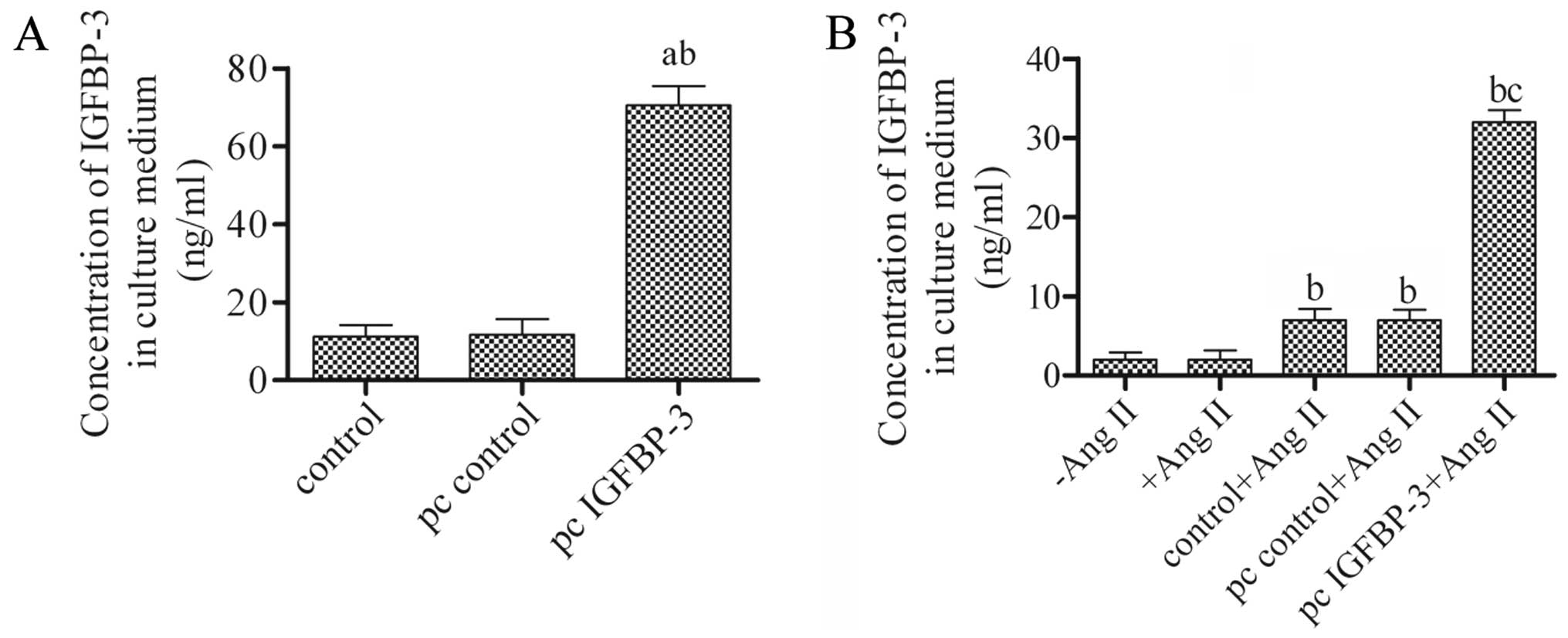
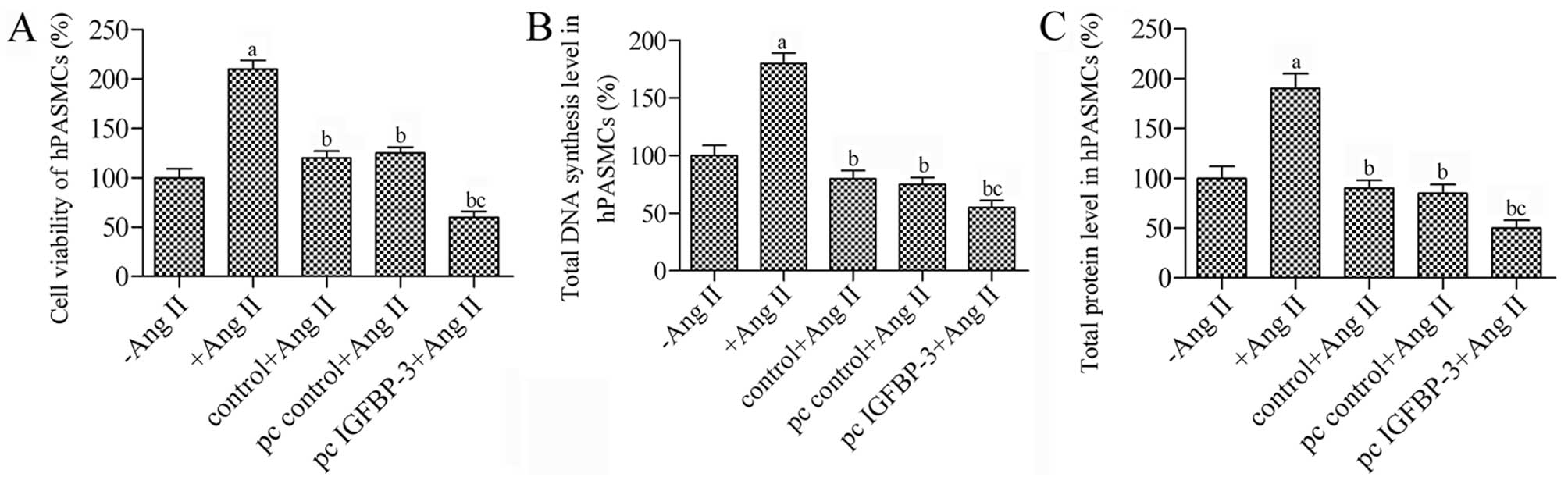
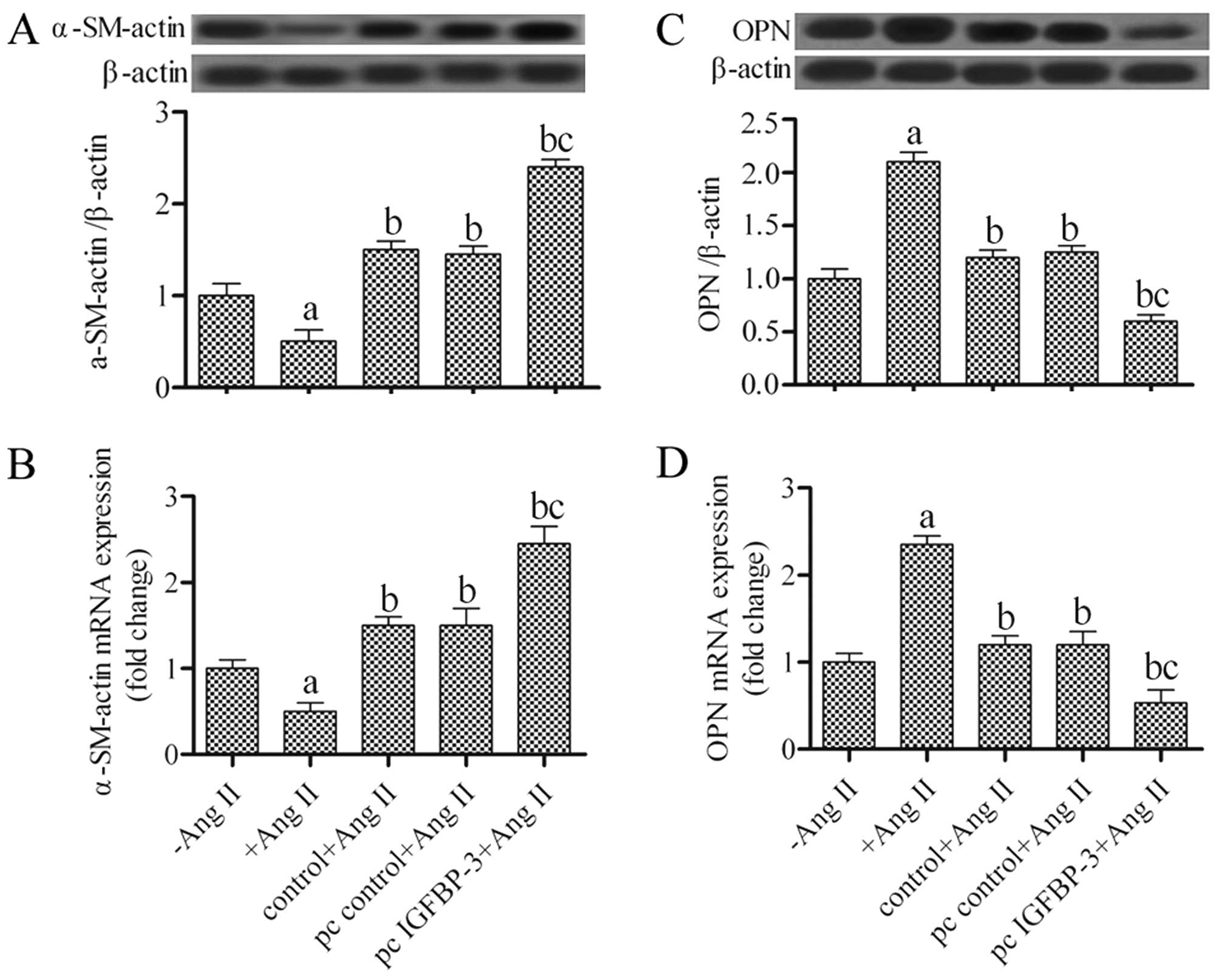
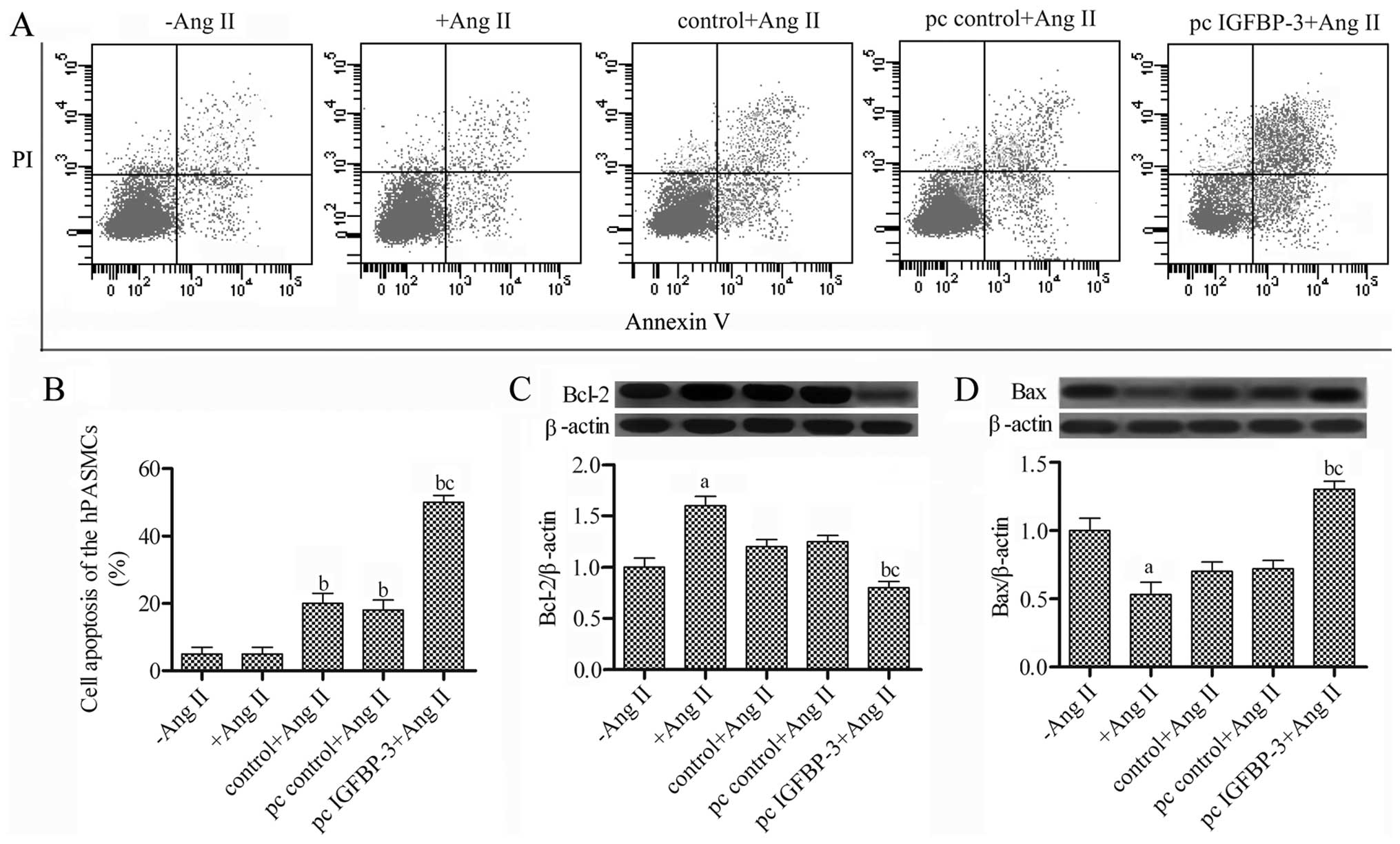
|
1
|
Ibrahim el-SH and Bajwa AA: Severe
pulmonary arterial hypertension: Comprehensive evaluation by
magnetic resonance imaging. Case Rep Radiol. 2015:946–920.
2015.
|
|
2
|
Nogueira-Ferreira R, Vitorino R, Ferreira
R and Henriques-Coelho T: Exploring the monocrotaline animal model
for the study of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A network
approach. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 35:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perrin S, Chaumais MC, O'Connell C, Amar
D, Savale L, Jaïs X, Montani D, Humbert M, Simonneau G and Sitbon
O: New pharmacotherapy options for pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 16:2113–2131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weitzenblum E, Chaouat A, Canuet M and
Kessler R: Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease and interstitial lung diseases. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
30:458–470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiao ZC and Liu YB: Treatment advance and
tendency of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Med Engineering.
23:257–260. 2016.In Chinese.
|
|
6
|
Wang CH and An Y: Progress of stem cell
treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chin J Clin Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 23:294–298. 2016.In Chinese.
|
|
7
|
Firth AL, Yao W, Ogawa A, Madani MM, Lin
GY and Yuan JX: Multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells are
present in endarterectomized tissues from patients with chronic
thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C1217–C1225. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takemiya K, Kai H, Yasukawa H, Tahara N,
Kato S and Imaizumi T: Mesenchymal stem cell-based prostacyclin
synthase gene therapy for pulmonary hypertension rats. Basic Res
Cardiol. 105:409–417. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bach LA: Insulin-like growth factor
binding proteins - an update. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 13:521–530.
2015.
|
|
10
|
Kielczewski JL, Jarajapu YP, McFarland EL,
Cai J, Afzal A, Li Calzi S, Chang KH, Lydic T, Shaw LC, Busik J, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 mediates vascular
repair by enhancing nitric oxide generation. Circ Res. 105:897–905.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moser DR, Lowe WL Jr, Dake BL, Booth BA,
Boes M, Clemmons DR and Bar RS: Endothelial cells express
insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins 2 to 6. Mol Endocrinol.
6:1805–1814. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Johnson MA and Firth SM: IGFBP-3: A cell
fate pivot in cancer and disease. Growth Horm IGF Res. 24:164–173.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valentinis B, Bhala A, DeAngelis T,
Baserga R and Cohen P: The human insulin-like growth factor (IGF)
binding protein-3 inhibits the growth of fibroblasts with a
targeted disruption of the IGF-I receptor gene. Mol Endocrinol.
9:361–367. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lofqvist C, Chen J, Connor KM, Smith AC,
Aderman CM, Liu N, Pintar JE, Ludwig T, Hellstrom A and Smith LE:
IGFBP3 suppresses retinopathy through suppression of oxygen-induced
vessel loss and promotion of vascular regrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:10589–10594. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tajsic T and Morrell NW: Smooth muscle
cell hypertrophy, proliferation, migration and apoptosis in
pulmonary hypertension. Compr Physiol. 1:295–317. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen PK, Shi B, Long XP, Liu ZJ, Wang ZL
and Wang DM: Effects of rat mesenchymal stem cells modified by CGRP
on proliferation and phenotype transformation of vascular smooth
muscle cells in vitro. Chin J Pathophysiology. 29:1777–1782.
2013.In Chinese.
|
|
17
|
Su XY, Jiang XM and Chen SL: The
expression profile of IGFBP family in pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells of rats with pulmonary hypertension. Zhonghua
Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 9:1143–1148. 2015.In Chinese.
|
|
18
|
Schinköthe T, Bloch W and Schmidt A: In
vitro secreting profile of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells
Dev. 17:199–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Firth SM, Ganeshprasad U and Baxter RC:
Structural determinants of ligand and cell surface binding of
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3. J Biol Chem.
273:2631–2638. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia Y, Bhattacharyya A, Roszell EE, Sandig
M and Mequanint K: The role of endothelial cell-bound Jagged1 in
Notch3-induced human coronary artery smooth muscle cell
differentiation. Biomaterials. 33:2462–2472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Liu G, Cai D, Pan B, Lin Y, Li X, Li
S, Zhu L, Liao X and Wang H: H2S inhibition of chemical
hypoxia-induced proliferation of HPASMCs is mediated by the
upregulation of COX-2/PGI2. Int J Mol Med. 33:359–366. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Tian HY, Yan XL, Fan FL, Wang WP,
Han JL, Zhang JB, Ma Q, Meng Y and Wei F: Serotonin inhibits
apoptosis of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell by pERK1/2 and PDK
through 5-HT1B receptors and 5-HT transporters. Cardiovasc Pathol.
22:451–457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Squillaro T, Peluso G and Galderisi U:
Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: An update. Cell
Transplant. 25:829–848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Baraniak PR and McDevitt TC: Stem cell
paracrine actions and tissue regeneration. Regen Med. 5:121–143.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Chen JY, An R, Liu ZJ, Wang JJ, Chen SZ,
Hong MM, Liu JH, Xiao MY and Chen YF: Therapeutic effects of
mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles on pulmonary arterial
hypertension in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1121–1128. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Agostini-Dreyer A, Jetzt AE, Stires H and
Cohick WS: Endogenous IGFBP-3 mediates intrinsic apoptosis through
modulation of Nur77 phosphorylation and nuclear export.
Endocrinology. 156:4141–4151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Muzumdar RH, Ma X, Fishman S, Yang X,
Atzmon G, Vuguin P, Einstein FH, Hwang D, Cohen P and Barzilai N:
Central and opposing effects of IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-3 on
systemic insulin action. Diabetes. 55:2788–2796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chan SS, Twigg SM, Firth SM and Baxter RC:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 leads to insulin
resistance in adipocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90:6588–6595.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang RL, Lin JW, Hsieh DJ, Yeh YL, Shen
CY, Day CH, Ho TJ, Viswanadha VP, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Long-term
hypoxia exposure enhanced IGFBP-3 protein synthesis and secretion
resulting in cell apoptosis in H9c2 myocardial cells. Growth
Factors. 33:275–281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blouin MJ, Bazile M, Birman E, Zakikhani
M, Florianova L, Aleynikova O, Powell DR and Pollak M: Germ line
knockout of IGFBP-3 reveals influences of the gene on mammary gland
neoplasia. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 149:577–585. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Wilkins MR and
Grimminger F: Mechanisms of disease: Pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. 8:443–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mandegar M, Fung YC, Huang W, Remillard
CV, Rubin LJ and Yuan JX: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of
pulmonary vascular remodeling: Role in the development of pulmonary
hypertension. Microvasc Res. 68:75–103. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jeffery TK and Morrell NW: Molecular and
cellular basis of pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary
hypertension. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 45:173–202. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mohanraj L, Kim HS, Li W, Cai Q, Kim KE,
Shin HJ, Lee YJ, Lee WJ, Kim JH and Oh Y: IGFBP-3 inhibits
cytokine-induced insulin resistance and early manifestations of
atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 8:e550842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu J, Yu Z and Su D: BMP4 protects rat
pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells from apoptosis by
PI3K/AKT/Smad1/5/8 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 15:13738–13754. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kiss T and Kovacs K, Komocsi A, Tornyos A,
Zalan P, Sumegi B, Gallyas F Jr and Kovacs K: Novel mechanisms of
sildenafil in pulmonary hypertension involving
cytokines/chemokines, MAP kinases and Akt. PLoS One. 9:e1048902014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Garat CV, Crossno JT Jr, Sullivan TM,
Reusch JE and Klemm DJ: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery
remodeling and suppresses CREB depletion in arterial smooth muscle
cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 62:539–548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Biasin V, Chwalek K, Wilhelm J, Best J,
Marsh LM, Ghanim B, Klepetko W, Fink L, Schermuly RT, Weissmann N,
et al: Endothelin-1 driven proliferation of pulmonary arterial
smooth muscle cells is c-fos dependent. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
54:137–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mendivil A, Zhou C, Cantrell LA, Gehrig
PA, Malloy KM, Blok LJ, Burger CW and Bae-Jump VL: AMG 479, a novel
IGF-1-R antibody, inhibits endometrial cancer cell proliferation
through disruption of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. Reprod Sci.
18:832–841. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zha Z, Zhang QH, Jiang ZX, Chen L, Lin H
and Liang XM: Effect of angiotensin II on pregnancy-associated
plasma protein A and insulin-like growth factor 1 gene expression
in human umbilical artery smooth muscle cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da
Xue Xue Bao. 29:195–198. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|