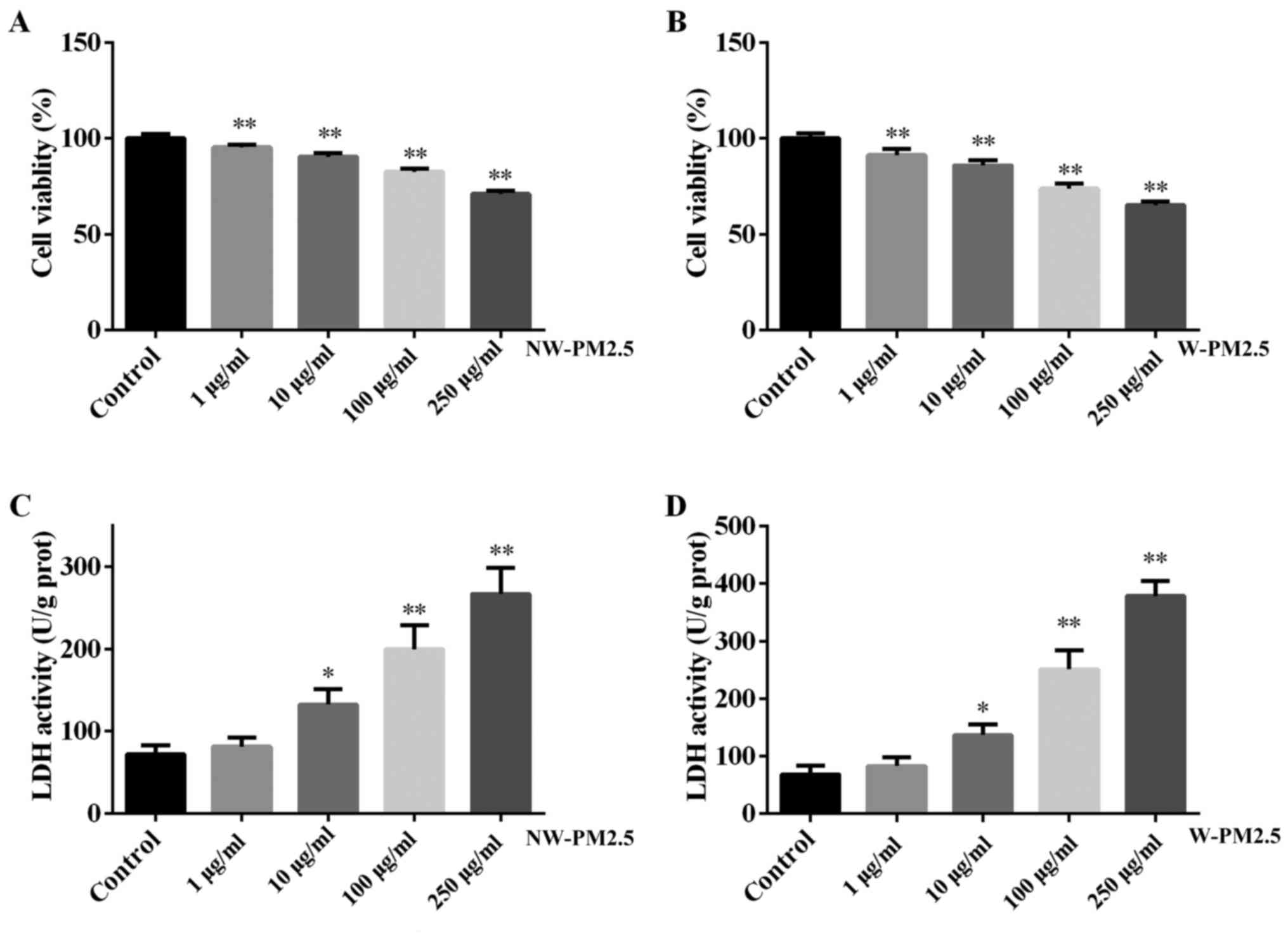
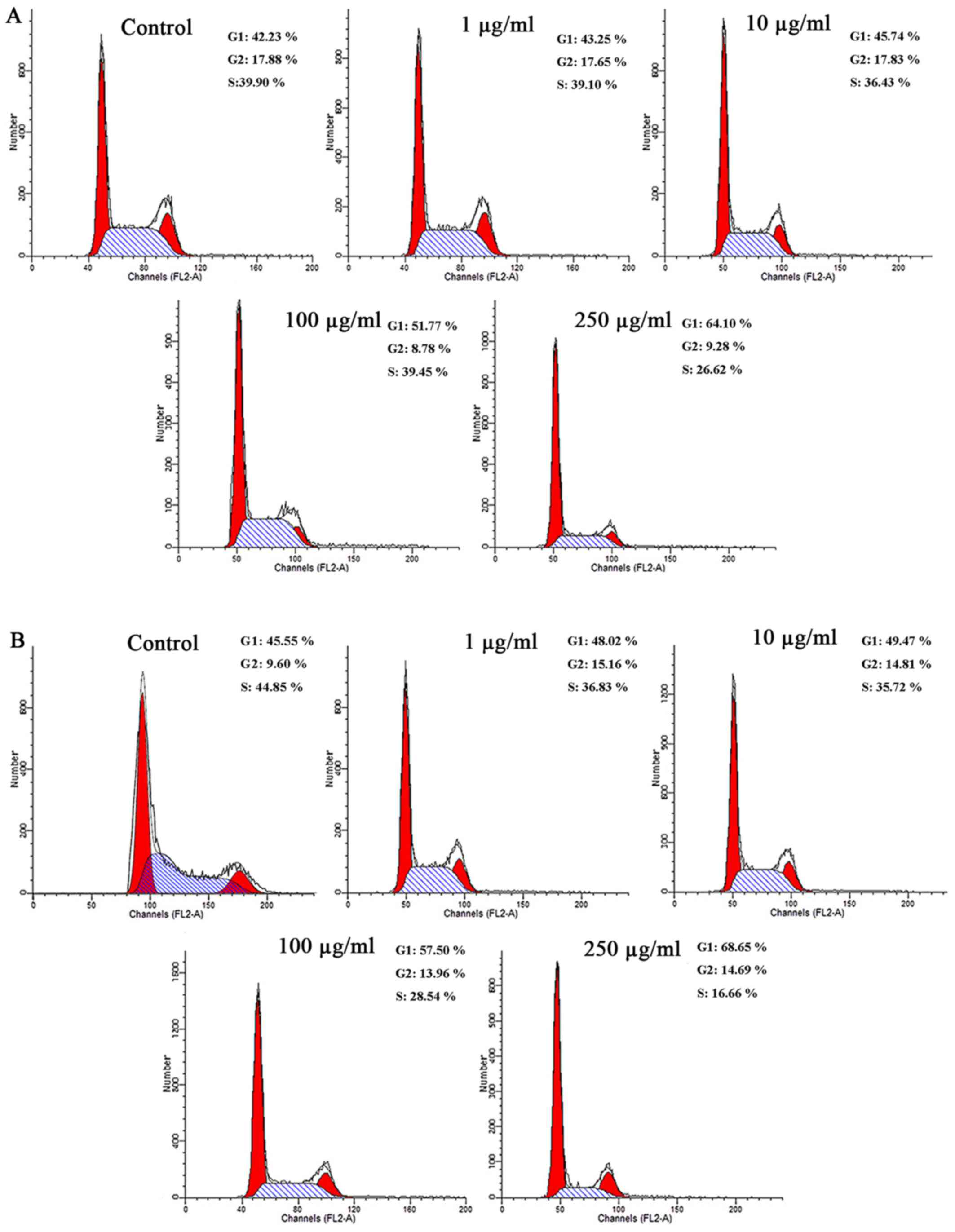
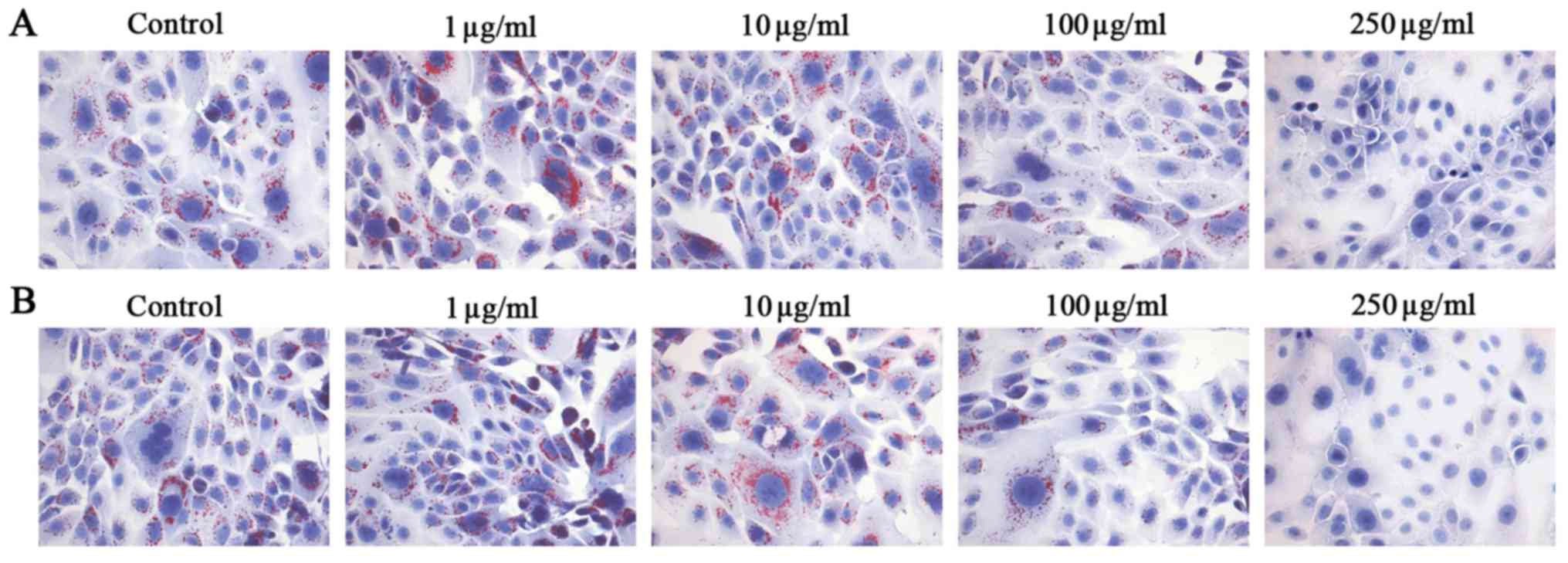
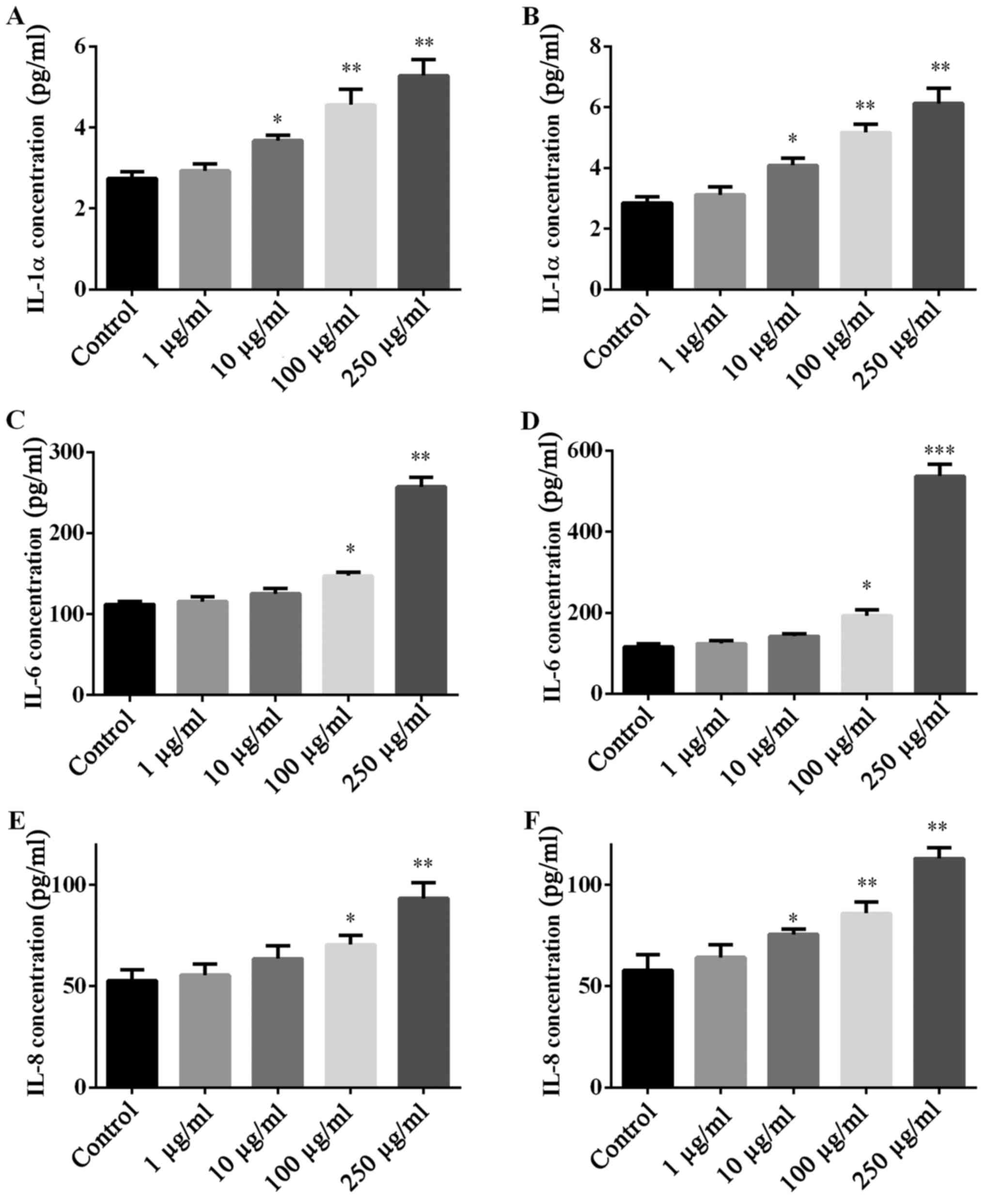
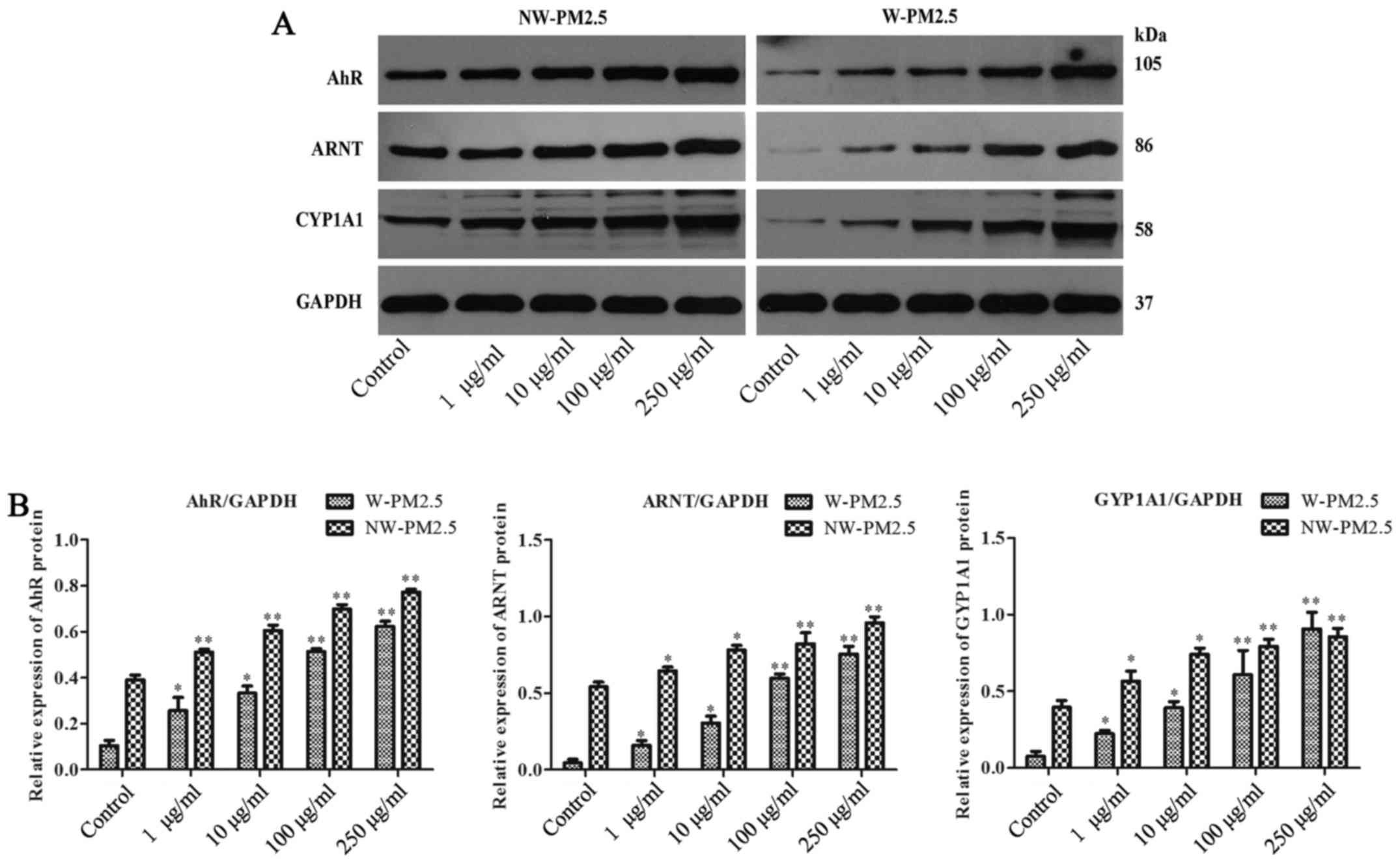
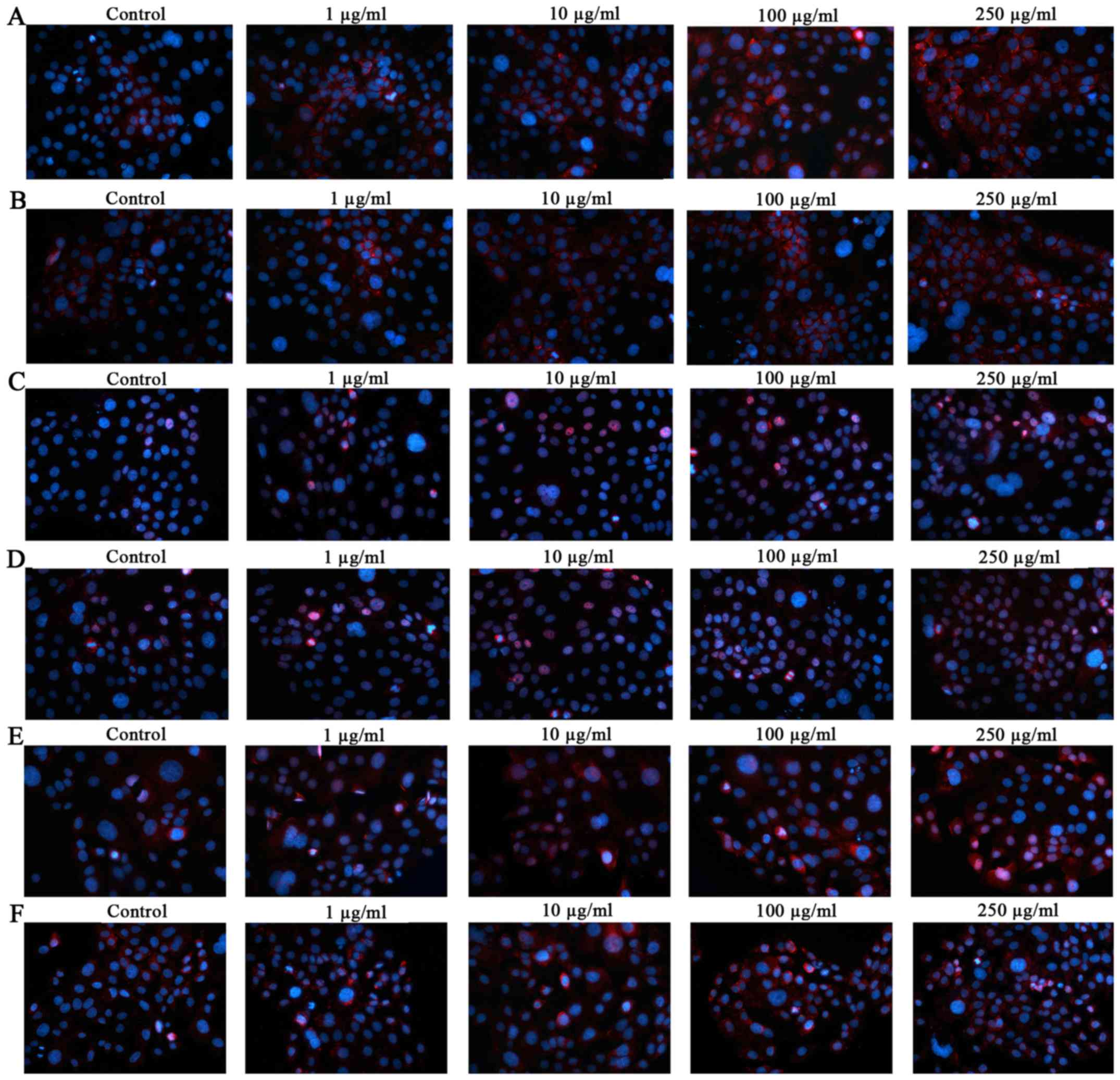
|
1
|
Kim KE, Cho D and Park HJ: Air pollution
and skin diseases: Adverse effects of airborne particulate matter
on various skin diseases. Life Sci. 152:126–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krutmann J, Liu W, Li L, Pan X, Crawford
M, Sore G and Seite S: Pollution and skin: From epidemiological and
mechanistic studies to clinical implications. J Dermatol Sci.
76:163–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ju Q, Zouboulis CC and Xia L:
Environmental pollution and acne: Chloracne. Dermatoendocrinol.
1:125–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ju Q and Zouboulis CC:
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and skin manifestations. Rev Endocr
Metab Disord. 17:449–457. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ju Q, Fimmel S, Hinz N, Stahlmann R, Xia L
and Zouboulis CC: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin alters
sebaceous gland cell differentiation in vitro. Exp Dermatol.
20:320–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu T, Pan Z, Yu Q, Mo X, Song N, Yan M,
Zouboulis CC, Xia L and Ju Q: Benzo(a)pyrene induces interleukin
(IL)-6 production and reduces lipid synthesis in human SZ95
sebocytes via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 43:54–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ju Q, Yiang K, Zouboulis CC, Ring J and
Chen W: Chloracne: From clinic to research. Zhonghua Pifuke Yixue
Zazhi. 30:2–6. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Díaz RV and Rosa Dominguez E: Health risk
by inhalation of PM2.5 in the metropolitan zone of the City of
Mexico. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 72:866–871. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dockery DW: Health effects of particulate
air pollution. Ann Epidemiol. 19:257–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weichenthal SA, Godri-Pollitt K and
Villeneuve PJ: PM2.5, oxidant defence and cardiorespiratory health:
A review. Environ Health. 12:402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Q, Kang Z, Jiang S, Zhao J, Yan S, Xu F
and Xu J: Effects of ambient fine particles PM2.5 on human HaCaT
cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 14:E722017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sugihara K, Kitamura S, Yamada T, Ohta S,
Yamashita K, Yasuda M and Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor (AhR)-mediated induction of xanthine oxidase/xanthine
dehydrogenase activity by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 281:1093–1099. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hong CH, Lee CH, Yu HS and Huang SK:
Benzopyrene, a major polyaromatic hydrocarbon in smoke fume,
mobilizes Langerhans cells and polarizes Th2/17 responses in
epicutaneous protein sensitization through the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. Int Immunopharmacol. 36:111–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jux B, Kadow S and Esser C: Langerhans
cell maturation and contact hypersensitivity are impaired in aryl
hydrocarbon receptor-null mice. J Immunol. 182:6709–6717. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho YC, Zheng W and Jefcoate CR:
Disruption of cell-cell contact maximally but transiently activates
AhR-mediated transcription in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 199:220–238. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu T, Wang D, Yu Q, Li L, Mo X, Pan Z,
Zouboulis CC, Peng L, Xia L and Ju Q: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
negatively regulates lipid synthesis and involves in cell
differentiation of SZ95 sebocytes in vitro. Chem Biol Interact.
258:52–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ju Q, Yu Q, Song N, Tan Y, Xia L and
Zouboulis CC: Expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in human
epidermis, hair follicles and sebaceous glands and its
significance. Zhonghua Pifuke Zazhi. 44:761–764. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Esser C, Bargen I, Weighardt H,
Haarmann-Stemmann T and Krutmann J: Functions of the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in the skin. Semin Immunopathol. 35:677–691.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu Q, Hu T, Mo X, Zhang C, Xia L,
Zouboulis CC and Ju Q: Effect of tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on the
expression of cytochrome P4501A1 in human SZ95 sebocytes and its
significance. Zhonghua Pifuke Zazhi. 46:557–560. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Kalmes M, Hennen J, Clemens J and Blömeke
B: Impact of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) knockdown on cell
cycle progression in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Biol Chem.
392:643–651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tauchi M, Hida A, Negishi T, Katsuoka F,
Noda S, Mimura J, Hosoya T, Yanaka A, Aburatani H, Fujii-Kuriyama
Y, et al: Constitutive expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
keratinocytes causes inflammatory skin lesions. Mol Cell Biol.
25:9360–9368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kakimoto K, Nagayoshi H, Konishi Y,
Kajimura K, Ohura T, Nakano T, Hata M, Furuuchi M, Tang N, Hayakawa
K, et al: Size distribution of chlorinated polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons in atmospheric particles. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol.
72:58–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jeong SC, Song MK, Cho Y, Lee E and Ryu
JC: Integrative analysis of mRNA and microRNA expression of a human
alveolar epithelial cell(A549) exposed to water and organic-soluble
extract from particulate matter (PM)2.5. Environ Toxicol.
32:302–310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang B, Chen D, Zhao H and Xiao C: The
effects for PM2.5 exposure on non-small-cell lung cancer induced
motility and proliferation. Springerplus. 5:20592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Z, Liu Y, Duan F, Qin M, Wu F, Sheng
W, Yang L, Liu J and He K: Transcriptomic analyses of the
biological effects of airborne PM2.5 exposure on human bronchial
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01382672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang Q, Zhang J, Peng S, Tian M, Chen J
and Shen H: Effects of water soluble PM2.5 extracts exposure on
human lung epithelial cells (A549): A proteomic study. J Appl
Toxicol. 34:675–687. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Ghio AJ, Gao M, Wei K, Rosen GD
and Upadhyay D: Ambient particulate matter induces alveolar
epithelial cell cycle arrest: Role of G cyclins. FEBS Lett.
581:5315–5320. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Longhin E, Holme JA, Gutzkow KB, Arlt VM,
Kucab JE, Camatini M and Gualtieri M: Cell cycle alterations
induced by urban PM2.5 in bronchial epithelial cells:
Characterization of the process and possible mechanisms involved.
Part Fibre Toxicol. 10:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen W, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Hong J-B,
Melnik BC, Yamasaki O, Dessinioti C, Ju Q, Liakou AI, Al-Khuzaei S,
Katsambas A, et al: Acne-associated syndromes: Models for better
understanding of acne pathogenesis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
25:637–646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zouboulis CC, Picardo M, Ju Q, Kurokawa I,
Törőcsik D, Bíró T and Schneider MR: Beyond acne: Current aspects
of sebaceous gland biology and function. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.
17:319–334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zouboulis CC, Jourdan E and Picardo M:
Acne is an inflammatory disease and alterations of sebum
composition initiate acne lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
28:527–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ganceviciene R, Graziene V, Fimmel S and
Zouboulis CC: Involvement of the corticotropin-releasing hormone
system in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol.
160:345–352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang H, Yao Y, Chen Y, Yue C, Chen J,
Tong J, Jiang Y and Chen T: Crosstalk between AhR and wnt/β-catenin
signal pathways in the cardiac developmental toxicity of PM2.5 in
zebrafish embryos. Toxicology. 355–356:31–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Borgie M, Ledoux F, Verdin A, Cazier F,
Greige H, Shirali P, Courcot D and Dagher Z: Genotoxic and
epigenotoxic effects of fine particulate matter from rural and
urban sites in Lebanon on human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ
Res. 136:352–362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Líbalová H, Krčková S, Uhlířová K, Milcová
A, Schmuczerová J, Ciganek M, Kléma J, Machala M, Šrám RJ and
Topinka J: Genotoxicity but not the AhR-mediated activity of PAHs
is inhibited by other components of complex mixtures of ambient air
pollutants. Toxicol Lett. 225:350–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|