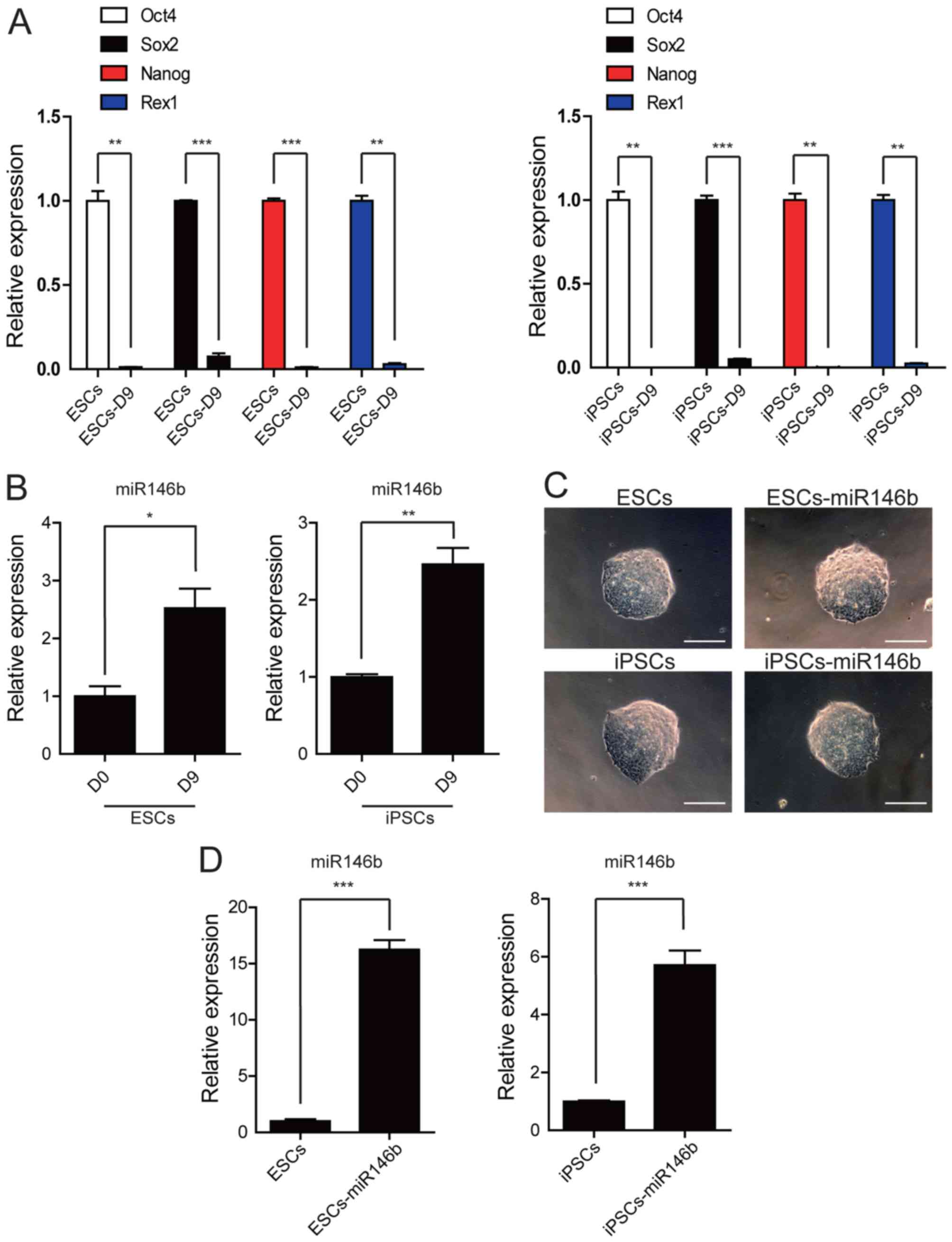
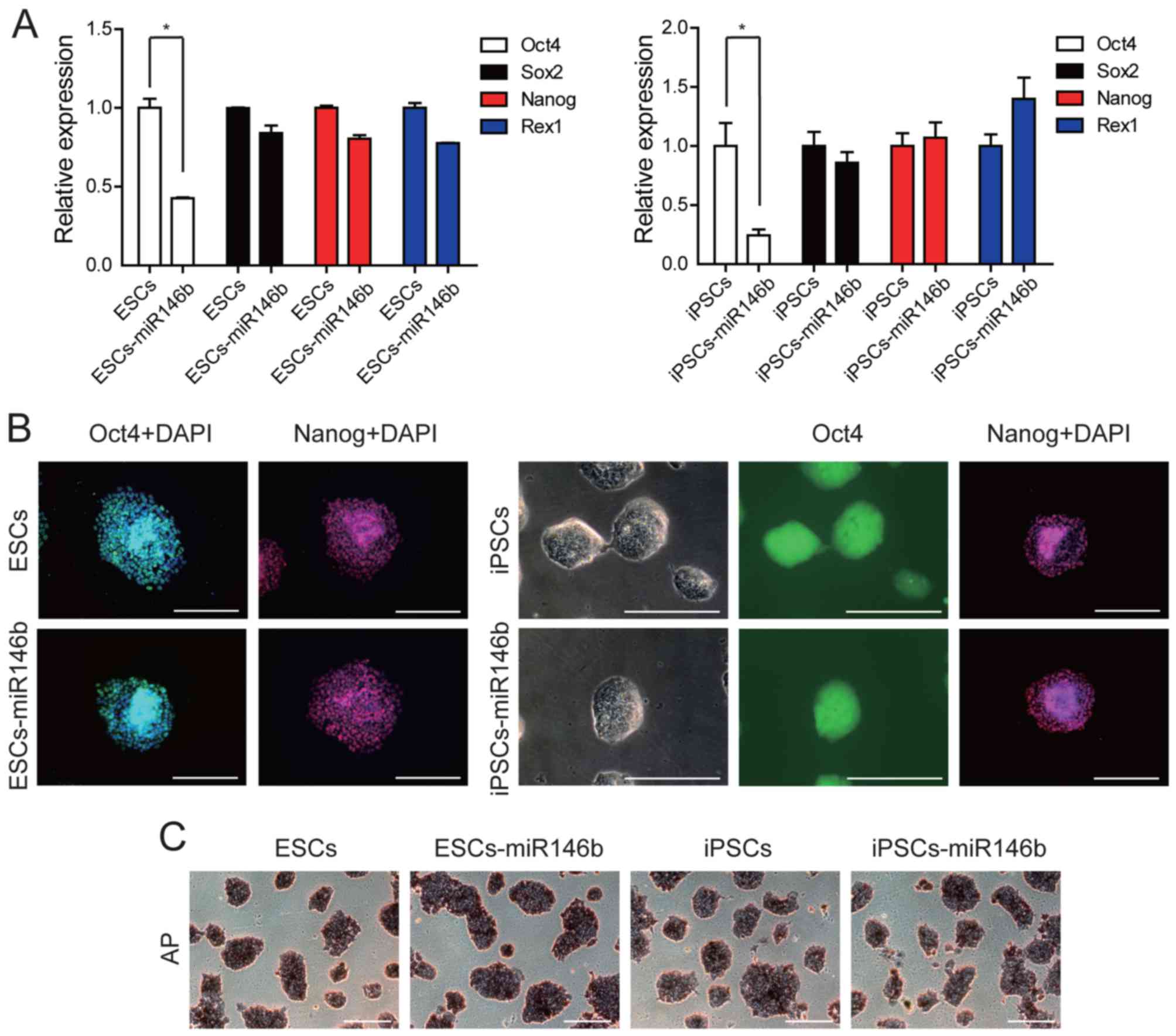
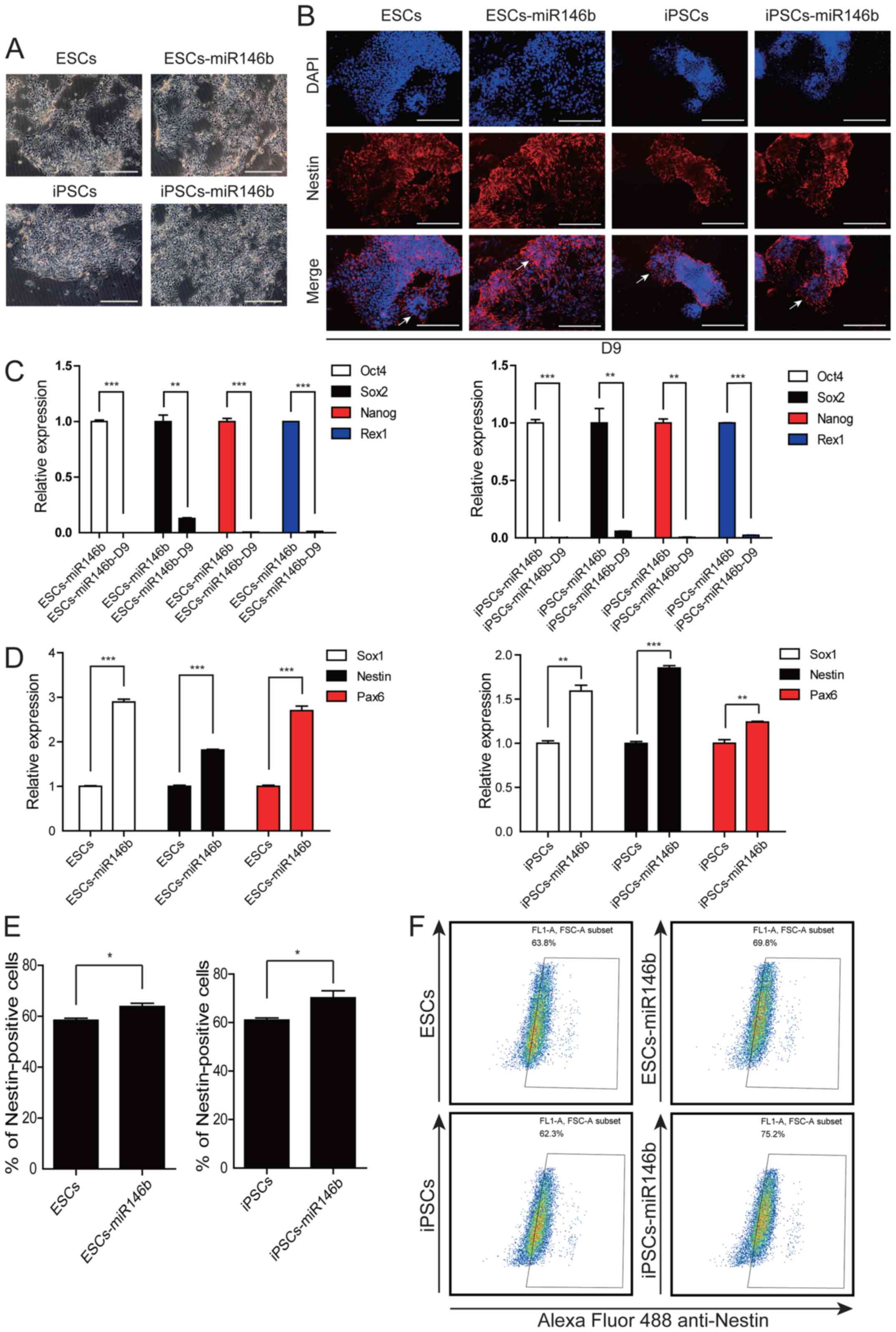
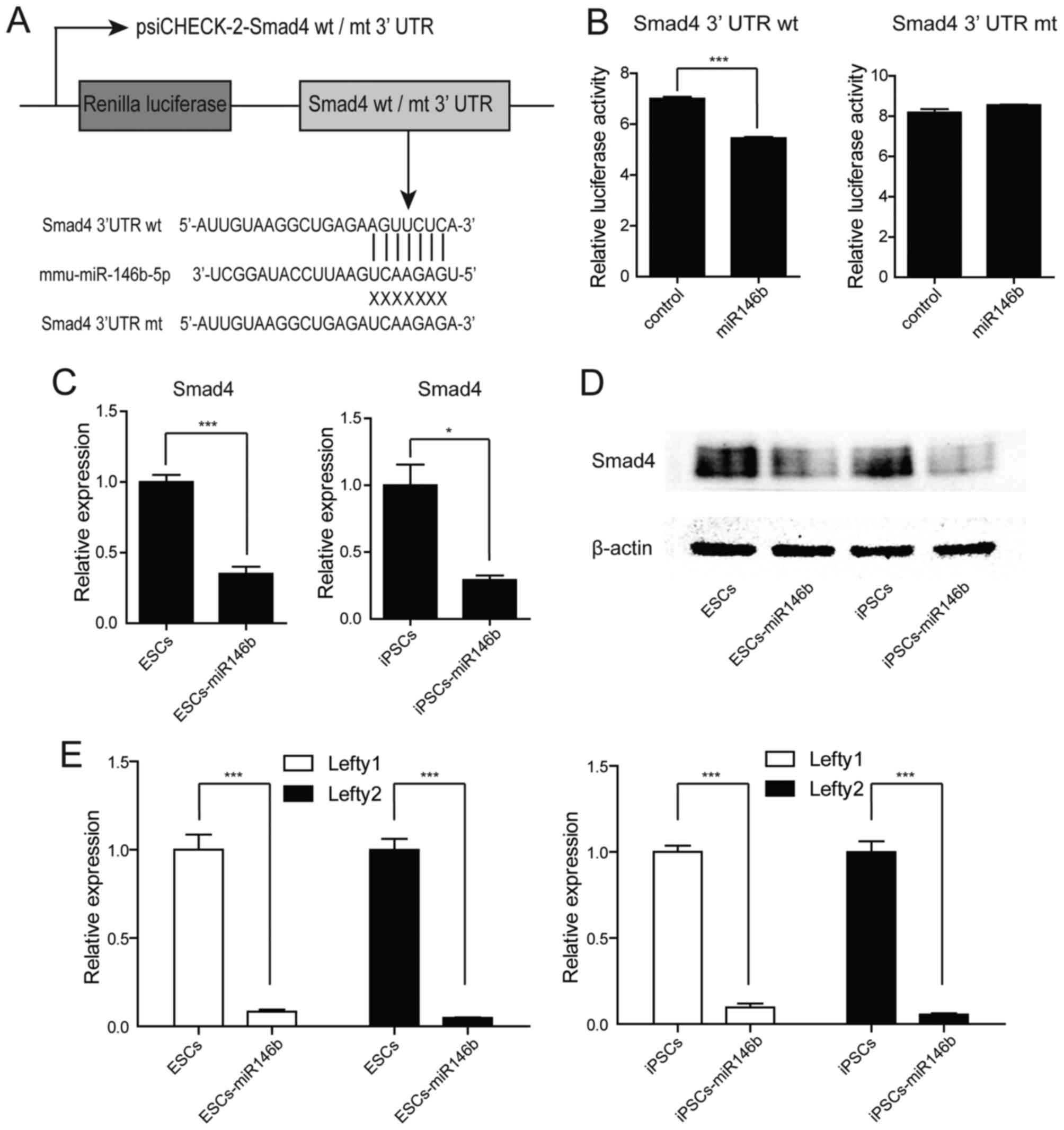
|
1
|
Fridley KM, Kinney MA and McDevitt TC:
Hydrodynamic modulation of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 3:452012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lewandowski J and Kurpisz M: Techniques of
human embryonic stem cell andinduced pluripotent stem cell
derivation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 64:349–370. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Nefzger CM, Su CT, Fabb SA, Hartley BJ,
Beh SJ, Zeng WR, Haynes JM and Pouton CW: Lmx1a allows
context-specific isolation of progenitors of GABAergic or
dopaminergic neurons during neural differentiation of embryonic
stem cells. Stem Cells. 30:1349–1361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sonntag KC, Pruszak J, Yoshizaki T, van
Arensbergen J, Sanchez-Pernaute R and Isacson O: Enhanced yield of
neuroepithelial precursors and midbrain-like dopaminergic neurons
from human embryonic stem cells using the bone morphogenic protein
antagonist noggin. Stem Cells. 25:411–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sundberg M, Bogetofte H, Lawson T, Jansson
J, Smith G, Astradsson A, Moore M, Osborn T, Cooper O, Spealman R,
et al: Improved cell therapy protocols for Parkinson's disease
based on differentiation efficiency and safety of hESC-, hiPSC-,
and non-human primate iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons. Stem
Cells. 31:1548–1562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doi D, Morizane A, Kikuchi T, Onoe H,
Hayashi T, Kawasaki T, Motono M, Sasai Y, Saiki H, Gomi M, et al:
Prolonged maturation culture favors a reduction in the
tumorigenicity and the dopaminergic function of human ESC-derived
neural cells in a primate model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cells.
30:935–945. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Míguez DG, Gil-Guiñón E, Pons S and Martí
E: Smad2 and Smad3 cooperate and antagonize simultaneously in
vertebrate neurogenesis. J Cell Sci. 126:5335–5343. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seuntjens E, Umans L, Zwijsen A,
Sampaolesi M, Verfaillie CM and Huylebroeck D: Transforming growth
factor type β and Smad family signaling in stem cell function.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:449–458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rodríguez-Martínez G and Velasco I:
Activin and TGF-β effects on brain development and neural stem
cells. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 11:844–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Neely MD, Litt MJ, Tidball AM, Li GG,
Aboud AA, Hopkins CR, Chamberlin R, Hong CC, Ess KC and Bowman AB:
DMH1, a highly selective small molecule BMP inhibitor promotes
neurogenesis of hiPSCs: comparison of PAX6 and SOX1 expression
during neural induction. ACS Chem Neurosci. 3:482–491. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Role of Smads
in TGFβ signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 347:21–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Miyazono K and Miyazawa K: Id: a target of
BMP signaling. Sci STKE. 2002:pe402002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yao G, Yin M, Lian J, Tian H, Liu L, Li X
and Sun F: Micro- RNA-224 is involved in transforming growth
factor-β-mediated mouse granulosa cell proliferation and granulosa
cell function by targeting Smad4. Mol Endocrinol. 24:540–551. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tian T and Meng AM: Nodal signals pattern
vertebrate embryos. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:672–685. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fortunel NO, Hatzfeld A and Hatzfeld JA:
Transforming growth factor-beta: pleiotropic role in the regulation
of hematopoiesis. Blood. 96:2022–2036. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hao J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Liu C, Hu X and
Shao C: MicroRNA 421 suppresses DPC4/Smad4 in pancreatic cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 406:552–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hao J, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Hu X and Shao C:
MicroRNA 483-3p suppresses the expression of DPC4/Smad4 in
pancreatic cancer. FEBS Lett. 585:207–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang DY, Zhu J, Zhang T
and Wang C: MicroRNA 126 inhibits the transition of endothelial
progenitor cells to mesenchymal cells via the PIK3R2-PI3K/Akt
signalling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e832942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xia X, Zhang K, Cen G, Jiang T, Cao J,
Huang K, Huang C, Zhao Q and Qiu Z: MicroRNA-301a-3p promotes
pancreatic cancer progression via negative regulation of SMAD4.
Oncotarget. 6:21046–21063. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu L, Nie J, Chen L, Dong G, Du X, Wu X,
Tang Y and Han W: The oncogenic role of microRNA-130a/301a/454 in
human colorectal cancer via targeting Smad4 expression. PLoS One.
8:e555322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hirata H, Ueno K, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y,
Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R: Oncogenic miRNA-182-5p targets
Smad4 and RECK in human bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e510562012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L and Wu
D: MicroRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human
cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer. 15:4692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Fan KJ, Sun Q, Chen AZ, Shen WL,
Zhao ZH, Zheng XF and Yang X: Functional screening for miRNAs
targeting Smad4 identified miR-199a as a negative regulator of
TGF-β signalling pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:9286–9297. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Ji S, Wang J, Huang J and Zheng P:
mRNA-Seq and microRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analyses of rhesus
monkey embryonic stem cell neural differentiation revealed the
potential regulators of rosette neural stem cells. DNA Res.
21:541–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Geraldo MV, Yamashita AS and Kimura ET:
MicroRNA miR-146b-5p regulates signal transduction of TGF-β by
repressing SMAD4 in thyroid cancer. Oncogene. 31:1910–1922. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ying QL, Stavridis M, Griffiths D, Li M
and Smith A: Conversion of embryonic stem cells into
neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nat Biotechnol.
21:183–186. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Klincumhom N, Tharasanit T,
Thongkittidilok C, Tiptanavattana N, Rungarunlert S, Dinnyés A and
Techakumphu M: Selective TGF-β1/ALK inhibitor improves neuronal
differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Neurosci Lett.
578:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hwang M, Lee JM, Kim Y and Geum D:
Functional role of parkin against oxidative stress in neural cells.
Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 29:62–69. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Su H, Wang L, Huang W, Qin D, Cai J, Yao
X, Feng C, Li Z, Wang Y, So KF, et al: Immediate expression of Cdh2
is essential for efficient neural differentiation of mouse induced
pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 10:338–348. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Štefková K, Procházková J and Pacherník J:
Alkaline phosphatase in stem cells. Stem Cells Int.
2015:6283682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Souquet B, Tourpin S, Messiaen S, Moison
D, Habert R and Livera G: Nodal signaling regulates the entry into
meiosis in fetal germ cells. Endocrinology. 153:2466–2473. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guzman-Ayala M, Lee KL, Mavrakis KJ,
Goggolidou P, Norris DP and Episkopou V: Graded Smad2/3 activation
is converted directly into levels of target gene expression in
embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 4:e42682009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Wang L, Su Z, Wu W, Cai X, Li D,
Hou J, Pei D and Pan G: A reciprocal antagonism between miR-376c
and TGF-β signaling regulates neural differentiation of human
pluripotent stem cells. FASEB J. 28:4642–4656. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Du J, Wu Y, Ai Z, Shi X, Chen L and Guo Z:
Mechanism of SB431542 in inhibiting mouse embryonic stem cell
differentiation. Cell Signal. 26:2107–2116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tay YM, Tam WL, Ang YS, Gaughwin PM, Yang
H, Wang W, Liu R, George J, Ng HH, Perera RJ, et al: MicroRNA-134
modulates the differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells, where
it causes post-transcriptional attenuation of Nanog and LRH1. Stem
Cells. 26:17–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Boissart C, Nissan X, Giraud-Triboult K,
Peschanski M and Benchoua A: miR-125 potentiates early neural
specification of human embryonic stem cells. Development.
139:1247–1257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Wang F, Lee JA and Gao FB:
MicroRNA-9a ensures the precise specification of sensory organ
precursors in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 20:2793–2805. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yoon SO, Kim EK, Lee M, Jung WY, Lee H,
Kang Y, Jang YJ, Hong SW, Choi SH and Yang WI: NOVA1 inhibition by
miR-146b-5p in the remnant tissue microenvironment defines occult
residual disease after gastric cancer removal. Oncotarget.
7:2475–2495. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Wang H, Jiang M, Xu Z, Huang H, Gong P,
Zhu H and Ruan C: miR-146b-5p promotes VSMC proliferation and
migration. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12901–12907. 2015.
|
|
40
|
Stevanato L and Sinden JD: The effects of
microRNAs on human neural stem cell differentiation in two- and
three-dimensional cultures. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Avery S, Zafarana G, Gokhale PJ and
Andrews PW: The role of SMAD4 in human embryonic stem cell
self-renewal and stem cell fate. Stem Cells. 28:863–873.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thomson M, Liu SJ, Zou LN, Smith Z,
Meissner A and Ramanathan S: Pluripotency factors in embryonic stem
cells regulate differentiation into germ layers. Cell. 145:875–889.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ozair MZ, Noggle S, Warmflash A, Krzyspiak
JE and Brivanlou AH: SMAD7 directly converts human embryonic stem
cells to telencephalic fate by a default mechanism. Stem Cells.
31:35–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ozair MZ, Kintner C and Brivanlou AH:
Neural induction and early patterning in vertebrates. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2:479–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Björklund L,
Cooper O, Pruszak J, Kowalke F, Gilmartin J, Ding J, Hu YP, Shen
MM, et al: Context-dependent neuronal differentiation and germ
layer induction of Smad4−/− and
Cripto−/− embryonic stem cells.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 28:417–429. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tropepe V, Hitoshi S, Sirard C, Mak TW,
Rossant J and van der Kooy D: Direct neural fate specification from
embryonic stem cells: a primitive mammalian neural stem cell stage
acquired through a default mechanism. Neuron. 30:65–78. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Park KS: Tgf-Beta family signaling in
embryonic stem cells. Int J Stem Cells. 4:18–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|