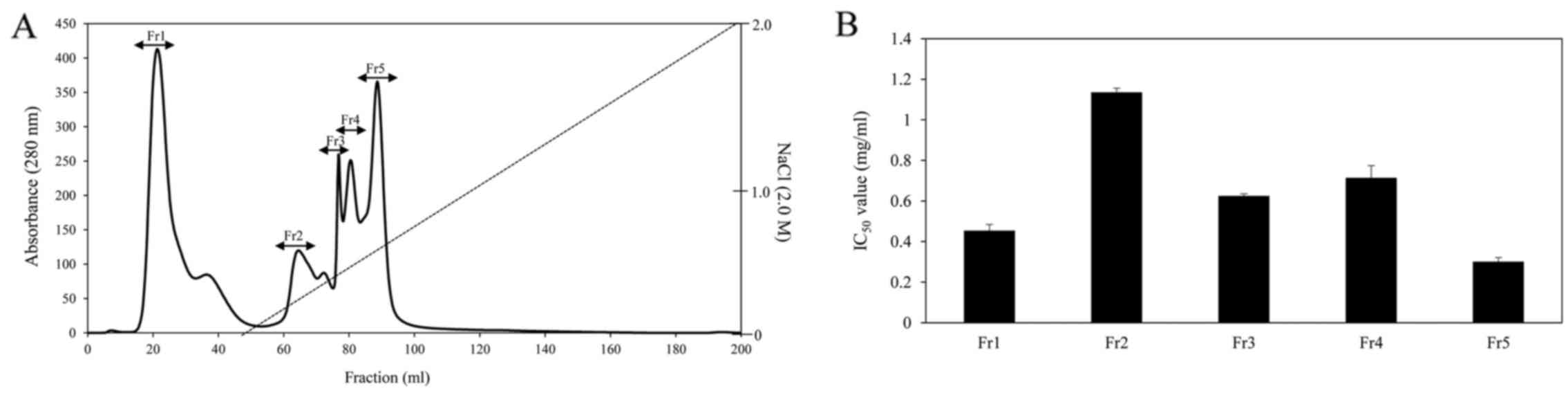
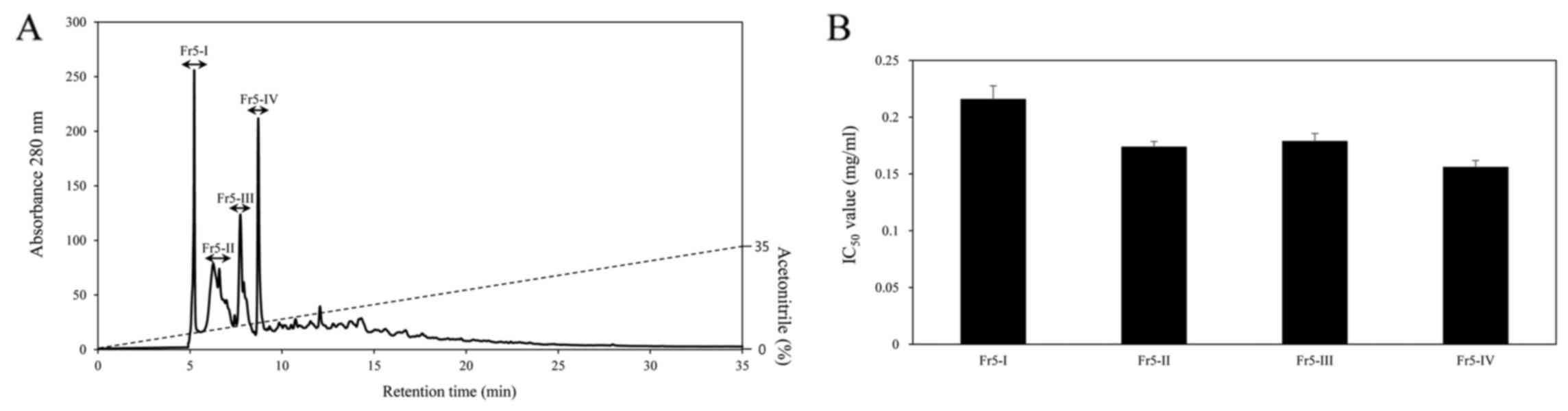
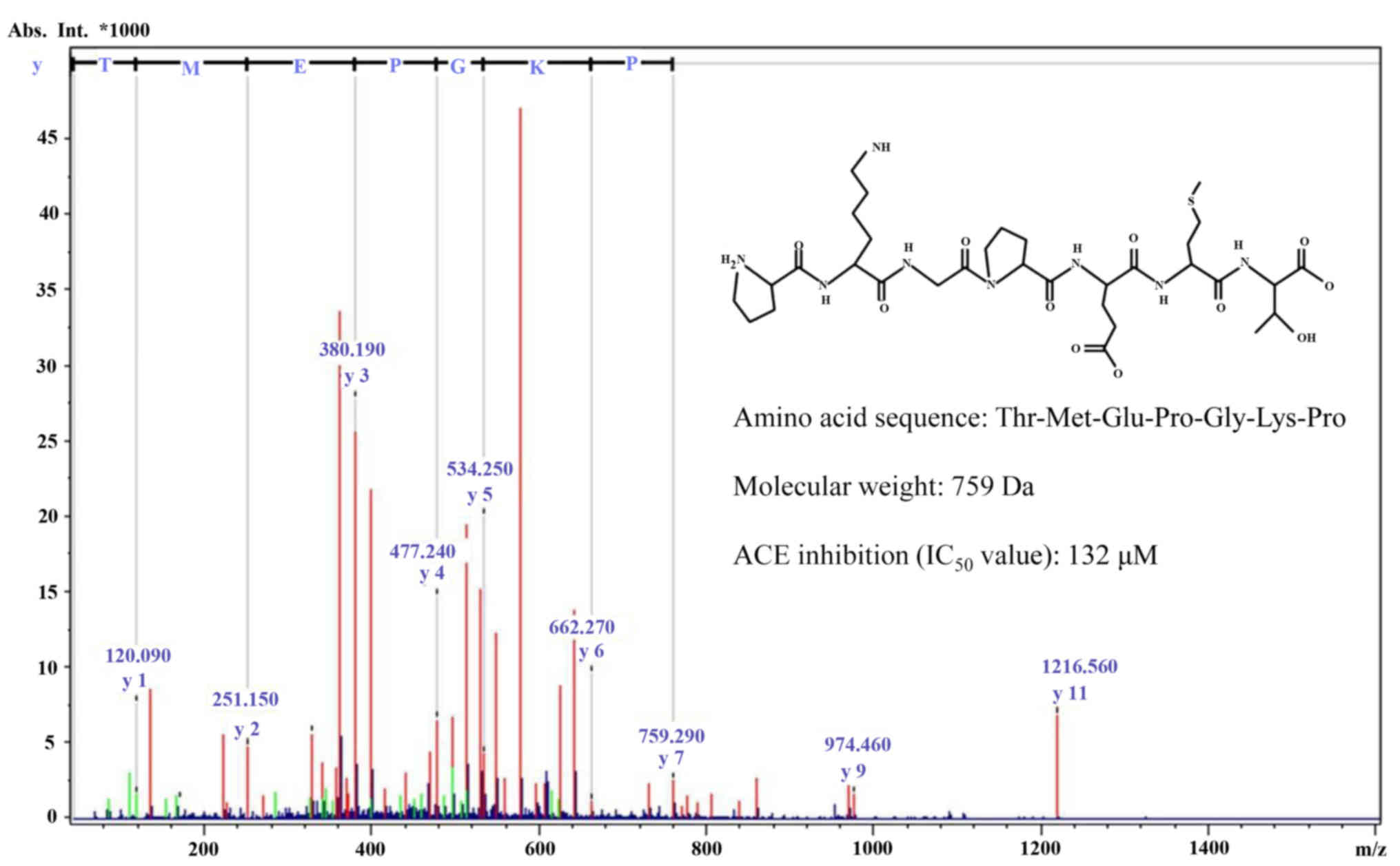
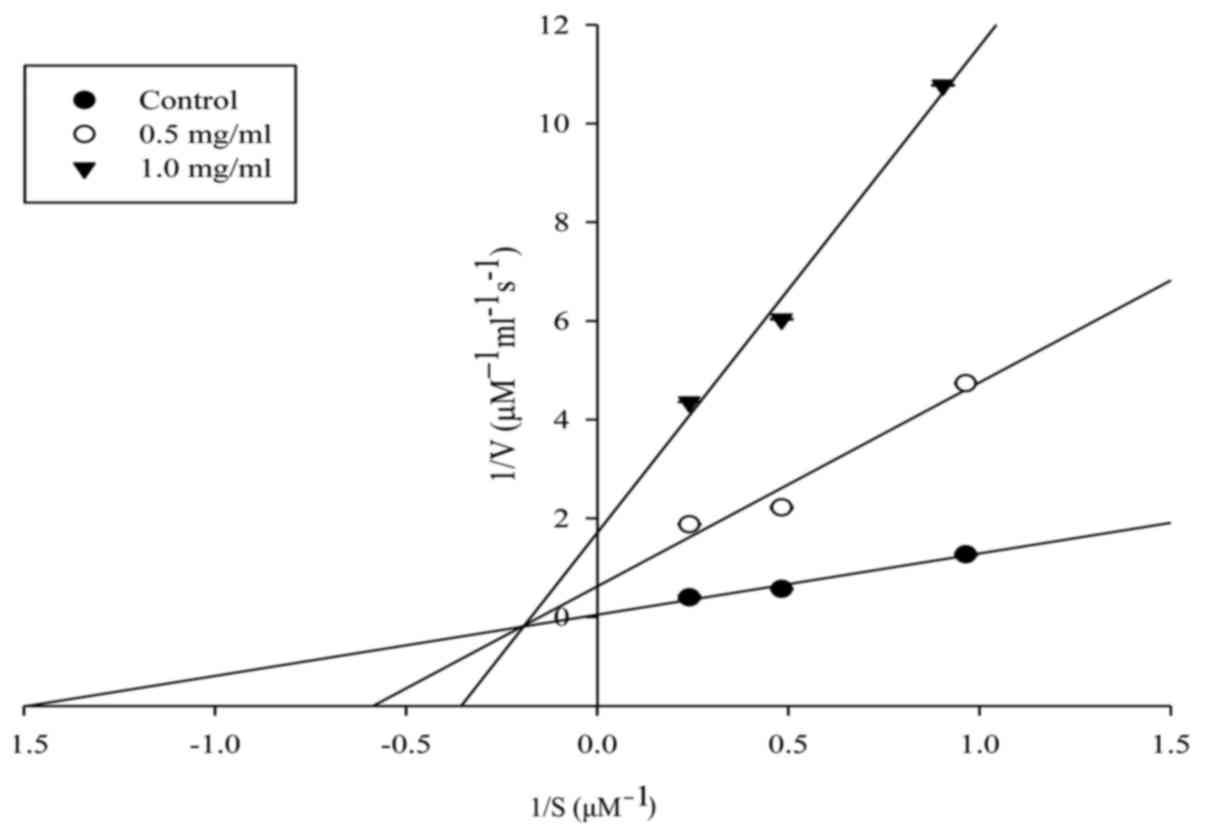
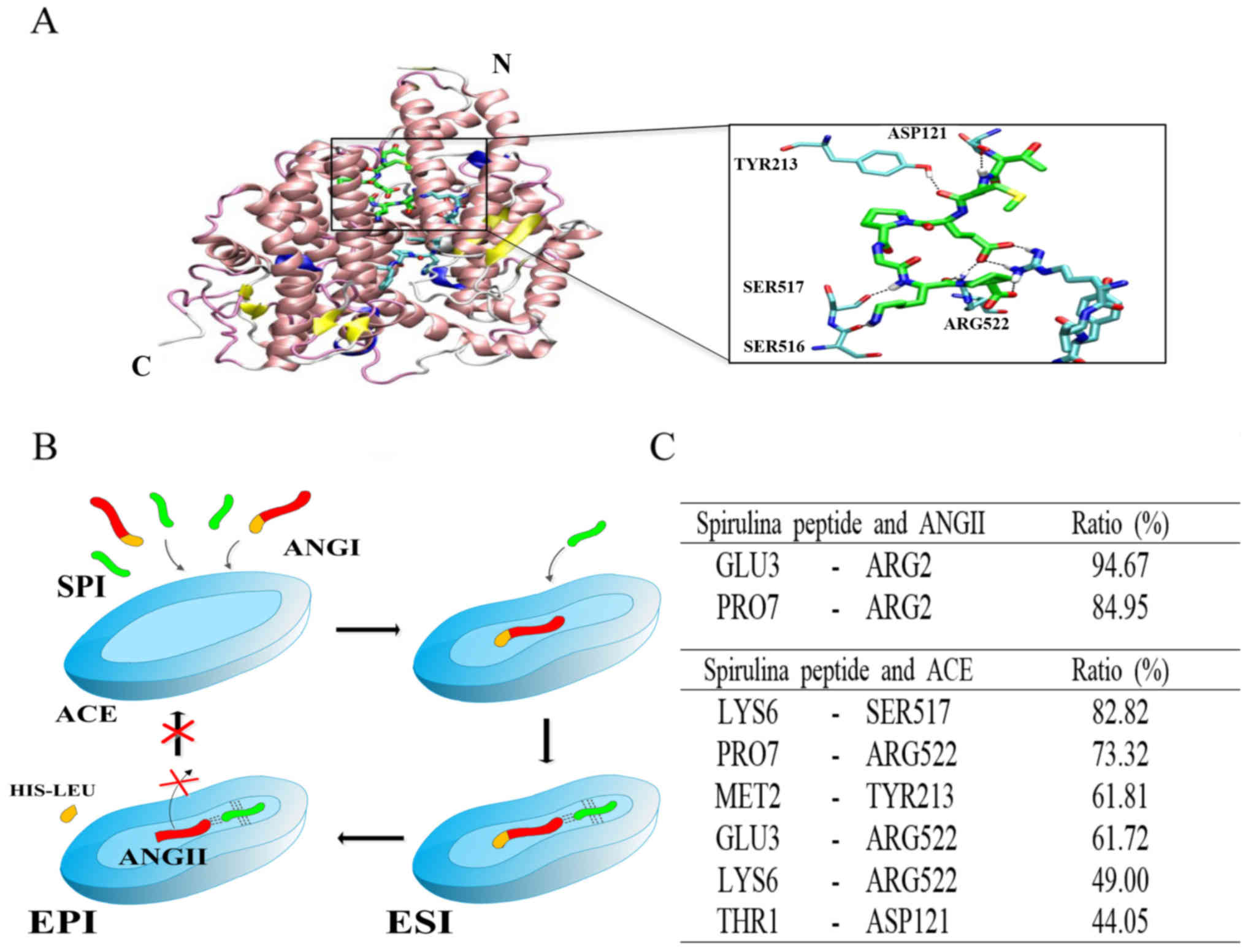
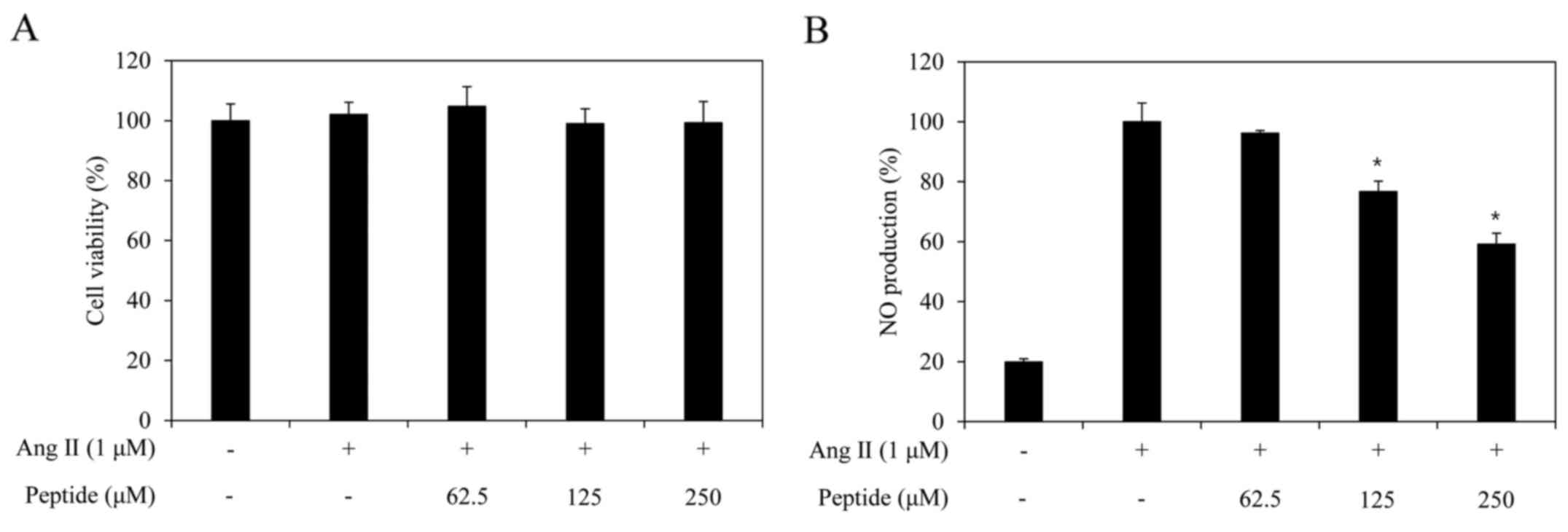
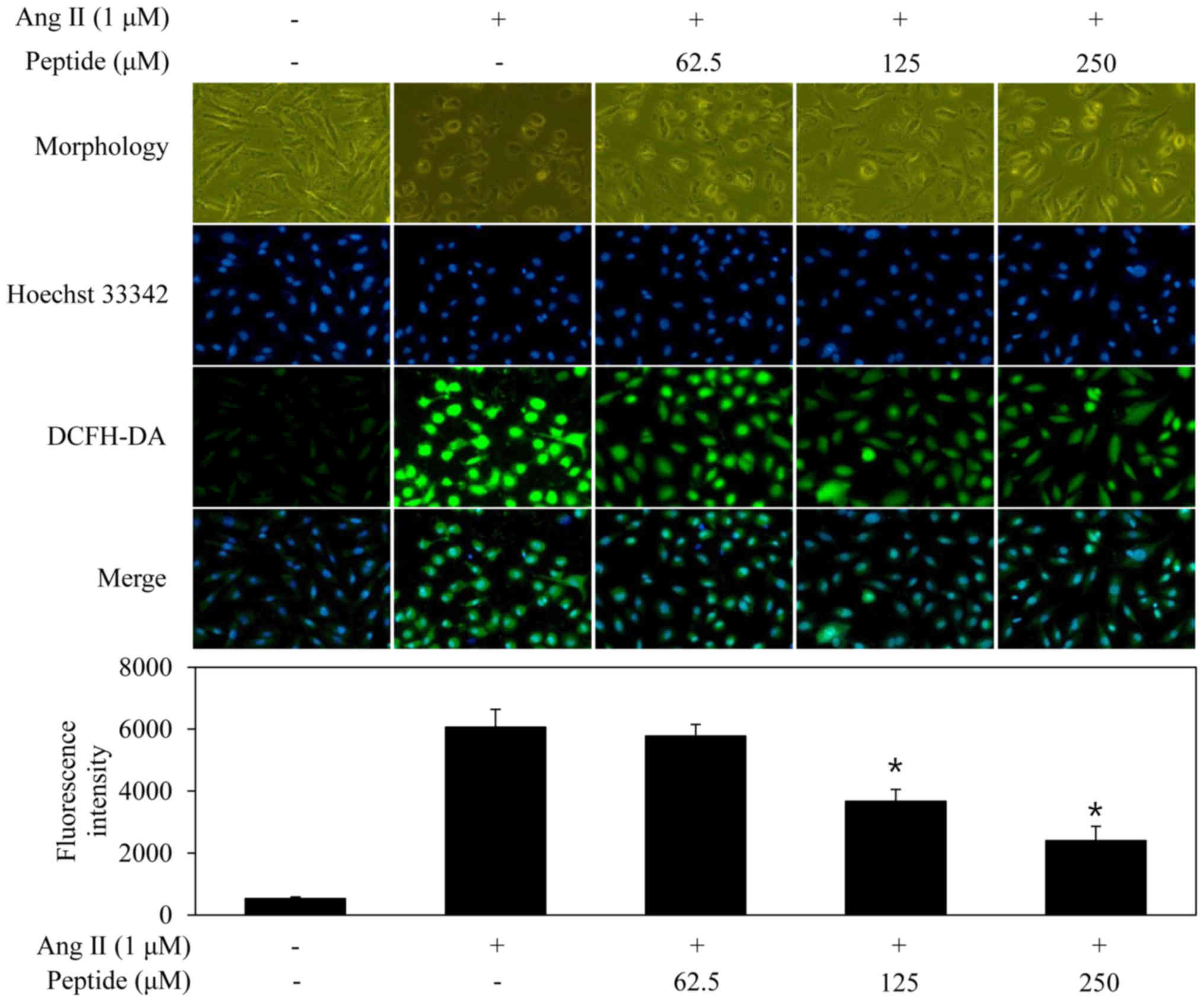
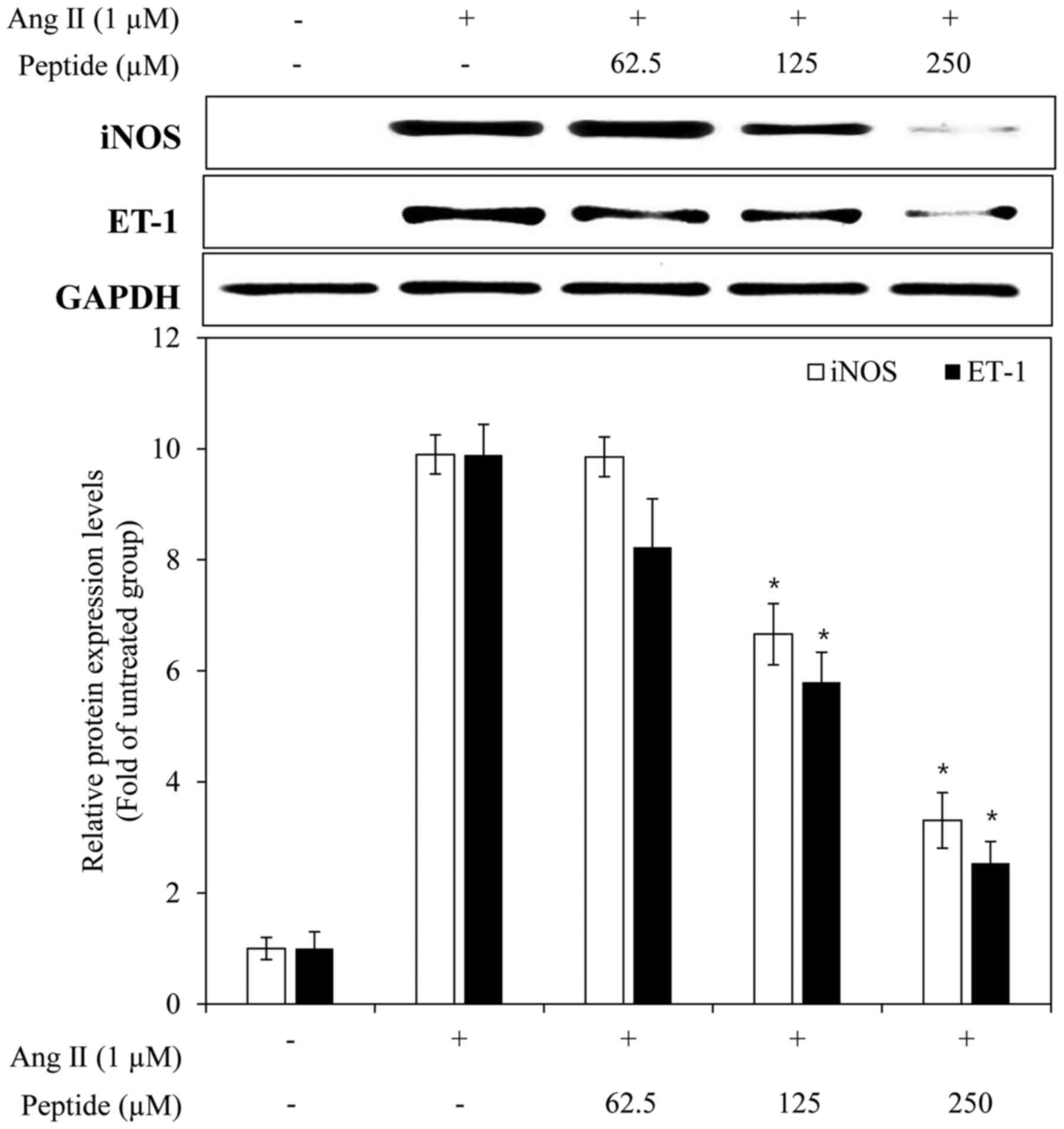
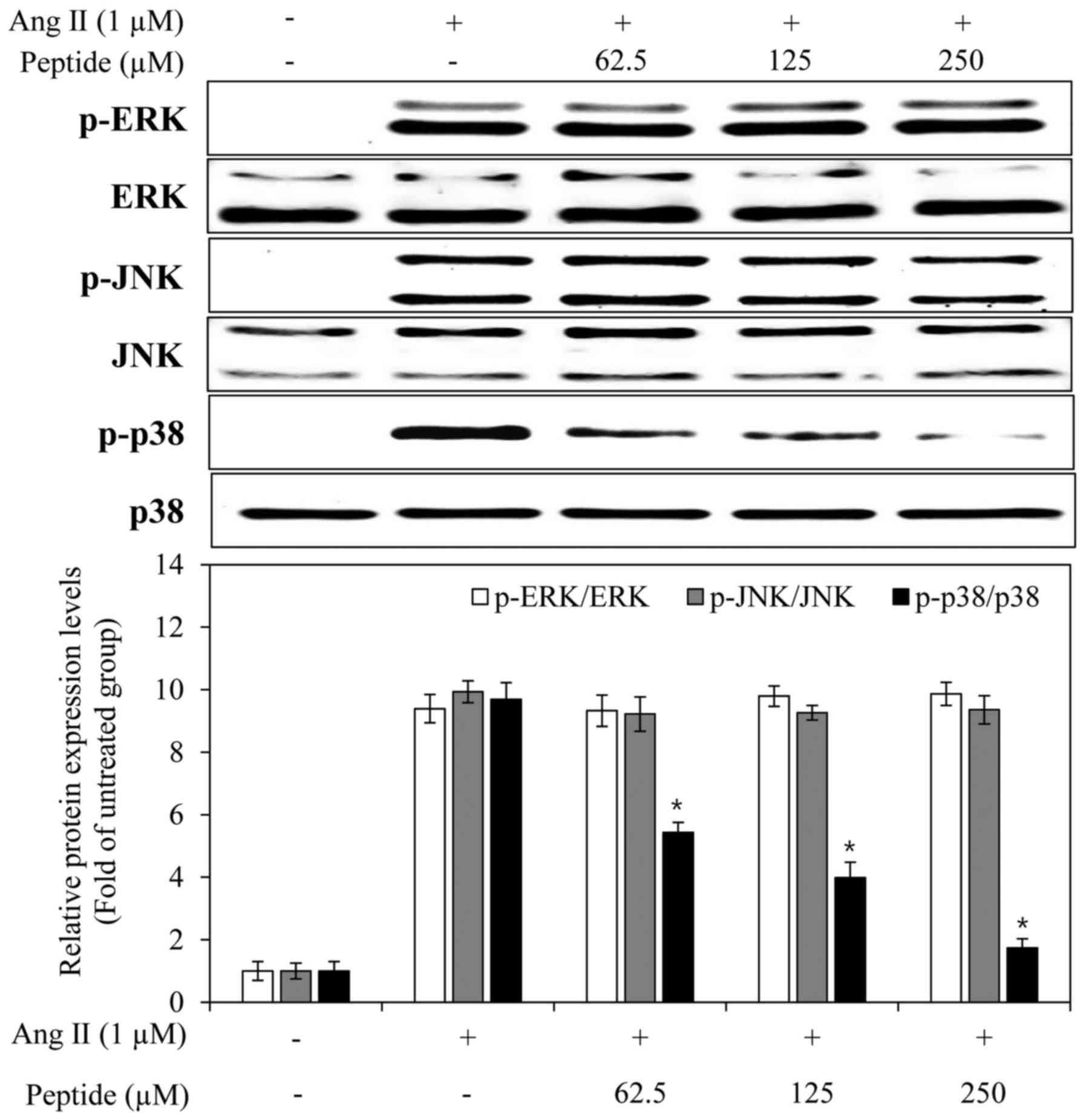
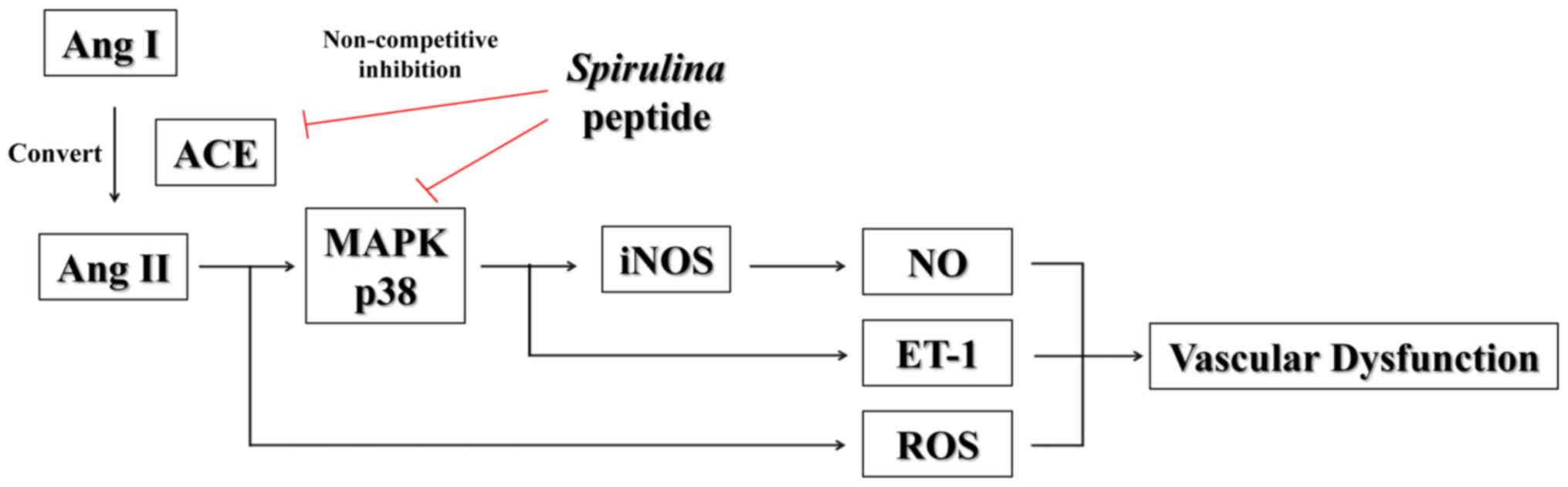
|
1
|
Yamada Y, Kato K, Yoshida T, Yokoi K,
Matsuo H, Watanabe S, Ichihara S, Metoki N, Yoshida H, Satoh K, et
al: Association of polymorphisms of ABCA1 and ROS1 with
hypertension in Japanese individuals. Int J Mol Med. 21:83–89.
2008.
|
|
2
|
Ko SC, Jung WK, Kang SM, Lee SH, Kang MC,
Heo SJ, Kang KH, Kim YT, Park SJ, Jeong Y, et al: Angio-tensin
I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition and nitric oxide (NO)-mediated
antihypertensive effect of octaphlorethol A isolated from Ishige
sinicola: in vitro molecular mechanism and in vivo SHR model. J
Funct Foods. 18:289–299. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sanae M and Yasuo A: Green asparagus
(Asparagus officinalis) prevented hypertension by an inhibitory
effect on angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in the kidney of
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Agric Food Chem. 61:5520–5525.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahn CB, Jeon YJ, Kim YT and Je JY:
Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from
salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by alcalase hydrolysis.
Process Biochem. 47:2240–2245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tomita N, Yamasaki K, Izawa K, Kunugiza Y,
Osako MK, Ogihara T and Morishita R: Improvement of organ damage by
a non-depressor dose of imidapril in diabetic spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Int J Mol Med. 19:571–579. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ko SC, Kang N, Kim EA, Kang MC, Lee SH,
Kang SM, Lee JB, Jeon BT, Kim SK, Park SJ, et al: A novel
angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from a
marine Chlorella ellipsoidea and its antihypertensive effect in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem. 47:2005–2011.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Qian ZJ, Je JY and Kim SK:
Antihypertensive effect of angiotensin I converting
enzyme-inhibitory peptide from hydrolysates of Bigeye tuna dark
muscle, Thunnus obesus. J Agric Food Chem. 55:8398–8403. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen J, Li D, Schaefer R and Mehta JL:
Cross-talk between dyslipidemia and renin-angiotensin system and
the role of LOX-1 and MAPK in atherogenesis studies with the
combined use of rosuvastatin and candesartan. Atherosclerosis.
184:295–301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li JM and Shah AM: Mechanism of
endothelial cell NADPH oxidase activation by angiotensin II. Role
of the p47phox subunit. J Biol Chem. 278:12094–12100.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alonso-Galicia M, Maier KG, Greene AS,
Cowley AW Jr and Roman RJ: Role of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
in the renal and vasoconstrictor actions of angiotensin II. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 283:R60–R68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gragasin FS, Xu Y, Arenas IA, Kainth N and
Davidge ST: Estrogen reduces angiotensin II-induced nitric oxide
synthase and NAD(P)H oxidase expression in endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:38–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hahn AW, Resink TJ, Scott-Burden T, Powell
J, Dohi Y and Bühler FR: Stimulation of endothelin mRNA and
secretion in rat vascular smooth muscle cells: a novel autocrine
function. Cell Regul. 1:649–659. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qian ZJ, Heo SJ, Oh CH, Kang DH, Jeong SH,
Park WS, Choi IW, Jeon YJ and Jung WK: Angiotensin I-converting
enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide isolated from biodiesel byproducts
of marine microalgae, Nannochloropsis oculata. J Biobased Mater
Bioenergy. 7:135–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Servaes K, Maesen M, Prandi B, Sforza S
and Elst K: Polar lipid profile of Nannochloropsis oculata
determined using a variety of lipid extraction procedures. J Agric
Food Chem. 63:3931–3941. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oh GW, Ko SC, Heo SY, Nguyen VT, Kim G,
Jang CH, Park WS, Choi IW, Qian ZJ and Jung WK: A novel peptide
purified from the fermented microalga Pavlova lutheri attenuates
oxidative stress and melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells.
Process Biochem. 50:1318–1326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Suetsuna K and Chen JR: Identification of
antihypertensive peptides from peptic digest of two microalgae,
Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Mar Biotechnol (NY).
3:305–309. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vo TS, Ryu B and Kim SK: Purification of
novel anti-inflammatory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of the
edible microalgal Spirulina maxima. J Funct Foods. 5:1336–1346.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Samuels R, Mani UV, Iyer UM and Nayak US:
Hypocholesterolemic effect of Spirulina in patients with
hyperlipidemic nephrotic syndrome. J Med Food. 5:91–96. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung WK, Qian ZJ, Lee SH, Choi SY, Sung
NJ, Byun HG and Kim SK: Free radical scavenging activity of a novel
anti-oxidative peptide isolated from in vitro gastrointestinal
digests of Mytilus coruscus. J Med Food. 10:197–202. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cushman DW and Cheung HS:
Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the
angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol.
20:1637–1648. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bush K, Henry PR and Slusarchyk DS:
Muraceins - muramyl peptides produced by Nocardia orientalis as
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. I. Taxonomy, fermentation
and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 37:330–335. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Raveh B, London N and Schueler-Furman O:
Sub-angstrom modeling of complexes between flexible peptides and
globular proteins. Proteins. 78:2029–2040. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD,
Impey RW and Klein ML: Comparison of simple potential functions for
simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys. 79:926–935. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J,
Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kalé L and Schulten K:
Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem. 26:1781–1802.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
MacKerell AD Jr, Bashford D, Bellott M,
Dunbrack RL Jr, Evanseck JD, Field MJ, Fischer S, Gao J, Guo H, Ha
S, et al: All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and
dynamics studies of proteins. J Phys Chem B. 102:3586–3616. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toukmaji A, Sagui C, Board J and Darden T:
Efficient particle-mesh Ewald based approach to fixed and induced
dipolar interactions. J Chem Phys. 113:10913–10927. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ko SC, Lee JK, Byun HG, Lee SC and Jeon
YJ: Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting
enzyme inhibitory peptide from enzymatic hydrolysates of Styela
clava flesh tissue. Process Biochem. 47:34–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Qian ZJ, Jung WK, Byun HG and Kim SK:
Protective effect of an antioxidative peptide purified from
gastrointestinal digests of oyster, Crassostrea gigas against free
radical induced DNA damage. Bioresour Technol. 99:3365–3371. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Himaya SWA, Ngo DH, Ryu B and Kim SK: An
active peptide purified from gastrointestinal enzyme hydrolysate of
Pacific cod skin gelatin attenuates angiotensin-1 converting enzyme
(ACE) activity and cellular oxidative stress. Food Chem.
132:1872–1882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jung WK, Mendis E, Je JY, Park PJ, Son BW,
Kim HC, Choi YK and Kim SK: Angiotensin I-converting enzyme
inhibitory peptide from yellow sole (Limanda aspera) frame protein
and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Food Chem. 94:26–32. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Nguyen VT, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Kim KN, Kim D,
Kim YM, Jeon YJ, Park WS, Choi IW, Kim GH, et al: Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) inhibitory effects of an octameric
oligopeptide isolated from abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Food
Chem. 141:503–509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Park WS, Choi IW and Jung
WK: Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanism of an
anti-inflammatory peptide isolated from intestine of abalone,
Haliotis discus hannai on LPS-induced cytokine production via the
p-38/p-JNK pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages. J Food Biochem.
4:690–698. 2016.
|
|
33
|
Wu Q, Jia J, Yan H, Du J and Gui Z: A
novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from
gastrointestinal protease hydrolysate of silkworm pupa (Bombyx
mori) protein: biochemical characterization and molecular docking
study. Peptides. 68:17–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tsai JS, Chen JL and Pan BS:
ACE-inhibitory peptides identified from the muscle protein
hydrolysate of hard clam (Meretrix lusoria). Process Biochem.
43:743–747. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ko SC, Kang MC, Lee JK, Byun HG, Kim SK,
Lee SC, Jeon BT, Park PJ, Jung WK and Jeon YJ: Effect of
angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide purified
from enzymatic hydrolysates of Styela plicata. Eur Food Res
Technol. 233:915–922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Griendling KK, Murphy TJ and Alexander RW:
Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. Circulation.
87:1816–1828. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kagiyama S, Eguchi S, Frank GD, Inagami T,
Zhang YC and Phillips MI: Angiotensin II-induced cardiac
hypertrophy and hypertension are attenuated by epidermal growth
factor receptor antisense. Circulation. 106:909–912. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cai H and Harrison DG: Endothelial
dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress.
Circ Res. 87:840–844. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Millatt LJ, Abdel-Rahman EM and Siragy HM:
Angiotensin II and nitric oxide: a question of balance. Regul Pept.
81:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Olson SC, Dowds TA, Pino PA, Barry MT and
Burke-Wolin T: ANG II stimulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase
expression in bovine pulmonary artery endothelium. Am J Physiol.
273:L315–L321. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hemmrich K, Suschek CV, Lerzynski G and
Kolb-Bachofen V: iNOS activity is essential for endothelial stress
gene expression protecting against oxidative damage. J Appl
Physiol. 95:1937–1946. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ito H, Hirata Y, Adachi S, Tanaka M,
Tsujino M, Koike A, Nogami A, Murumo F and Hiroe M: Endothelin-1 is
an autocrine/paracrine factor in the mechanism of angiotensin
II-induced hypertrophy in cultured rat cardiomyocytes. J Clin
Invest. 92:398–403. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jung WK, Choi I, Lee DY, Yea SS, Choi YH,
Kim MM, Park SG, Seo SK, Lee SW and Lee CM: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock and inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric
oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via the p38/ERK
and NF-kappaB pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:2572–2582.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kyaw M, Yoshizumi M, Tsuchiya K, Kirima K,
Suzaki Y, Abe S, Hasegawa T and Tamaki T: Antioxidants inhibit
endothelin-1 (1–31)-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle
cells via the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase
and activator protein-1 (AP-1). Biochem Pharmacol. 64:1521–1531.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|