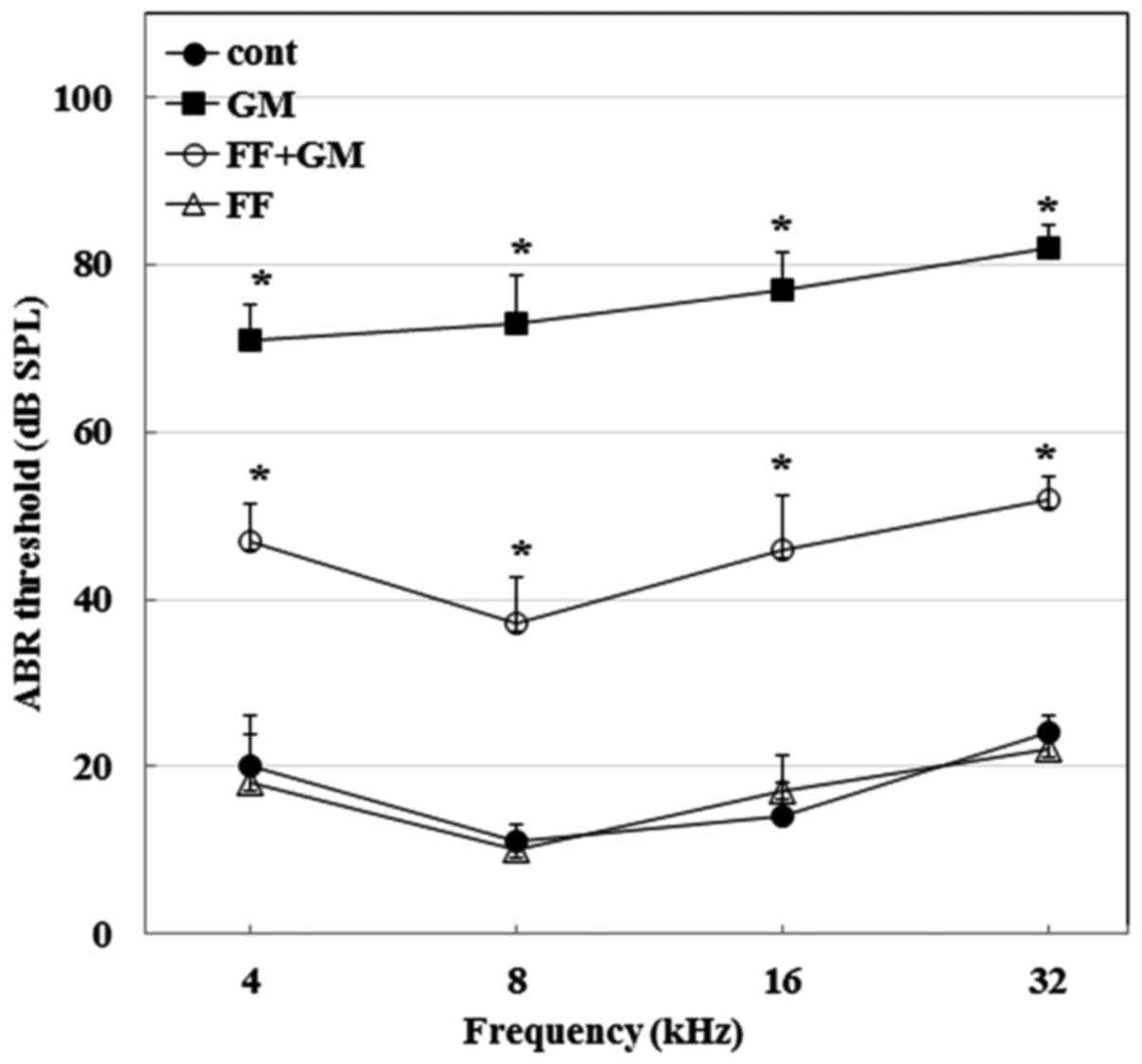
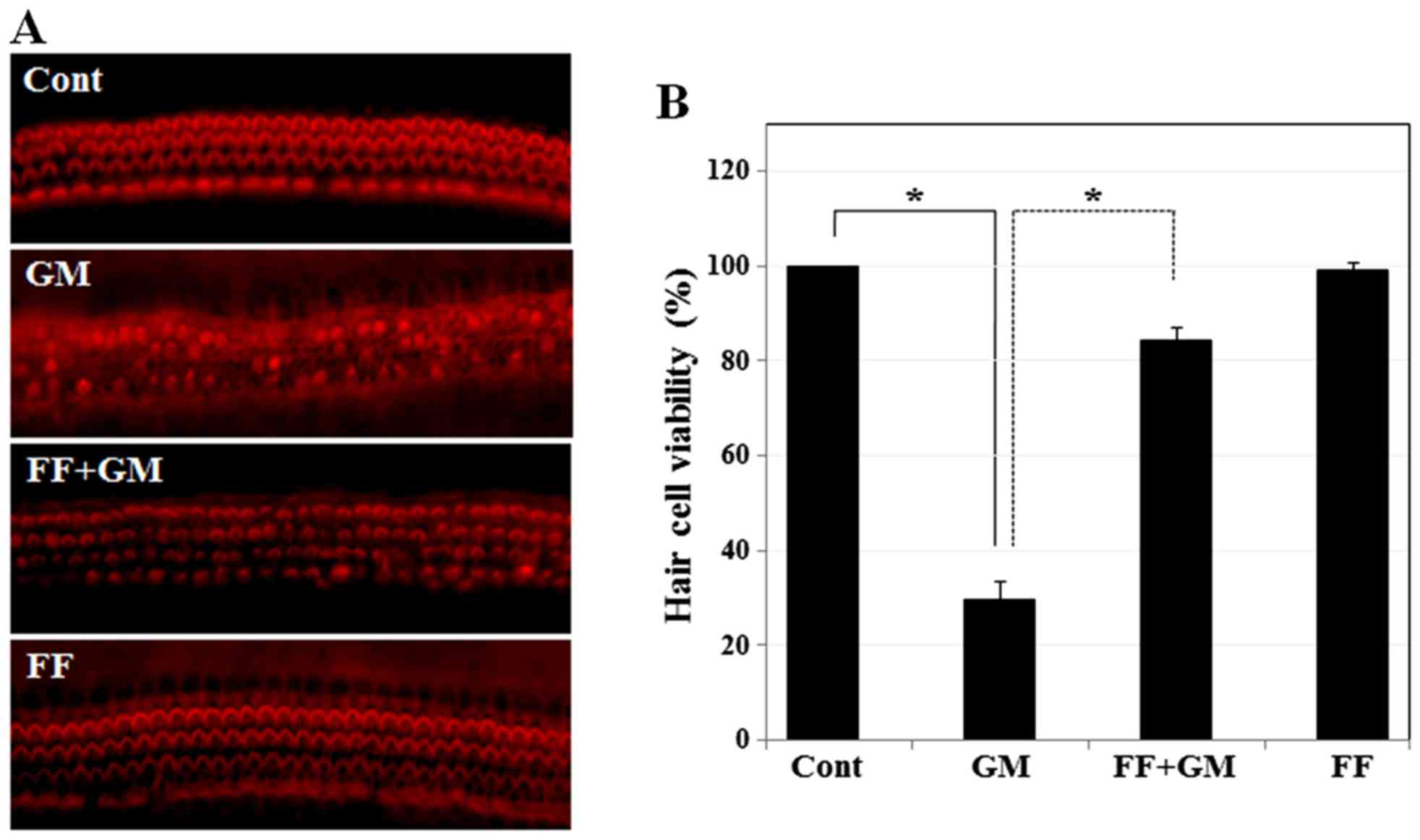
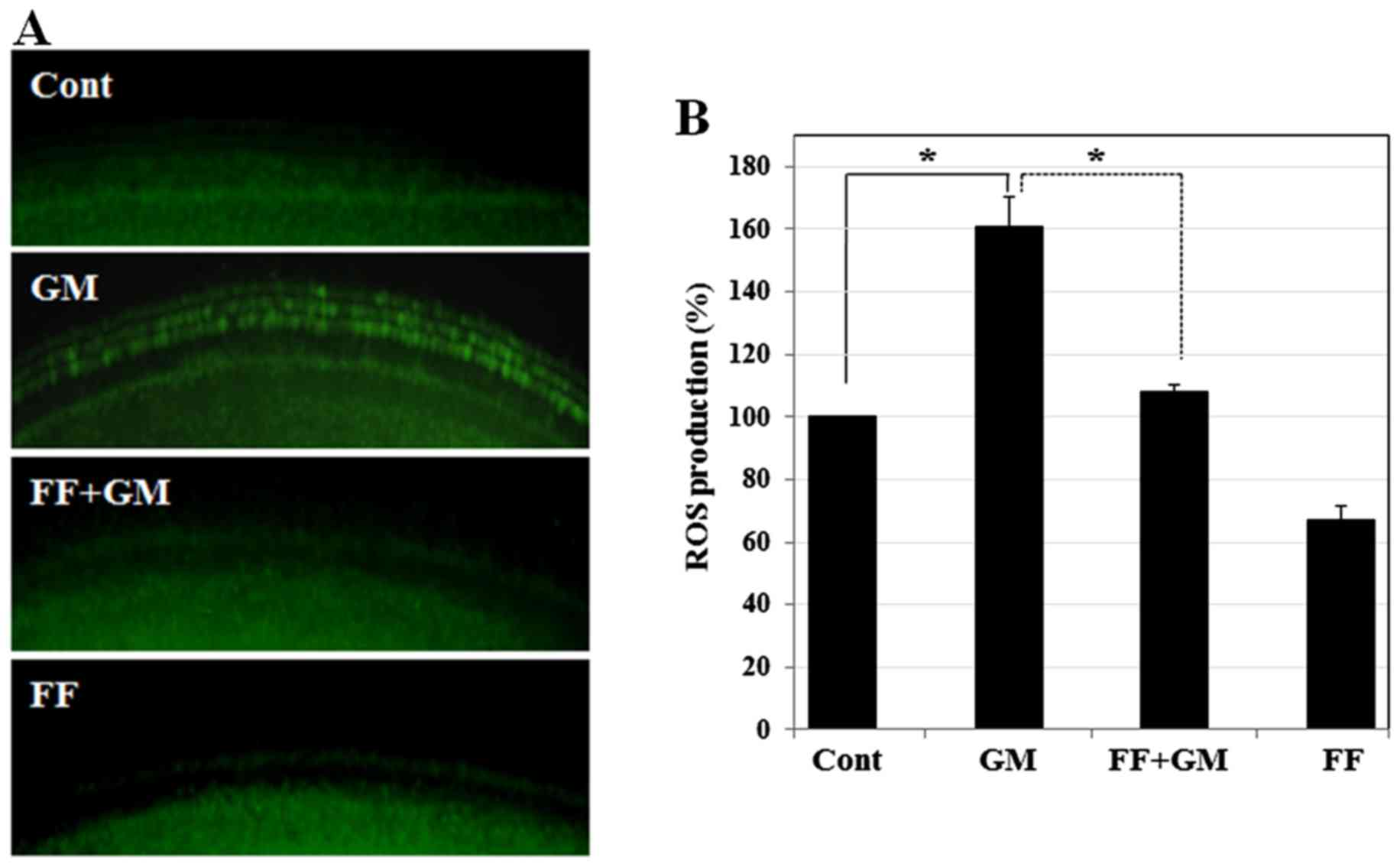
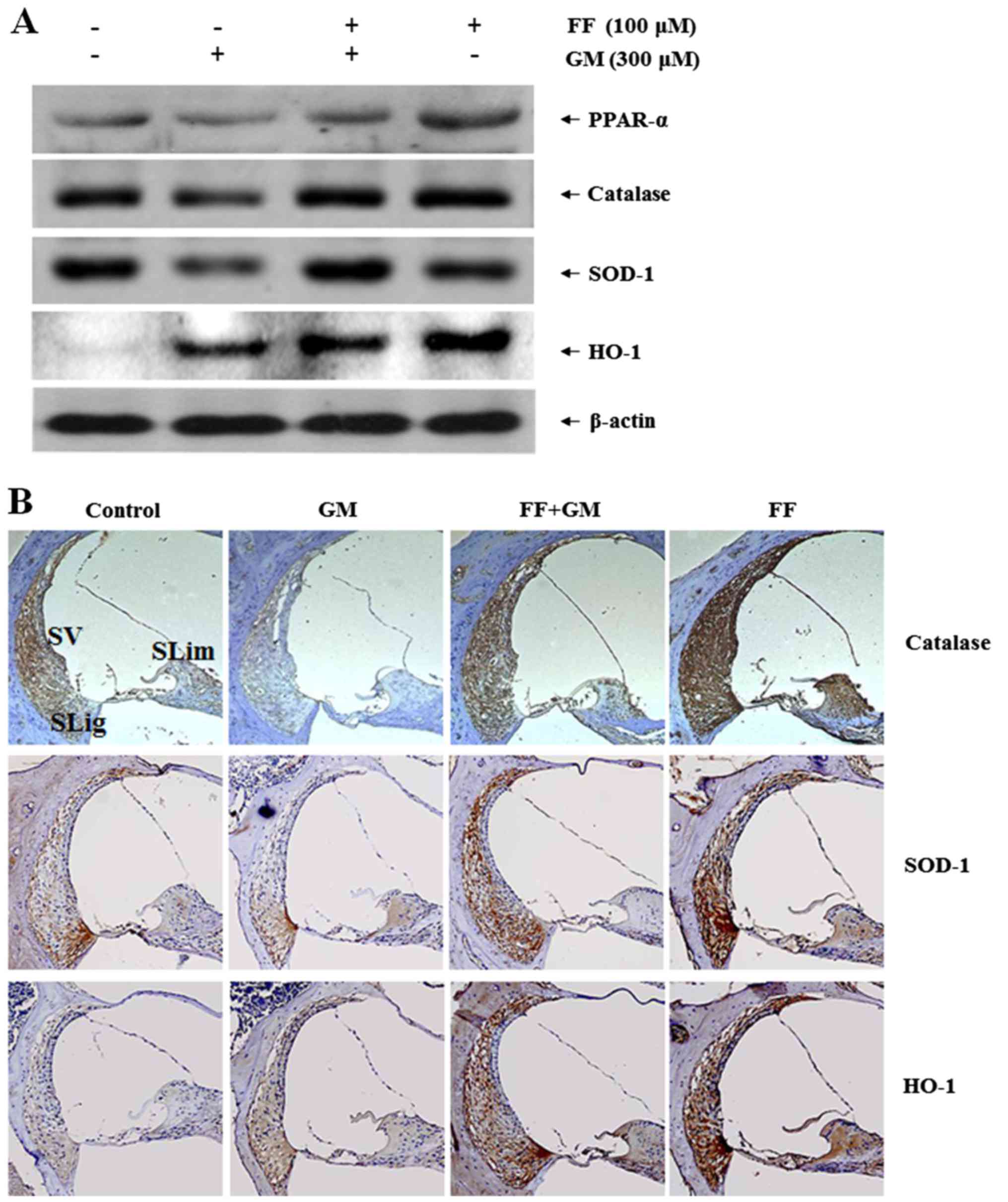
|
1
|
Heller J: Effect of some simple manoeuvres
on the course of acute renal failure after gentamycin treatment in
rats. Int Urol Nephrol. 16:243–251. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jao RL and Jackson GG: Gentamicin sulfate,
new antibiotic against Gram-negative bacilli. Laboratory,
pharmacological, and clinical evaluation. JAMA. 189:817–822. 1964.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Assimakopoulos D and Patrikakos G:
Treatment of Ménière's disease by intratympanic gentamicin
application. J Laryngol Otol. 117:10–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen Y, Huang WG, Zha DJ, Qiu JH, Wang JL,
Sha SH and Schacht J: Aspirin attenuates gentamicin ototoxicity:
from the laboratory to the clinic. Hear Res. 226:178–182. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Heinrich UR, Helling K, Sifferath M,
Brieger J, Li H, Schmidtmann I and Mann WJ: Gentamicin increases
nitric oxide production and induces hearing loss in guinea pigs.
Laryngoscope. 118:1438–1442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
López-González MA, Lucas M, Delgado F and
Diaz P: The production of free oxygen radicals and nitric oxide in
the rat cochlea. Neurochem Int. 33:55–59. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sha SH and Schacht J: Stimulation of free
radical formation by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Hear Res.
128:112–118. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takumida M, Popa R and Anniko M: Free
radicals in the guinea pig inner ear following gentamicin exposure.
ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 61:63–70. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu WJ, Sha SH and Schacht J: Recent
advances in understanding aminoglycoside ototoxicity and its
prevention. Audiol Neurootol. 7:171–174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung HW, Chang SO, Kim CS, Rhee CS and Lim
DH: Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on the cochlear damage induced
by local gentamicin installation in guinea pigs. J Korean Med Sci.
13:525–528. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sha SH and Schacht J: Antioxidants
attenuate gentamicin-induced free radical formation in vitro and
ototoxicity in vivo: D-methionine is a potential protectant. Hear
Res. 142:34–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McFadden SL, Ding D, Salvemini D and Salvi
RJ: M40403, a superoxide dismutase mimetic, protects cochlear hair
cells from gentamicin, but not cisplatin toxicity. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 186:46–54. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang AM, Sha SH, Lesniak W and Schacht J:
Tanshinone (Salviae miltiorrhizae extract) preparations attenuate
aminoglycoside-induced free radical formation in vitro and
ototoxicity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 47:1836–1841.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fetoni AR, Sergi B, Ferraresi A, Paludetti
G and Troiani D: alpha-Tocopherol protective effects on gentamicin
ototoxicity: an experimental study. Int J Audiol. 43:166–171. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matés JM: Effects of antioxidant enzymes
in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology.
Toxicology. 153:83–104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chan PH, Yang GY, Chen SF, Carlson E and
Epstein CJ: Cold-induced brain edema and infarction are reduced in
transgenic mice overexpressing CuZn-superoxide dismutase. Ann
Neurol. 29:482–486. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kinouchi H, Epstein CJ, Mizui T, Carlson
E, Chen SF and Chan PH: Attenuation of focal cerebral ischemic
injury in transgenic mice overexpressing CuZn superoxide dismutase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:11158–11162. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
White CW, Avraham KB, Shanley PF and
Groner Y: Transgenic mice with expression of elevated levels of
copper-zinc superoxide dismutase in the lungs are resistant to
pulmonary oxygen toxicity. J Clin Invest. 87:2162–2168. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mikawa S, Kinouchi H, Kamii H, Gobbel GT,
Chen SF, Carlson E, Epstein CJ and Chan PH: Attenuation of acute
and chronic damage following traumatic brain injury in copper,
zinc-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. J Neurosurg. 85:885–891.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alam J and Cook JL: Transcriptional
regulation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene via the stress response
element pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 9:2499–2511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He X, Lin GX, Chen MG, Zhang JX and Ma Q:
Protection against chromium (VI)-induced oxidative stress and
apoptosis by Nrf2. Recruiting Nrf2 into the nucleus and disrupting
the nuclear Nrf2/Keap1 association. Toxicol Sci. 98:298–309. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li HY, Zhong YF, Wu SY and Shi N: NF-E2
related factor 2 activation and heme oxygenase-1 induction by
tert-butylhydroquinone protect against deltamethrin-mediated
oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 20:1242–1251.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SJ, Park C, Han AL, Youn MJ, Lee JH,
Kim Y, Kim ES, Kim HJ, Kim JK, Lee HK, et al: Ebselen attenuates
cisplatin-induced ROS generation through Nrf2 activation in
auditory cells. Hear Res. 251:70–82. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sher T, Yi HF, McBride OW and Gonzalez FJ:
cDNA cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional characterization
of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor.
Biochemistry. 32:5598–5604. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Staels B, Koenig W, Habib A, Merval R,
Lebret M, Torra IP, Delerive P, Fadel A, Chinetti G, Fruchart JC,
et al: Activation of human aortic smooth-muscle cells is inhibited
by PPARalpha but not by PPARgamma activators. Nature. 393:790–793.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Inoue I, Goto S, Matsunaga T, Nakajima T,
Awata T, Hokari S, Komoda T and Katayama S: The ligands/activators
for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha)
and PPARgamma increase Cu2+, Zn2+-superoxide
dismutase and decrease P22p hox message expressions in primary
endothelial cells. Metabolism. 50:3–11. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inoue H, Jiang XF, Katayama T, Osada S,
Umesono K and Namura S: Brain protection by resveratrol and
fenofibrate against stroke requires peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha in mice. Neurosci Lett.
352:203–206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Toyama T, Nakamura H, Harano Y, Yamauchi
N, Morita A, Kirishima T, Minami M, Itoh Y and Okanoue T: PPARalpha
ligands activate antioxidant enzymes and suppress hepatic fibrosis
in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 324:697–704. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lo Verme J, Fu J, Astarita G, La Rana G,
Russo R, Calignano A and Piomelli D: The nuclear receptor
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha mediates the
anti-inflammatory actions of palmitoylethanolamide. Mol Pharmacol.
67:15–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bordet R, Ouk T, Petrault O, Gelé P,
Gautier S, Laprais M, Deplanque D, Duriez P, Staels B, Fruchart JC,
et al: PPAR: a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in
stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Soc Trans.
34:1341–1346. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lemberger T, Desvergne B and Wahli W:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: a nuclear receptor
signaling pathway in lipid physiology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
12:335–363. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Girnun GD, Domann FE, Moore SA and Robbins
ME: Identification of a functional peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor response element in the rat
catalase promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 16:2793–2801. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hou X, Shen YH, Li C, Wang F, Zhang C, Bu
P and Zhang Y: PPARalpha agonist fenofibrate protects the kidney
from hypertensive injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats via
inhibition of oxidative stress and MAPK activity. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 394:653–659. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choung YH, Taura A, Pak K, Choi SJ, Masuda
M and Ryan AF: Generation of highly-reactive oxygen species is
closely related to hair cell damage in rat organ of Corti treated
with gentamicin. Neuroscience. 161:214–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Clerici WJ, Hensley K, DiMartino DL and
Butterfield DA: Direct detection of ototoxicant-induced reactive
oxygen species generation in cochlear explants. Hear Res.
98:116–124. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hirose K, Hockenbery DM and Rubel EW:
Reactive oxygen species in chick hair cells after gentamicin
exposure in vitro. Hear Res. 104:1–14. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sha SH and Schacht J: Formation of
reactive oxygen species following bioactivation of gentamicin. Free
Radic Biol Med. 26:341–347. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tanaka Y, Kume S, Araki S, Isshiki K,
Chin-Kanasaki M, Sakaguchi M, Sugimoto T, Koya D, Haneda M,
Kashiwagi A, et al: Fenofibrate, a PPARα agonist, has
renoprotective effects in mice by enhancing renal lipolysis. Kidney
Int. 79:871–882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang S, Hannafon BN, Zhou J and Ding WQ:
Clofibrate induces heme oxygenase 1 expression through a
PPARα-independent mechanism in human cancer cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:1255–1264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yoo HY, Chang MS and Rho HM: Induction of
the rat Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene through the peroxisome
proliferator-responsive element by arachidonic acid. Gene.
234:87–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chiu LL, Cunningham LL, Raible DW, Rubel
EW and Ou HC: Using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for
ototoxicity. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 9:178–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Montgomery J, Carton G, Voigt R, Baker C
and Diebel C: Sensory processing of water currents by fishes.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 355:1325–1327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van Trump WJ, Coombs S, Duncan K and
McHenry MJ: Gentamicin is ototoxic to all hair cells in the fish
lateral line system. Hear Res. 261:42–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Winkel O, Hansen MM, Kaaber K and Rozarth
K: A prospective study of gentamicin ototoxicity. Acta Otolaryngol.
86:212–216. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Matz GJ: Aminoglycoside cochlear
ototoxicity. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 26:705–712. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cotanche DA: Genetic and pharmacological
intervention for treatment/prevention of hearing loss. J Commun
Disord. 41:421–443. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Garetz SL, Altschuler RA and Schacht J:
Attenuation of gentamicin ototoxicity by glutathione in the guinea
pig in vivo. Hear Res. 77:81–87. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ding D, Stracher A and Salvi RJ: Leupeptin
protects cochlear and vestibular hair cells from gentamicin
ototoxicity. Hear Res. 164:115–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Priuska EM and Schacht J: Formation of
free radicals by gentamicin and iron and evidence for an
iron/gentamicin complex. Biochem Pharmacol. 50:1749–1752. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Forcheron F, Cachefo A, Thevenon S,
Pinteur C and Beylot M: Mechanisms of the triglycerideand
cholesterol-lowering effect of fenofibrate in hyperlipidemic type 2
diabetic patients. Diabetes. 51:3486–3491. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jeong S, Kim M, Han M, Lee H, Ahn J, Kim
M, Song YH, Shin C, Nam KH, Kim TW, et al: Fenofibrate prevents
obesity and hypertriglyceridemia in low-density lipoprotein
receptor-null mice. Metabolism. 53:607–613. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Willson TM, Brown PJ, Sternbach DD and
Henke BR: The PPARs: from orphan receptors to drug discovery. J Med
Chem. 43:527–550. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Forge A and Li L: Apoptotic death of hair
cells in mammalian vestibular sensory epithelia. Hear Res.
139:97–115. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Olukman M, Sezer ED, Ulker S, Sözmen EY
and Cınar GM: Fenofibrate treatment enhances antioxidant status and
attenuates endothelial dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res. 2010:8285312010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kikuchi G, Yoshida T and Noguchi M: Heme
oxygenase and heme degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
338:558–567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Krönke G, Kadl A, Ikonomu E, Blüml S,
Fürnkranz A, Sarembock IJ, Bochkov VN, Exner M, Binder BR and
Leitinger N: Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human vascular cells
is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:1276–1282. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim HJ, So HS, Lee JH, Lee JH, Park C,
Park SY, Kim YH, Youn MJ, Kim SJ, Chung SY, et al: Heme oxygenase-1
attenuates the cisplatin-induced apoptosis of auditory cells via
down-regulation of reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radic
Biol Med. 40:1810–1819. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|