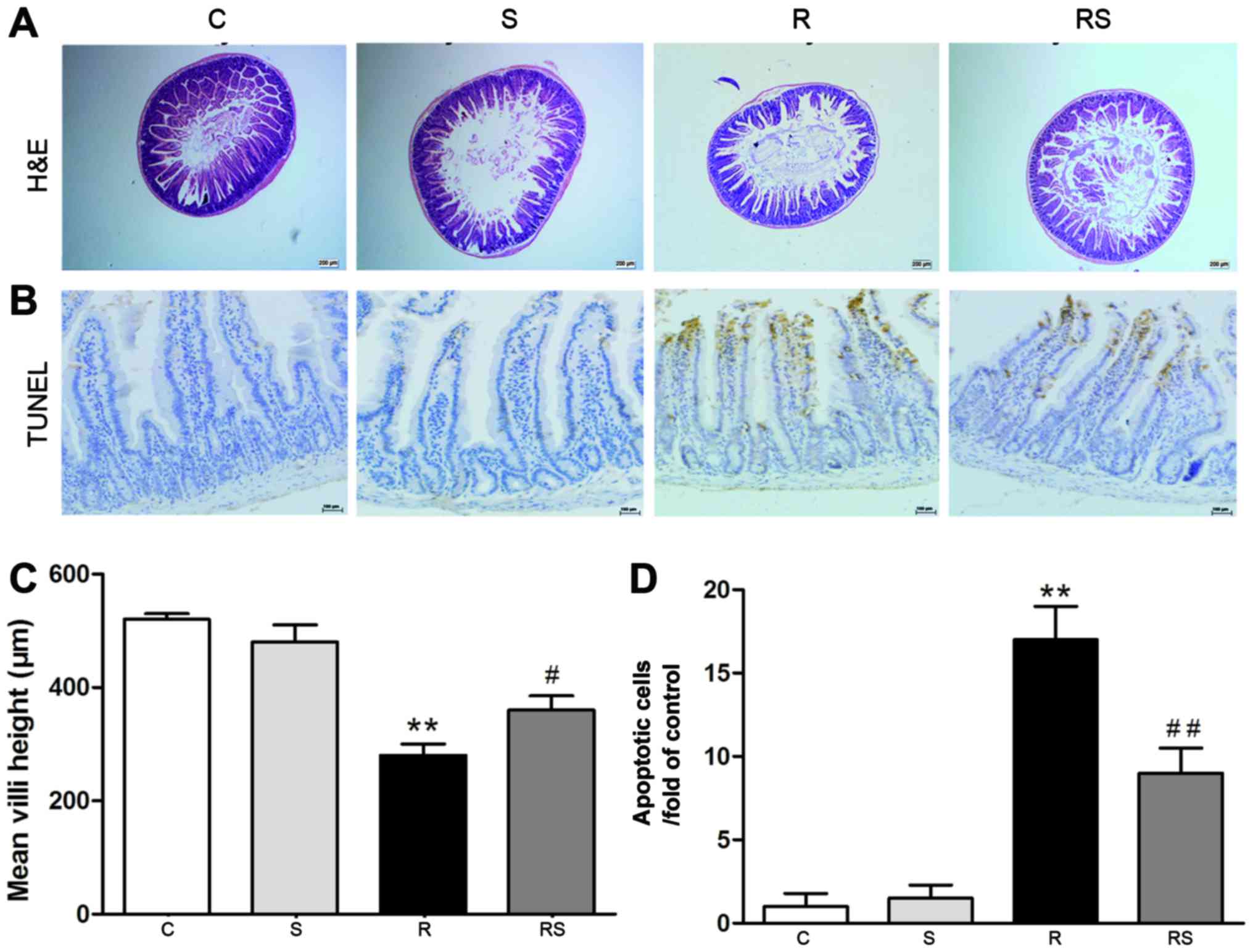
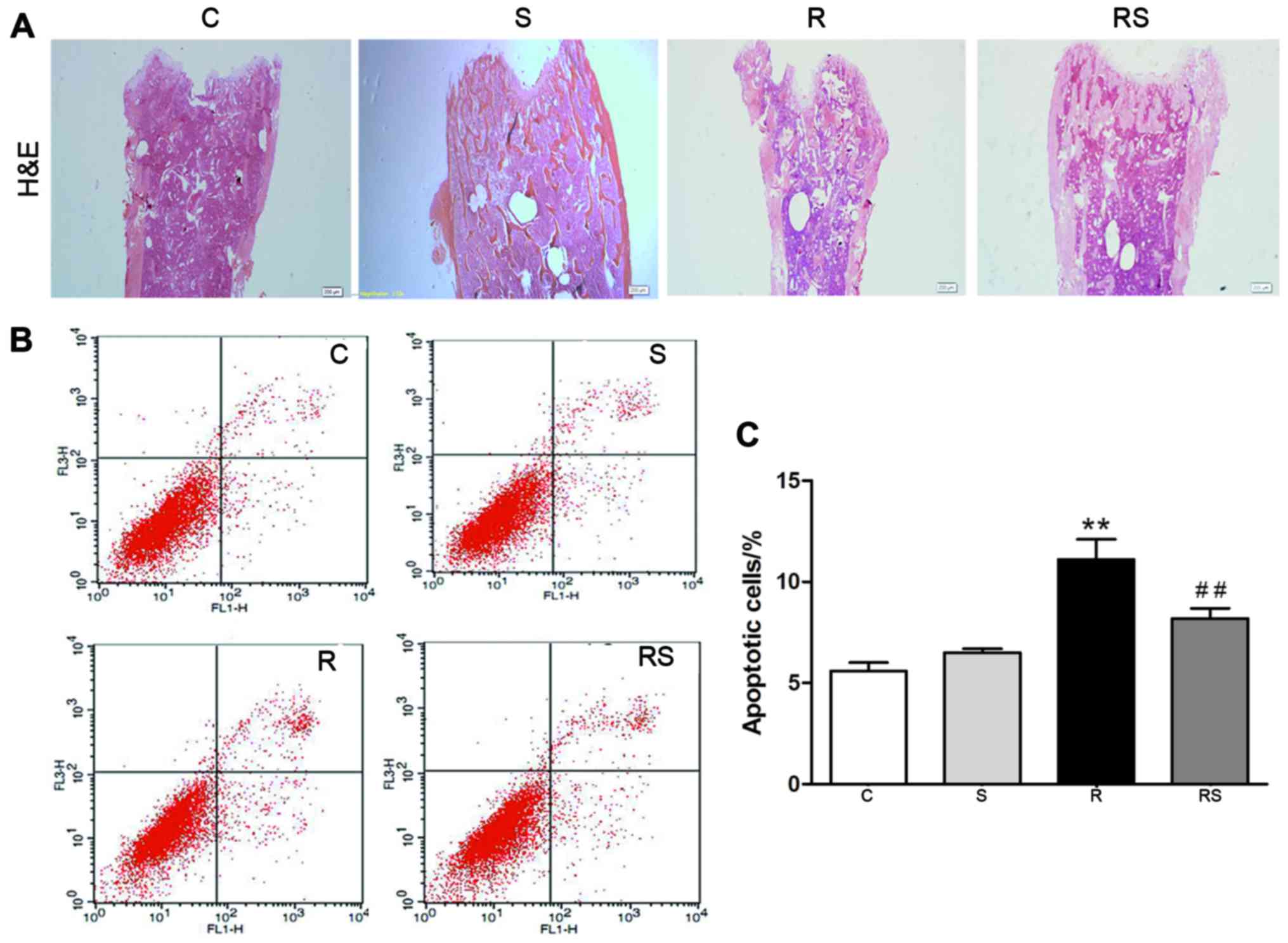
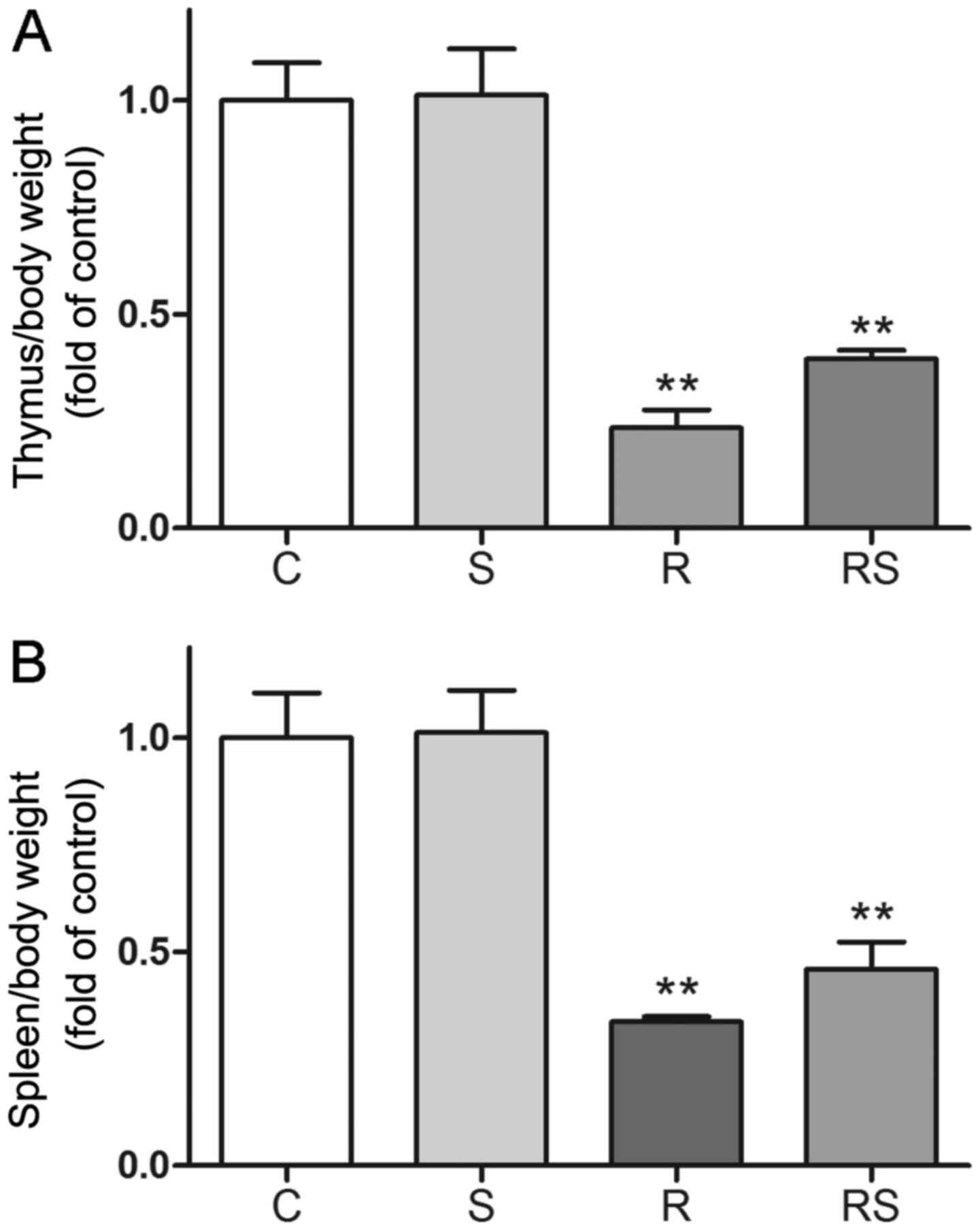
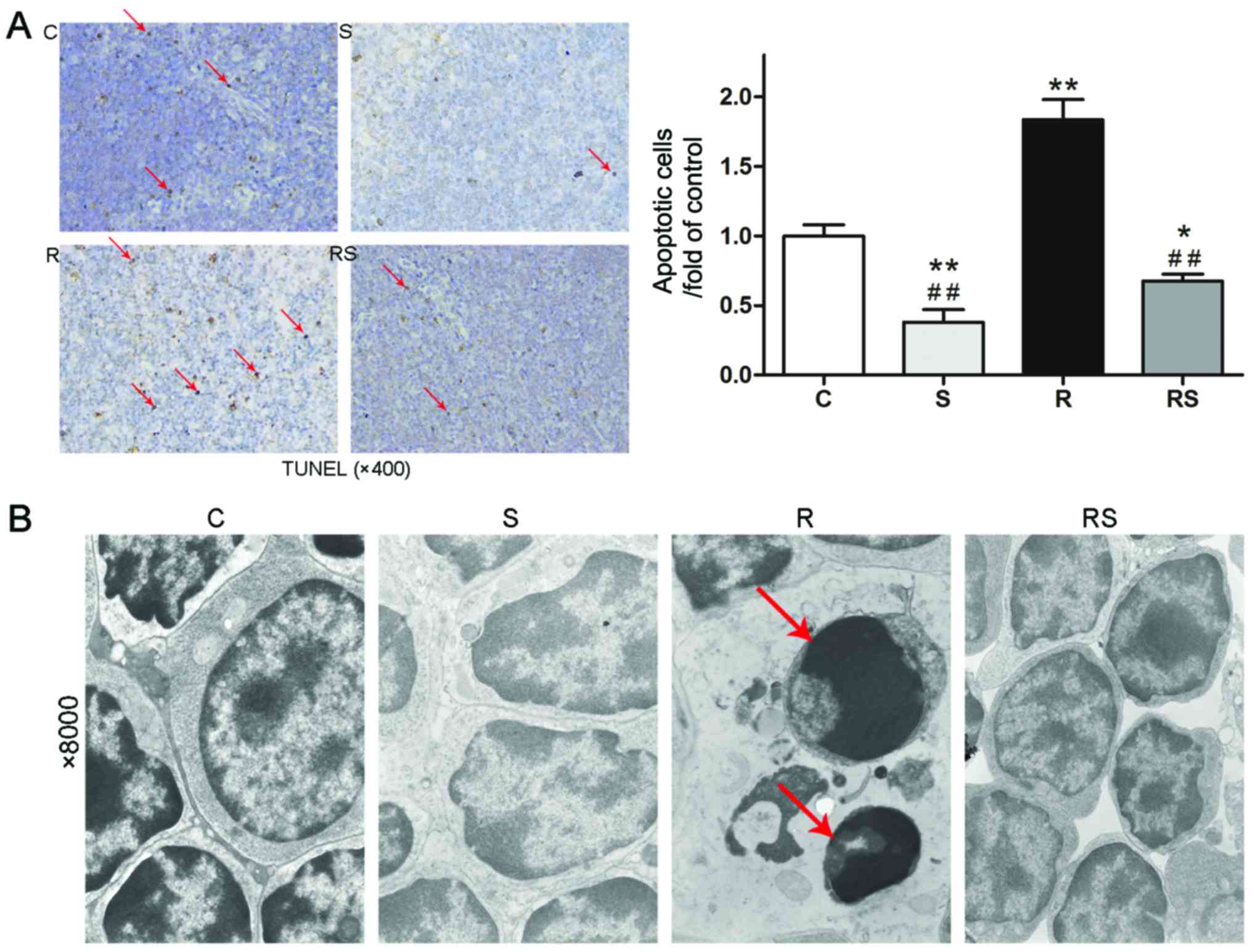
|
1
|
Wang J, Boerma M, Fu Q, Kulkarni A, Fink
LM and Hauer-Jensen M: Simvastatin ameliorates radiation
enteropathy development after localized, fractionated irradiation
by a protein C-independent mechanism. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
68:1483–1490. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Christiansen H, Saile B, Neubauer-Saile K,
Tippelt S, Rave-Fränk M, Hermann RM, Dudas J, Hess CF, Schmidberger
H and Ramadori G: Irradiation leads to susceptibility of
hepatocytes to TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis. Radiother Oncol.
72:291–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stewart FA and Dörr W: Milestones in
normal tissue radiation biology over the past 50 years: From
clonogenic cell survival to cytokine networks and back to stem cell
recovery. Int J Radiat Biol. 85:574–586. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kolesnick R and Fuks Z: Radiation and
ceramide-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 22:5897–5906. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okunieff P, Chen Y, Maguire DJ and Huser
AK: Molecular markers of radiation-related normal tissue toxicity.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:363–374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim Y and He YY: Ultraviolet
radiation-induced non-melanoma skin cancer: Regulation of DNA
damage repair and inflammation. Genes Dis. 1:188–198. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Najafi M, Fardid R, Hadadi G and Fardid M:
The mechanisms of radiation-induced bystander effect. J Biomed Phys
Eng. 4:163–172. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Stoecklein VM, Osuka A, Ishikawa S,
Lederer MR, Wanke-Jellinek L and Lederer JA: Radiation exposure
induces inflammasome pathway activation in immune cells. J Immunol.
194:1178–1189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Lowe SW, Schmitt EM, Smith SW, Osborne BA
and Jacks T: p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in
mouse thymocytes. Nature. 362:847–849. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
May P and May E: Twenty years of p53
research: Structural and functional aspects of the p53 protein.
Oncogene. 18:7621–7636. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
McBride OW, Merry D and Givol D: The gene
for human p53 cellular tumor antigen is located on chromosome 17
short arm (17p13). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:130–134. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tjalma WA, Weyler JJ, Bogers JJ,
Pollefliet C, Baay M, Goovaerts GC, Vermorken JB, van Dam PA, van
Marck EA and Buytaert PM: The importance of biological factors
(Bcl-2, bax, p53 PCNA, MI, HPV and angiogenesis) in invasive
cervical cancer. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 97:223–230.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cleary ML, Smith SD and Sklar J: Cloning
and structural analysis of cDNAs for Bcl-2 and a hybrid
Bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18)
translocation. Cell. 47:19–28. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC
and Croce CM: Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B
cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science.
226:1097–1099. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adán N, Guzmán-Morales J, Ledesma-Colunga
MG, Perales-Canales SI, Quintanar-Stéphano A, López-Barrera F,
Méndez I, Moreno-Carranza B, Triebel J, Binart N, et al: Prolactin
promotes cartilage survival and attenuates inflammation in
inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest. 123:3902–3913. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Follis AV, Llambi F, Ou L, Baran K, Green
DR and Kriwacki RW: The DNA-binding domain mediates both nuclear
and cytosolic functions of p53. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 21:535–543.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li HF, Kim JS and Waldman T:
Radiation-induced Akt activation modulates radioresistance in human
glioblastoma cells. Radiat Oncol. 4:432009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edwards E, Geng L, Tan J, Onishko H,
Donnelly E and Hallahan DE: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
signaling in the response of vascular endothelium to ionizing
radiation. Cancer Res. 62:4671–4677. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen WS, Xu PZ, Gottlob K, Chen ML, Sokol
K, Shiyanova T, Roninson I, Weng W, Suzuki R, Tobe K, et al: Growth
retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous
disruption of the Akt1 gene. Genes Dev. 15:2203–2208. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Zhang KY, Zhang P, Chen LX, Wang L,
Xie M, Wang CY and Tang XQ: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
formaldehyde-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC12 cells by
upregulation of SIRT-1. PLoS One. 9:e898562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pillai VB, Sundaresan NR and Gupta MP:
Regulation of Akt signaling by sirtuins: Its implication in cardiac
hypertrophy and aging. Circ Res. 114:368–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Q, Sun X, Li X, Dong X, Li P and Zhao
L: Resveratrol attenuates intermittent hypoxia-induced insulin
resistance in rats: Involvement of Sirtuin 1 and the
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 11:151–158. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Isabelle M, Moreel X, Gagné JP, Rouleau M,
Ethier C, Gagné P, Hendzel MJ and Poirier GG: Investigation of
PARP-1, PARP-2, and PARG interactomes by affinity-purification mass
spectrometry. Proteome Sci. 8:222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu SW, Andrabi SA, Wang H, Kim NS, Poirier
GG, Dawson TM and Dawson VL: Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates
poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer-induced cell death. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:18314–18319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lindahl T, Satoh MS, Poirier GG and
Klungland A: Post-translational modification of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase induced by DNA strand breaks. Trends Biochem Sci.
20:405–411. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Albert JM, Cao C, Kim KW, Willey CD, Geng
L, Xiao D, Wang H, Sandler A, Johnson DH, Colevas AD, et al:
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase enhances cell death and
improves tumor growth delay in irradiated lung cancer models. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:3033–3042. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Veuger SJ, Hunter JE and Durkacz BW:
Ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation requires PARP-1
function to confer radioresistance. Oncogene. 28:832–842. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bryant HE and Helleday T: Poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibitors as potential chemotherapeutic agents. Biochem
Soc Trans. 32:959–961. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lopez-Pedrera C, Ruiz-Limon P,
Valverde-Estepa A, Barbarroja N and Rodriguez-Ariza A: To
cardiovascular disease and beyond: New therapeutic perspectives of
statins in autoimmune diseases and cancer. Curr Drug Targets.
13:829–841. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fritz G, Henninger C and Huelsenbeck J:
Potential use of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) as
radioprotective agents. Br Med Bull. 97:17–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao X, Yang H, Jiang G, Ni M, Deng Y, Cai
J, Li Z, Shen F and Tao X: Simvastatin attenuates radiation-induced
tissue damage in mice. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 55:257–264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mathew B, Huang Y, Jacobson JR, Berdyshev
E, Gerhold LM, Wang T, Moreno-Vinasco L, Lang G, Zhao Y, Chen CT,
et al: Simvastatin attenuates radiation-induced murine lung injury
and dysregulated lung gene expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
44:415–422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Lacerda L, Reddy JP, Liu D, Larson R, Li
L, Masuda H, Brewer T, Debeb BG, Xu W, Hortobágyi GN, et al:
Simvastatin radiosensitizes differentiated and stem-like breast
cancer cell lines and is associated with improved local control in
inflammatory breast cancer patients treated with postmastectomy
radiation. Stem Cells Transl Med. 3:849–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oh DS, Koontz B, Freedland SJ, Gerber L,
Patel P, Lewis S, Yoo DS, Oleson J and Salama JK: Statin use is
associated with decreased prostate cancer recurrence in men treated
with brachytherapy. World J Urol. 33:93–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ostrau C, Hülsenbeck J, Herzog M, Schad A,
Torzewski M, Lackner KJ and Fritz G: Lovastatin attenuates ionizing
radiation-induced normal tissue damage in vivo. Radiother Oncol.
92:492–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi DW, Na W, Kabir MH, Yi E, Kwon S,
Yeom J, Ahn JW, Choi HH, Lee Y, Seo KW, et al: WIP1, a homeostatic
regulator of the DNA damage response, is targeted by HIPK2 for
phosphorylation and degradation. Mol Cell. 51:374–385. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Contreras AU, Mebratu Y, Delgado M,
Montano G, Hu CA, Ryter SW, Choi AM, Lin Y, Xiang J, Chand H, et
al: Deacetylation of p53 induces autophagy by suppressing Bmf
expression. J Cell Biol. 201:427–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xie L, Pi X, Mishra A, Fong G, Peng J and
Patterson C: PHD3-dependent hydroxylation of HCLK2 promotes the DNA
damage response. J Clin Invest. 122:2827–2836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR,
Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA, Bruncko M, Deckwerth TL, Dinges
J, Hajduk PJ, et al: An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces
regression of solid tumours. Nature. 435:677–681. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang XY, Ma ZC, Wang YG, Tan HL, Xiao CR,
Liang QD, Tang XL, Cheng Y and Gao Y: Tetramethylpyrazine protects
lymphocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis through nuclear
factor-κB. Chin J Nat Med. 12:730–737. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Milyavsky M, Gan OI, Trottier M, Komosa M,
Tabach O, Notta F, Lechman E, Hermans KG, Eppert K, Konovalova Z,
et al: A distinctive DNA damage response in human hematopoietic
stem cells reveals an apoptosis-independent role for p53 in
self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell. 7:186–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sidi S, Sanda T, Kennedy RD, Hagen AT,
Jette CA, Hoffmans R, Pascual J, Imamura S, Kishi S, Amatruda JF,
et al: Chk1 suppresses a caspase-2 apoptotic response to DNA damage
that bypasses p53 Bcl-2, and caspase-3. Cell. 133:864–877. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Strom E, Sathe S, Komarov PG, Chernova OB,
Pavlovska I, Shyshynova I, Bosykh DA, Burdelya LG, Macklis RM,
Skaliter R, et al: Small-molecule inhibitor of p53 binding to
mitochondria protects mice from gamma radiation. Nat Chem Biol.
2:474–479. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ and Kaanders
JH: Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for
radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol.
9:288–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu N, Hegarat N, Black EJ, Scott MT,
Hochegger H and Gillespie DA: Akt/PKB suppresses DNA damage
processing and checkpoint activation in late G2. J Cell Biol.
190:297–305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tessner TG, Muhale F, Riehl TE, Anant S
and Stenson WF: Prostaglandin E2 reduces radiation-induced
epithelial apoptosis through a mechanism involving AKT activation
and bax translocation. J Clin Invest. 114:1676–1685. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hong EH, Lee SJ, Kim JS, Lee KH, Um HD,
Kim JH, Kim SJ, Kim JI and Hwang SG: Ionizing radiation induces
cellular senescence of articular chondrocytes via negative
regulation of SIRT1 by p38 kinase. J Biol Chem. 285:1283–1295.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Li J, Feng L, Xing Y, Wang Y, Du L, Xu C,
Cao J, Wang Q, Fan S, Liu Q, et al: Radioprotective and antioxidant
effect of resveratrol in hippocampus by activating Sirt1. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:5928–5939. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nerurkar PV and Nerurkar VR: Can Sir(2)
regulate cancer? Cellscience. 4:50–56. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gao Z, Wang H, Xiao FJ, Shi XF, Zhang YK,
Xu QQ, Zhang XY, Ha XQ and Wang LS: SIRT1 mediates
Sphk1/S1P-induced proliferation and migration of endothelial cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 74:152–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Koga T, Suico MA, Shimasaki S, Watanabe E,
Kai Y, Koyama K, Omachi K, Morino-Koga S, Sato T, Shuto T, et al:
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress Induces Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)
Expression via the PI3K-Akt-GSK3β Signaling Pathway and Promotes
Hepatocellular Injury. J Biol Chem. 290:30366–30374. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ge Z, Zhang P, Hong T, Tang S, Meng R, Bi
Y and Zhu D: Erythropoietin alleviates hepatic insulin resistance
via PPARγ-dependent AKT activation. Sci Rep. 5:178782015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kotsopoulos IC, Kucukmetin A, Mukhopadhyay
A, Lunec J and Curtin NJ: Poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase in cervical
cancer pathogenesis: Mechanism and potential role for PARP
inhibitors. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 26:763–769. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu Y and Little JB: p53 is involved in but
not required for ionizing radiation-induced caspase-3 activation
and apoptosis in human lymphoblast cell lines. Cancer Res.
58:4277–4281. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|