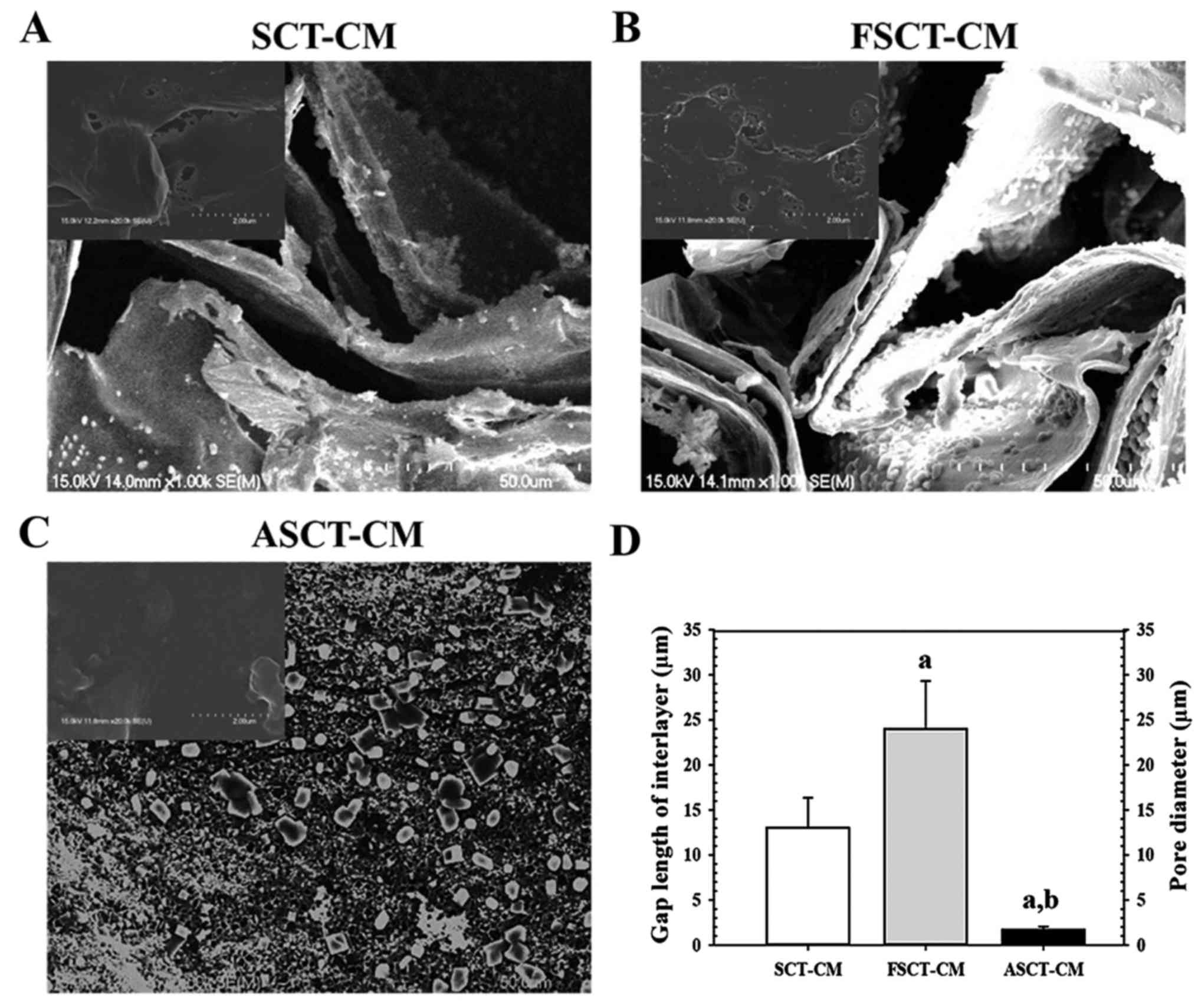
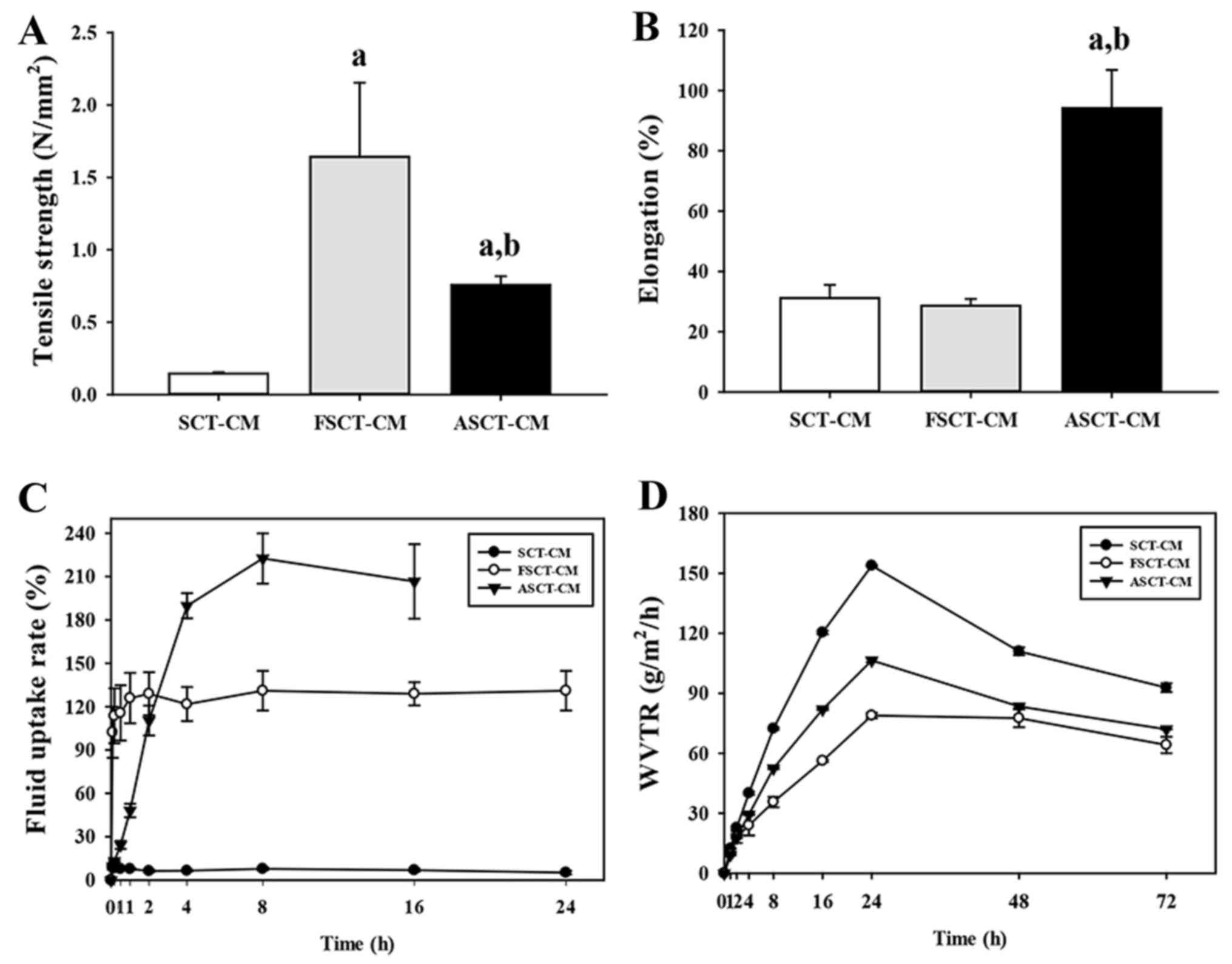
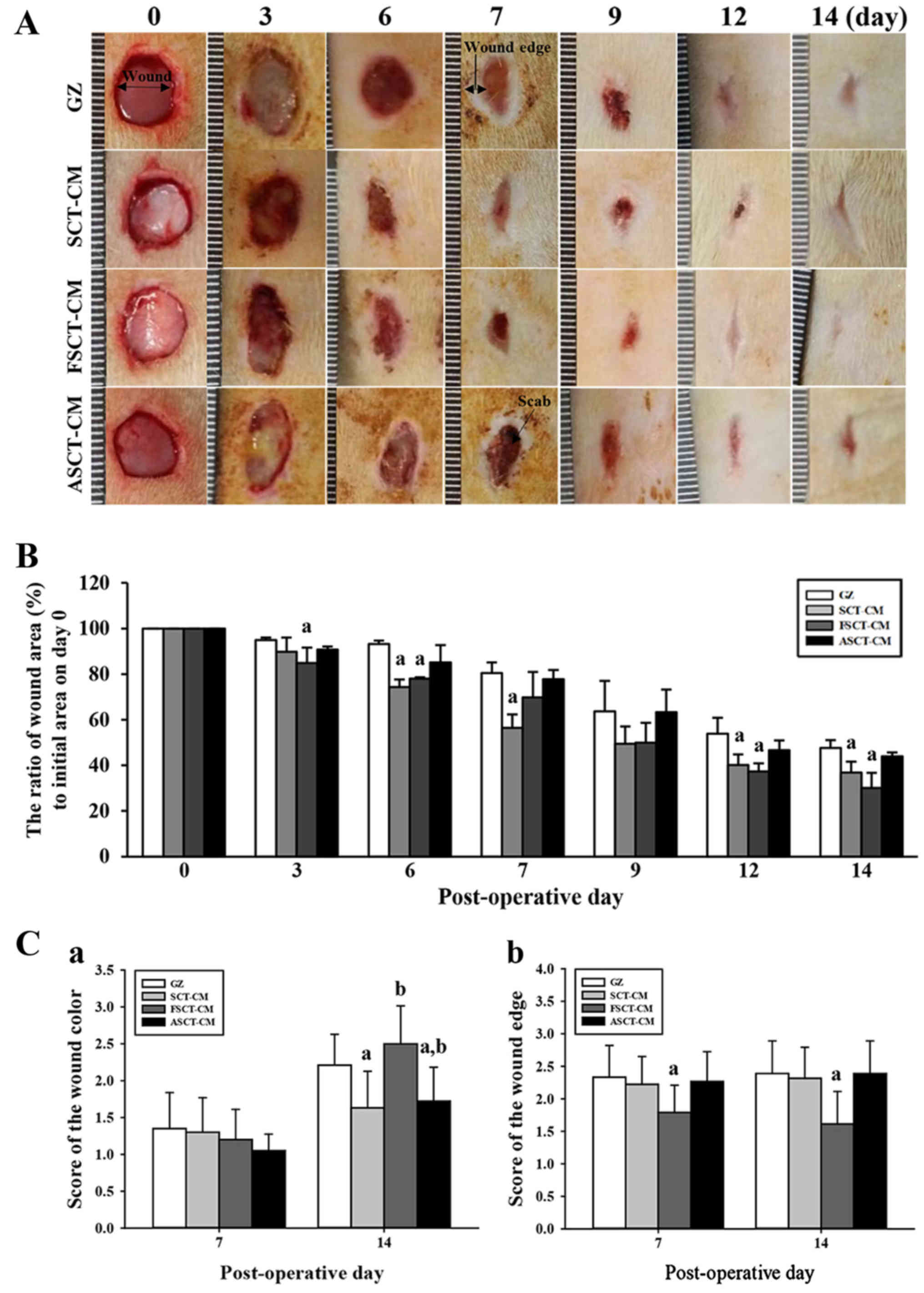
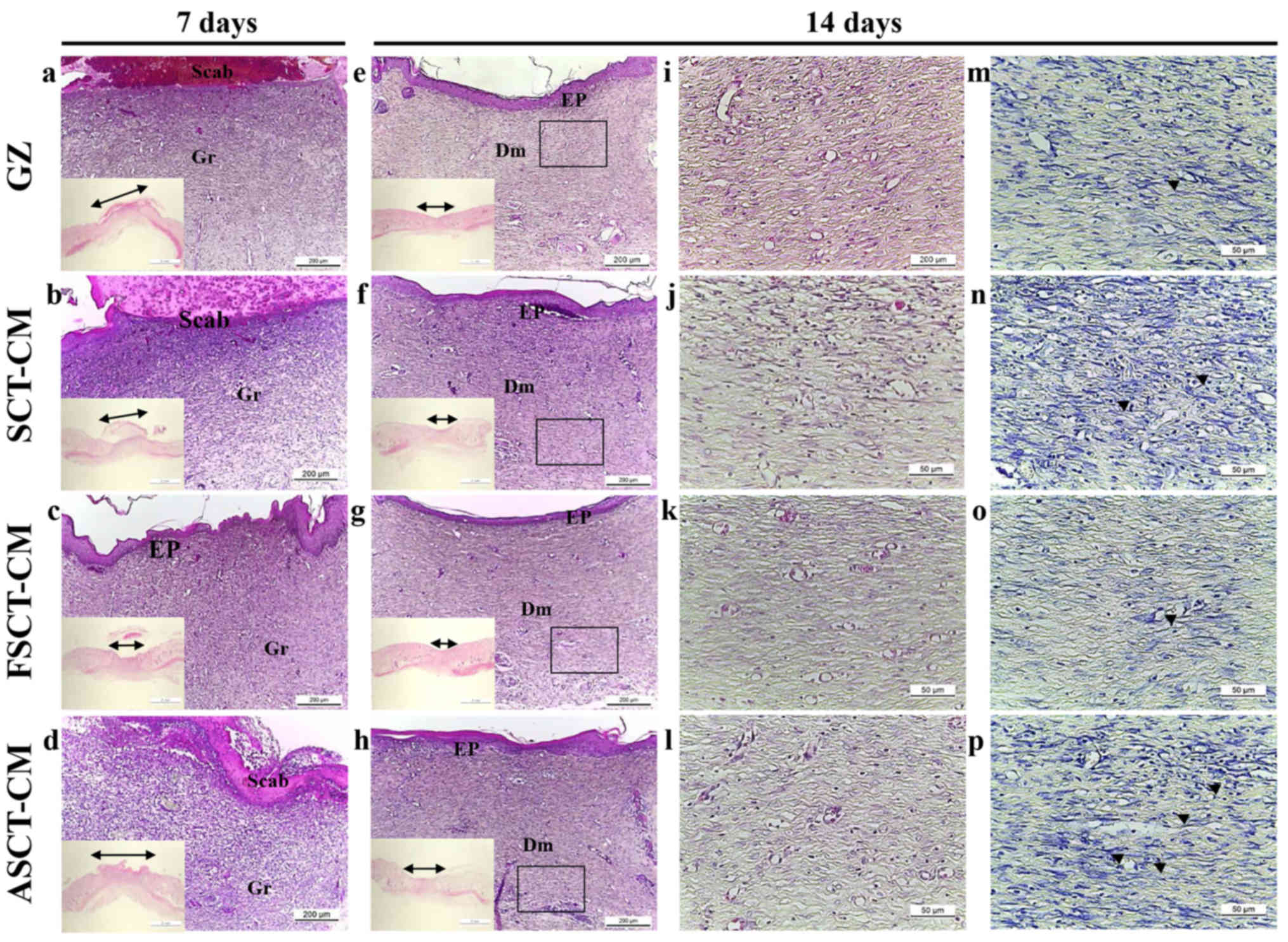
|
1
|
Eaglstein WH: Moist wound healing with
occlusive dressings: A clinical focus. Dermatol Surg. 27:175–181.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mark GL, Warren RH, John BJ and Ian C:
Treatment of skin disease: comprehensive therapeutic strategies.
Decubitus Ulcers. 4th edition. Joseph AW, Lawrence CP, Caren C and
Jennifer LP: Elsevier Health Sciences; UK: pp. 167–171. 2013
|
|
3
|
Kim JO, Choi JY, Park JK, Kim JH, Jin SG,
Chang SW, Li DX, Hwang MR, Woo JS, Kim JA, et al: Development of
clindamycin-loaded wound dressing with polyvinyl alcohol and sodium
alginate. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:2277–2282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crépy L, Monchau F, Chai F, Raoul G,
Hivart P, Hildebrand HF, Martin P and Joly N: Evaluation of a
bio-based hydrophobic cellulose laurate film as biomaterial - study
on biodegradation and cytocompatibility. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl
Biomater. 100:1000–1008. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Thomas S: Wound Management and Dressing.
Pharmaceutical Press; London: 1990
|
|
6
|
Woodley DT, Chen JD, Kim JP, Sarret Y,
Iwasaki T, Kim YH and O'Keefe EJ: Re-epithelialization. Human
keratinocyte locomotion. Dermatol Clin. 11:641–646. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Sudheesh Kumar
PT, Nair SV and Tamura H: Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan
in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 29:322–337. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Witthayaprapakorn C: Design and
preparation of synthetic hydrogels via photopolymerisation for
biomedical uses as wound dressings. Procedia Eng. 8:286–291. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang JM and Lin HT: Properties of chitosan
containing PP-g-AA-g-IPAAm bigraft nonwoven fabric for wound
dressing. J Membr Sci. 243:1–7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Camargo MC, Nogueira RM, Sanches OC, Saab
MG, Batista A, Vasconcelos D, Luvisotto LY and Lúcio MA:
Applicability of crystalline cellulose membrane in the treatment of
skin wounds induced in Wistar rats. Acta Cir Bras. 29:429–437.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kwak MH, Go J, Kim JE, Lee YJ, Lee SH, Lee
HS, Son HJ, Jung YJ and Hwang DY: Property and efficacy analysis of
hydrocolloid membrane containing Styela clava tunic on the wound
repair of skin in SD rats. Biomater Res. 17:91–101. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Hart J, Silcock D, Gunnigle S, Cullen B,
Light ND and Watt PW: The role of oxidised regenerated
cellulose/collagen in wound repair: Effects in vitro on fibroblast
biology and in vivo in a model of compromised healing. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 34:1557–1570. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung YJ: Properties of regenerated
cellulose films prepared from the tunicate Styela clava. J Kor Fish
Soc. 41:237–242. 2008.
|
|
14
|
Song SH, Kim JE, Lee YJ, Kwak MH, Sung GY,
Kwon SH, Son HJ, Lee HS, Jung YJ and Hwang DY: Cellulose film
regenerated from Styela clava tunics have biodegradability,
toxicity and biocompatibility in the skin of SD rats. J Mater Sci
Mater Med. 25:1519–1530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jung YJ, An BJ, Hwang DY, Kim HD, Park SM,
Cho H and Kim HS: Preparation and properties of regenerated
cellulosic biomaterial made from Styela Clava tunics. Biomater Res.
12:71–76. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Pereira RF, Mendes A and Bártolo PJ: Novel
alginate/Aloe Vera hydrogel blends as wound dressings for the
treatment of several types of wounds. Chem Eng Prog. 32:1009–1014.
2013.
|
|
17
|
ASTM standard E96-00. Standard test
methods for water vapour transmission of materials.
|
|
18
|
Kim HJ, Kim J, Kim SJ, Lee SH, Park YS,
Park BK, Kim BS, Kim SK, Cho SD, Jung JW, et al: Anti-inflammatory
effect of Quercetin on picryl chloride-induced contact dermatitis
in BALB/c mice. Lab Anim Res. 26:7–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Baum CL and Arpey CJ: Normal cutaneous
wound healing: Clinical correlation with cellular and molecular
events. Dermatol Surg. 31:674–686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Derynck R and Zhang YE: Smad-dependent and
Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature.
425:577–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu L, Hébert MC and Zhang YE: TGF-beta
receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent
TGF-beta responses. EMBO J. 21:3749–3759. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Matasuzaki K, Yamamoto I, Sato T and
Oshima R: Synthesis of water-soluble branched polysaccharides and
their antitumor activity, 1. Branched polysaccharides from
cellulose acetate. Macromol Chem Phys. 186:449–456. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ito H, Shibata T, Miyamoto T, Inagaki H
and Noishiki Y: Formation of polyelectrolyte complexes between
cellulose derivatives and their blood compatibility. J Appl Polym
Sci. 31:2491–2500. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hirano S: Chitin biotechnology
applications. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2:237–258. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Müller FA, Müller L, Hofmann I, Greil P,
Wenzel MM and Staudenmaier R: Cellulose-based scaffold materials
for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 27:3955–3963. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seong KY, Koh EK, Lee SH, Kwak MH, Son HJ,
Lee HS, Hwang DY and Jung YJ: Preparation and characterization of
high absorptive cellulose film derived from Styela Clava tunic for
wound dressing. Text Coloration Finish. 27:70–79. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Ruan D and Gao S: Dissolution and
regeneration of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J
Polym Sci Pol Phys. 40:1521–1529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cheng Y, Lu J, Liu S, Zhao P, Lu G and
Chen J: The preparation, characterization and evaluation of
regenerated cellulose/collagen composite hydrogel films. Carbohydr
Polym. 107:57–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pang J, Liu X, Zhang X, Wu Y and Sun R:
Fabrication of cellulose film with enhanced mechanical properties
in ionic liquid 1-Allyl-3-methylimidaxolium chloride (AmimCl).
Materials (Basel). 6:1270–1284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Queen D, Evans JH, Gaylor JDS, Courtney JM
and Reid WH: An in vitro assessment of wound dressing
conformability. Biomaterials. 8:372–376. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mi FL, Shyu SS, Wu YB, Lee ST, Shyong JY
and Huang RN: Fabrication and characterization of a sponge-like
asymmetric chitosan membrane as a wound dressing. Biomaterials.
22:165–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu P, Fisher AC, Foo PP, Queen D and
Gaylor JD: In vitro assessment of water vapour transmission of
synthetic wound dressings. Biomaterials. 16:171–175. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ulrich D, Smeets R, Unglaub F, Wöltje M
and Pallua N: Effect of oxidized regenerated cellulose/collagen
matrix on proteases in wound exudate of patients with diabetic foot
ulcers. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 38:522–528. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trabucchi E, Radaelli E, Marazzi M, Foschi
D, Musazzi M, Veronesi AM and Montorsi W: The role of mast cells in
wound healing. Int J Tissue React. 10:367–372. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu SA, Cheng CC, Chen JS, Hung YW, Chen
FJ and Chiu YT: Effect of oxidized regenerated cellulose on the
healing of pharyngeal wound: An experimental animal study. J Chin
Med Assoc. 75:176–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Andrikopoulou E, Zhang X, Sebastian R,
Marti G, Liu L, Milner SM and Harmon JW: Current Insights into the
role of HIF-1 in cutaneous wound healing. Curr Mol Med. 11:218–235.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pessoa WS, Estevão LR, Simões RS, Barros
ME, Mendonça FS, Baratella-Evêncio L and Evêncio-Neto J: Effects of
angico extract (Anadenanthera colubrina var. cebil) in cutaneous
wound healing in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 27:655–670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park SU, Lee BK, Kim MS, Park KK, Sung WJ,
Kim HY, Han DG, Shim JS, Lee YJ, Kim SH, et al: The possibility of
microbial cellulose for dressing and scaffold materials. Int Wound
J. 11:35–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mian M, Beghè F and Mian E: Collagen as a
pharmacological approach in wound healing. Int J Tissue React.
14(Suppl): 1–9. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim YS, Cho IH, Jeong MJ, Jeong SJ, Nah
SY, Cho YS, Kim SH, Go A, Kim SE, Kang SS, et al: Therapeutic
effect of total ginseng saponin on skin wound healing. J Ginseng
Res. 35:360–367. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ramirez H, Patel SB and Pastar I: The role
of TGFβ signaling in wound epithelialization. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 3:482–491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Willis BC, Borok Z and Am J:
TGF-beta-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung
disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ihn H: Autocrine TGF-beta signaling in the
pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol Sci. 49:103–113.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qi SH, Xie JL, Pan S, Xu YB, Li TZ, Tang
JM, Liu XS, Shu B and Liu P: Effects of asiaticoside on the
expression of Smad protein by normal skin fibroblasts and
hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Clin Exp Dermatol. 33:171–175. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|