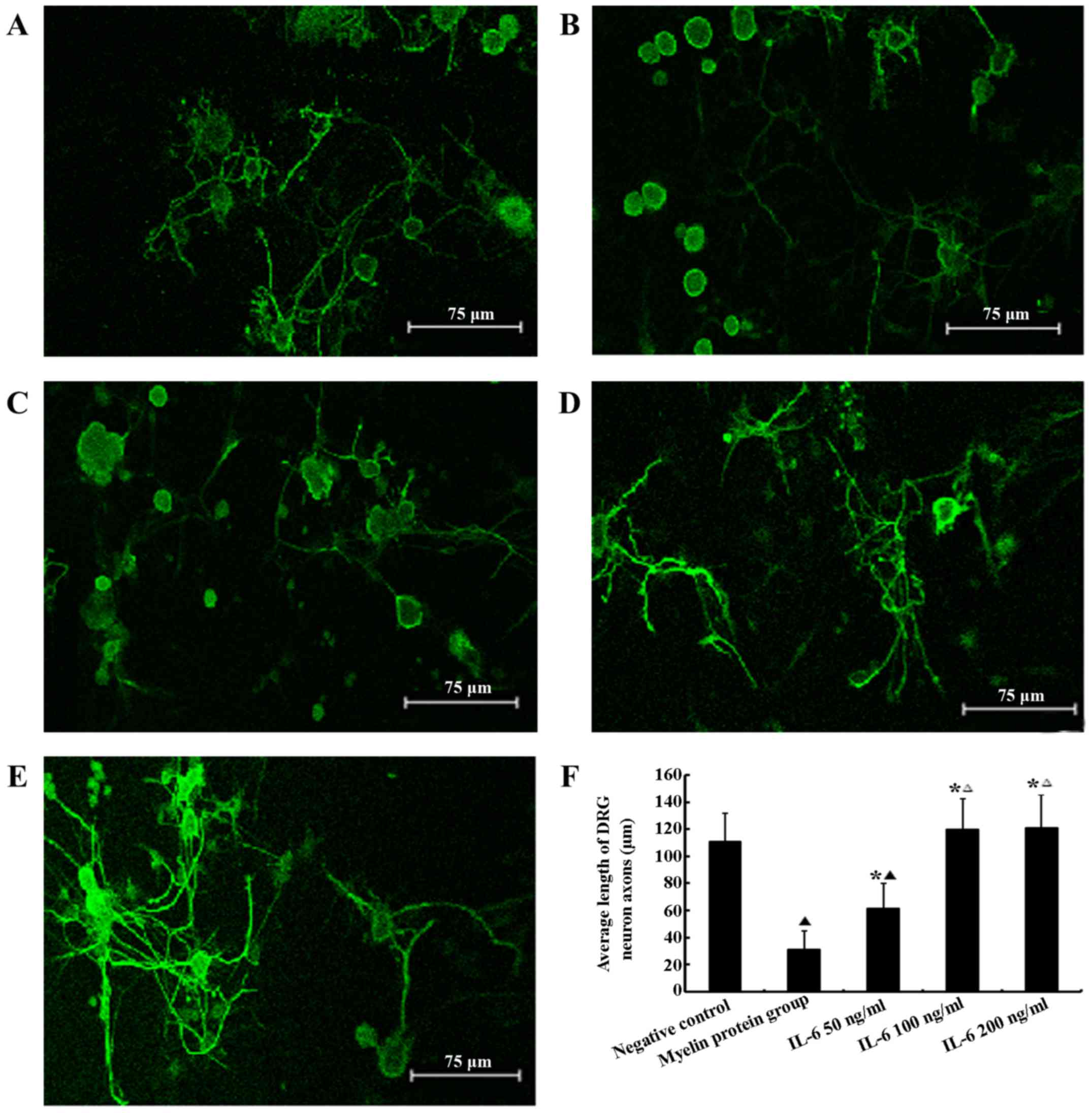
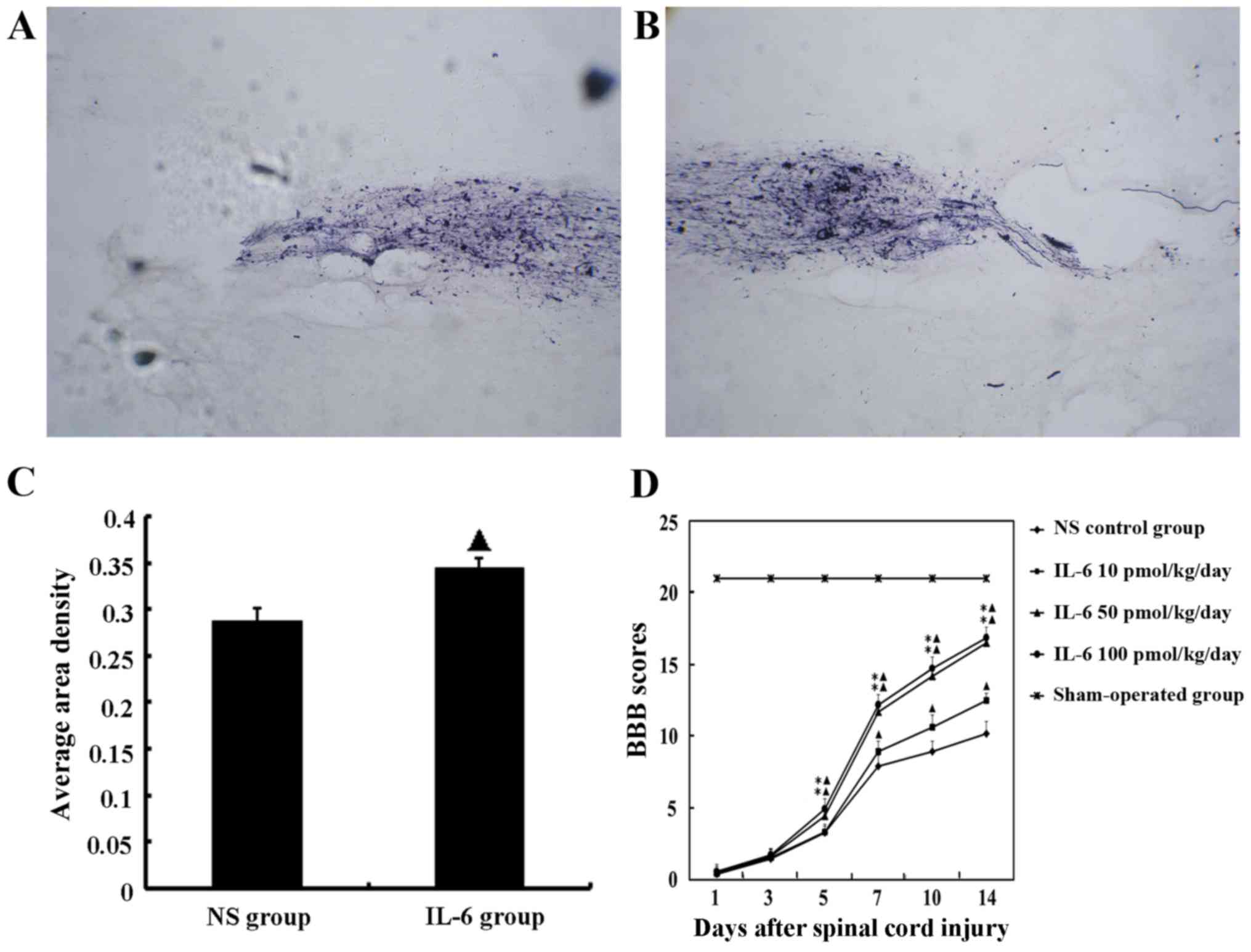
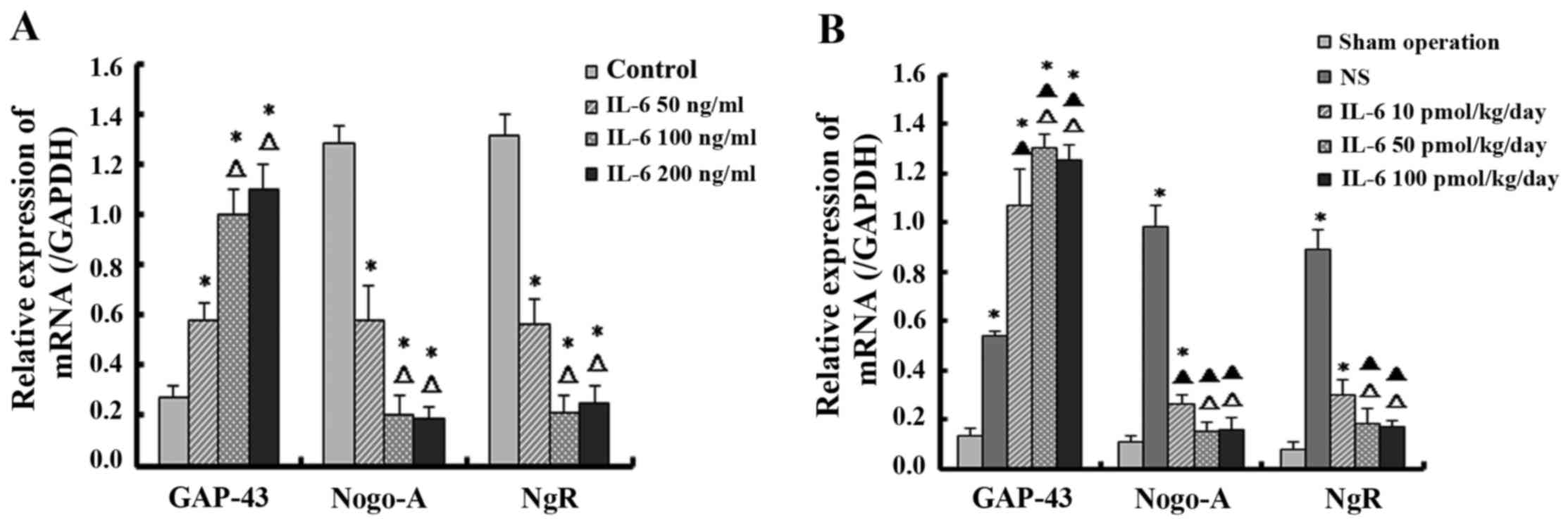
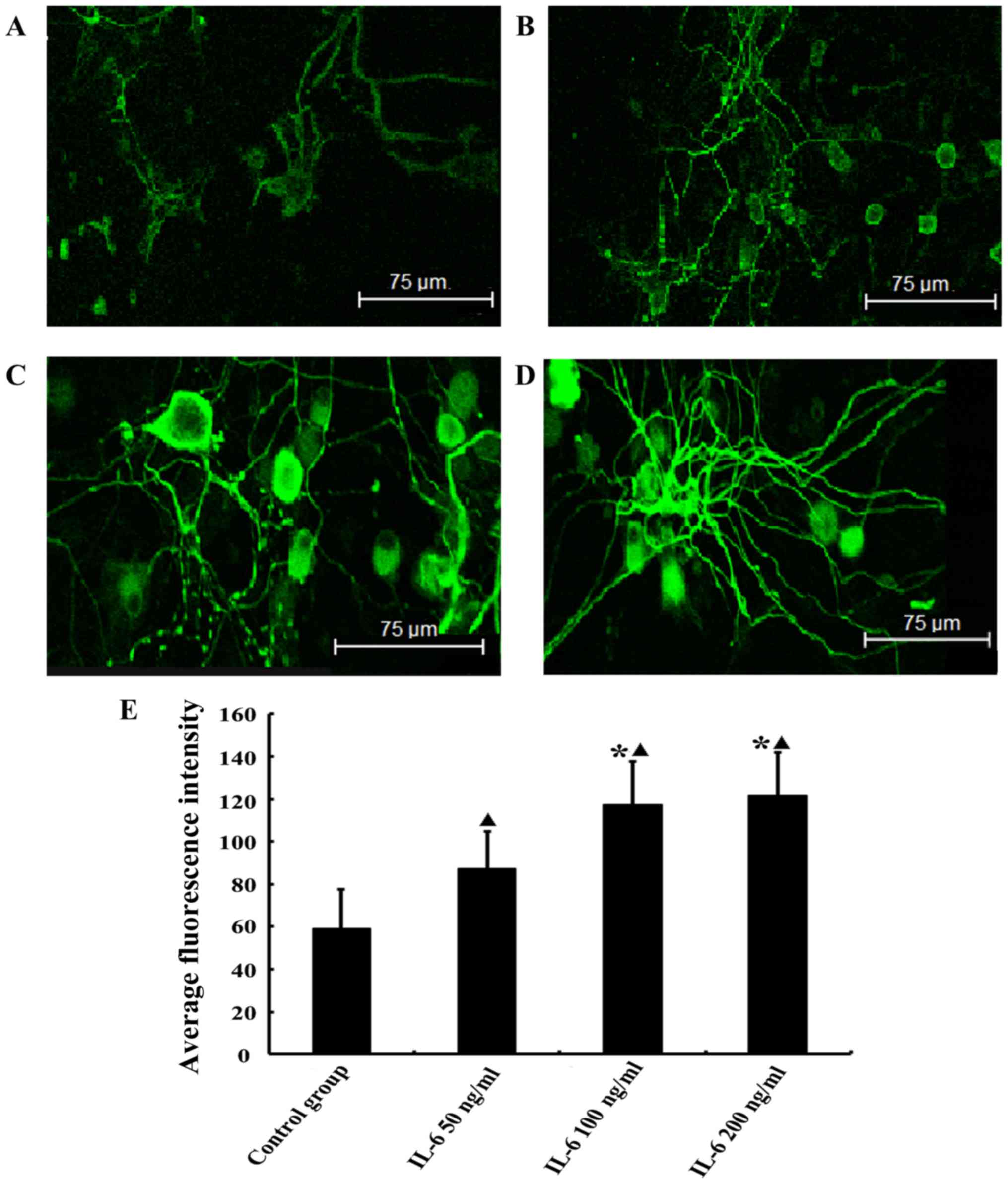
|
1
|
Wang KC, Koprivica V, Kim JA, Sivasankaran
R, Guo Y, Neve RL and He Z: Oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is
a Nogo receptor ligand that inhibits neurite outgrowth. Nature.
417:941–944. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Filbin MT: Myelin-associated inhibitors of
axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci.
4:703–713. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geoffroy CG and Zheng B: Myelin-associated
inhibitors in axonal growth after CNS injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
27:31–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JK and Zheng B: Role of
myelin-associated inhibitors in axonal repair after spinal cord
injury. Exp Neurol. 235:33–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Leibinger M, Andreadaki A, Diekmann H and
Fischer D: Neuronal STAT3 activation is essential for CNTF- and
inflammatory stimulation-induced CNS axon regeneration. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e8052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hakkoum D, Stoppini L and Muller D:
Interleukin-6 promotes sprouting and functional recovery in
lesioned organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurochem.
100:747–757. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chidlow G, Wood JP, Ebneter A and Casson
RJ: Interleukin-6 is an efficacious marker of axonal transport
disruption during experimental glaucoma and stimulates
neuritogenesis in cultured retinal ganglion cells. Neurobiol Dis.
48:568–581. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang T, Xiong JQ, Ren XB and Sun W: The
role of Nogo-A in neuroregeneration: a review. Brain Res Bull.
87:499–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pernet V and Schwab ME: The role of Nogo-A
in axonal plasticity, regrowth and repair. Cell Tissue Res.
349:97–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu CH, Yhee JY, Kim JH, Im KS, Kim NH,
Jung DI, Lee HC, Chon SK and Sur JH: Pro- and anti-inflammatory
cytokine expression and histopathological characteristics in canine
brain with traumatic brain injury. J Vet Sci. 12:299–301. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okada S, Nakamura M, Mikami Y, Shimazaki
T, Mihara M, Ohsugi Y, Iwamoto Y, Yoshizaki K, Kishimoto T, Toyama
Y, et al: Blockade of interleukin-6 receptor suppresses reactive
astrogliosis and ameliorates functional recovery in experimental
spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res. 76:265–276. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guerrero AR, Uchida K, Nakajima H,
Watanabe S, Nakamura M, Johnson WE and Baba H: Blockade of
interleukin-6 signaling inhibits the classic pathway and promotes
an alternative pathway of macrophage activation after spinal cord
injury in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 9:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang XQ, Peng YP, Lu JH, Cao BB and Qiu
YH: Neuroprotection of interleukin-6 against NMDA attack and its
signal transduction by JAK and MAPK. Neurosci Lett. 450:122–126.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ou S, Zhao YD, Xiao Z, Wen HZ, Cui J and
Ruan HZ: Effect of lappaconitine on neuropathic pain mediated by
P2X3 receptor in rat dorsal root ganglion. Neurochem
Int. 58:564–573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bareyre FM, Haudenschild B and Schwab ME:
Long-lasting sprouting and gene expression changes induced by the
monoclonal antibody IN-1 in the adult spinal cord. J Neurosci.
22:7097–7110. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsushita H, Endo S, Kobayashi E,
Sakamoto Y, Kobayashi K, Kitaguchi K, Kuroki K, Söderhäll A,
Maenaka K, Nakamura A, et al: Differential but competitive binding
of Nogo protein and class i major histocompatibility complex (MHCI)
to the PIR-B ectodomain provides an inhibition of cells. J Biol
Chem. 286:25739–25747. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao Z, Gao Y, Bryson JB, Hou J, Chaudhry
N, Siddiq M, Martinez J, Spencer T, Carmel J, Hart RB, et al: The
cytokine interleukin-6 is sufficient but not necessary to mimic the
peripheral conditioning lesion effect on axonal growth. J Neurosci.
26:5565–5573. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Siddiq MM and Hannila SS: Looking
downstream: the role of cyclic AMP-regulated genes in axonal
regeneration. Front Mol Neurosci. 8:262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hannila SS and Filbin MT: The role of
cyclic AMP signaling in promoting axonal regeneration after spinal
cord injury. Exp Neurol. 209:321–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lau BY, Fogerson SM, Walsh RB and Morgan
JR: Cyclic AMP promotes axon regeneration, lesion repair and
neuronal survival in lampreys after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol.
250:31–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peace AG and Shewan DA: New perspectives
in cyclic AMP-mediated axon growth and guidance: the emerging epoch
of Epac. Brain Res Bull. 84:280–288. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schumann G, Huell M, Machein U, Hocke G
and Fiebich BL: Interleukin-6 activates signal transducer and
activator of transcription and mitogen-activated protein kinase
signal transduction pathways and induces de novo protein synthesis
in human neuronal cells. J Neurochem. 73:2009–2017. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pizzi M, Sarnico I, Boroni F, Benarese M,
Dreano M, Garotta G, Valerio A and Spano P: Prevention of neuron
and oligodendrocyte degeneration by interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-6
receptor/IL-6 fusion protein in organotypic hippocampal slices. Mol
Cell Neurosci. 25:301–311. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Agthong S, Koonam J, Kaewsema A and
Chentanez V: Inhibition of MAPK ERK impairs axonal regeneration
without an effect on neuronal loss after nerve injury. Neurol Res.
31:1068–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu RY and Snider WD: Different signaling
pathways mediate regenerative versus developmental sensory axon
growth. J Neurosci. 21:RC1642001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wiklund P, Ekström PA and Edström A:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition reveals differences in
signalling pathways activated by neurotrophin-3 and other
growth-stimulating conditions of adult mouse dorsal root ganglia
neurons. J Neurosci Res. 67:62–68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Teng FY and Tang BL: Axonal regeneration
in adult CNS neurons - signaling molecules and pathways. J
Neurochem. 96:1501–1508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hellenbrand DJ, Kaeppler KE, Hwang E,
Ehlers ME, Toigo RD, Giesler JD, Vassar-Olsen ER and Hanna A: Basic
techniques for long distance axon tracing in the spinal cord.
Microsc Res Tech. 76:1240–1249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grasselli G, Mandolesi G, Strata P and
Cesare P: Impaired sprouting and axonal atrophy in cerebellar
climbing fibres following in vivo silencing of the
growth-associated protein GAP-43. PLoS One. 6:e207912011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan Q, Hu B, Su H, So KF, Lin Z and Wu W:
GAP-43 expression correlates with spinal motoneuron regeneration
following root avulsion. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj.
4:182009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Strittmatter SM: GAP-43 as a modulator of
G protein transduction in the growth cone. Perspect Dev Neurobiol.
1:13–19. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fenrich KK, Skelton N, MacDermid VE,
Meehan CF, Armstrong S, Neuber-Hess MS and Rose PK: Axonal
regeneration and development of de novo axons from distal dendrites
of adult feline commissural interneurons after a proximal axotomy.
J Comp Neurol. 502:1079–1097. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Denny JB: Molecular mechanisms, biological
actions, and neuropharmacology of the growth-associated protein
GAP-43. Curr Neuropharmacol. 4:293–304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huo Y, Yin XL, Ji SX, Zou H, Lang M, Zheng
Z, Cai XF, Liu W, Chen CL, Zhou YG, et al: Amino-Nogo inhibits
optic nerve regeneration and functional recovery via the integrin
αv signaling pathway in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:616–626.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schwab ME and Strittmatter SM: Nogo limits
neural plasticity and recovery from injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol.
27:53–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kempf A and Schwab ME: Nogo-A represses
anatomical and synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system.
Physiology (Bethesda). 28:151–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wälchli T, Pernet V, Weinmann O, Shiu JY,
Guzik-Kornacka A, Decrey G, Yüksel D, Schneider H, Vogel J, Ingber
DE, et al: Nogo-A is a negative regulator of CNS angiogenesis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1943–E1952. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ahmed Z, Dent RG, Suggate EL, Barrett LB,
Seabright RJ, Berry M and Logan A: Disinhibition of
neurotrophin-induced dorsal root ganglion cell neurite outgrowth on
CNS myelin by siRNA-mediated knockdown of NgR, p75NTR
and Rho-A. Mol Cell Neurosci. 28:509–523. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang T, Wang J, Yin C, Liu R, Zhang JH and
Qin X: Down-regulation of Nogo receptor promotes functional
recovery by enhancing axonal connectivity after experimental stroke
in rats. Brain Res. 1360:147–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|