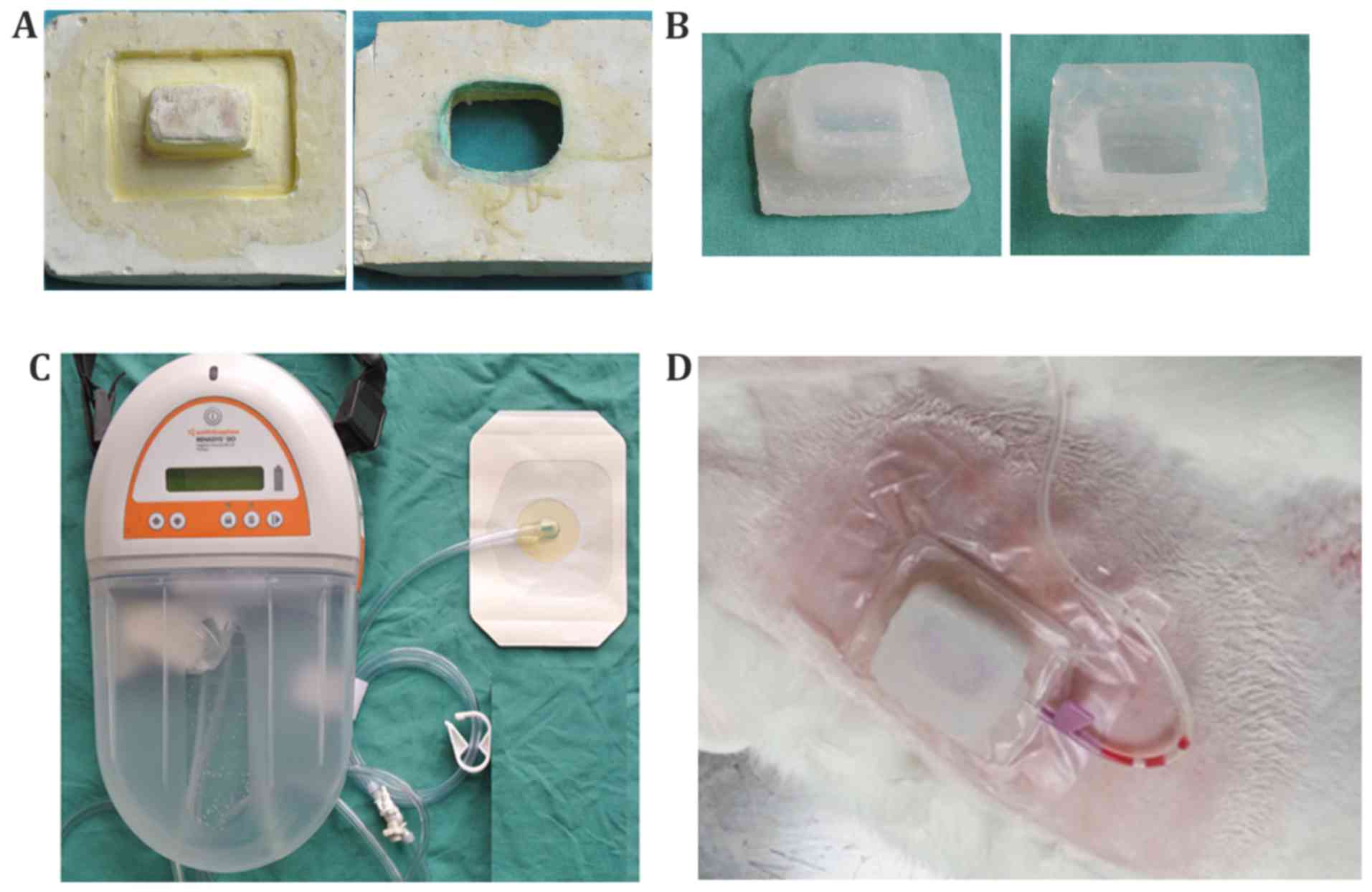
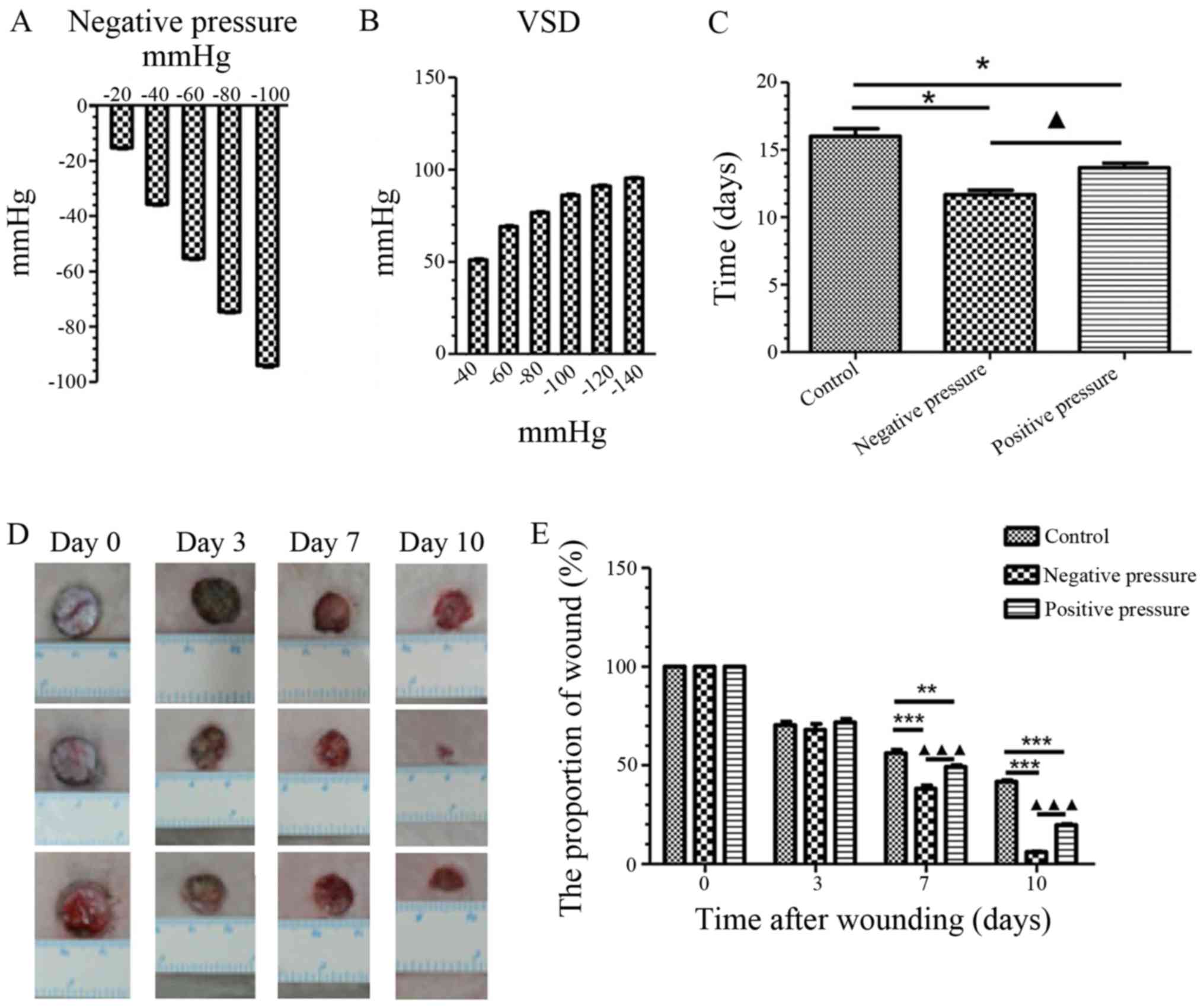
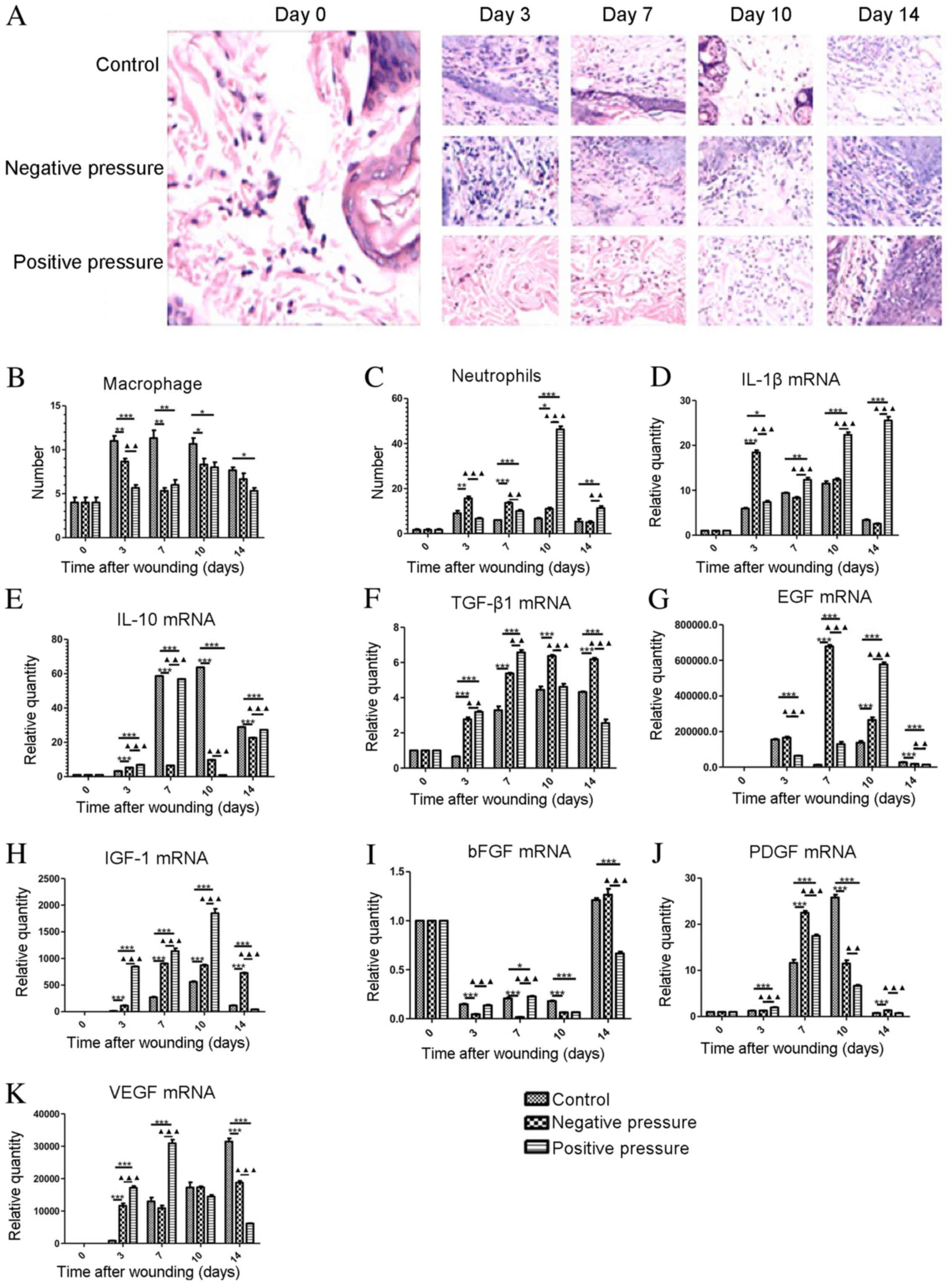
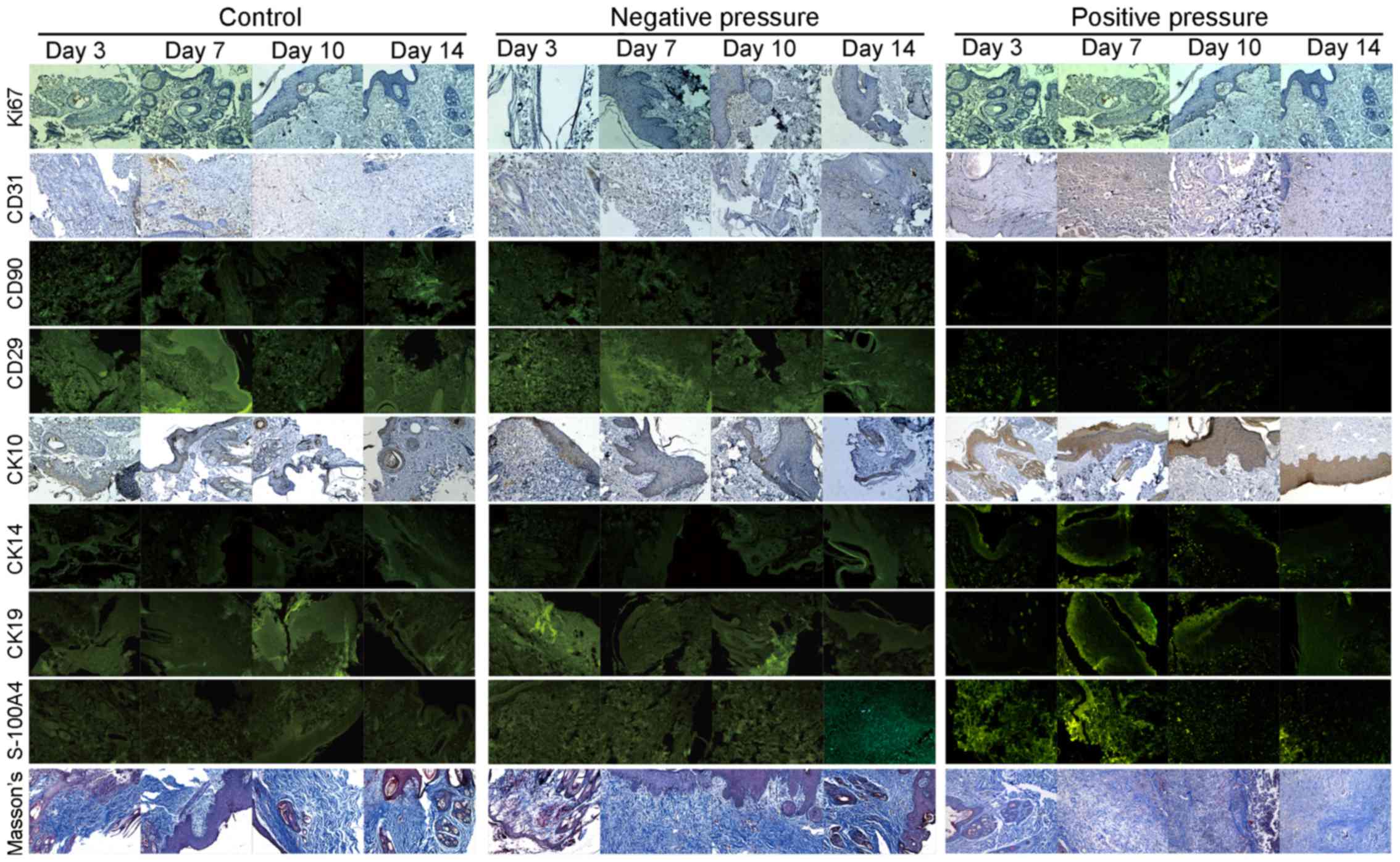
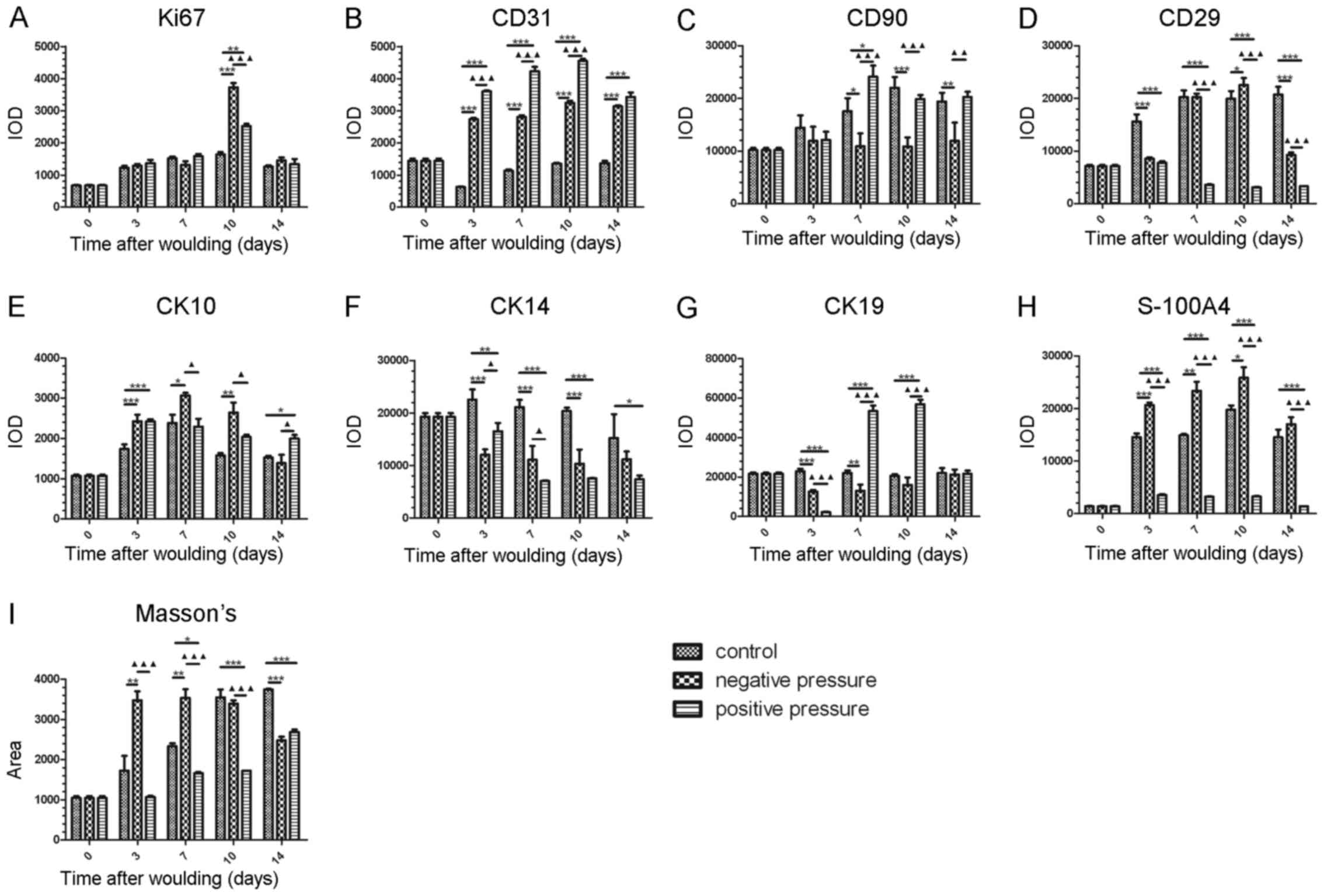
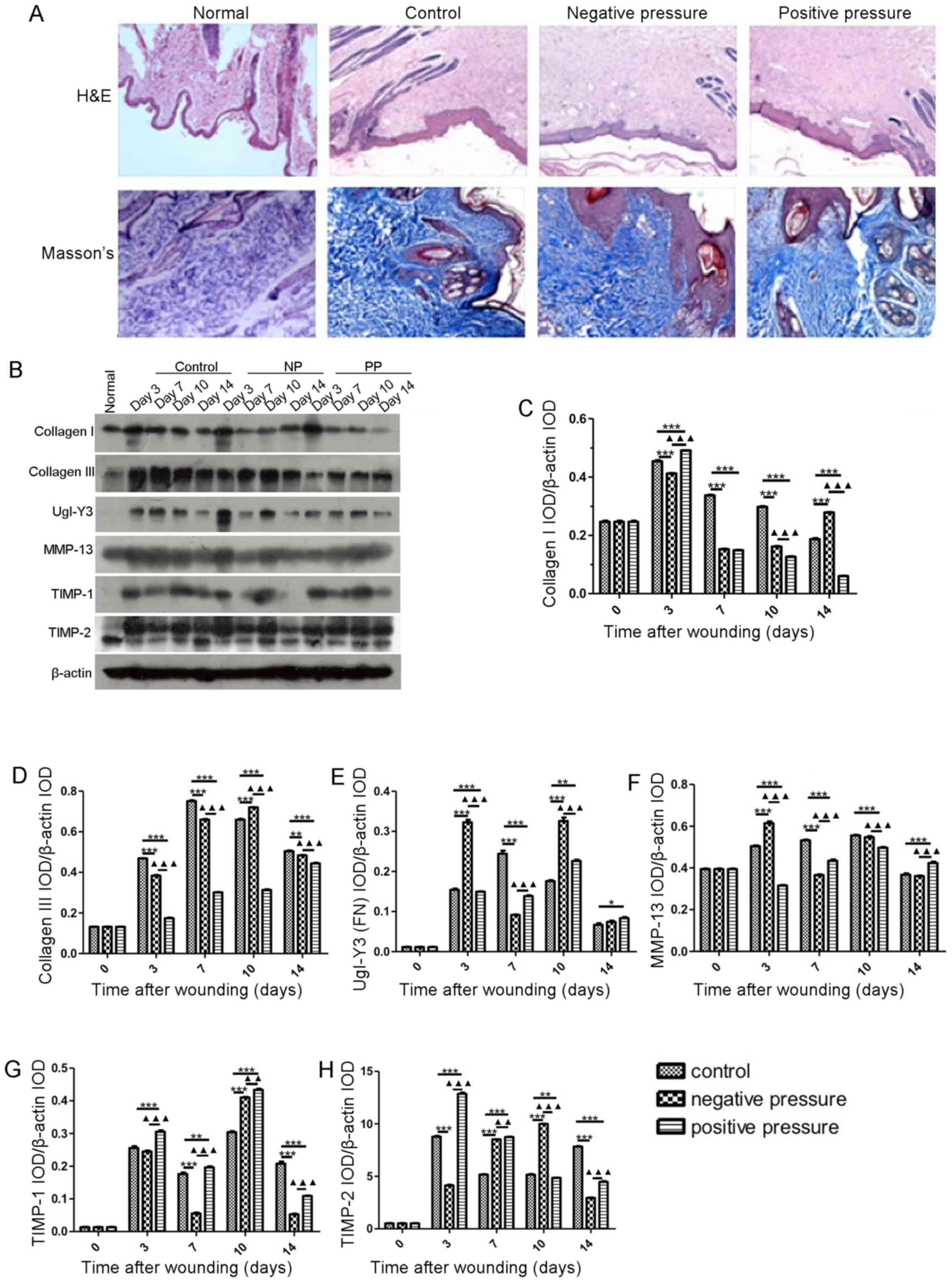
|
1
|
Watterson KR, Lanning DA, Diegelmann RF
and Spiegel S: Regulation of fibroblast functions by
lysophospholipid mediators: Potential roles in wound healing. Wound
Repair Regen. 15:607–616. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ko SH, Nauta A, Wong V, Glotzbach J,
Gurtner GC and Longaker MT: The role of stem cells in cutaneous
wound healing: What do we really know? Plast Reconstr Surg.
127(Suppl 1): 10S–20S. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Evans ND, Oreffo RO, Healy E, Thurner PJ
and Man YH: Epithelial mechanobiology, skin wound healing, and the
stem cell niche. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 28:397–409. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maxson S, Lopez EA, Yoo D,
Danilkovitch-Miagkova A and Leroux MA: Concise review: Role of
mesenchymal stem cells in wound repair. Stem Cells Transl Med.
1:142–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Darby IA and Hewitson TD: Fibroblast
differentiation in wound healing and fibrosis. Int Rev Cytol.
257:143–179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nuschke A: Activity of mesenchymal stem
cells in therapies for chronic skin wound healing. Organogenesis.
10:29–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Shi J, Xi W, Yi C, Wang Z, Guo S and Han
Y: Vacuum sealing drainage promotes experimental pig explosive
abdomen wound healing. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
30:312–315. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Argenta LC, Morykwas MJ, Marks MW,
DeFranzo AJ, Molnar JA and David LR: Vacuum-assisted closure: State
of clinic art. Plast Reconstr Surg. 117(Suppl): 127S–142S. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Banwell P and Téot L: Topical negative
pressure (TNP): The evolution of a novel wound therapy. J Tissue
Viability. 16:16–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morykwas MJ, Simpson J, Punger K, Argenta
A, Kremers L and Argenta J: Vacuum-assisted closure: State of basic
research and physiologic foundation. Plast Reconstr Surg.
117(Suppl): 121S–126S. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banwell PE: Topical negative pressure
therapy in wound care. J Wound Care. 8:79–84. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fonder MA, Lazarus GS, Cowan DA,
Aronson-Cook B, Kohli AR and Mamelak AJ: Treating the chronic
wound: A practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and
wound care dressings. J Am Acad Dermatol. 58:185–206. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hunter JE, Teot L, Horch R and Banwell PE:
Evidence-based medicine: Vacuum-assisted closure in wound care
management. Int Wound J. 4:256–269. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen SZ, Li J, Li XY and Xu LS: Effects of
vacuum-assisted closure on wound microcirculation: An experimental
study. Asian J Surg. 28:211–217. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Evans D and Land L: Topical negative
pressure for treating chronic wounds: A systematic review. Br J
Plast Surg. 54:238–242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kairinos N, Solomons M and Hudson DA: The
paradox of negative pressure wound therapy - in vitro studies. J
Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 63:174–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Muller MJ, Hollyoak MA, Moaveni Z, Brown
TL, Herndon DN and Heggers JP: Retardation of wound healing by
silver sulfadiazine is reversed by Aloe vera and nystatin. Burns.
29:834–836. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Greenhalgh DG: The role of apoptosis in
wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 30:1019–1030. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nuutila K, Siltanen A, Peura M, Harjula A,
Nieminen T, Vuola J, Kankuri E and Aarnio P: Gene expression
profiling of negative-pressure-treated skin graft donor site
wounds. Burns. 39:687–693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Baldwin C, Potter M, Clayton E, Irvine L
and Dye J: Topical negative pressure stimulates endothelial
migration and proliferation: A suggested mechanism for improved
integration of Integra. Ann Plast Surg. 62:92–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Potter MJ, Banwell P, Baldwin C, Clayton
E, Irvine L, Linge C, Grobbelaar AO, Sanders R and Dye JF: In vitro
optimisation of topical negative pressure regimens for angiogenesis
into synthetic dermal replacements. Burns. 34:164–174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McNulty AK, Schmidt M, Feeley T and
Kieswetter K: Effects of negative pressure wound therapy on
fibroblast viability, chemotactic signaling, and proliferation in a
provisional wound (fibrin) matrix. Wound Repair Regen. 15:838–846.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu F, Ogawa R, Nguyen DT, Chen B, Guo D,
Helm DL, Zhan Q, Murphy GF and Orgill DP: Microdeformation of
three-dimensional cultured fibroblasts induces gene expression and
morphological changes. Ann Plast Surg. 66:296–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Michel M, Török N, Godbout MJ, Lussier M,
Gaudreau P, Royal A and Germain L: Keratin 19 as a biochemical
marker of skin stem cells in vivo and in vitro: Keratin 19
expressing cells are differentially localized in function of
anatomic sites, and their number varies with donor age and culture
stage. J Cell Sci. 109:1017–1028. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balaji S, Keswani SG and Crombleholme TM:
The role of mesenchymal stem cells in the regenerative wound
healing phenotype. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 1:159–165. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ankrum J and Karp JM: Mesenchymal stem
cell therapy: Two steps forward, one step back. Trends Mol Med.
16:203–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang C, Leavitt T, Bayer LR and Orgill
DP: Effect of negative pressure wound therapy on wound healing.
Curr Probl Surg. 51:301–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|