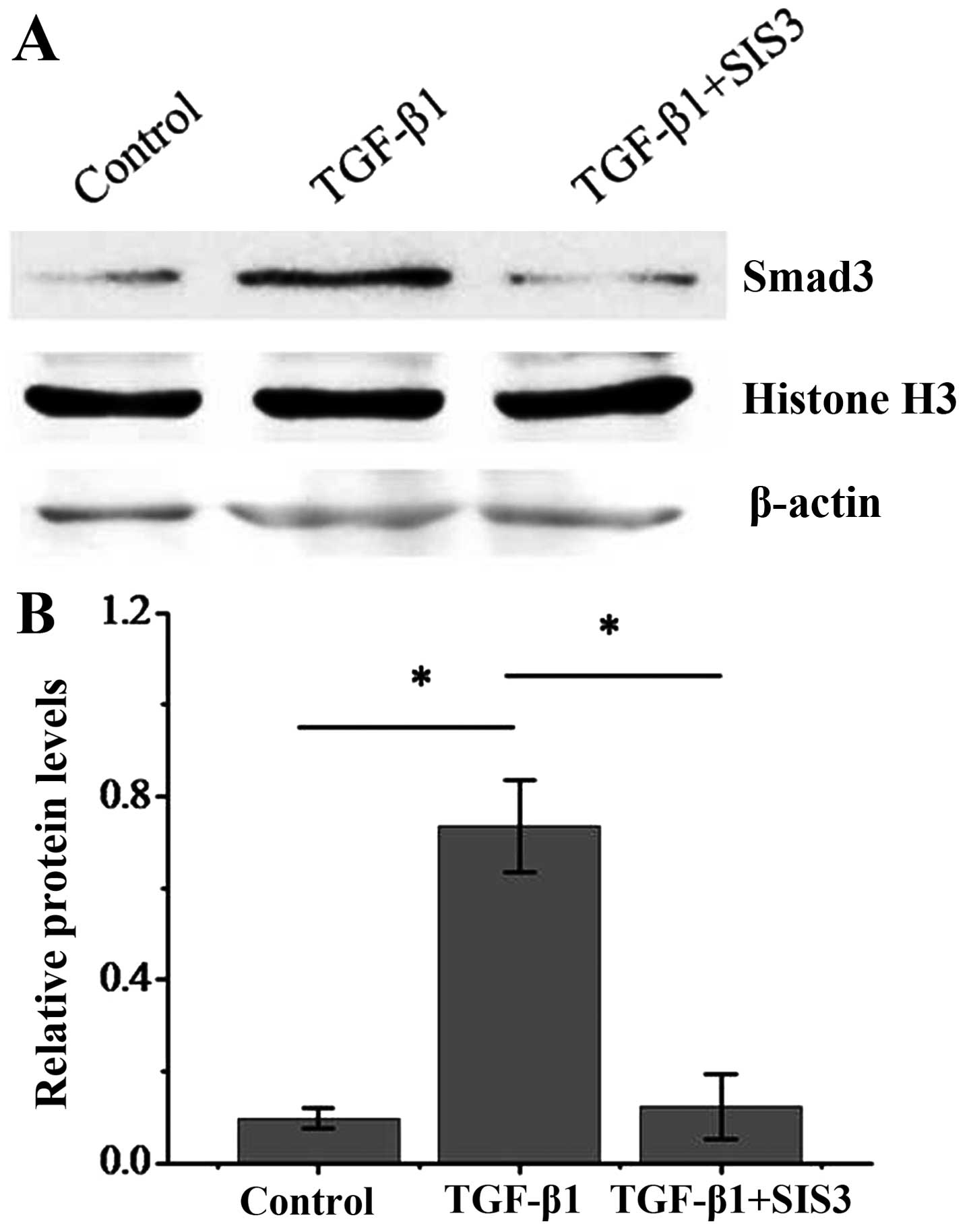
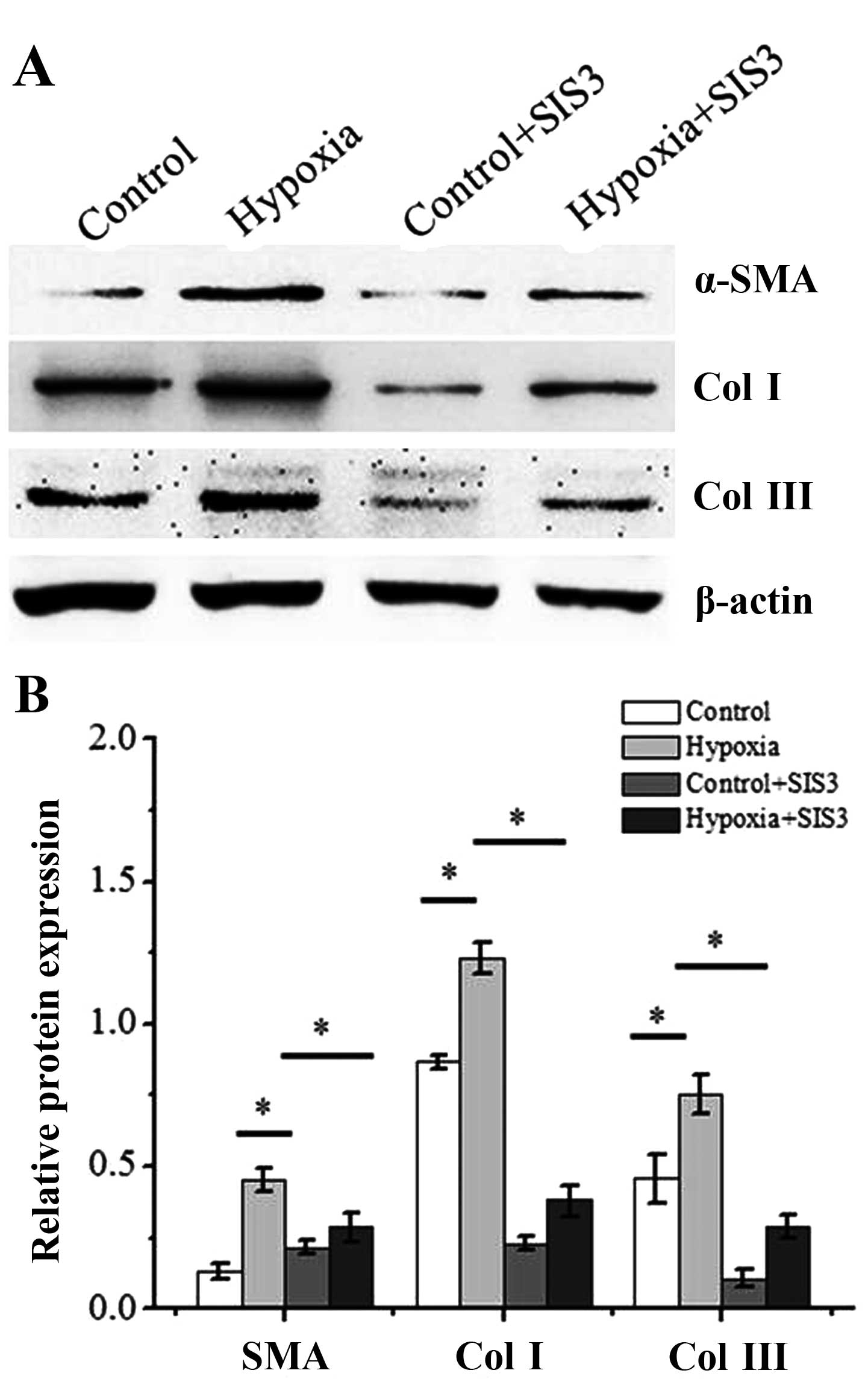
|
1
|
Bran GM, Goessler UR, Hormann K, Riedel F
and Sadick H: Keloids: current concepts of pathogenesis (Review).
Int J Mol Med. 24:283–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meyer LJ, Russell SB, Russell JD, Trupin
JS, Egbert BM, Shuster S and Stern R: Reduced hyaluronan in keloid
tissue and cultured keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol.
114:953–959. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daian T, Ohtsuru A, Rogounovitch T,
Ishihara H, Hirano A, Akiyama-Uchida Y, Saenko V, Fujii T and
Yamashita S: Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances transforming
growth factor-beta-induced extracellular matrix protein production
through the P38/activating transcription factor-2 signaling pathway
in keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 120:956–962. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dong X, Mao S and Wen H: Upregulation of
proinflammatory genes in skin lesions may be the cause of keloid
formation (Review). Biomed Rep. 1:833–836. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Olman MA: Beyond TGF-beta: a prostaglandin
promotes fibrosis. Nat Med. 15:1360–1361. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ong CT, Khoo YT, Mukhopadhyay A, Do DV,
Lim IJ, Aalami O and Phan TT: mTOR as a potential therapeutic
target for treatment of keloids and excessive scars. Exp Dermatol.
16:394–404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan L, Huang C, Meng XM, Song Y, Wu XQ,
Yang Y and Li J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hepatic
fibrosis: a promising therapeutic target. Biochimie. 108:1–7. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
O'Connell MP and Weeraratna AT: Change is
in the air: the hypoxic induction of phenotype switching in
melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2316–2317. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Nie F, Kang C, Chen B, Qin Z, Ma
J, Ma Y and Zhao X: Increased periostin expression affects the
proliferation, collagen synthesis, migration and invasion of keloid
fibroblasts under hypoxic conditions. Int J Mol Med. 34:253–261.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cash TP, Pan Y and Simon MC: Reactive
oxygen species and cellular oxygen sensing. Free Radic Biol Med.
43:1219–1225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gaber T, Dziurla R, Tripmacher R,
Burmester GR and Buttgereit F: Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) in
rheumatology: low O2! See what HIF can do! Ann Rheum
Dis. 64:971–980. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Ann DK, Messadi DV, Tuan
TL, Kelly AP, Bertolami CN and Le AD: Mechanisms of hypoxic
regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expression in
keloid fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 121:1005–1012. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ueda K, Yasuda Y, Furuya E and Oba S:
Inadequate blood supply persists in keloids. Scand J Plast Reconstr
Surg Hand Surg. 38:267–271. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Steinbrech DS, Mehrara BJ, Chau D, Rowe
NM, Chin G, Lee T, Saadeh PB, Gittes GK and Longaker MT: Hypoxia
upregulates VEGF production in keloid fibroblasts. Ann Plast Surg.
42:514–519; discussion 519–520. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ruthenborg RJ, Ban JJ, Wazir A, Takeda N
and Kim JW: Regulation of wound healing and fibrosis by hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Mol Cells. 37:637–643. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lebrin F, Deckers M, Bertolino P and Ten
Dijke P: TGF-beta receptor function in the endothelium. Cardiovasc
Res. 65:599–608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Santibañez JF, Quintanilla M and Bernabeu
C: TGF-β/TGF-β receptor system and its role in physiological and
pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:233–251. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jinnin M, Ihn H and Tamaki K:
Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and
its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced
extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol. 69:597–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Pan Q, Su Y, Zhang Z, Han
J, Zhu X, Tang C and Hu D: Wnt/β-catenin pathway forms a negative
feedback loop during TGF-β1 induced human normal skin
fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition. J Dermatol Sci. 65:38–49.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier
C and Brown RA: Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective
tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:349–363. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Desmoulière A, Chaponnier C and Gabbiani
G: Tissue repair, contraction, and the myofibroblast. Wound Repair
Regen. 13:7–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hinz B, Celetta G, Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G
and Chaponnier C: Alpha-smooth muscle actin expression upregulates
fibroblast contractile activity. Mol Biol Cell. 12:2730–2741. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Nie F, Chen X, Qin Z, Kang C,
Chen B, Ma J, Pan B and Ma Y: Upregulated periostin promotes
angiogenesis in keloids through activation of the ERK 1/2 and focal
adhesion kinase pathways, as well as the upregulated expression of
VEGF and angiopoietin 1. Mol Med Rep. 11:857–864. 2015.
|
|
24
|
Jiang HS, Zhu LL, Zhang Z, Chen H, Chen Y
and Dai YT: Estradiol attenuates the TGF-β1-induced conversion of
primary TAFs into myofibroblasts and inhibits collagen production
and myofibroblast contraction by modulating the Smad and Rho/Rock
signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 36:801–807. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bosco MC, Puppo M, Blengio F, Fraone T,
Cappello P, Giovarelli M and Varesio L: Monocytes and dendritic
cells in a hypoxic environment: spotlights on chemotaxis and
migration. Immunobiology. 213:733–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sen CK and Roy S: Oxygenation state as a
driver of myofibroblast differentiation and wound contraction:
hypoxia impairs wound closure. J Invest Dermatol. 130:2701–2703.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nauta TD, van Hinsbergh VW and Koolwijk P:
Hypoxic signaling during tissue repair and regenerative medicine.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:19791–19815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kelly BD, Hackett SF, Hirota K, Oshima Y,
Cai Z, Berg-Dixon S, Rowan A, Yan Z, Campochiaro PA and Semenza GL:
Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene
expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a
constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ Res.
93:1074–1081. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haase VH: Oxygen regulates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: insights into molecular
mechanisms and relevance to disease. Kidney Int. 76:492–499. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sloan DF, Brown RD, Wells CH and Hilton
JG: Tissue gases in human hypertrophic burn scars. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 61:431–436. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGF-beta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 24:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Copple BL: Hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by hypoxia-inducible factor
and transforming growth factor-beta-dependent mechanisms. Liver
Int. 30:669–682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Watson CJ, Collier P, Tea I, Neary R,
Watson JA, Robinson C, Phelan D, Ledwidge MT, McDonald KM, McCann
A, et al: Hypoxia-induced epigenetic modifications are associated
with cardiac tissue fibrosis and the development of a
myofibroblast-like phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 23:2176–2188. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y,
Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, Pellicoro A, Raschperger E,
Betsholtz C, Ruminski PG, et al: Targeting of αv integrin
identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in
several organs. Nat Med. 19:1617–1624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|