|
1
|
Kanno Y and Loewenstein WR: Low-resistance
coupling between gland cells. Some observations on intercellular
contact membranes and intercellular space. Nature. 201:194–195.
1964. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lawrence TS, Beers WH and Gilula NB:
Transmission of hormonal stimulation by cell-to-cell communication.
Nature. 272:501–506. 1978. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou JZ and Jiang JX: Gap junction and
hemichannel-independent actions of connexins on cell and tissue
functions - an update. FEBS Lett. 588:1186–1192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Electrophysiological
mechanisms of long and short QT syndromes: Insights from mouse
models. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. In press.
|
|
5
|
Veeraraghavan R, Lin J, Hoeker GS, Keener
JP, Gourdie RG and Poelzing S: Sodium channels in the Cx43 gap
junction perinexus may constitute a cardiac ephapse: An
experimental and modeling study. Pflugers Arch. 467:2093–2105.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Veeraraghavan R, Gourdie RG and Poelzing
S: Mechanisms of cardiac conduction: A history of revisions. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 306:H619–H627. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koval M, Isakson BE and Gourdie RG:
Connexins, pannexins and innexins: Protein cousins with overlapping
functions. FEBS Lett. 588:11852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tse G: Both transmural dispersion of
repolarization and transmural dispersion of refractoriness are poor
predictors of arrhythmogenicity: A role for the index of Cardiac
Electrophysiological Balance (QT/QRS)? J Geriatr Cardiol. In
press.
|
|
9
|
Harris AL: Emerging issues of connexin
channels: Biophysics fills the gap. Q Rev Biophys. 34:325–472.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Söhl G and Willecke K: Gap junctions and
the connexin protein family. Cardiovasc Res. 62:228–232. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ke Q, Li L, Cai B, Liu C, Yang Y, Gao Y,
Huang W, Yuan X, Wang T, Zhang Q, et al: Connexin 43 is involved in
the generation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Mol
Genet. 22:2221–2233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Becker DL, Thrasivoulou C and Phillips AR:
Connexins in wound healing; perspectives in diabetic patients.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:2068–2075. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Crespo Yanguas S, Willebrords J, Maes M,
da Silva TC, Veloso Alves Pereira I, Cogliati B, Zaidan Dagli ML
and Vinken M: Connexins and pannexins in liver damage. EXCLI J.
15:177–186. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tse G and Yeo JM: Conduction abnormalities
and ventricular arrhythmogenesis: The roles of sodium channels and
gap junctions. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 9:75–82. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Goldberg GS, Valiunas V and Brink PR:
Selective permeability of gap junction channels. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1662:96–101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilgenbus KK, Kirkpatrick CJ, Knuechel R,
Willecke K and Traub O: Expression of Cx26, Cx32 and Cx43 gap
junction proteins in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Int J
Cancer. 51:522–529. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bukauskas FF and Verselis VK: Gap junction
channel gating. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1662:42–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao L, Sachs F and Dahl G: Connexins are
mechanosensitive. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 287:C1389–C1395. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tse G, Yeo JM, Tse V, Kwan J and Sun B:
Gap junction inhibition by heptanol increases ventricular
arrhythmogenicity by reducing conduction velocity without affecting
repolarization properties or myocardial refractoriness in
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Mol Med Rep. 14:4069–4074.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Musil LS and Goodenough DA: Biochemical
analysis of connexin43 intracellular transport, phosphorylation,
and assembly into gap junctional plaques. J Cell Biol.
115:1357–1374. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bennett MV and Verselis VK: Biophysics of
gap junctions. Semin Cell Biol. 3:29–47. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meyer RA, Lampe PD, Malewicz B, Baumann WJ
and Johnson RG: Enhanced gap junction formation with LDL and
apolipoprotein B. Exp Cell Res. 196:72–81. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meyer R, Malewicz B, Baumann WJ and
Johnson RG: Increased gap junction assembly between cultured cells
upon cholesterol supplementation. J Cell Sci. 96:231–238.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Carroll SJ, Becker DL, Davidson JO, Gunn
AJ, Nicholson LF and Green CR: The use of connexin-based
therapeutic approaches to target inflammatory diseases. Methods Mol
Biol. 1037:519–546. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Beyer EC and Berthoud VM: Gap junction
synthesis and degradation as therapeutic targets. Curr Drug
Targets. 3:409–416. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Plum A, Hallas G, Magin T, Dombrowski F,
Hagendorff A, Schumacher B, Wolpert C, Kim J, Lamers WH, Evert M,
et al: Unique and shared functions of different connexins in mice.
Curr Biol. 10:1083–1091. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scott CA, Tattersall D, O'Toole EA and
Kelsell DP: Connexins in epidermal homeostasis and skin disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:1952–1961. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Richard G: Connexin disorders of the skin.
Clin Dermatol. 23:23–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Labarthe MP, Bosco D, Saurat JH, Meda P
and Salomon D: Upregulation of connexin 26 between keratinocytes of
psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 111:72–76. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lucke T, Choudhry R, Thom R, Selmer IS,
Burden AD and Hodgins MB: Upregulation of connexin 26 is a feature
of keratinocyte differentiation in hyperproliferative epidermis,
vaginal epithelium, and buccal epithelium. J Invest Dermatol.
112:354–361. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Djalilian AR, McGaughey D, Patel S, Seo
EY, Yang C, Cheng J, Tomic M, Sinha S, Ishida-Yamamoto A and Segre
JA: Connexin 26 regulates epidermal barrier and wound remodeling
and promotes psoriasiform response. J Clin Invest. 116:1243–1253.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iossa S, Marciano E and Franzé A: GJB2
gene mutations in syndromic skin diseases with sensorineural
hearing loss. Curr Genomics. 12:475–785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Levit NA and White TW: Connexin
hemichannels influence genetically determined inflammatory and
hyperproliferative skin diseases. Pharmacol Res. 99:337–343. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Masgrau-Peya E, Salomon D, Saurat JH and
Meda P: In vivo modulation of connexins 43 and 26 of human
epidermis by topical retinoic acid treatment. J Histochem Cytochem.
45:1207–1215. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kanady JD, Dellinger MT, Munger SJ, Witte
MH and Simon AM: Connexin37 and Connexin43 deficiencies in mice
disrupt lymphatic valve development and result in lymphatic
disorders including lymphedema and chylothorax. Dev Biol.
354:253–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Meens MJ, Sabine A, Petrova TV and Kwak
BR: Connexins in lymphatic vessel physiology and disease. FEBS
Lett. 588:1271–1277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wick N, Saharinen P, Saharinen J,
Gurnhofer E, Steiner CW, Raab I, Stokic D, Giovanoli P, Buchsbaum
S, Burchard A, et al: Transcriptomal comparison of human dermal
lymphatic endothelial cells ex vivo and in vitro. Physiol Genomics.
28:179–192. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Finegold DN, Schacht V, Kimak MA, Lawrence
EC, Foeldi E, Karlsson JM, Baty CJ and Ferrell RE: HGF and MET
mutations in primary and secondary lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol.
6:65–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Finegold DN, Baty CJ, Knickelbein KZ,
Perschke S, Noon SE, Campbell D, Karlsson JM, Huang D, Kimak MA,
Lawrence EC, et al: Connexin 47 mutations increase risk for
secondary lymphedema following breast cancer treatment. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2382–2390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Losa D and Chanson M: The lung
communication network. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:2793–2808. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Freund-Michel V, Muller B, Marthan R,
Savineau JP and Guibert C: Expression and role of connexin-based
gap junctions in pulmonary inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Ther.
164:105–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Okamoto T, Akiyama M, Takeda M, Gabazza
EC, Hayashi T and Suzuki K: Connexin32 is expressed in vascular
endothelial cells and participates in gap-junction intercellular
communication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 382:264–268. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ram A, Singh SK, Singh VP, Kumar S and
Ghosh B: Inhaled carbenoxolone prevents allergic airway
inflammation and airway hyperreactivity in a mouse model of asthma.
Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 149:38–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tamaya T, Sato S and Okada HH: Possible
mechanism of steroid action of the plant herb extracts
glycyrrhizin, glycyrrhetinic acid, and paeoniflorin: Inhibition by
plant herb extracts of steroid protein binding in the rabbit. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 155:1134–1139. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park SJ, Lee KS, Kim SR, Min KH, Lee KY,
Choe YH, Park SY, Hong SH and Lee YC: Change of connexin 37 in
allergen-induced airway inflammation. Exp Mol Med. 39:629–640.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koval M, Billaud M, Straub AC, Johnstone
SR, Zarbock A, Duling BR and Isakson BE: Spontaneous lung
dysfunction and fibrosis in mice lacking connexin 40 and
endothelial cell connexin 43. Am J Pathol. 178:2536–2546. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim J, Hwangbo C, Hu X, Kang Y, Papangeli
I, Mehrotra D, Park H, Ju H, McLean DL, Comhair SA, et al:
Restoration of impaired endothelial myocyte enhancer factor 2
function rescues pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation.
131:190–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang J, Wang W, Sun J, Li Q, Liu J, Zhu
H, Chen T, Wang H, Yu S and Sun G: Gap junction channel modulates
pulmonary vascular permeability through calcium in acute lung
injury: An experimental study. Respiration. 80:236–245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chadjichristos CE, Scheckenbach KE, van
Veen TA, Richani Sarieddine MZ, de Wit C, Yang Z, Roth I, Bacchetta
M, Viswambharan H and Foglia B: Endothelial-specific deletion of
connexin40 promotes atherosclerosis by increasing CD73-dependent
leukocyte adhesion. Circulation. 121:123–131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Rignault S, Haefliger JA, Waeber B,
Liaudet L and Feihl F: Acute inflammation decreases the expression
of connexin 40 in mouse lung. Shock. 28:78–85. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
O'Donnell JJ III, Birukova AA, Beyer EC
and Birukov KG: Gap junction protein connexin43 exacerbates lung
vascular permeability. PLoS One. 9:e1009312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kasper M, Traub O, Reimann T, Bjermer L,
Grossmann H, Müller M and Wenzel KW: Upregulation of gap junction
protein connexin43 in alveolar epithelial cells of rats with
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem Cell Biol.
106:419–424. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fernandez-Cobo M, Gingalewski C and De
Maio A: Expression of the connexin 43 gene is increased in the
kidneys and the lungs of rats injected with bacterial
lipopolysaccharide. Shock. 10:97–102. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Yang GM, Zhu Y, Peng XY, Li T and
Liu LM: Role of connexin 43 in vascular hyperpermeability and
relationship to Rock1-MLC20 pathway in septic rats. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L1323–L1332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Molina SA, Stauffer B, Moriarty HK, Kim
AH, McCarty NA and Koval M: Junctional abnormalities in human
airway epithelial cells expressing F508del CFTR. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L475–L487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Trovato-Salinaro A, Trovato-Salinaro E,
Failla M, Mastruzzo C, Tomaselli V, Gili E, Crimi N, Condorelli DF
and Vancheri C: Altered intercellular communication in lung
fibroblast cultures from patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Respir Res. 7:1222006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Montani D, Günther S, Dorfmüller P, Perros
F, Girerd B, Garcia G, Jaïs X, Savale L, Artaud-Macari E, Price LC,
et al: Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
8:972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yen CH, Leu S, Lin YC, Kao YH, Chang LT,
Chua S, Fu M, Wu CJ, Sun CK and Yip HK: Sildenafil limits
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats through
suppression of pulmonary vascular remodeling. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 55:574–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
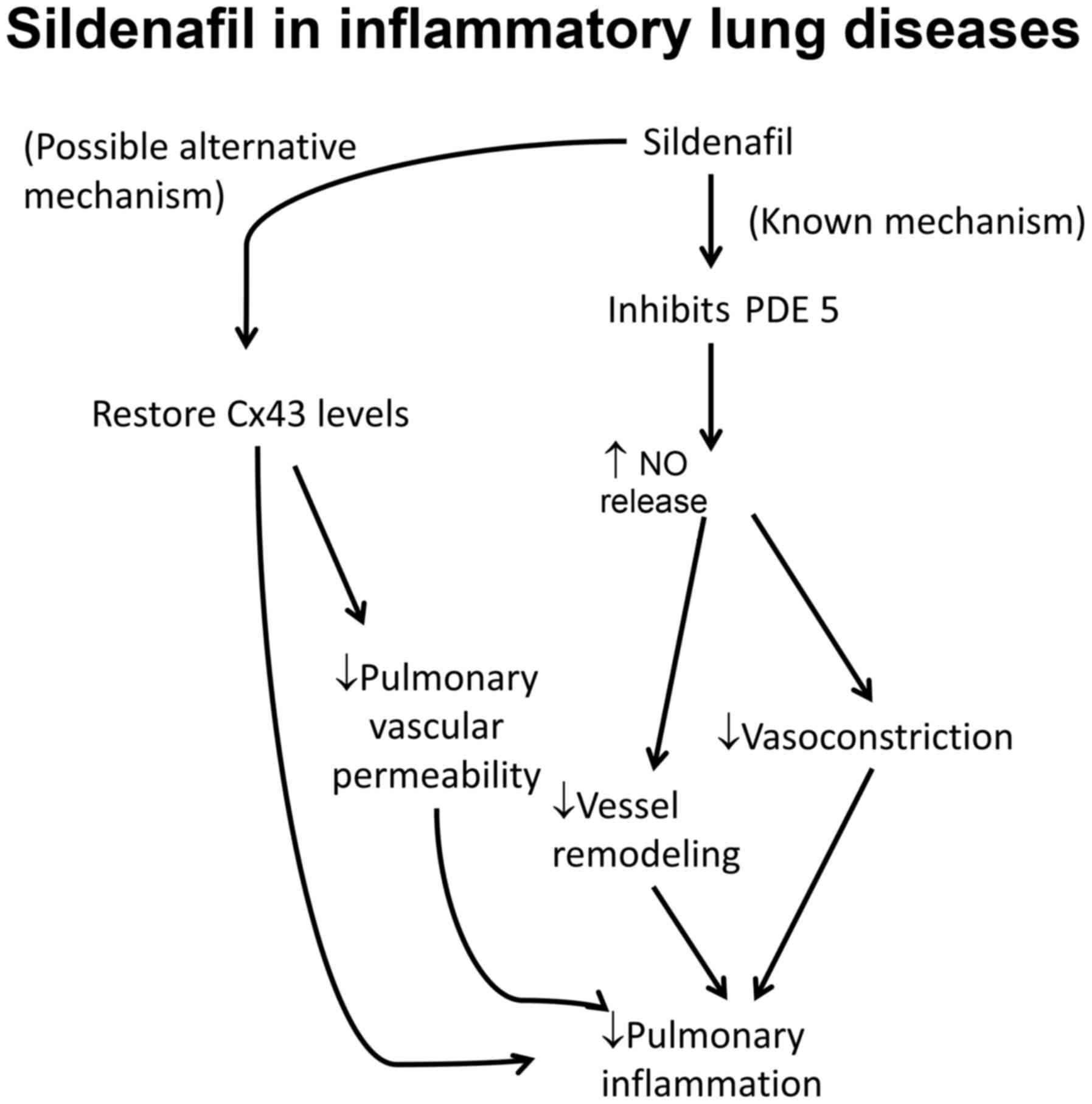
59
|
Gairhe S, Bauer NN, Gebb SA and McMurtry
IF: Myoendothelial gap junctional signaling induces differentiation
of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 301:L527–L535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Segretain D and Falk MM: Regulation of
connexin biosynthesis, assembly, gap junction formation, and
removal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1662:3–21. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Patel SJ, King KR, Casali M and Yarmush
ML: DNA-triggered innate immune responses are propagated by gap
junction communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12867–12872.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Naiki-Ito A, Asamoto M, Naiki T, Ogawa K,
Takahashi S, Sato S and Shirai T: Gap junction dysfunction reduces
acetaminophen hepatotoxicity with impact on apoptotic signaling and
connexin 43 protein induction in rat. Toxicol Pathol. 38:280–286.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Asamoto M, Hokaiwado N, Murasaki T and
Shirai T: Connexin 32 dominant-negative mutant transgenic rats are
resistant to hepatic damage by chemicals. Hepatology. 40:205–210.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hokaiwado N, Asamoto M, Futakuchi M, Ogawa
K, Takahashi S and Shirai T: Both early and late stages of
hepatocarcinogenesis are enhanced in Cx32 dominant negative mutant
transgenic rats with disrupted gap junctional intercellular
communication. J Membr Biol. 218:101–106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Maes M, McGill MR, da Silva TC, Abels C,
Lebofsky M, Maria Monteiro, de Araújo C, Tiburcio T, Veloso Alves
Pereira I, Willebrords J, Crespo Yanguas S, et al: Involvement of
connexin43 in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1862:1111–1121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Balasubramaniyan V, Dhar DK, Warner AE,
Vivien Li WY, Amiri AF, Bright B, Mookerjee RP, Davies NA, Becker
DL and Jalan R: Importance of connexin-43 based gap junction in
cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol.
58:1194–1200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gotthardt D, Riediger C, Weiss KH, Encke
J, Schemmer P, Schmidt J and Sauer P: Fulminant hepatic failure:
etiology and indications for liver transplantation. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 22(Suppl 8): viii5–viii8. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Maes M, McGill MR, da Silva TC, Lebofsky
M, Maria Monteiro, de Araújo C, Tiburcio T, Veloso Alves Pereira I,
Willebrords J, Crespo Yanguas S, Farhood A, et al: Connexin32: A
mediator of acetaminophen-induced liver injury? Toxicol Mech
Methods. 26:88–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Igarashi I, Maejima T, Kai K, Arakawa S,
Teranishi M and Sanbuissho A: Role of connexin 32 in acetaminophen
toxicity in a knockout mice model. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 66:103–110.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Du K, Williams CD, McGill MR, Xie Y,
Farhood A, Vinken M and Jaeschke H: The gap junction inhibitor
2-aminoethoxy-diphenyl-borate protects against acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity by inhibiting cytochrome P450 enzymes and c-jun
N-terminal kinase activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 273:484–491.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Patel SJ, Milwid JM, King KR, Bohr S,
Iracheta-Vellve A, Li M, Vitalo A, Parekkadan B, Jindal R and
Yarmush ML: Gap junction inhibition prevents drug-induced liver
toxicity and fulminant hepatic failure. Nat Biotechnol. 30:179–183.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ogawa K, Pitchakarn P, Suzuki S,
Chewonarin T, Tang M, Takahashi S, Naiki-Ito A, Sato S, Takahashi
S, Asamoto M, et al: Silencing of connexin 43 suppresses invasion,
migration and lung metastasis of rat hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Cancer Sci. 103:860–867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang D, Kaneda M, Nakahama K, Arii S and
Morita I: Connexin 43 expression promotes malignancy of HuH7
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the inhibition of cell-cell
communication. Cancer Lett. 252:208–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ionta M, Ferreira RA, Pfister SC and
Machado-Santelli GM: Exogenous Cx43 expression decrease cell
proliferation rate in rat hepatocarcinoma cells independently of
functional gap junction. Cancer Cell Int. 9:222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Igarashi I, Makino T, Suzuki Y, Kai K,
Teranishi M, Takasaki W and Furuhama K: Background lesions during a
24-month observation period in connexin 32-deficient mice. J Vet
Med Sci. 75:207–210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Loch-Caruso R, Galvez MM, Brant K and
Chung D: Cell and toxicant specific phosphorylation of conexin43:
Effects of lindane and TPA on rat myometrial and WB-F344 liver cell
gap junctions. Cell Biol Toxicol. 20:147–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mograbi B, Corcelle E, Defamie N, Samson
M, Nebout M, Segretain D, Fénichel P and Pointis G: Aberrant
connexin 43 endocytosis by the carcinogen lindane involves
activation of the ERK/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 24:1415–1423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Caruso RL, Upham BL, Harris C and Trosko
JE: Biphasic lindane-induced oxidation of glutathione and
inhibition of gap junctions in myometrial cells. Toxicol Sci.
86:417–426. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Defamie N, Mograbi B, Roger C, Cronier L,
Malassine A, Brucker-Davis F, Fenichel P, Segretain D and Pointis
G: Disruption of gap junctional intercellular communication by
lindane is associated with aberrant localization of connexin43 and
zonula occludens-1 in 42GPA9 Sertoli cells. Carcinogenesis.
22:1537–1542. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van't Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Plante I, Stewart MK, Barr K, Allan AL and
Laird DW: Cx43 suppresses mammary tumor metastasis to the lung in a
Cx43 mutant mouse model of human disease. Oncogene. 30:1681–1692.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Sirnes S, Bruun J, Kolberg M, Kjenseth A,
Lind GE, Svindland A, Brech A, Nesbakken A, Lothe RA, Leithe E, et
al: Connexin43 acts as a colorectal cancer tumor suppressor and
predicts disease outcome. Int J Cancer. 131:570–581. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
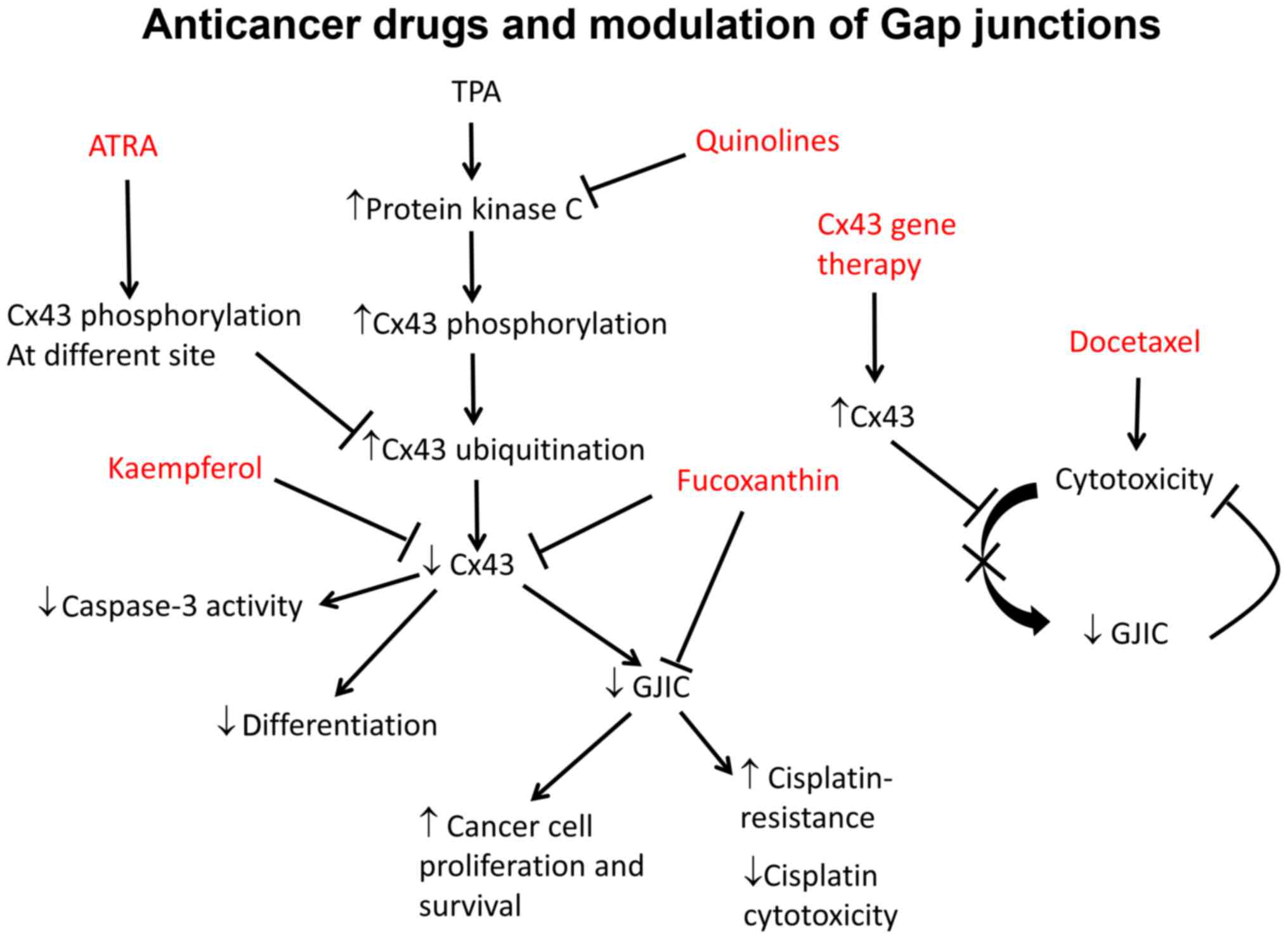
Bernzweig J, Heiniger B, Prasain K, Lu J,
Hua DH and Nguyen TA: Anti-breast cancer agents, quinolines,
targeting gap junction. Med Chem. 7:448–453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu CL, Huang YS, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K
and Hu ML: Inhibition of proliferation of a hepatoma cell line by
fucoxanthin in relation to cell cycle arrest and enhanced gap
junctional inter-cellular communication. Chem Biol Interact.
182:165–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Soobrattee MA, Bahorun T and Aruoma OI:
Chemopreventive actions of polyphenolic compounds in cancer.
Biofactors. 27:19–35. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wang L, Zeng Y, Liu Y, Hu X, Li S, Wang Y,
Li L, Lei Z and Zhang Z: Fucoxanthin induces growth arrest and
apoptosis in human bladder cancer T24 cells by up-regulation of p21
and down-regulation of mortalin. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 46:877–884. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Marchenko ND, Zaika A and Moll UM: Death
signal-induced localization of p53 protein to mitochondria. A
potential role in apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
275:16202–16212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Januar HI, Dewi AS, Marraskuranto E and
Wikanta T: In silico study of fucoxanthin as a tumor cytotoxic
agent. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 4:56–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Nakamura Y, Chang CC, Mori T, Sato K,
Ohtsuki K, Upham BL and Trosko JE: Augmentation of differentiation
and gap junction function by kaempferol in partially differentiated
colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:665–671. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Ding Y and Nguyen TA: Gap junction
enhancer potentiates cytotoxicity of cisplatin in breast cancer
cells. J Cancer Sci Ther. 4:371–378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sáez CG, Velásquez L, Montoya M, Eugenín E
and Alvarez MG: Increased gap junctional intercellular
communication is directly related to the anti-tumor effect of
all-trans-retinoic acid plus tamoxifen in a human mammary cancer
cell line. J Cell Biochem. 89:450–461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wernyj RP and Morin PJ: Molecular
mechanisms of platinum resistance: Still searching for the
Achilles' heel. Drug Resist Updat. 7:227–232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Peterson-Roth E, Brdlik CM and Glazer PM:
Src-Induced cisplatin resistance mediated by cell-to-cell
communication. Cancer Res. 69:3619–3624. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Isakov N, Bleackley RC, Shaw J and Altman
A: Teleocidin and phorbol ester tumor promoters exert similar
mitogenic effects on human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
130:724–731. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Procopio A, Gismondi A, Paolini R, Morrone
S, Testi R, Piccoli M, Frati L, Herberman RB and Santoni A:
Proliferative effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)
and calcium ionophores on human large granular lymphocytes (LGL).
Cell Immunol. 113:70–81. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Bigelow K and Nguyen TA: Increase of gap
junction activities in SW480 human colorectal cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 14:5022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Leithe E and Rivedal E: Ubiquitination and
down-regulation of gap junction protein connexin-43 in response to
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate treatment. J Biol Chem.
279:50089–50096. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Solomon VR and Lee H: Quinoline as a
privileged scaffold in cancer drug discovery. Curr Med Chem.
18:1488–1508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lim YC, Kang HJ, Kim YS and Choi EC:
All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits growth of head and neck cancer
stem cells by suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Cancer.
48:3310–3318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ara C, Massimi M and Devirgiliis Conti L:
Retinoic acid modulates gap junctional intercellular communication
in hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1758–1765.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang J, Dai Y, Huang Y, Chen X, Wang H,
Hong Y, Xia J and Cheng B: All-trans retinoic acid restores gap
junctional intercellular communication between oral cancer cells
with upregulation of Cx32 and Cx43 expressions in vitro. Med Oral
Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 18:e569–e577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Belliveau DJ, Bechberger JF, Rogers KA and
Naus CC: Differential expression of gap junctions in neurons and
astrocytes derived from P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Dev Genet.
21:187–200. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bani-Yaghoub M, Bechberger JF and Naus CC:
Reduction of connexin43 expression and dye-coupling during neuronal
differentiation of human NTera2/clone D1 cells. J Neurosci Res.
49:19–31. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Rudkin GH, Carlsen BT, Chung CY, Huang W,
Ishida K, Anvar B, Yamaguchi DT and Miller TA: Retinoids inhibit
squamous cell carcinoma growth and intercellular communication. J
Surg Res. 103:183–189. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Picus J and Schultz M: Docetaxel
(Taxotere) as monotherapy in the treatment of hormone-refractory
prostate cancer: Preliminary results. Semin Oncol. 26(Suppl 17):
14–18. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Petrylak DP, Tangen CM, Hussain MH, Lara
PN Jr, Jones JA, Taplin ME, Burch PA, Berry D, Moinpour C, Kohli M,
et al: Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and
prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:1513–1520. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Hwang C: Overcoming docetaxel resistance
in prostate cancer: A perspective review. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
4:329–340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Fukushima M, Hattori Y, Yoshizawa T and
Maitani Y: Combination of non-viral connexin 43 gene therapy and
docetaxel inhibits the growth of human prostate cancer in mice. Int
J Oncol. 30:225–231. 2007.
|
|
109
|
Tang N, Wang Q, Wu D, Zhang S, Zhang Y and
Tao L: Differential effects of paclitaxel and docetaxel on gap
junctions affects their cytotoxicities in transfected HeLa cells.
Mol Med Rep. 8:638–644. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang M, Berthoud VM and Beyer EC:
Connexin43 increases the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to
TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 120:320–329. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nomura S, Maeda K, Noda E, Inoue T,
Fukunaga S, Nagahara H and Hirakawa K: Clinical significance of the
expression of connexin26 in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Knösel T, Emde A, Schlüns K, Chen Y,
Jürchott K, Krause M, Dietel M and Petersen I: Immunoprofiles of 11
biomarkers using tissue microarrays identify prognostic subgroups
in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia. 7:741–747. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Mesnil M, Krutovskikh V, Piccoli C,
Elfgang C, Traub O, Willecke K and Yamasaki H: Negative growth
control of HeLa cells by connexin genes: Connexin species
specificity. Cancer Res. 55:629–639. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Goulet AC, Watts G, Lord JL and Nelson MA:
Profiling of selenomethionine responsive genes in colon cancer by
microarray analysis. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:494–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Dilber MS and Gahrton G: Suicide gene
therapy: Possible applications in haematopoietic disorders. J
Intern Med. 249:359–367. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
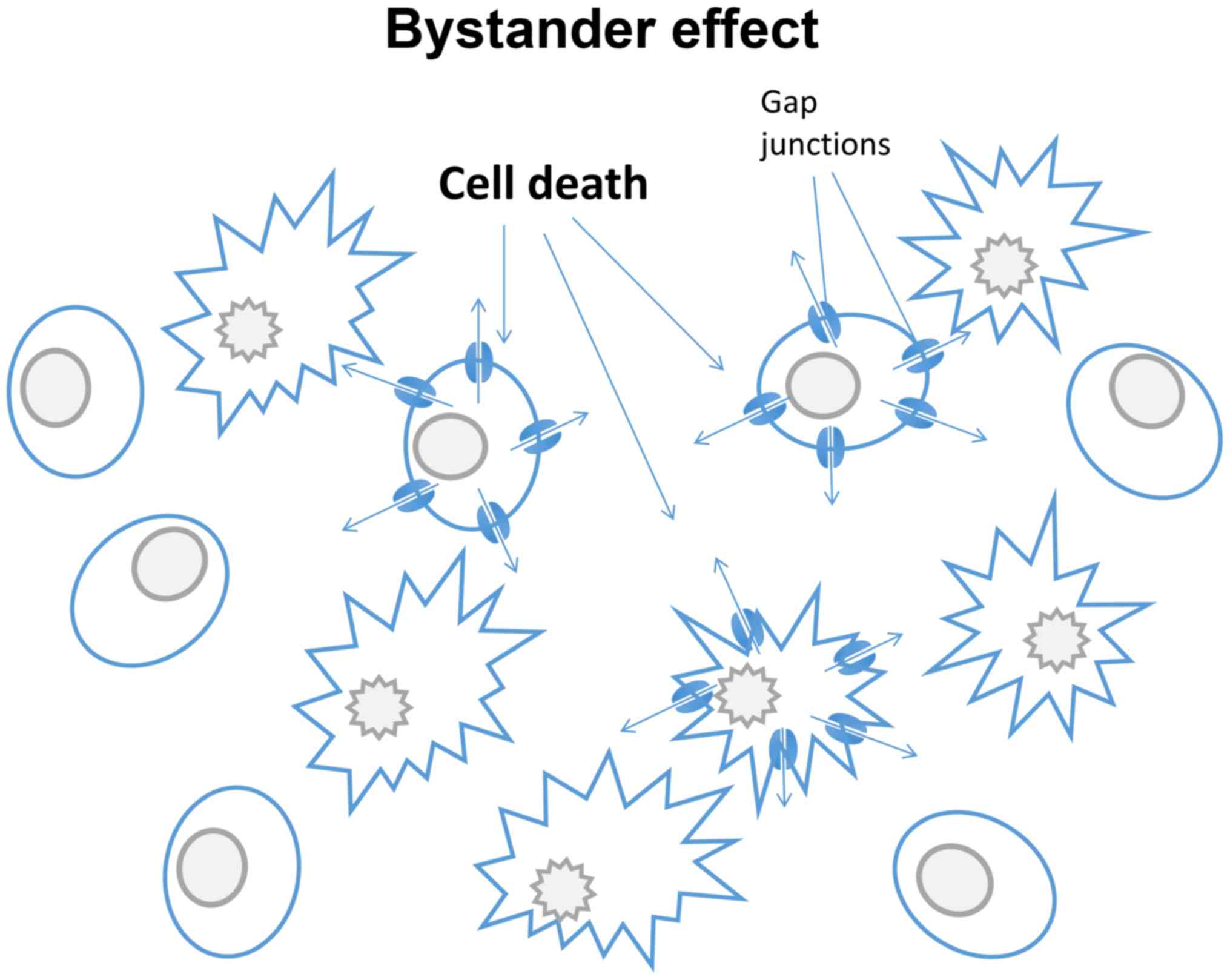
Mesnil M, Piccoli C, Tiraby G, Willecke K
and Yamasaki H: Bystander killing of cancer cells by herpes simplex
virus thymidine kinase gene is mediated by connexins. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:1831–1835. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Boucher PD, Ruch RJ and Shewach DS:
Differential ganciclovir-mediated cytotoxicity and bystander
killing in human colon carcinoma cell lines expressing herpes
simplex virus thymidine kinase. Hum Gene Ther. 9:801–814. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Grek CL, Rhett JM and Ghatnekar GS:
Cardiac to cancer: Connecting connexins to clinical opportunity.
FEBS Lett. 588:1349–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Tanaka T, Yamasaki H and Mesnil M:
Induction of a bystander effect in HeLa cells by using a bigenic
vector carrying viral thymidine kinase and connexin32 genes. Mol
Carcinog. 30:176–180. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Mesnil M and Yamasaki H: Bystander effect
in herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase/ganciclovir cancer gene
therapy: Role of gap-junctional intercellular communication. Cancer
Res. 60:3989–3999. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM and Little JB:
Direct evidence for the participation of gap junction-mediated
intercellular communication in the transmission of damage signals
from alpha -particle irradiated to nonirradiated cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:473–478. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Eloff BC, Lerner DL, Yamada KA, Schuessler
RB, Saffitz JE and Rosenbaum DS: High resolution optical mapping
reveals conduction slowing in connexin43 deficient mice. Cardiovasc
Res. 51:681–690. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Tse G: Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias.
J Arrhythm. 32:75–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V, Lee YT, Lin HY and
Yeo JM: Cardiac dynamics: Alternans and arrhythmogenesis. J
Arrhythm. 32:411–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Schalper KA, Carvajal-Hausdorf D and
Oyarzo MP: Possible role of hemichannels in cancer. Front Physiol.
5:2372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Depolarization vs. repolarization: What is the mechanism of
ventricular arrhythmogenesis underlying sodium channel
haploinsufficiency in mouse hearts? Acta Physiol (Oxf).
218:234–235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Tse G: (Tpeak-Tend)/QRS and
(Tpeak-Tend)/(QT x QRS): Novel markers for predicting arrhythmic
risk in the Brugada syndrome. Europace. Oct 5–2016.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Determination of action potential wavelength restitution in Scn5a/-
mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome. J Physiol. In
press.
|
|
129
|
Tse G: Novel conduction repolarization
indices for the stratification of arrhythmic risk. J Geriatr
Cardiol. 13:811–812. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Variability in local action potential durations, dispersion of
repolarization and wavelength restitution in aged wild type and
Scn5a/- mouse hearts modelling human Brugada syndrome. J Geriatr
Cardiol. In press.
|
|
131
|
Hu Z, Chen Z, Wang Y, et al: Effects of
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on rabbit carotid and swine
heart models of chronic obliterative arterial disease. Mol Med Rep.
In press.
|
|
132
|
Tse G, Tse V and Yeo JM: Ventricular
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in hypokalaemic,
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:313–324.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Tse G, Tse V, Yeo JM and Sun B: Atrial
anti-arrhythmic effects of heptanol in Langendorff-perfused mouse
hearts. PLoS One. 11:e01488582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Restitution analysis of alternans using dynamic pacing and its
comparison with S1S2 restitution in heptanol-treated, hypokalaemic
Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep. 4:673–680.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Tse G, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Monophasic action potential recordings: Which is the recording
electrode? J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 27:457–462. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Yeo JM, Tse V and Wong SH:
Mechanisms of electrical activation and conduction in the
gastrointestinal system: Lessons from cardiac electrophysiology.
Front Physiol. 7:1822016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Tse V and Yeo JM: Molecular
and electrophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiac
arrhythmogenesis in diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res.
2016:28487592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Yeo JM and Yan BP:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of Bayés syndrome: Insights from
clinical and mouse studies. Front Physiol. 7:1882016.
|
|
139
|
Tse G, Sun B, Wong ST, Tse V and Yeo JM:
Anti-arrhythmic effects of hypercalcaemia treatment in
hyperkalaemic, Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. Biomed Rep.
5:301–310. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Chen Z, Sun B, Tse G, Jiang J and Xu W:
Reversibility of both sinus node dysfunction and reduced HCN4 mRNA
expression level in an atrial tachycardia pacing model of
tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome in rabbit hearts. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 9:8526–8531. 2016.
|
|
141
|
Tse G, Yeo JM, Chan YW, Lai ET and Yan BP:
What is the arrhythmic substrate in viral myocarditis? Insights
from clinical and animal studies. Front Physiol. 7:3082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Choy L, Yeo JM, Tse V, Chan SP and Tse G:
Cardiac disease and arrhythmogenesis: Mechanistic insights from
mouse models. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 12:1–10. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Novel arrhythmic risk
markers incorporating QRS dispersion: QRSd x (Tpeak - Tend)/QRS and
QRSd x (Tpeak - Tend)/(QT x QRS). Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol.
Aug 18–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Tse G, Lai ET, Lee AP, Yan BP and Wong SH:
Electrophysiological mechanisms of gastrointestinal
arrhythmogenesis: Lessons from the heart. Front Physiol.
7:2302016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Tse G and Yan BP: Traditional and novel
electrocardiographic conduction and repolarization markers of
sudden cardiac death. Europace. Oct 4–2016.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Tse G, Yan BP, Chan YW, Tian XY and Huang
Y: Reactive oxygen species, endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction: The link with cardiac arrhythmogenesis.
Front Physiol. 7:3132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Sun B, Chen Z, Gu J, Tse G, Jiang J, Huang
F and Zhao C: Tight junction proteins and gap junction proteins
play important roles in high fat dietary atherosclerosis
pathogenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 9:7969–7976. 2016.
|
|
148
|
Tse G, Ali A, Prasad SK, Vassiliou V and
Raphael CE: Atypical case of post-partum cardiomyopathy: an overlap
syndrome with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy?
BJR|case reports. 1:201501822015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Tse G, Ali A, Alpendurada F, Prasad S,
Raphael CE and Vassiliou V: Tuberculous constrictive pericarditis.
Res Cardiovasc Med. 4:e296142015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Mayosi BM, Ntsekhe M, Bosch J, Pandie S,
Jung H, Gumedze F, Pogue J, Thabane L, Smieja M, Francis V, et al
IMPI Trial Investigators: Prednisolone and Mycobacterium indicus
pranii in tuberculous pericarditis. N Engl J Med. 371:1121–1130.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Vassiliou V, Chin C, Perperoglou A, Tse G,
Ali A, Raphael C, Jabbour A, Newby D, Pennell D, Dweck M and Prasad
S: 93 Ejection fraction by cardiovascular magnetic resonance
predicts adverse outcomes post aortic valve replacement. Heart.
100(Suppl 3): A53–A54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Tse G, Hothi SS, Grace AA and Huang CL:
Ventricular arrhythmogenesis following slowed conduction in
heptanol-treated, Langendorff-perfused mouse hearts. J Physiol Sci.
62:79–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wong J, Tan T, Chan C, Laxton V, Chan Y,
Liu T, Wong J and Tse G: The role of connexins in wound healing and
repair: novel therapeutic approaches. Front Physiol. 7:5962016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|