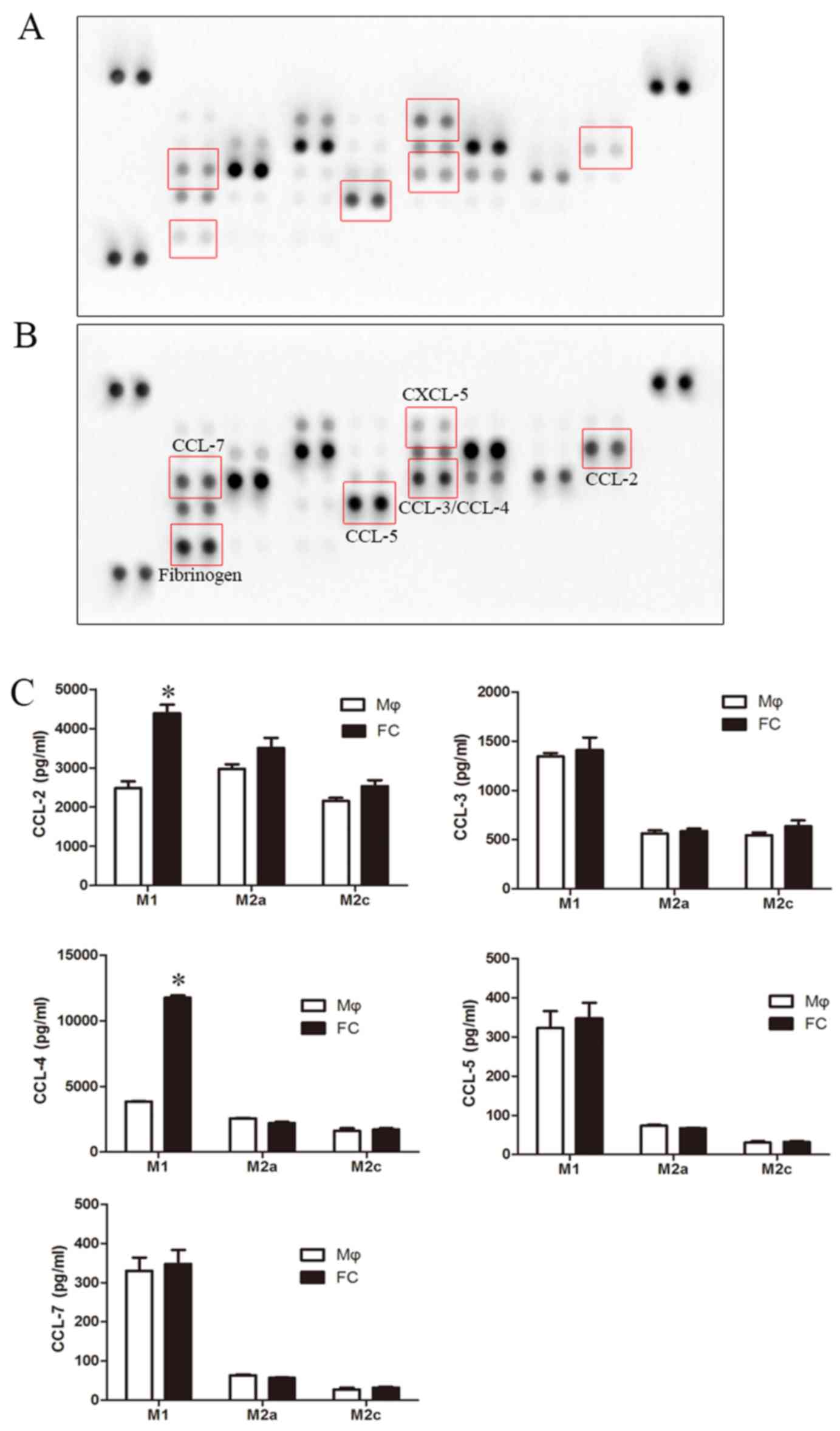
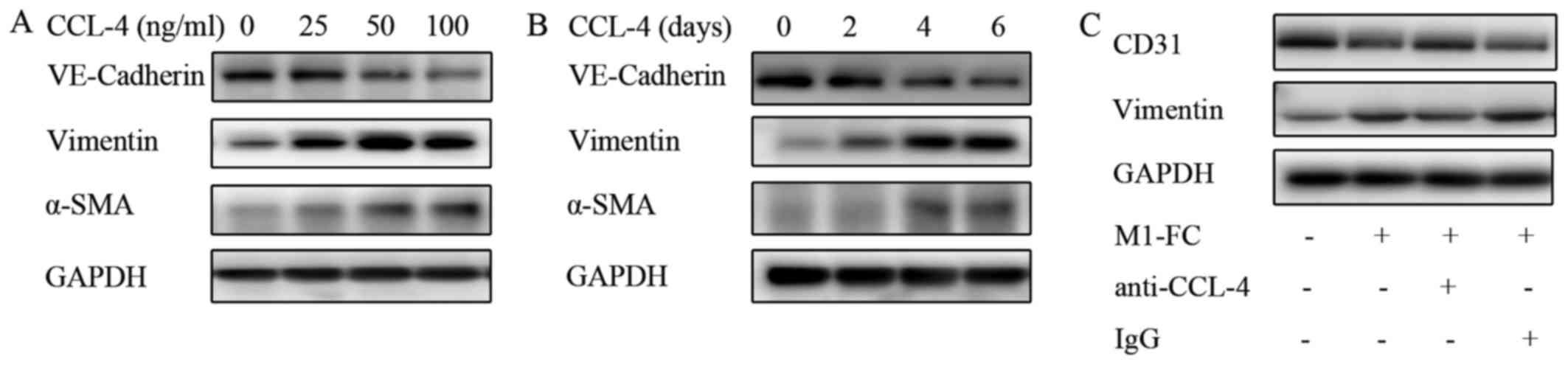
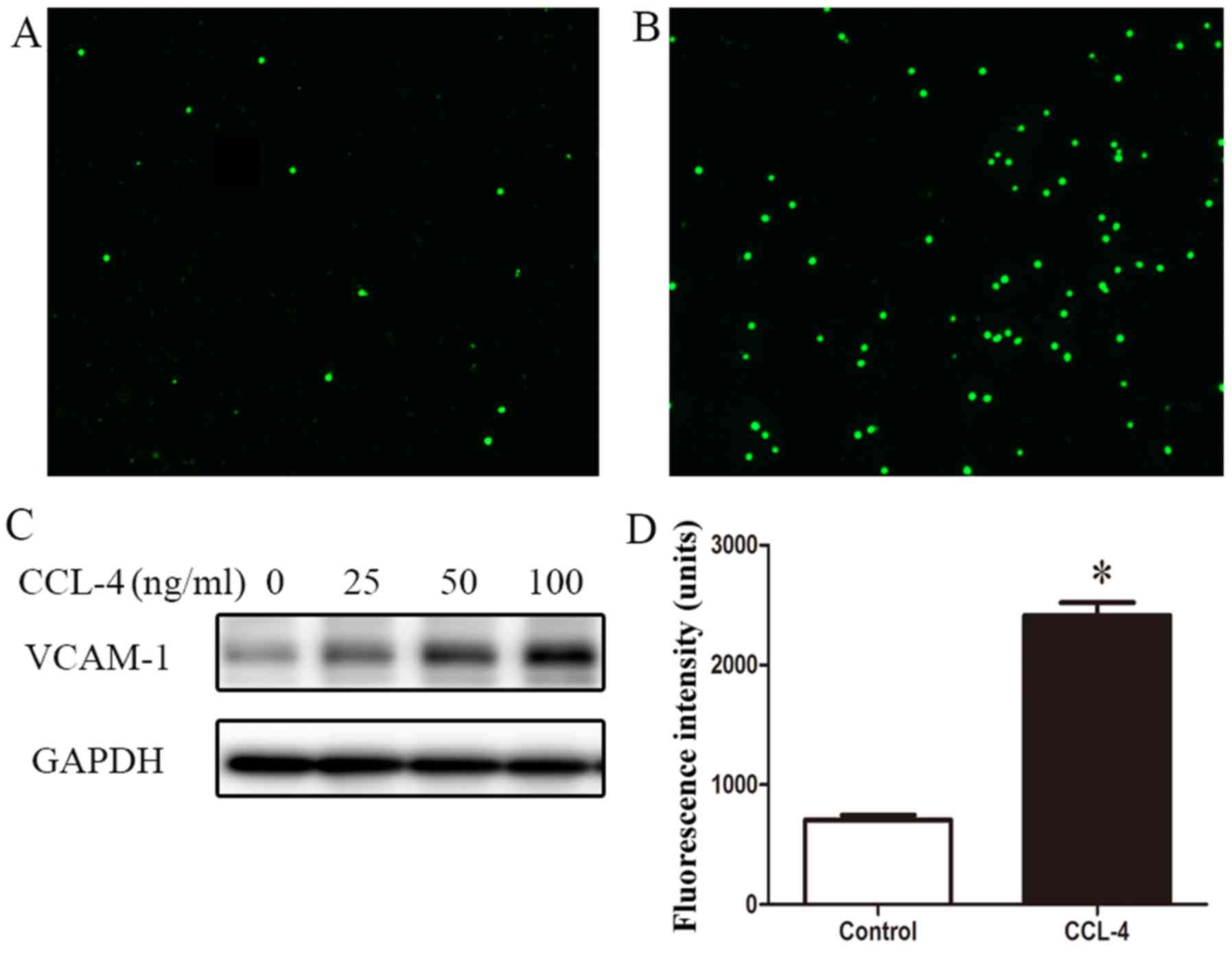
|
1
|
Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P,
Armitage J and Lewington S: Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the
potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease.
Circ Res. 118:535–546. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schulte D, Küppers V, Dartsch N, Broermann
A, Li H, Zarbock A, Kamenyeva O, Kiefer F, Khandoga A, Massberg S,
et al: Stabilizing the VE-cadherin-catenin complex blocks leukocyte
extravasation and vascular permeability. EMBO J. 30:4157–4170.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Giannotta M, Trani M and Dejana E:
VE-cadherin and endothelial adherens junctions: Active guardians of
vascular integrity. Dev Cell. 26:441–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Steffensen LB, Mortensen MB, Kjolby M,
Hagensen MK, Oxvig C and Bentzon JF: Disturbed laminar blood flow
vastly augments lipoprotein retention in the artery wall: A key
mechanism distinguishing susceptible from resistant sites.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1928–1935. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Monette JS, Hutchins PM, Ronsein GE,
Wimberger J, Irwin AD, Tang C, Sara JD, Shao B, Vaisar T, Lerman A,
et al: Patients with coronary endothelial dysfunction have impaired
cholesterol efflux capacity and reduced HDL particle concentration.
Circ Res. 119:83–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts AB, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Good RB, Gilbane AJ, Trinder SL, Denton
CP, Coghlan G, Abraham DJ and Holmes AM: Endothelial to mesenchymal
transition contributes to endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Am J Pathol. 185:1850–1858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan Z, Wang ZG, Segev N, Hu S, Minshall
RD, Dull RO, Zhang M, Malik AB and Hu G: Rab11a mediates vascular
endothelial-cadherin recycling and controls endothelial barrier
function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:339–349. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H,
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via
endothelial-to-mesen-chymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:2282–2287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ranchoux B, Antigny F, Rucker-Martin C,
Hautefort A, Péchoux C, Bogaard HJ, Dorfmüller P, Remy S, Lecerf F,
Planté S, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary
hypertension. Circulation. 131:1006–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi SH, Hong ZY, Nam JK, Lee HJ, Jang J,
Yoo RJ, Lee YJ, Lee CY, Kim KH, Park S, et al: A hypoxia-induced
vascular endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in development of
radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Cancer Res.
21:3716–3726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yung LM, Sánchez-Duffhues G, Ten Dijke P
and Yu PB: Bone morphogenetic protein 6 and oxidized low-density
lipoprotein synergistically recruit osteogenic differentiation in
endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res. 108:278–287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu X, Friehs I, Zhong Hu T, Melnychenko I,
Tampe B, Alnour F, Iascone M, Kalluri R, Zeisberg M, Del Nido PJ,
et al: Endocardial fibroelastosis is caused by aberrant endothelial
to mesenchymal transition. Circ Res. 116:857–866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim M, Choi SH, Jin YB, Lee HJ, Ji YH, Kim
J, Lee YS and Lee YJ: The effect of oxidized low-density
lipoprotein (ox-LDL) on radiation-induced
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Int J Radiat Biol.
89:356–363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moonen JR, Lee ES, Schmidt M, Maleszewska
M, Koerts JA, Brouwer LA, van Kooten TG, van Luyn MJ, Zeebregts CJ,
Krenning G, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to fibro-proliferative vascular disease and is
modulated by fluid shear stress. Cardiovasc Res. 108:377–386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen PY, Qin L, Baeyens N, Li G, Afolabi
T, Budatha M, Tellides G, Schwartz MA and Simons M:
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives atherosclerosis
progression. J Clin Invest. 125:4514–4528. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Evrard SM, Lecce L, Michelis KC,
Nomura-Kitabayashi A, Pandey G, Purushothaman KR, d'Escamard V, Li
JR, Hadri L, Fujitani K, et al: Endothelial to mesenchymal
transition is common in atherosclerotic lesions and is associated
with plaque instability. Nat Commun. 7:118532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Badimon L, Storey RF and Vilahur G: Update
on lipids, inflammation and atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost.
105(Suppl 1): S34–S42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2045–2051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Webb NR and Moore KJ: Macrophage-derived
foam cells in atherosclerosis: lessons from murine models and
implications for therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 8:1249–1263. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Randolph GJ: Mechanisms that regulate
macrophage burden in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 114:1757–1771.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hung Y, Hong M and Huang GS: Cholesterol
loading augments oxidative stress in macrophages. FEBS Lett.
580:849–861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Colin S and Staels B:
Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:10–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Leitinger N and Schulman IG: Phenotypic
polarization of macrophages in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:1120–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fang S, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Tian J, Li J, Li Z,
He Z, Chai R, Liu F, Zhang T, et al: Irgm1 promotes M1 but not M2
macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis pathogenesis and
development. Atherosclerosis. 251:282–290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McAlpine CS, Huang A, Emdin A, Banko NS,
Beriault DR, Shi Y and Werstuck GH: Deletion of myeloid GSK3α
attenuates atherosclerosis and promotes an M2 macrophage phenotype.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1113–1122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin K, You Y, Swier V, Tang L, Radwan MM,
Pandya AN, Agrawal DK and Vitamin D: Vitamin D protects against
atherosclerosis via regulation of cholesterol efflux and macrophage
polarization in hypercholesterolemic swine. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 35:2432–2442. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y, Choksi S, Chen K, Pobezinskaya Y,
Linnoila I and Liu ZG: ROS play a critical role in the
differentiation of alternatively activated macrophages and the
occurrence of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Res. 23:898–914.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai J, Adriani G, Dang TM, Tu TY, Penny
HX, Wong SC, Kamm RD and Thiery JP: Contact-dependent carcinoma
aggregate dispersion by M2a macrophages via ICAM-1 and β2 integrin
interactions. Oncotarget. 6:25295–25307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mai J, Qiu Q, Lin YQ, Luo NS, Zhang HF,
Wen ZZ, Wang JF and YangXin C: Angiotensin II-derived reactive
oxygen species promote angiogenesis in human late endothelial
progenitor cells through heme oxygenase-1 via ERK1/2 and AKT/PI3K
pathways. Inflammation. 37:858–870. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim M, Neinast MD, Frank AP, Sun K, Park
J, Zehr JA, Vishvanath L, Morselli E, Amelotte M, Palmer BF, et al:
ERα upregulates Phd3 to ameliorate HIF-1 induced fibrosis and
inflammation in adipose tissue. Mol Metab. 3:642–651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mai J, Hu Q, Xie Y, Su S, Qiu Q, Yuan W,
Yang Y, Song E, Chen Y and Wang J: Dyssynchronous pacing triggers
endothelial-mesenchymal transition through heterogeneity of
mechanical stretch in a canine model. Circ J. 79:201–209. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Su S, Liu Q, Chen J, Chen J, Chen F, He C,
Huang D, Wu W, Lin L, Huang W, et al: A positive feedback loop
between mesenchymal-like cancer cells and macrophages is essential
to breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell. 25:605–620. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yeung OW, Lo CM, Ling CC, Qi X, Geng W, Li
CX, Ng KT, Forbes SJ, Guan XY, Poon RT, et al: Alternatively
activated (M2) macrophages promote tumour growth and invasiveness
in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 62:607–616. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zernecke A and Weber C: Chemokines in
atherosclerosis: proceedings resumed. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 34:742–750. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Drechsler M, Duchene J and Soehnlein O:
Chemokines control mobilization, recruitment, and fate of monocytes
in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1050–1055.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ishida Y, Kimura A, Kuninaka Y, Inui M,
Matsushima K, Mukaida N and Kondo T: Pivotal role of the CCL5/CCR5
interaction for recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells in
mouse wound healing. J Clin Invest. 122:711–721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sugg KB, Lubardic J, Gumucio JP and
Mendias CL: Changes in macrophage phenotype and induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition genes following acute Achilles
tenotomy and repair. J Orthop Res. 32:944–951. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tripathi C, Tewari BN, Kanchan RK, Baghel
KS, Nautiyal N, Shrivastava R, Kaur H, Bhatt ML and Bhadauria S:
Macrophages are recruited to hypoxic tumor areas and acquire a
pro-angiogenic M2-polarized phenotype via hypoxic cancer cell
derived cytokines Oncostatin M and Eotaxin. Oncotarget.
5:5350–5368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post
MJ, De Winther MP and Donners MM: Anti-inflammatory M2, but not
pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo.
Angiogenesis. 17:109–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV,
Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP and Narula J: Atherosclerotic plaque
progression and vulnerability to rupture: Angiogenesis as a source
of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:2054–2061. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hutter R, Speidl WS, Valdiviezo C, Sauter
B, Corti R, Fuster V and Badimon JJ: Macrophages transmit potent
proangiogenic effects of oxLDL in vitro and in vivo involving
HIF-1α activation: A novel aspect of angiogenesis in
atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 6:558–569. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Giannarelli C, Alique M, Rodriguez DT,
Yang DK, Jeong D, Calcagno C, Hutter R, Millon A, Kovacic JC, Weber
T, et al: Alternatively spliced tissue factor promotes plaque
angiogenesis through the activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. Circulation.
130:1274–1286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ouimet M, Ediriweera HN, Gundra UM, Sheedy
FJ, Ramkhelawon B, Hutchison SB, Rinehold K, van Solingen C,
Fullerton MD, Cecchini K, et al: MicroRNA-33-dependent regulation
of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 125:4334–4348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ying R, Wang XQ, Yang Y, Gu ZJ, Mai JT,
Qiu Q, Chen YX and Wang JF: Hydrogen sulfide suppresses endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
through Src pathway. Life Sci. 144:208–217. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xu F, Lv S, Chen Y, Song X, Jin Z, Yuan F,
Zhou Y and Li H: Macrophage inflammatory protein-1β and fibrinogen
are synergistic predictive markers of prognosis of intermediate
coronary artery lesions. Cardiology. 121:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Edsfeldt A, Grufman H, Asciutto G,
Nitulescu M, Persson A, Nilsson M, Nilsson J and Gonçalves I:
Circulating cytokines reflect the expression of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in athero-sclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis.
241:443–449. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gentili A, Zaibi MS, Alomar SY, De Vuono
S, Ricci MA, Alaeddin A, Siepi D, Boni M, Vaudo G, Trayhurn P, et
al: Circulating levels of the adipokines monocyte chemotactic
protein-4 (MCP-4), macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β), and
eotaxin-3 in severe obesity and following bariatric surgery. Horm
Metab Res. 48:847–853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vistnes M: Macrophage inflammatory
protein-1β: A novel prognostic biomarker in atherosclerosis?
Cardiology. 121:149–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Salic K, Morrison MC, Verschuren L,
Wielinga PY, Wu L, Kleemann R, Gjorstrup P and Kooistra T: Resolvin
E1 attenuates atherosclerosis in absence of cholesterol-lowering
effects and on top of atorvastatin. Atherosclerosis. 250:158–165.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hsu DC, Ma YF, Hur S, Li D, Rupert A,
Scherzer R, Kalapus SC, Deeks S, Sereti I and Hsue PY: Plasma IL-6
levels are independently associated with atherosclerosis and
mortality in HIV-infected individuals on suppressive antiretroviral
therapy. AIDS. 30:2065–2074. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Herbin O, Regelmann AG, Ramkhelawon B,
Weinstein EG, Moore KJ and Alexandropoulos K: Monocyte adhesion and
plaque recruitment during atherosclerosis development is regulated
by the adapter protein Chat-H/SHEP1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
36:1791–1801. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cipriani S, Francisci D, Mencarelli A,
Renga B, Schiaroli E, D'Amore C, Baldelli F and Fiorucci S:
Efficacy of the CCR5 antagonist maraviroc in reducing early,
ritonavir-induced athero-genesis and advanced plaque progression in
mice. Circulation. 127:2114–2124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|