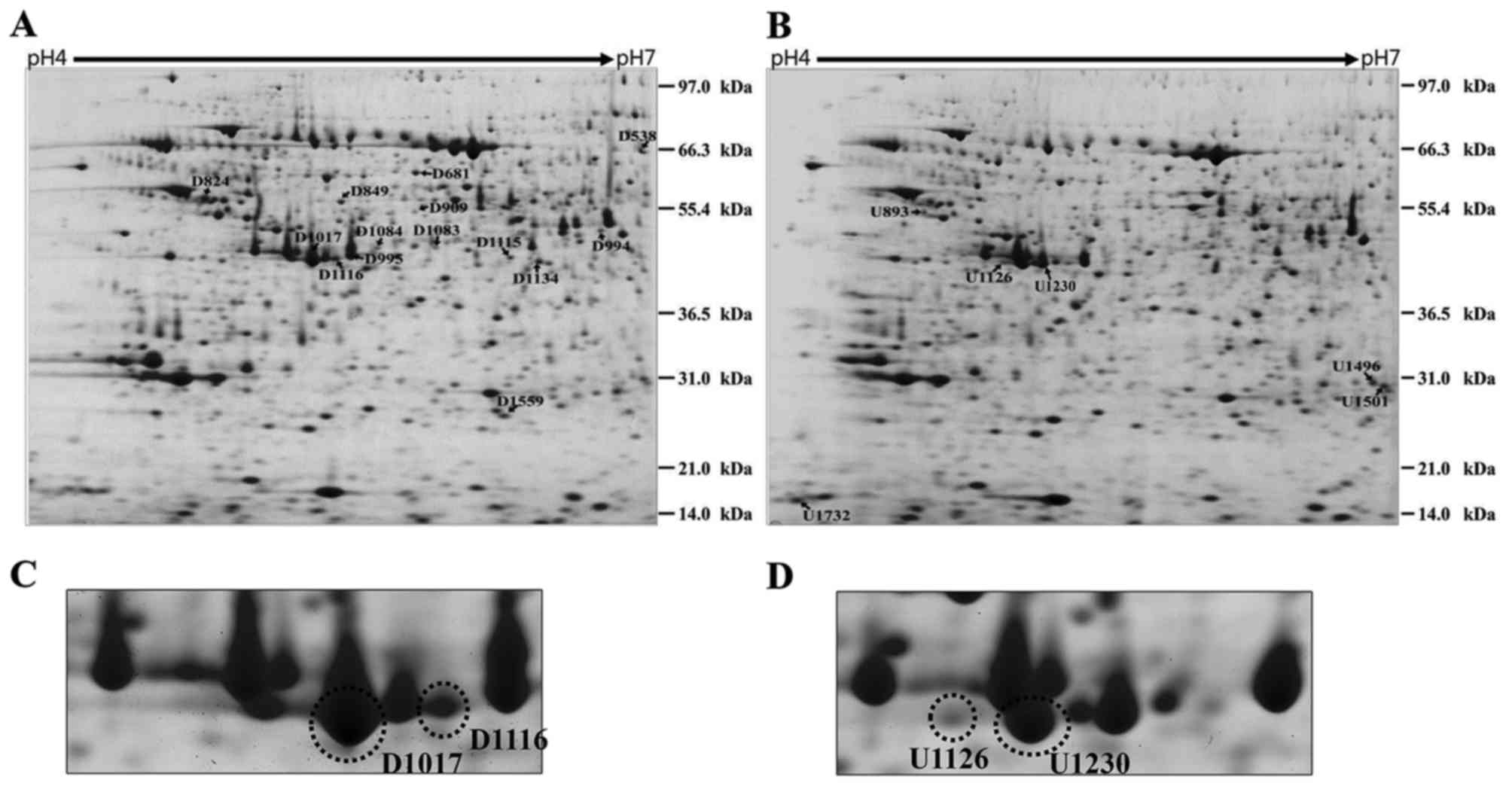
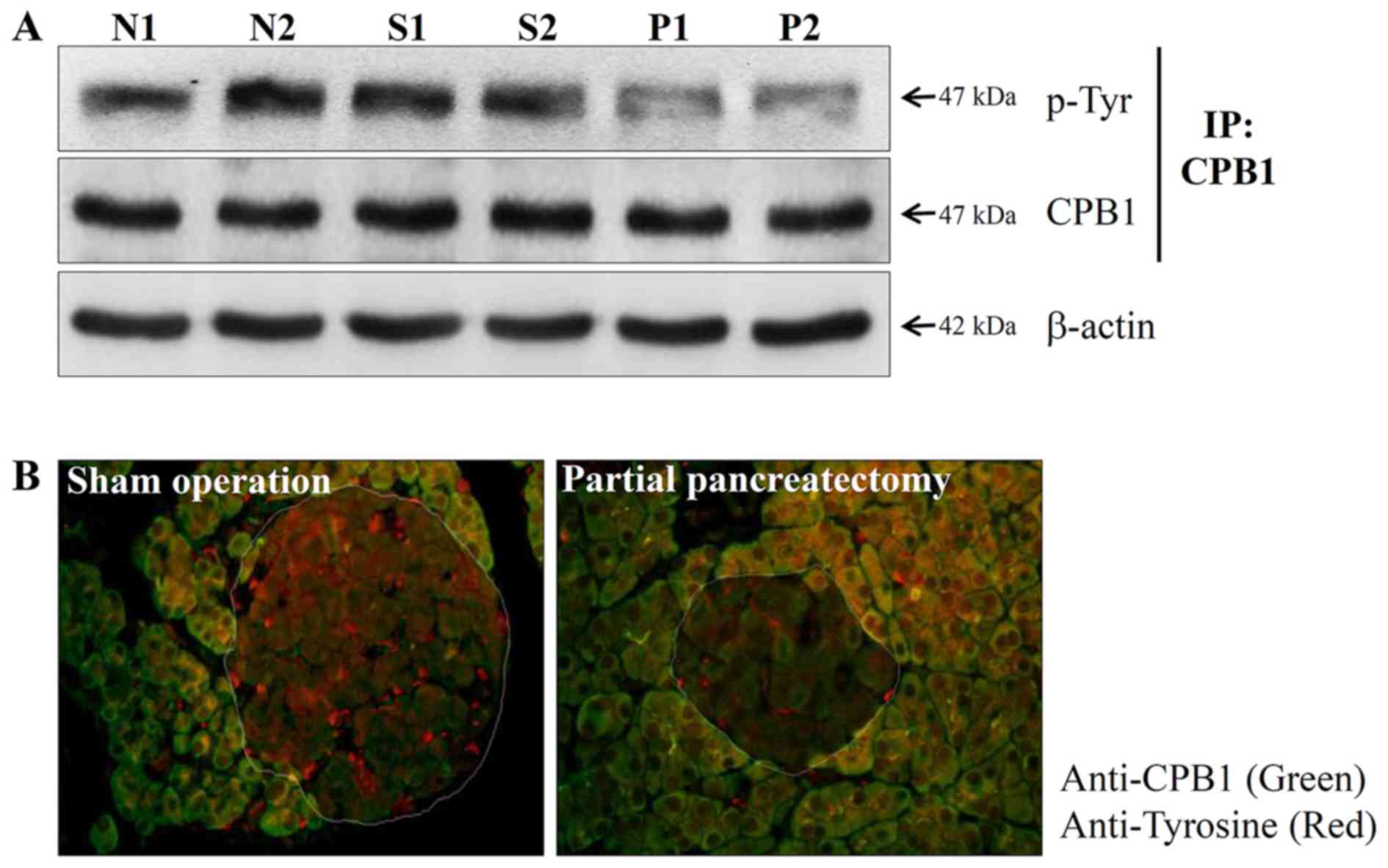
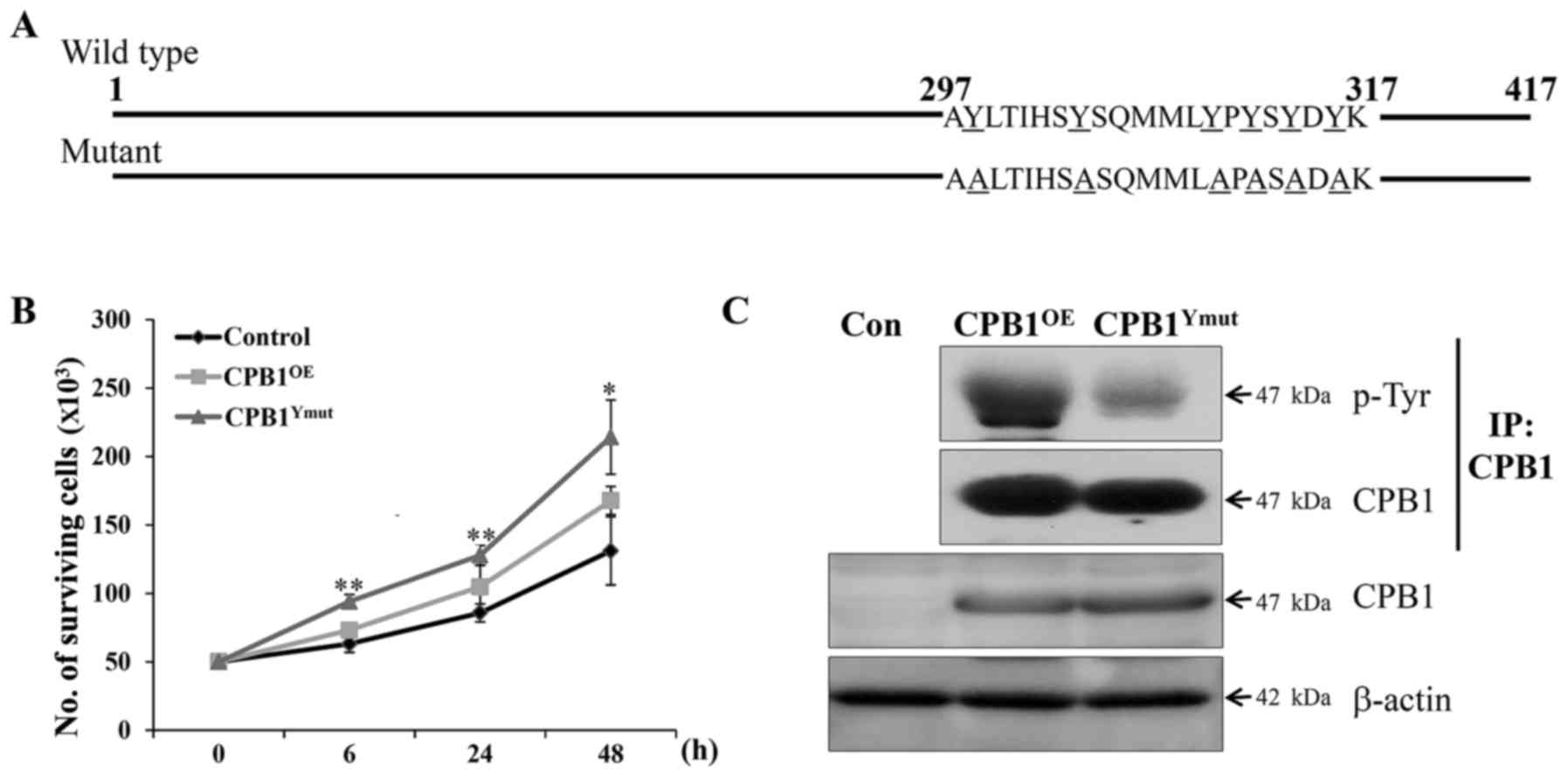
|
1
|
Seaberg RM, Smukler SR, Kieffer TJ,
Enikolopov G, Asghar Z, Wheeler MB, Korbutt G and van der Kooy D:
Clonal identification of multipotent precursors from adult mouse
pancreas that generate neural and pancreatic lineages. Nat
Biotechnol. 22:1115–1124. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
D'Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, Kelly OG,
Agulnick AD, Smart NG, Moorman MA, Kroon E, Carpenter MK and Baetge
EE: Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells
from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 24:1392–1401.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K, Bang AG,
Kelly OG, Eliazer S, Young H, Richardson M, Smart NG, Cunningham J,
et al: Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells
generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat
Biotechnol. 26:443–452. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lampeter EF, Gurniak M, Brocker U, Klemens
C, Tubes M, Friemann J and Kolb H: Regeneration of beta-cells in
response to islet inflammation. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.
103(Suppl 2): 74–78. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayashi KY, Tamaki H, Handa K, Takahashi
T, Kakita A and Yamashina S: Differentiation and proliferation of
endocrine cells in the regenerating rat pancreas after 90%
pancreatectomy. Arch Histol Cytol. 66:163–174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kopp JL, Dubois CL, Schaffer AE, Hao E,
Shih HP, Seymour PA, Ma J and Sander M: Sox9+ ductal
cells are multipotent progenitors throughout development but do not
produce new endocrine cells in the normal or injured adult
pancreas. Development. 138:653–665. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Criscimanna A, Coudriet GM, Gittes GK,
Piganelli JD and Esni F: Activated macrophages create
lineage-specific microenvironments for pancreatic acinar- and
β-cell regeneration in mice. Gastroenterology. 147:1106–1118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI and Melton DA:
Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather
than stem-cell differentiation. Nature. 429:41–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thorel F, Népote V, Avril I, Kohno K,
Desgraz R, Chera S and Herrera PL: Conversion of adult pancreatic
alpha-cells to betacells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature.
464:1149–1154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chera S, Baronnier D, Ghila L, Cigliola V,
Jensen JN, Gu G, Furuyama K, Thorel F, Gribble FM, Reimann F, et
al: Diabetes recovery by age-dependent conversion of pancreatic
δ-cells into insulin producers. Nature. 514:503–507. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Inada A, Nienaber C, Katsuta H, Fujitani
Y, Levine J, Morita R, Sharma A and Bonner-Weir S: Carbonic
anhydrase II-positive pancreatic cells are progenitors for both
endocrine and exocrine pancreas after birth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:19915–19919. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, D'Hoker J, Stangé G, Bonné S, De Leu
N, Xiao X, Van de Casteele M, Mellitzer G, Ling Z, Pipeleers D, et
al: Beta cells can be generated from endogenous progenitors in
injured adult mouse pancreas. Cell. 132:197–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lim HW, Lee JE, Shin SJ, Lee YE, Oh SH,
Park JY, Seong JK and Park JS: Identification of differentially
expressed mRNA during pancreas regeneration of rat by mRNA
differential display. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 299:806–812.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shin JS, Lee JJ, Lee EJ, Kim YH, Chae KS
and Kim CW: Proteome analysis of rat pancreas induced by
pancreatectomy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1749:23–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De León DD, Farzad C, Crutchlow MF,
Brestelli J, Tobias J, Kaestner KH and Stoffers DA: Identification
of transcriptional targets during pancreatic growth after partial
pancreatectomy and exendin-4 treatment. Physiol Genomics.
24:133–143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang M, Liu W, Wang CY, Liu T, Zhou F, Tao
J, Wang Y and Li MT: Proteomic analysis of differential protein
expression in early process of pancreatic regeneration in
pancreatectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:568–578. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi JH, Lee MY, Kim Y, Shim JY, Han SM,
Lee KA, Choi YK, Jeon HM and Baek KH: Isolation of genes involved
in pancreas regeneration by subtractive hybridization. Biol Chem.
391:1019–1029. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi JH, Lee MY, Ramakrishna S, Kim Y,
Shim JY, Han SM, Kim JY, Lee DH, Choi YK and Baek KH: LCP1
up-regulated by partial pancreatectomy supports cell proliferation
and differentiation. Mol Biosyst. 7:3104–3111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rukstalis JM and Habener JF: Neurogenin3:
A master regulator of pancreatic islet differentiation and
regeneration. Islets. 1:177–184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Reichert M, Takano S, von Burstin J, Kim
SB, Lee JS, Ihida-Stansbury K, Hahn C, Heeg S, Schneider G, Rhim
AD, et al: The Prrx1 homeodomain transcription factor plays a
central role in pancreatic regeneration and carcinogenesis. Genes
Dev. 27:288–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Jonsson L, Simu K
and Edlund H: beta-cell-specific inactivation of the mouse
Ipf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the beta-cell phenotype and
maturity onset diabetes. Genes Dev. 12:1763–1768. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li S, Iakoucheva LM, Mooney SD and
Radivojac P: Loss of post-translational modification sites in
disease. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. Pac Symp Biocomput.
337–347. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Paulo JA, Kadiyala V, Brizard S, Banks PA,
Steen H and Conwell DL: Post-translational modifications of
pancreatic fluid proteins collected via the endoscopic pancreatic
function test (ePFT). J Proteomics. 92:216–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Petersen HV, Peshavaria M, Pedersen AA,
Philippe J, Stein R, Madsen OD and Serup P: Glucose stimulates the
activation domain potential of the PDX-1 homeodomain transcription
factor. FEBS Lett. 431:362–366. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khoo S, Griffen SC, Xia Y, Baer RJ, German
MS and Cobb MH: Regulation of insulin gene transcription by ERK1
and ERK2 in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 278:32969–32977.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lebrun P, Montminy MR and Van Obberghen E:
Regulation of the pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 protein by
DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:38203–38210. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boucher MJ, Selander L, Carlsson L and
Edlund H: Phosphorylation marks IPF1/PDX1 protein for degradation
by glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent mechanisms. J Biol Chem.
281:6395–6403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng R, Al-Quobaili F, Müller I, Götz C,
Thiel G and Montenarh M: CK2 phosphorylation of Pdx-1 regulates its
transcription factor activity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:2481–2489.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Frogne T, Sylvestersen KB, Kubicek S,
Nielsen ML and Hecksher-Sørensen J: Pdx1 is post-translationally
modified in vivo and serine 61 is the principal site of
phosphorylation. PLoS One. 7:e352332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grijalva JL, Huizenga M, Mueller K,
Rodriguez S, Brazzo J, Camargo F, Sadri-Vakili G and Vakili K:
Dynamic alterations in Hippo signaling pathway and YAP activation
during liver regeneration. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
307:G196–G204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moles A, Butterworth JA, Sanchez A, Hunter
JE, Leslie J, Sellier H, Tiniakos D, Cockell SJ, Mann DA, Oakley F,
et al: A RelA(p65) Thr505 phospho-site mutation reveals an
important mechanism regulating NF-κB-dependent liver regeneration
and cancer. Oncogene. 35:4623–4632. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bonner-Weir S, Trent DF and Weir GC:
Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in
glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 71:1544–1553. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim HR, Kang JK, Yoon JT, Seong HH, Jung
JK, Lee HM, Sik Park C and Jin DI: Protein profiles of bovine
placenta derived from somatic cell nuclear transfer. Proteomics.
5:4264–4273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Harding JD and Rutter WJ: Rat pancreatic
amylase mRNA. Tissue specificity and accumulation during embryonic
development. J Biol Chem. 253:8736–8740. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jelenik T and Roden M: Mitochondrial
plasticity in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Antioxid Redox Signal.
19:258–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Dephoure N, Gould KL, Gygi SP and Kellogg
DR: Mapping and analysis of phosphorylation sites: A quick guide
for cell biologists. Mol Biol Cell. 24:535–542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ackermann AM and Gannon M: Molecular
regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass development, maintenance,
and expansion. J Mol Endocrinol. 38:193–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li WC, Rukstalis JM, Nishimura W,
Tchipashvili V, Habener JF, Sharma A and Bonner-Weir S: Activation
of pancreaticduct-derived progenitor cells during pancreatic
regeneration in adult rats. J Cell Sci. 123:2792–2802. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marinkovic DV, Marinkovic JN, Erdös EG and
Robinson CJ: Purification of carboxypeptidase B from human
pancreas. Biochem J. 163:253–260. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pousette A, Fernstad R, Sköldefors H and
Carlström K: Novel assay for pancreatic cellular damage: 1.
Characterization of protein profiles in human pancreatic cytosol
and purification and characterization of a pancreatic specific
protein. Pancreas. 3:421–426. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yamamoto KK, Pousette A, Chow P, Wilson H,
el Shami S and French CK: Isolation of a cDNA encoding a human
serum marker for acute pancreatitis. Identification of
pancreas-specific protein as pancreatic procarboxypeptidase B. J
Biol Chem. 267:2575–2581. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen CC, Wang SS, Chao Y, Chen SJ, Lee SD,
Wu SL, Jeng FS and Lo KJ: Serum pancreas-specific protein in acute
pancreatitis. Its clinical utility in comparison with serum
amylase. Scand J G astroenterol. 29:87–90. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Printz H, Siegmund H, Wojte C, Schäfer C,
Hesse H, Rothmund M and Göke B: 'Human pancreas-specific protein'
(procarboxypeptidase B): A valuable marker in pancreatitis?
Pancreas. 10:222–230. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Burgos FJ, Salvà M, Villegas V, Soriano F,
Mendez E and Avilés FX: Analysis of the activation process of
porcine procarboxypeptidase B and determination of the sequence of
its activation segment. Biochemistry. 30:4082–4089. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Appelros S, Thim L and Borgström A:
Activation peptide of carboxypeptidase B in serum and urine in
acute pancreatitis. Gut. 42:97–102. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Müller CA, Appelros S, Uhl W, Büchler MW
and Borgström A: Serum levels of procarboxypeptidase B and its
activation peptide in patients with acute pancreatitis and
non-pancreatic diseases. Gut. 51:229–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sokolovsky M: Porcine carboxypeptidase B.
Nitration of the functional tyrosyl residue with tetranitromethane.
Eur J Biochem. 25:267–273. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chatterjee S, Lardinois O, Bonini MG,
Bhattacharjee S, Stadler K, Corbett J, Deterding LJ, Tomer KB,
Kadiiska M and Mason RP: Site-specific carboxypeptidase B1 tyrosine
nitration and pathophysiological implications following its
physical association with nitric oxide synthase-3 in experimental
sepsis. J Immunol. 183:4055–4066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
da Silva Xavier G, Leclerc I, Salt IP,
Doiron B, Hardie DG, Kahn A and Rutter GA: Role of AMP-activated
protein kinase in the regulation by glucose of islet beta cell gene
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4023–4028. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hussain MA, Porras DL, Rowe MH, West JR,
Song WJ, Schreiber WE and Wondisford FE: Increased pancreatic
beta-cell proliferation mediated by CREB binding protein gene
activation. Mol Cell Biol. 26:7747–7759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rütti S, Arous C, Nica AC, Kanzaki M,
Halban PA and Bouzakri K: Expression, phosphorylation and function
of the Rab-GTPase activating protein TBC1D1 in pancreatic
beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 588:15–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Khoury GA, Baliban RC and Floudas CA:
Proteome-wide post-translational modification statistics: Frequency
analysis and curation of the swiss-prot database. Sci Rep. 1:12011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
De León DD, Deng S, Madani R, Ahima RS,
Drucker DJ and Stoffers DA: Role of endogenous glucagon-like
peptide-1 in islet regeneration after partial pancreatectomy.
Diabetes. 52:365–371. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang X, Gaspard JP, Mizukami Y, Li J,
Graeme-Cook F and Chung DC: Overexpression of cyclin D1 in
pancreatic beta-cells in vivo results in islet hyperplasia without
hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 54:712–719. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Williams K, Abanquah D, Joshi-Gokhale S,
Otero A, Lin H, Guthalu NK, Zhang X, Mozar A, Bisello A, Stewart
AF, et al: Systemic and acute administration of parathyroid
hormone-related peptide (1-36) stimulates endogenous beta cell
proliferation while preserving function in adult mice.
Diabetologia. 54:2867–2877. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Alvarez-Perez JC, Ernst S, Demirci C,
Casinelli GP, Mellado-Gil JM, Rausell-Palamos F, Vasavada RC and
Garcia-Ocaña A: Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling is
required for β-cell regeneration. Diabetes. 63:216–223. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Gao L, Tang W, Ding Z, Wang D, Qi X, Wu H
and Guo J: Proteinbinding function of RNA-dependent protein kinase
promotes proliferation through TRAF2/RIP1/NF-κB/c-Myc pathway in
pancreatic β cells. Mol Med. 21:154–166. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Andersson O, Adams BA, Yoo D, Ellis GC,
Gut P, Anderson RM, German MS and Stainier DY: Adenosine signaling
promotes regeneration of pancreatic β cells in vivo. Cell Metab.
15:885–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sakano D, Choi S, Kataoka M, Shiraki N,
Uesugi M, Kume K and Kume S: Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated
regulation of pancreatic β cell mass. Stem Cell Reports. 7:95–109.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mozar A, Lin H, Williams K, Chin C, Li R,
Kondegowda NG, Stewart AF, Garcia-Ocaña A and Vasavada RC:
Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (1-36) enhances beta cell
regeneration and increases beta cell mass in a mouse model of
partial pancreatectomy. PLoS One. 11:e01584142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|