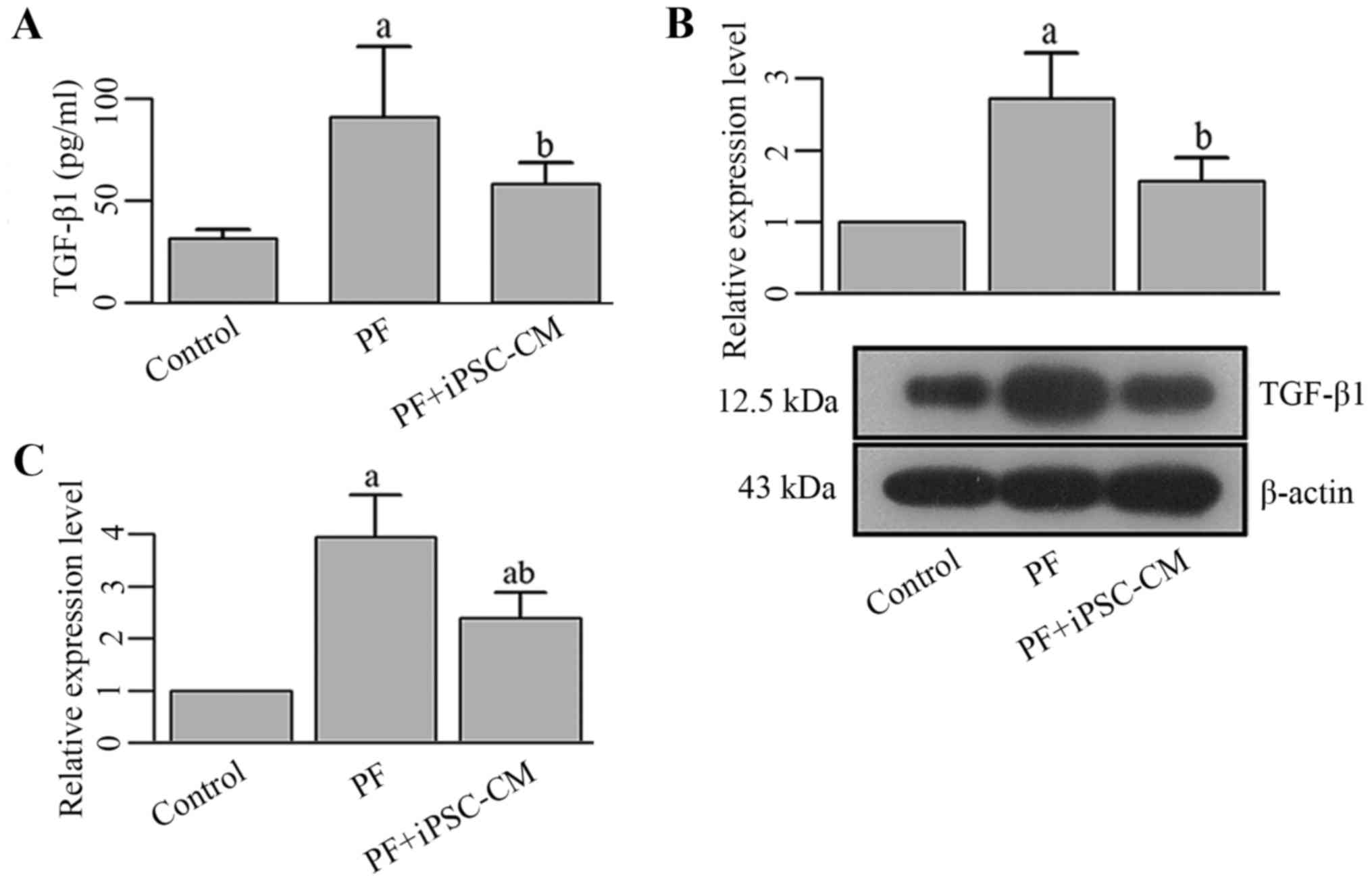
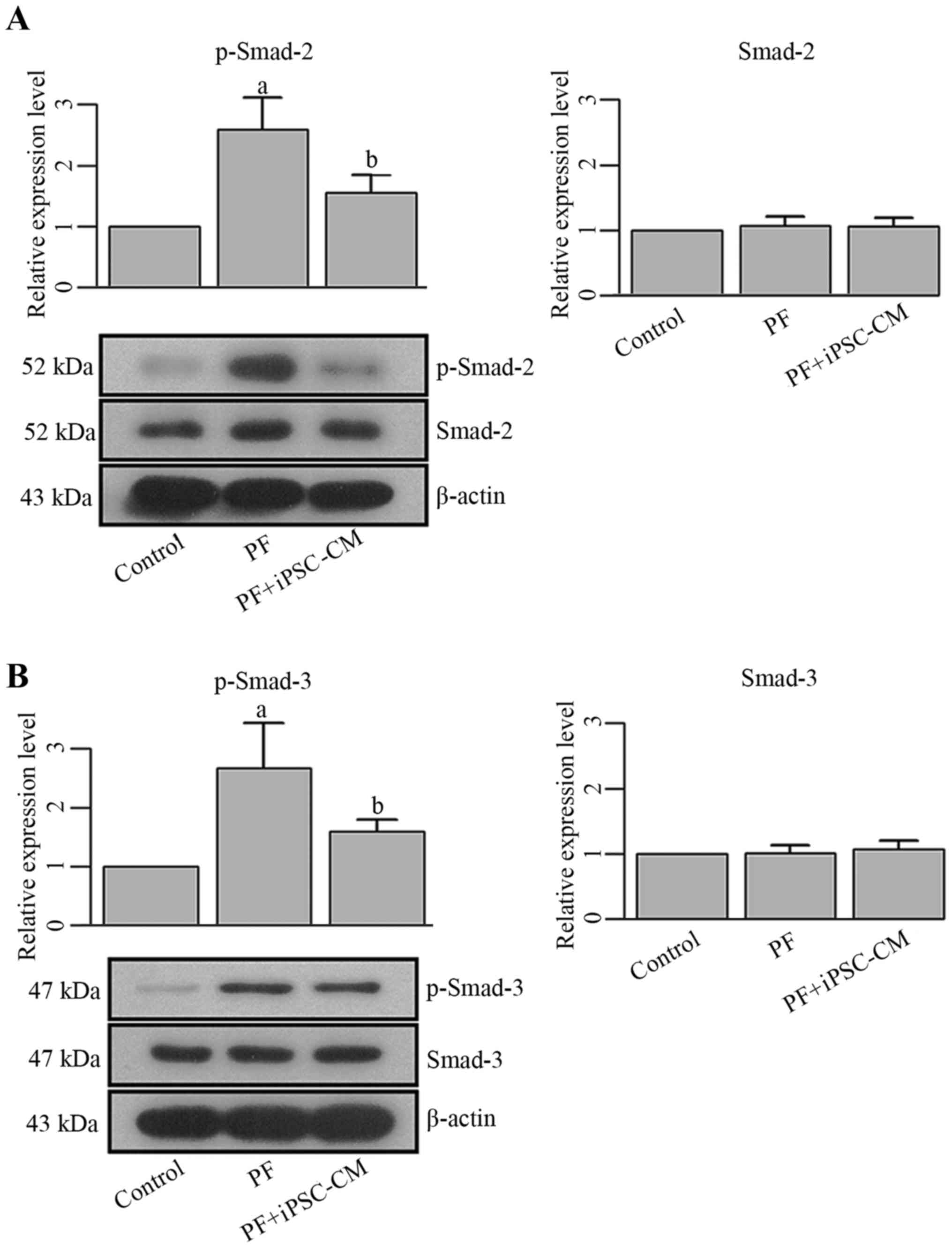
|
1
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perez A, Rogers RM and Dauber JH: The
prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 29(Suppl 3): S19–S26. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Phan SH: The myofibroblast in pulmonary
fibrosis. Chest. 122(Suppl 6): 286S–289S. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Evans RA, Tian YC, Steadman R and Phillips
AO: TGF-β1-mediated fibroblast-myofibroblast terminal
differentiation-the role of Smad proteins. Exp Cell Res.
282:90–100. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sime PJ, Xing Z, Graham FL, Csaky KG and
Gauldie J: Adeno-vector-mediated gene transfer of active
transforming growth factor-beta1 induces prolonged severe fibrosis
in rat lung. J Clin Invest. 100:768–776. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hawkins F and Kotton DN: Embryonic and
induced pluripotent stem cells for lung regeneration. Ann Am Thorac
Soc. 12(Suppl 1): S50–S53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
How CK, Chien Y, Yang KY, Shih HC, Juan
CC, Yang YP, Chiou GY, Huang PI, Chang YL, Chen LK, et al: Induced
pluripotent stem cells mediate the release of interferon
gamma-induced protein 10 and alleviate bleomycin-induced lung
inflammation and fibrosis. Shock. 39:261–270. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang KY, Shih HC, How CK, Chen CY, Hsu HS,
Yang CW, Lee YC, Perng RP, Peng CH, Li HY, et al: IV delivery of
induced pluripotent stem cells attenuates endotoxin-induced acute
lung injury in mice. Chest. 140:1243–1253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li HY, Chien Y, Chen YJ, Chen SF, Chang
YL, Chiang CH, Jeng SY, Chang CM, Wang ML, Chen LK, et al:
Reprogramming induced pluripotent stem cells in the absence of
c-Myc for differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells. Biomaterials.
32:5994–6005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Su VY, Chiou SH, Lin CS, Chen WC, Yu WK,
Chen YW, Chen CY and Yang KY: Induced pluripotent stem cells reduce
neutrophil chemotaxis via activating GRK2 in endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury. Respirology. 22:1156–1164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li F and Niyibizi C: Cells derived from
murine induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) by treatment with
members of TGF-beta family give rise to osteoblasts differentiation
and form bone in vivo. BMC Cell Biol. 13:352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Flint MH and Lyons MF: The effect of
heating and denaturation on the staining of collagen by the Masson
trichrome procedure. Histochem J. 7:547–555. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Munger JS, Huang X, Kawakatsu H, Griffiths
MJ, Dalton SL, Wu J, Pittet JF, Kaminski N, Garat C, Matthay MA, et
al: The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta
1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis.
Cell. 96:319–328. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, Mora AL, Spears
W, Roman J and Brigham KL: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
33:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen AS, Haslett C, Feldsien DC, Henson PM
and Cherniack RM: The intensity of chronic lung inflammation and
fibrosis after bleomycin is directly related to the severity of
acute injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 137:564–571. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakagawa M, Koyanagi M, Tanabe K,
Takahashi K, Ichisaka T, Aoi T, Okita K, Mochiduki Y, Takizawa N
and Yamanaka S: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
without Myc from mouse and human fibroblasts. Nat Biotechnol.
26:101–106. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Moodley Y, Ilancheran S, Samuel C,
Vaghjiani V, Atienza D, Williams ED, Jenkin G, Wallace E, Trounson
A and Manuelpillai U: Human amnion epithelial cell transplantation
abrogates lung fibrosis and augments repair. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 182:643–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumamoto M, Nishiwaki T, Matsuo N, Kimura
H and Matsushima K: Minimally cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells ameliorate fibrotic lung injury. Eur Respir J. 34:740–748.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fattman C, Pandey AC,
Torres G, Go K and Phinney DG: Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist
mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of
mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:11002–11007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SH, Jang AS, Kim YE, Cha JY, Kim TH,
Jung S, Park SK, Lee YK, Won JH, Kim YH, et al: Modulation of
cytokine and nitric oxide by mesenchymal stem cell transfer in lung
injury/fibrosis. Respir Res. 11:162010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sappino AP, Schürch W and Gabbiani G:
Differentiation repertoire of fibroblastic cells: expression of
cytoskeletal proteins as marker of phenotypic modulations. Lab
Invest. 63:144–161. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang HY and Phan SH: Inhibition of
myofibroblast apoptosis by transforming growth factor β1. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 21:658–665. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Midgley AC, Rogers M, Hallett MB, Clayton
A, Bowen T, Phillips AO and Steadman R: Transforming growth
factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-stimulated fibroblast to myofibroblast
differentiation is mediated by hyaluronan (HA)-facilitated
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and CD44 co-localization in
lipid rafts. J Biol Chem. 288:14824–14838. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Piek E, Ju WJ, Heyer J, Escalante-Alcalde
D, Stewart CL, Weinstein M, Deng C, Kucherlapati R, Bottinger EP
and Roberts AB: Functional characterization of transforming growth
factor β signaling in Smad2- and Smad3-deficient fibroblasts. J
Biol Chem. 276:19945–19953. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang YC, Piek E, Zavadil J, Liang D, Xie
D, Heyer J, Pavlidis P, Kucherlapati R, Roberts AB and Böttinger
EP: Hierarchical model of gene regulation by transforming growth
factor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:10269–10274. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Phanish MK, Wahab NA, Colville-Nash P,
Hendry BM and Dockrell ME: The differential role of Smad2 and Smad3
in the regulation of pro-fibrotic TGFbeta1 responses in human
proximal-tubule epithelial cells. Biochem J. 393:601–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ohnuki M and Takahashi K: Present and
future challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells. Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 370:201403672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harding J and Mirochnitchenko O:
Preclinical studies for induced pluripotent stem cell-based
therapeutics. J Biol Chem. 289:4585–4593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|