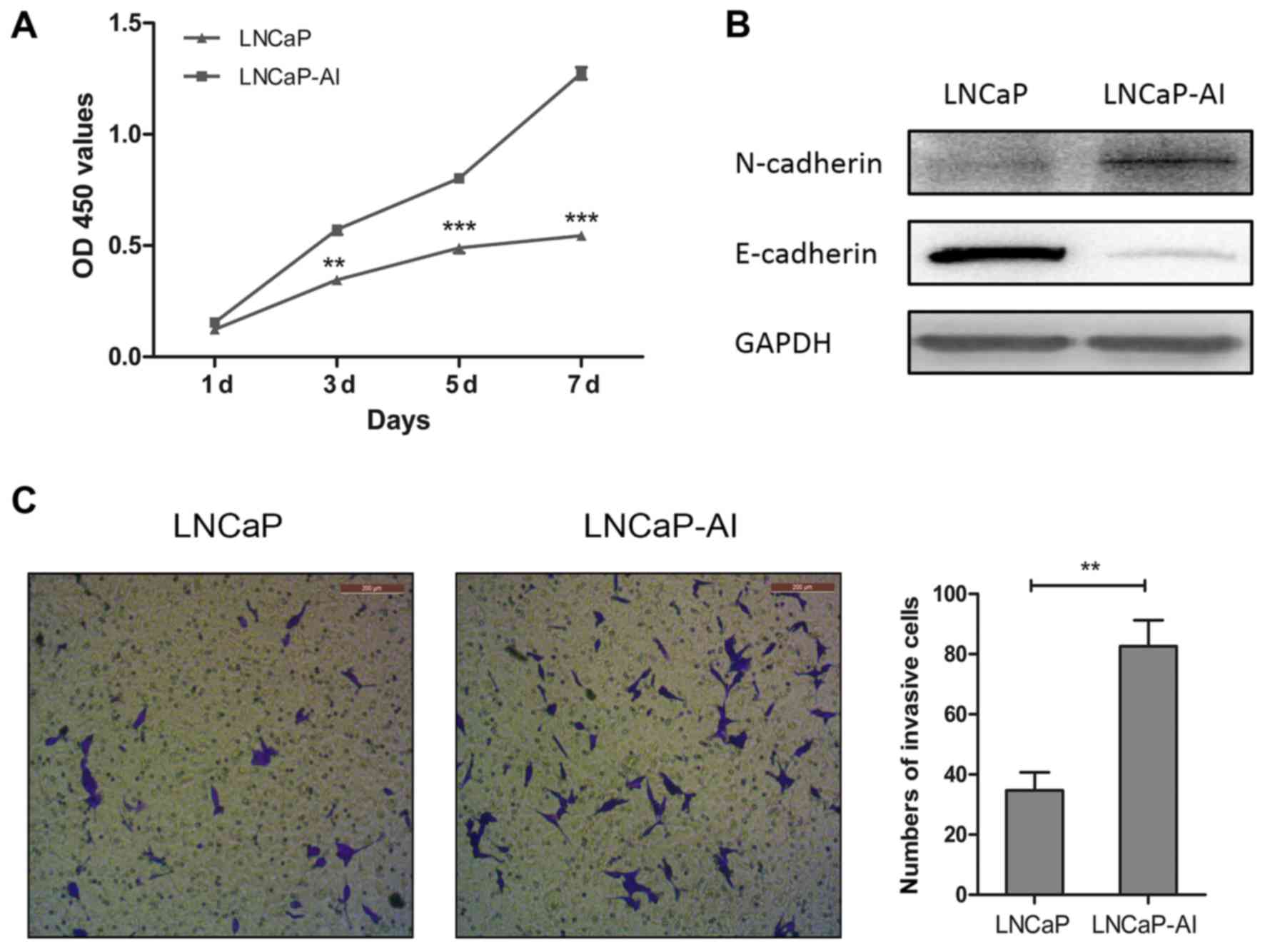
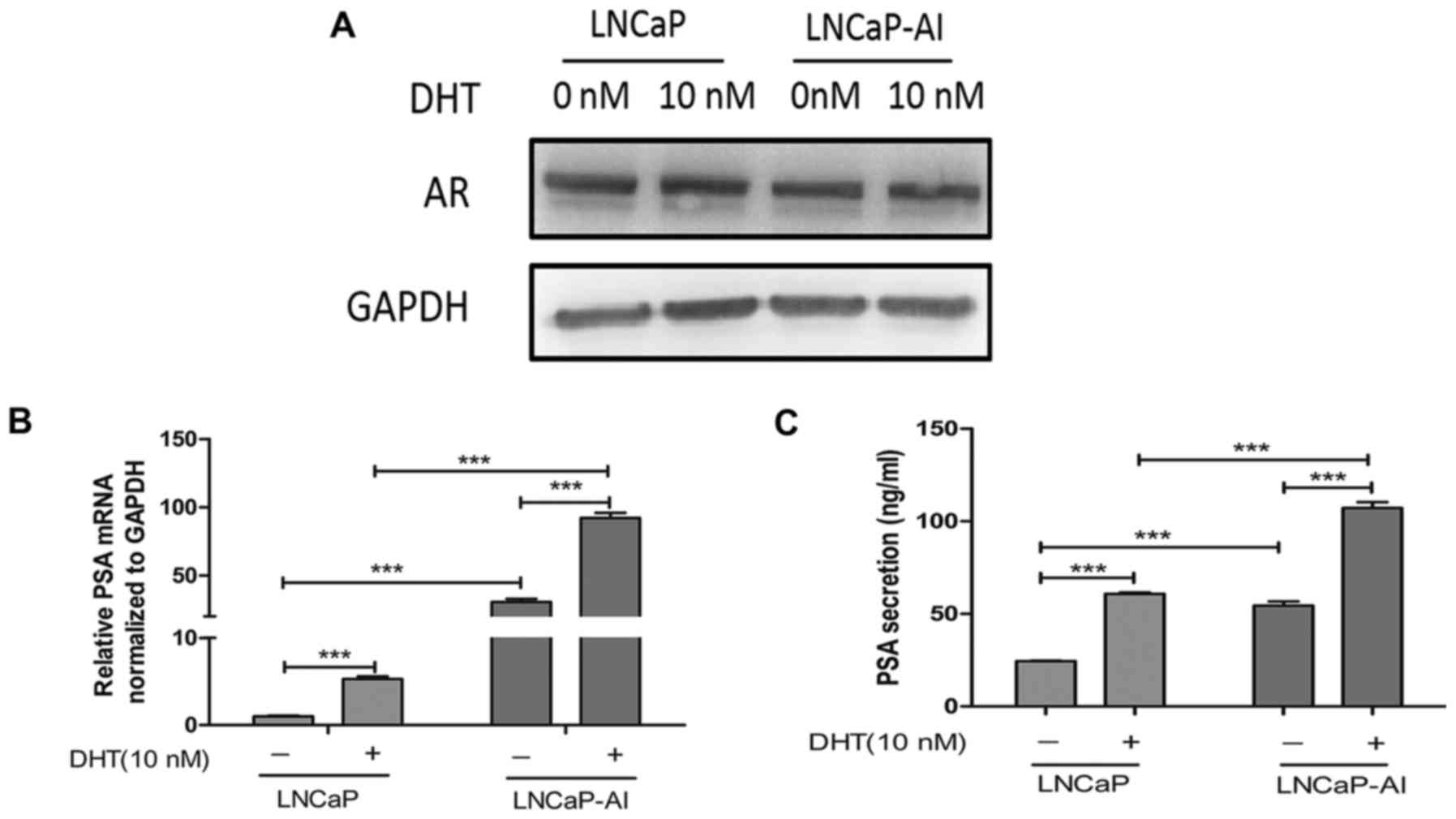
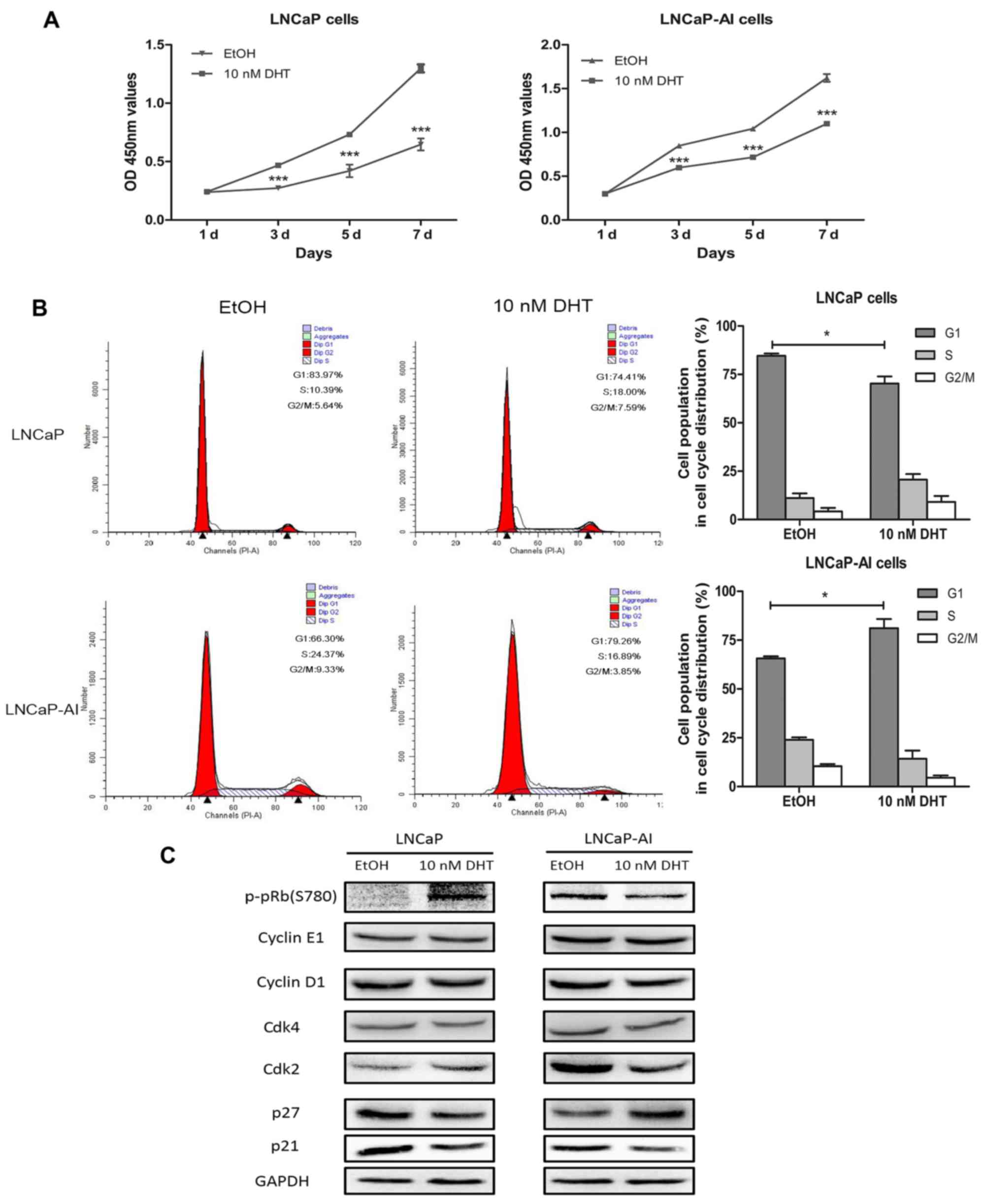
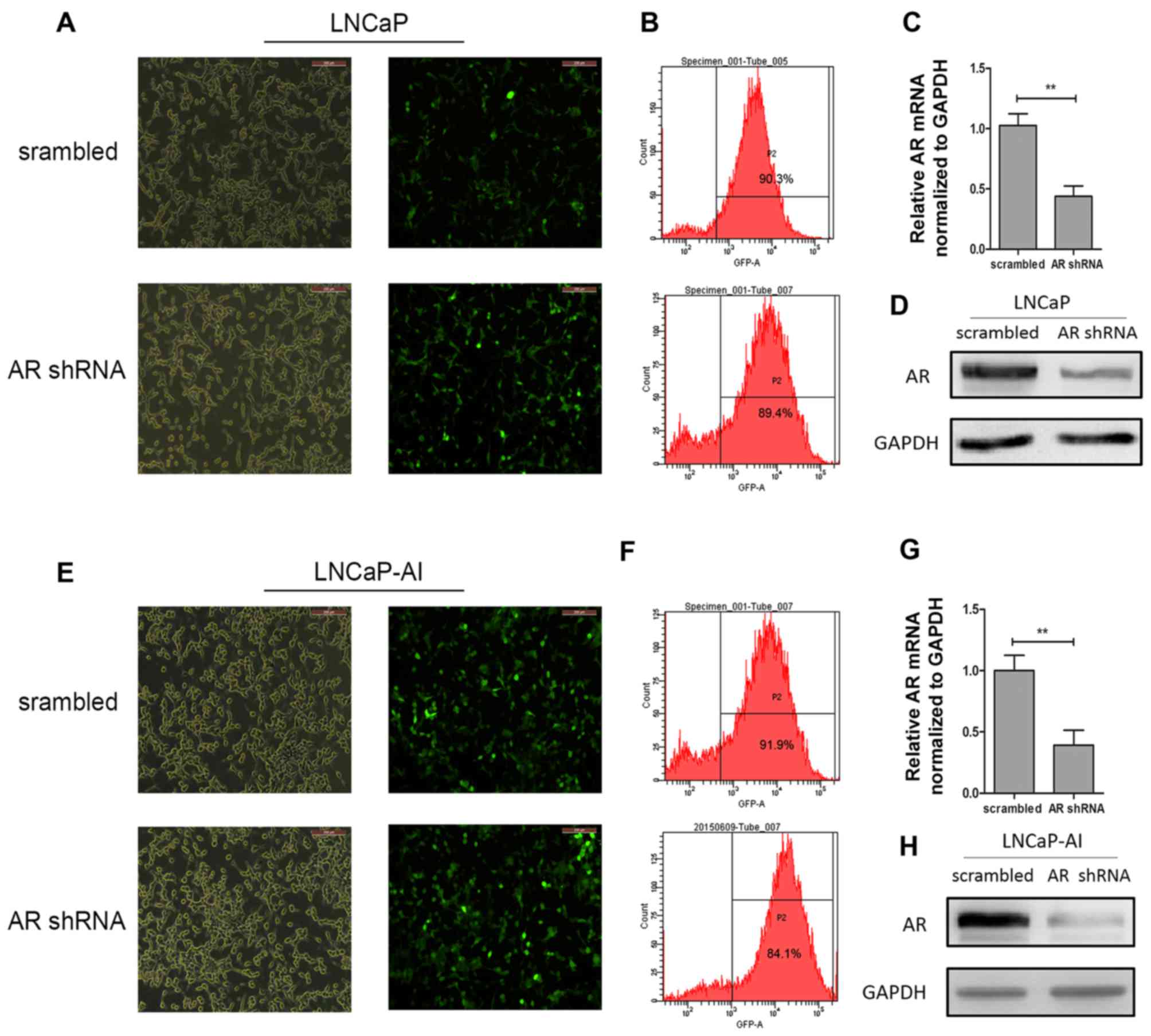
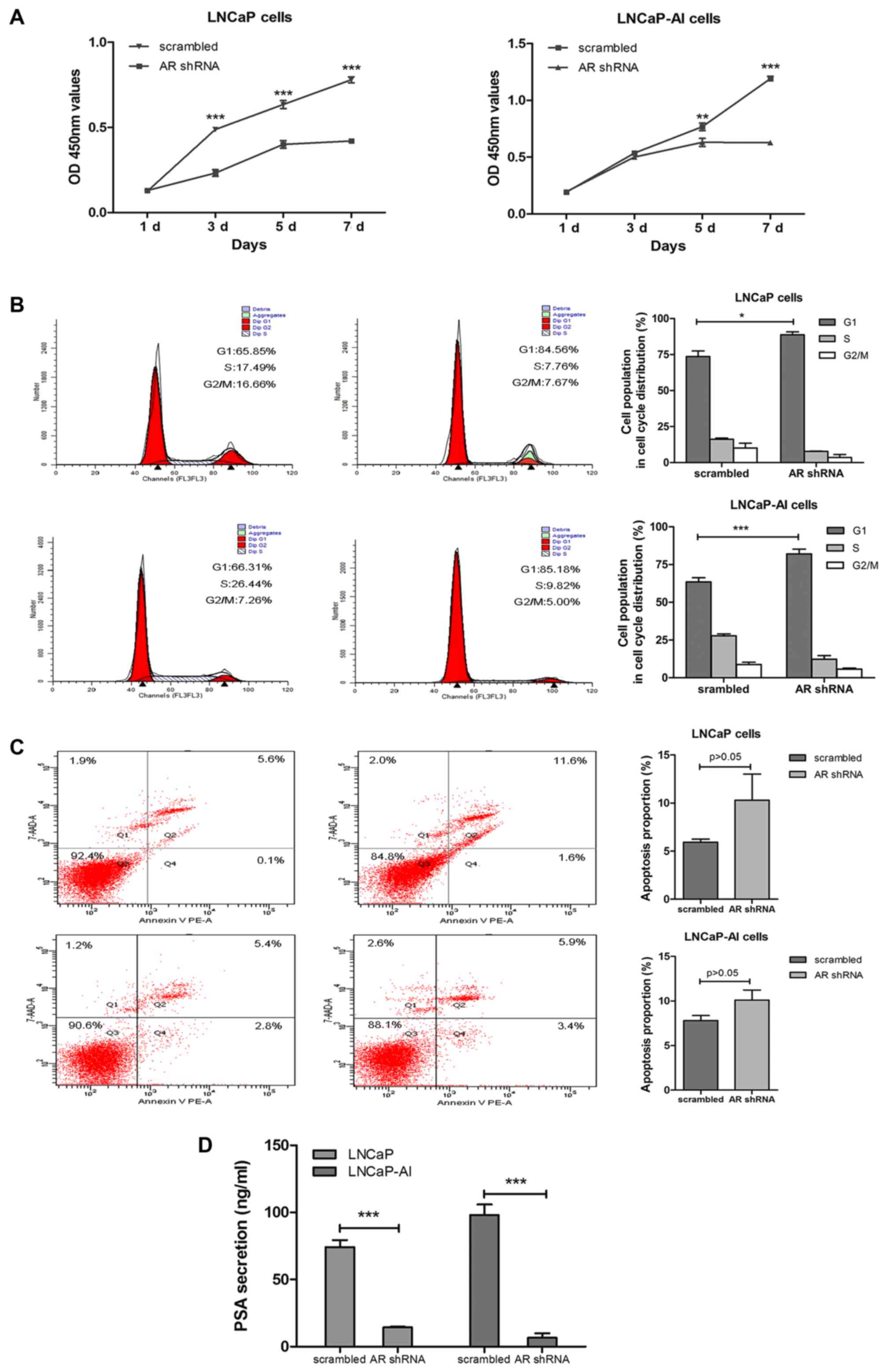
|
1
|
Attar RM, Takimoto CH and Gottardis MM:
Castration-resistant prostate cancer: locking up the molecular
escape routes. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3251–3255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharifi N, Kawasaki BT, Hurt EM and Farrar
WL: Stem cells in prostate cancer: Resolving the castrate-resistant
conundrum and implications for hormonal therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:901–906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Damber JE and Aus G: Prostate cancer.
Lancet. 371:1710–1721. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feldman BJ and Feldman D: The development
of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:34–45.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ryan CJ, Smith A, Lal P, Satagopan J,
Reuter V, Scardino P, Gerald W and Scher HI: Persistent
prostate-specific antigen expression after neoadjuvant androgen
depletion: An early predictor of relapse or incomplete androgen
suppression. Urology. 68:834–839. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan MH, Li J, Xu HE, Melcher K and Yong
EL: Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug
discovery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:3–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Heinlein CA and Chang C: Androgen receptor
in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 25:276–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsihlias J, Zhang W, Bhattacharya N,
Flanagan M, Klotz L and Slingerland J: Involvement of p27Kip1 in G1
arrest by high dose 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone in LNCaP human
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 19:670–679. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hofman K, Swinnen JV, Verhoeven G and
Heyns W: E2F activity is biphasically regulated by androgens in
LNCaP cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 283:97–101. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akakura K, Bruchovsky N, Goldenberg SL,
Rennie PS, Buckley AR and Sullivan LD: Effects of intermittent
androgen suppression on androgen-dependent tumors. Apoptosis and
serum prostate-specific antigen. Cancer. 71:2782–2790. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sciarra A, Abrahamsson PA, Brausi M,
Galsky M, Mottet N, Sartor O, Tammela TL and Calais da Silva F:
Intermittent androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer: A
critical review focused on phase 3 trials. Eur Urol. 64:722–730.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Chu TM, Wajsman
ZL, Friedman M, Papsidero L, Kim U, Chai LS, Kakati S, Arya SK, et
al: The LNCaP cell line - a new model for studies on human
prostatic carcinoma. Prog Clin biol Res. 37:115–132. 1980.
|
|
13
|
Xu G, Wu J, Zhou L, Chen B, Sun Z, Zhao F
and Tao Z: Characterization of the small RNA transcriptomes of
androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cell line by
deep sequencing. PLoS One. 5:e155192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu S, Tsai SY and Tsai MJ: Molecular
mechanisms of androgen-independent growth of human prostate cancer
LNCaP-AI cells. Endocrinology. 140:5054–5059. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Loblaw DA, Mendelson DS, Talcott JA, Virgo
KS, Somerfield MR, Ben-Josef E, Middleton R, Porterfield H, Sharp
SA, Smith TJ, et al American Society of Clinical Oncology: American
Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations for the initial
hormonal management of androgen-sensitive metastatic, recurrent, or
progressive prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:2927–2941. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sowery RD, So AI and Gleave ME:
Therapeutic options in advanced prostate cancer: Present and
future. Curr Urol Rep. 8:53–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Debes JD and Tindall DJ: Mechanisms of
androgen-refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 351:1488–1490.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Li W, Zhang Y, Yuan X, Xu K, Yu J,
Chen Z, Beroukhim R, Wang H, Lupien M, et al: Androgen receptor
regulates a distinct transcription program in androgen-independent
prostate cancer. Cell. 138:245–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chuu CP, Kokontis JM, Hiipakka RA, Fukuchi
J, Lin HP, Lin CY, Huo C, Su LC and Liao S: Androgen suppresses
proliferation of castration-resistant LNCaP 104-R2 prostate cancer
cells through androgen receptor, Skp2, and c-Myc. Cancer Sci.
102:2022–2028. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun Y, Wang BE, Leong KG, Yue P, Li L,
Jhunjhunwala S, Chen D, Seo K, Modrusan Z, Gao WQ, et al: Androgen
deprivation causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the
prostate: Implications for androgen-deprivation therapy. Cancer
Res. 72:527–536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen
R, Vessella R, Rosenfeld MG and Sawyers CL: Molecular determinants
of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med. 10:33–39. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scher HI, Buchanan G, Gerald W, Butler LM
and Tilley WD: Targeting the androgen receptor: Improving outcomes
for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
11:459–476. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scher HI and Sawyers CL: Biology of
progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: Directed
therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin
Oncol. 23:8253–8261. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lonergan PE and Tindall DJ: Androgen
receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression.
J Carcinog. 10:202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kokontis JM, Hay N and Liao S: Progression
of LNCaP prostate tumor cells during androgen deprivation:
Hormone-independent growth, repression of proliferation by
androgen, and role for p27Kip1 in androgen-induced cell cycle
arrest. Mol Endocrinol. 12:941–953. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Knudsen KE, Arden KC and Cavenee WK:
Multiple G1 regulatory elements control the androgen-dependent
proliferation of prostatic carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
273:20213–20222. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu Y, Chen SY, Ross KN and Balk SP:
Androgens induce prostate cancer cell proliferation through
mammalian target of rapamycin activation and post-transcriptional
increases in cyclin D proteins. Cancer Res. 66:7783–7792. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kokontis JM, Lin HP, Jiang SS, Lin CY,
Fukuchi J, Hiipakka RA, Chung CJ, Chan TM, Liao S, Chang CH, et al:
Androgen suppresses the proliferation of androgen receptor-positive
castration-resistant prostate cancer cells via inhibition of Cdk2,
CyclinA, and Skp2. PLoS One. 9:e1091702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vidal A and Koff A: Cell-cycle inhibitors:
Three families united by a common cause. Gene. 247:1–15. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gartel AL, Serfas MS and Tyner AL: p21-
negative regulator of the cell cycle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med.
213:138–149. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Labaer J, Garrett MD, Stevenson LF,
Slingerland JM, Sandhu C, Chou HS, Fattaey A and Harlow E: New
functional activities for the p21 family of CDK inhibitors. Genes
Dev. 11:847–862. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheng M, Olivier P, Diehl JA, Fero M,
Roussel MF, Roberts JM and Sherr CJ: The p21 (Cip1) and p27 (Kip1)
CDK 'inhibitors' are essential activators of cyclin D-dependent
kinases in murine fibroblasts. EMBO J. 18:1571–1583. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alt JR, Gladden AB and Diehl JA: p21(Cip1)
promotes cyclin D1 nuclear accumulation via direct inhibition of
nuclear export. J Biol Chem. 277:8517–8523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zegarra-Moro OL, Schmidt LJ, Huang H and
Tindall DJ: Disruption of androgen receptor function inhibits
proliferation of androgen-refractory prostate cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 62:1008–1013. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li TH, Zhao H, Peng Y, Beliakoff J, Brooks
JD and Sun Z: A promoting role of androgen receptor in
androgen-sensitive and -insensitive prostate cancer cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35:2767–2776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Snoek R, Cheng H, Margiotti K, Wafa LA,
Wong CA, Wong EC, Fazli L, Nelson CC, Gleave ME and Rennie PS: In
vivo knockdown of the androgen receptor results in growth
inhibition and regression of well-established, castration-resistant
prostate tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 15:39–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Comstock CE and Knudsen KE: The complex
role of AR signaling after cytotoxic insult: Implications for
cell-cycle-based chemotherapeutics. Cell Cycle. 6:1307–1313. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liao X, Tang S, Thrasher JB, Griebling TL
and Li B: Small-interfering RNA-induced androgen receptor silencing
leads to apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:505–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang Q, Fung KM, Day WV, Kropp BP and Lin
HK: Androgen receptor signaling is required for androgen-sensitive
human prostate cancer cell proliferation and survival. Cancer Cell
Int. 5:82005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yuan X, Li T, Wang H, Zhang T, Barua M,
Borgesi RA, Bubley GJ, Lu ML and Balk SP: Androgen receptor remains
critical for cell-cycle progression in androgen-independent CWR22
prostate cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 169:682–696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|