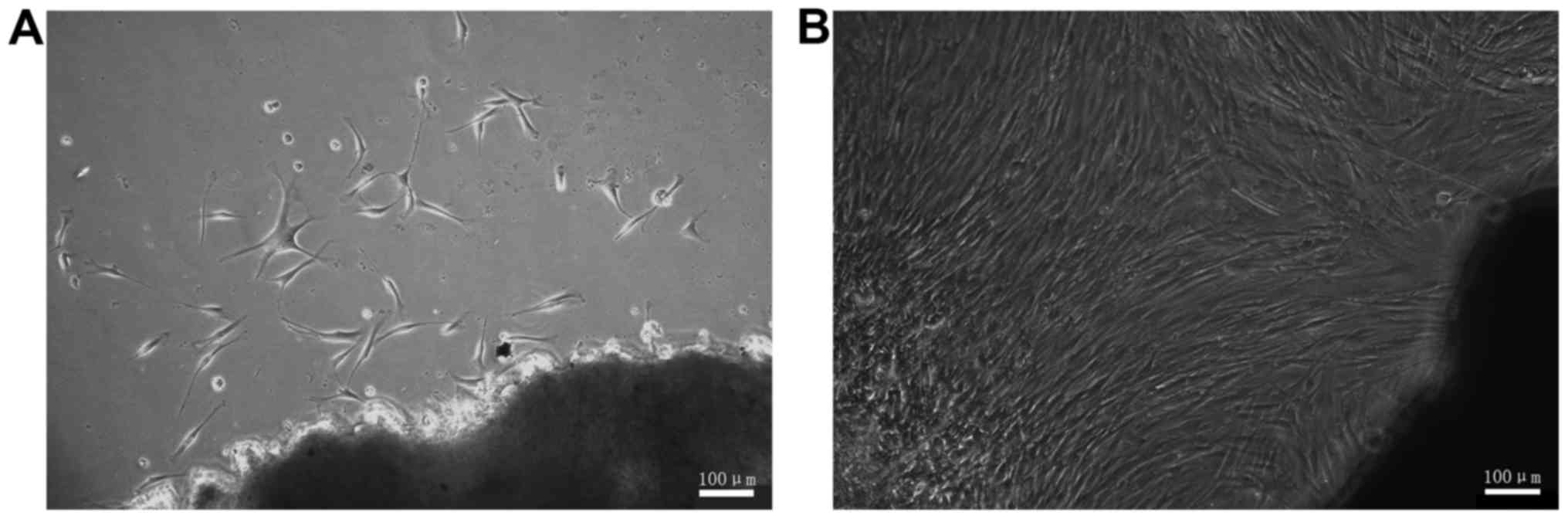
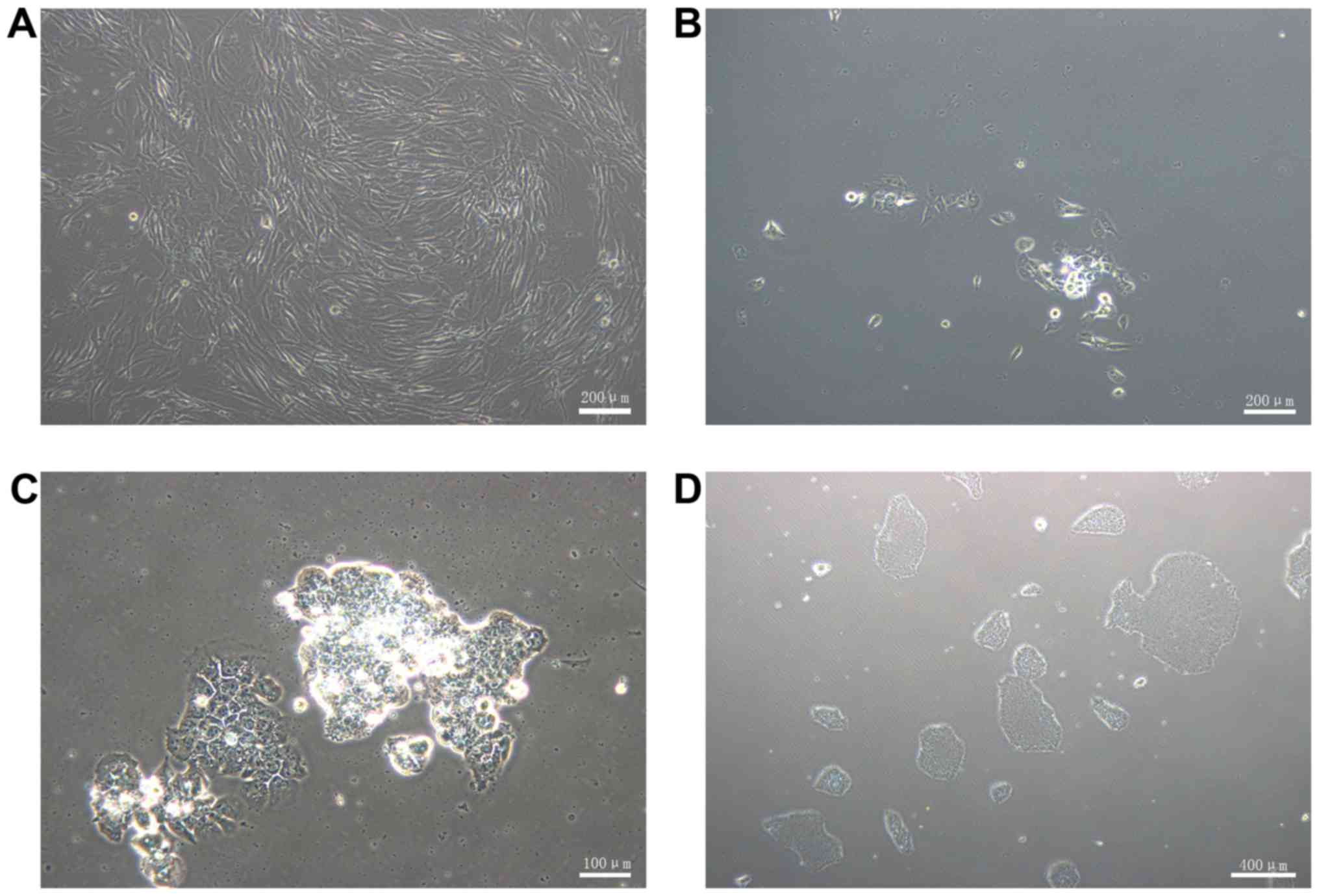
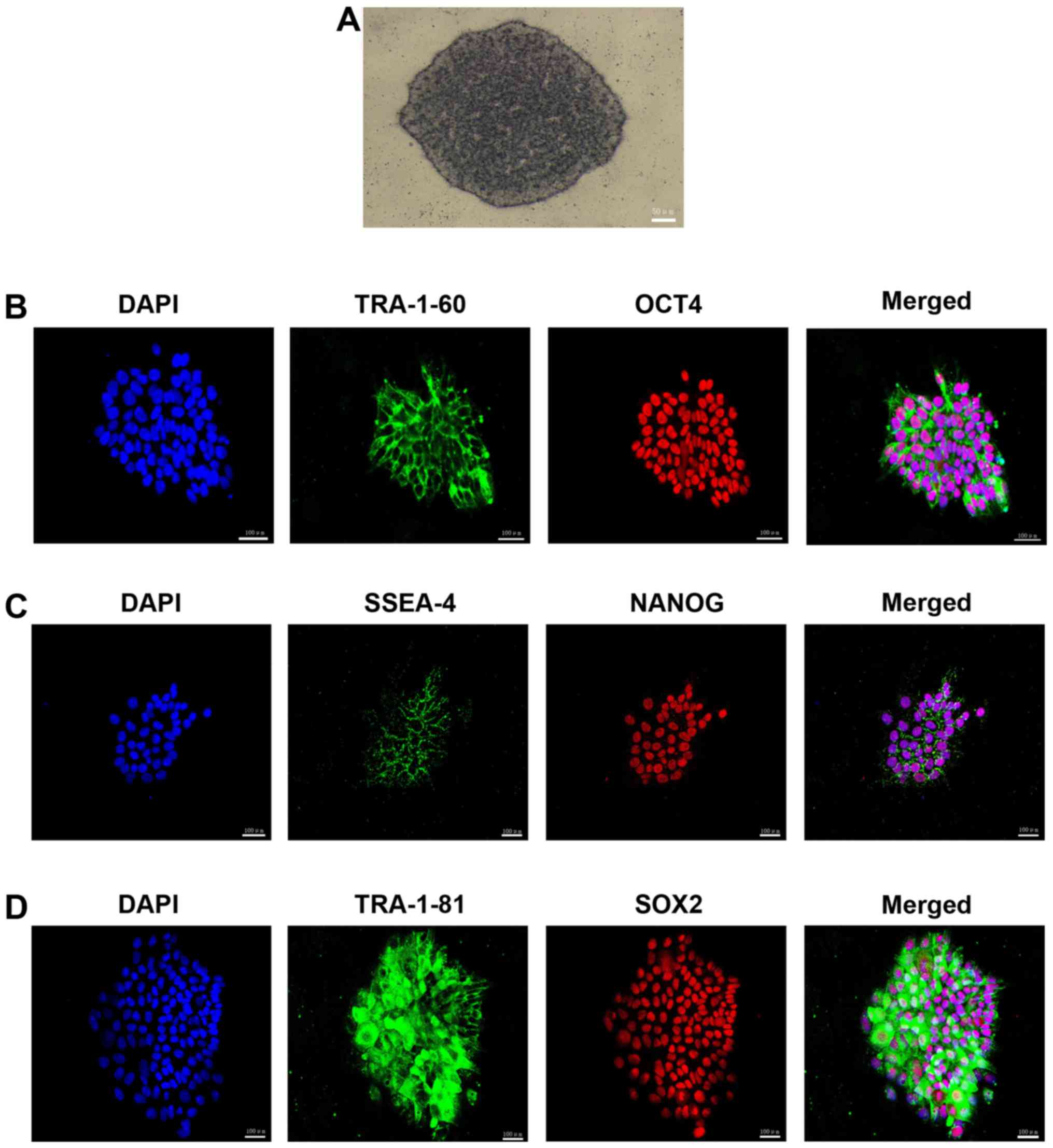
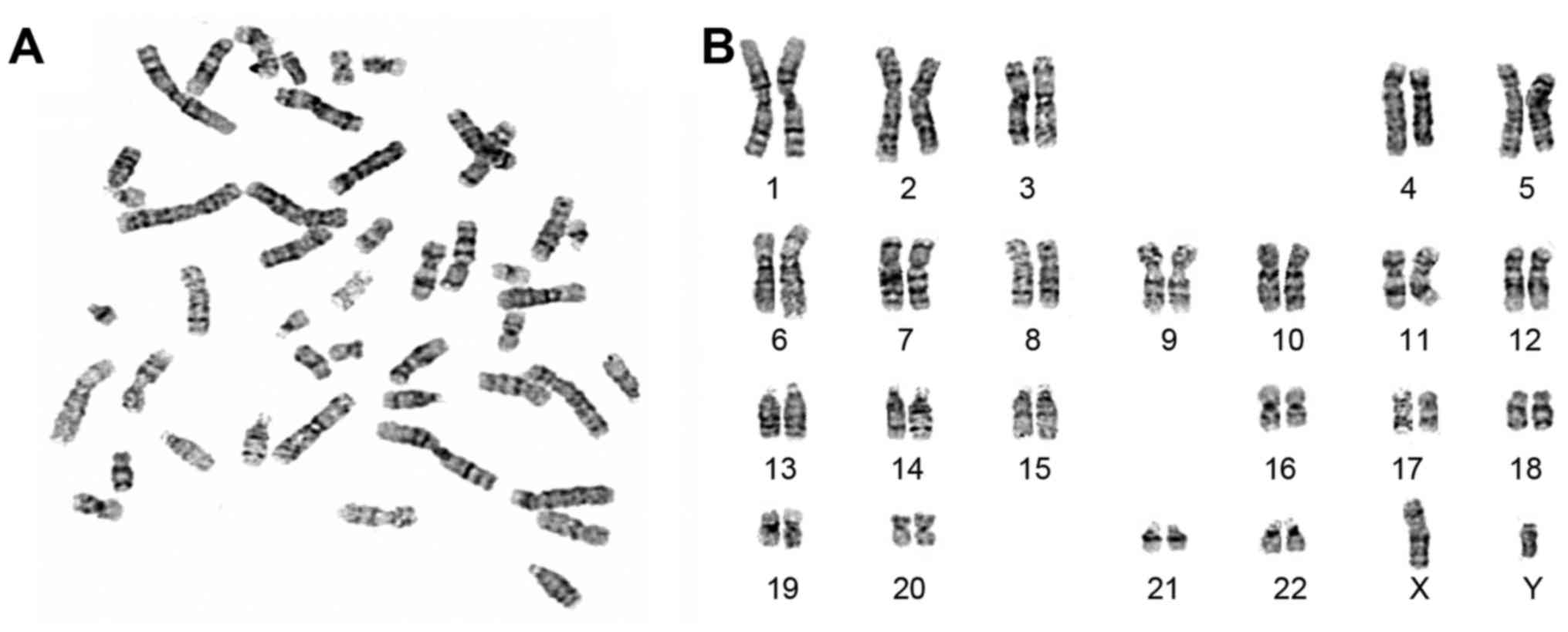
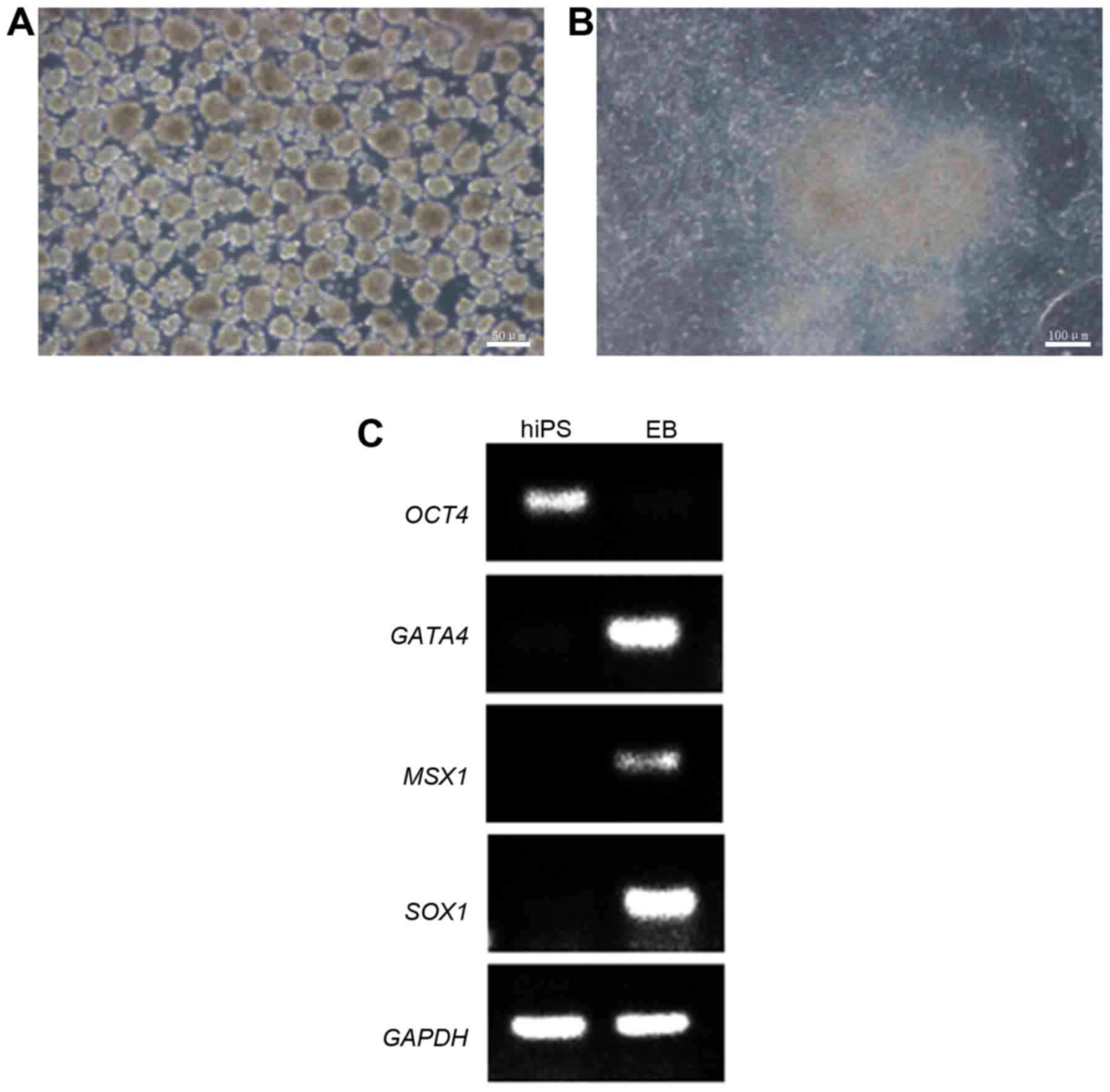
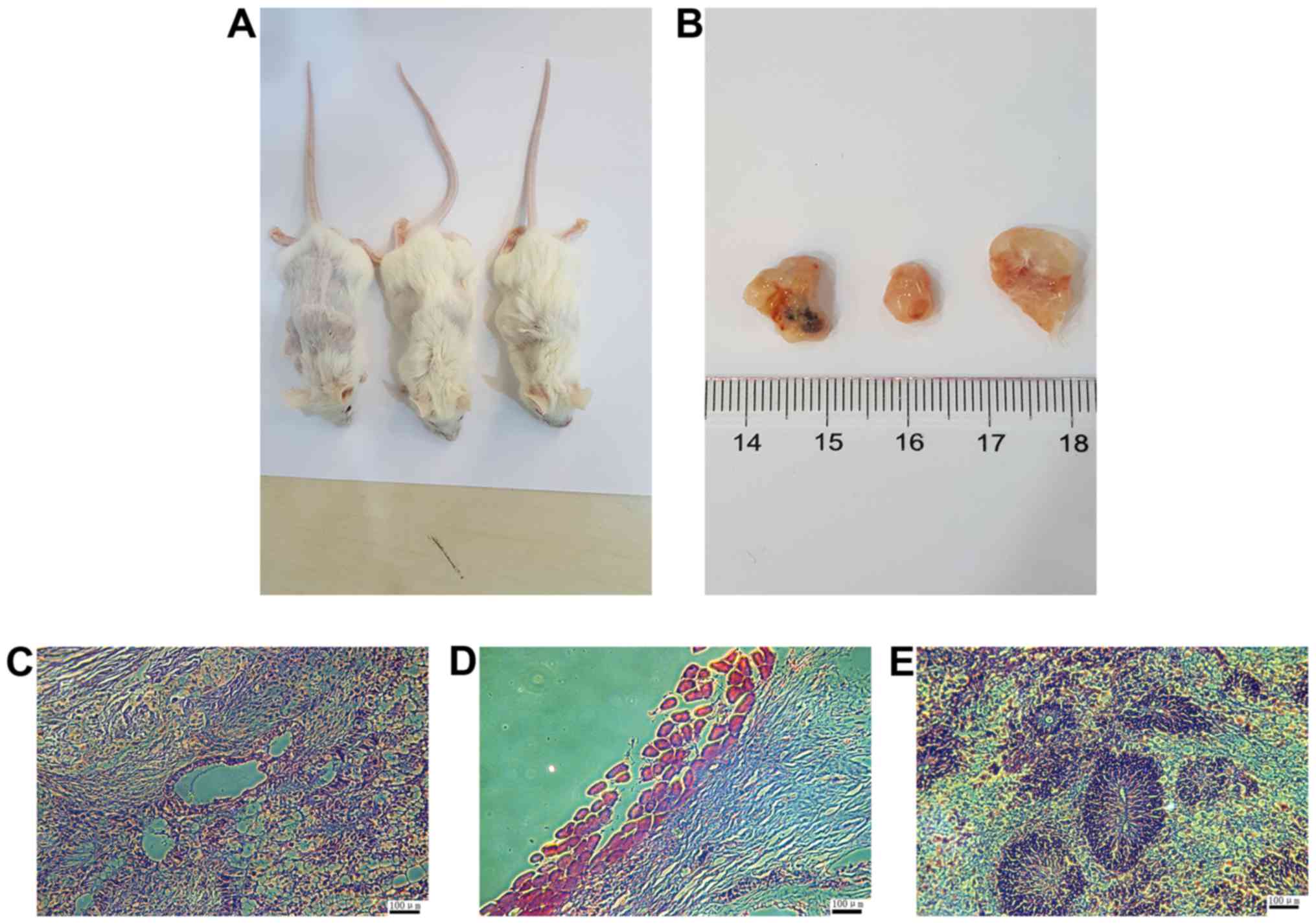
|
1
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vodyanik Yu J, Smuga-Otto MA,
Antosiewicz-Bourget K, Frane J, Tian JL, Nie S, Jonsdottir J,
Ruotti GA, Stewart VR, et al: Induced pluripotent stem cell lines
derived from human somatic cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huangfu D, Osafune K, Maehr R, Guo W,
Eijkelenboom A, Chen S, Muhlestein W and Melton DA: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from primary human fibroblasts with only
Oct4 and Sox2. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1269–1275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lowry WE, Richter L, Yachechko R, Pyle AD,
Tchieu J, Sridharan R, Clark AT and Plath K: Generation of human
induced pluripotent stem cells from dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:2883–2888. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E,
Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilić J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia
G, et al: Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent
stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 26:1276–1284.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sochacki J, Devalle S, Reis M, Mattos P
and Rehen S: Generation of urine iPS cell lines from patients with
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) using a
non-integrative method. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 17:102–106. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xue Y, Cai X, Wang L, Liao B, Zhang H,
Shan Y, Chen Q, Zhou T, Li X, Hou J, et al: Generating a
non-integrating human induced pluripotent stem cell bank from
urine-derived cells. PLoS One. 8:e705732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamanaka S: Induced pluripotent stem
cells: Past, present, and future. Cell Stem Cell. 10:678–684. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guha P, Morgan JW, Mostoslavsky G,
Rodrigues NP and Boyd AS: Lack of immune response to differentiated
cells derived from syngeneic induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell
Stem Cell. 12:407–412. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishida Y, Kawakami H, Kitajima H,
Nishiyama A, Sasai Y, Inoue H and Muguruma K: Vulnerability of
purkinje cells generated from spinocerebellar ataxia type 6
patient-derived iPSCs. Cell Rep. 17:1482–1490. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Son MY, Kim YD, Seol B, Lee MO, Na HJ, Yoo
B, Chang JS and Cho YS: Biomarker discovery by modeling Behçet's
disease with patient-specific human induced pluripotent stem cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 26:133–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ye L, Chang JC, Lin C, Sun X, Yu J and Kan
YW: Induced pluripotent stem cells offer new approach to therapy in
thalassemia and sickle cell anemia and option in prenatal diagnosis
in genetic diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:9826–9830. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilmut I: The first direct reprogramming
of adult human fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell. 1:593–594. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Okita K, Nakagawa M, Hyenjong H, Ichisaka
T and Yamanaka S: Generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem
cells without viral vectors. Science. 322:949–953. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mack AA, Kroboth S, Rajesh D and Wang WB:
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from CD34+
cells across blood drawn from multiple donors with non-integrating
episomal vectors. PLoS One. 6:e279562011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fusaki N, Ban H, Nishiyama A, Saeki K and
Hasegawa M: Efficient induction of transgene-free human pluripotent
stem cells using a vector based on Sendai virus, an RNA virus that
does not integrate into the host genome. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 85:348–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim K, Doi A, Wen B, Ng K, Zhao R, Cahan
P, Kim J, Aryee MJ, Ji H, Ehrlich LI, et al: Epigenetic memory in
induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 467:285–290. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stadtfeld M, Apostolou E, Akutsu H, Fukuda
A, Follett P, Natesan S, Kono T, Shioda T and Hochedlinger K:
Aberrant silencing of imprinted genes on chromosome 12qF1 in mouse
induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 465:175–181. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh M, Kiuru M, Cairo MS and Christiano
AM: Generation of keratinocytes from normal and recessive
dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-induced pluripotent stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:8797–8802. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ebert AD, Yu J, Rose FF Jr, Mattis VB,
Lorson CL, Thomson JA and Svendsen CN: Induced pluripotent stem
cells from a spinal muscular atrophy patient. Nature. 457:277–280.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Tousley A and Kegel-Gleason KB: Induced
pluripotent stem cells in Huntington's disease research: Progress
and opportunity. J Huntingtons Dis. 5:99–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borooah S, Phillips MJ, Bilican B, Wright
AF, Wilmut I, Chandran S, Gamm D and Dhillon B: Using human induced
pluripotent stem cells to treat retinal disease. Prog Retin Eye
Res. 37:163–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishimura K, Sano M, Ohtaka M, Furuta B,
Umemura Y, Nakajima Y, Ikehara Y, Kobayashi T, Segawa H, Takayasu
S, et al: Development of defective and persistent Sendai virus
vector: A unique gene delivery/expression system ideal for cell
reprogramming. J Biol Chem. 286:4760–4771. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Lieu PT, Fontes A, Vemuri MC and Macarthur
CC: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells with CytoTune, a
non-integrating Sendai virus. Methods Mol Biol. 997:45–56. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Churko JM, Burridge PW and Wu JC:
Generation of human iPSCs from human peripheral blood mononuclear
cells using non-integrative Sendai virus in chemically defined
conditions. Methods Mol Biol. 1036:81–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun N, Panetta NJ, Gupta DM, Wilson KD,
Lee A, Jia F, Hu S, Cherry AM, Robbins RC, Longaker MT, et al:
Feeder-free derivation of induced pluripotent stem cells from adult
human adipose stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:15720–15725.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Song Y, Ding J, Jin R, Jung J, Li S, Yang
J, Wang A and Li Z: Expression and purification of FGF21 in Pichia
pastoris and its effect on fibroblast-cell migration. Mol Med Rep.
13:3619–3626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao HX, Li Y, Jin HF, Xie L, Liu C, Jiang
F, Luo YN, Yin GW, Li Y, Wang J, et al: Rapid and efficient
reprogramming of human amnion-derived cells into pluripotency by
three factors OCT4/SOX2/NANOG. Differentiation. 80:123–129. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kogut I, Roop DR and Bilousova G:
Differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into a
keratinocyte lineage. Methods Mol Biol. 1195:1–12. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohta S, Imaizumi Y, Okada Y, Akamatsu W,
Kuwahara R, Ohyama M, Amagai M, Matsuzaki Y, Yamanaka S, Okano H,
et al: Generation of human melanocytes from induced pluripotent
stem cells. PLoS One. 6:e161822011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zanotelli MR, Ardalani H, Zhang J, Hou Z,
Nguyen EH, Swanson S, Nguyen BK, Bolin J, Elwell A, Bischel LL, et
al: Stable engineered vascular networks from human induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells cultured in
synthetic hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 35:32–41. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khayyatan F, Nemati S, Kiani S, Hojjati
Emami S and Baharvand H: Behaviour of human induced pluripotent
stem cell-derived neural progenitors on collagen scaffolds varied
in freezing temperature and laminin concentration. Cell J.
16:53–62. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ando M, Nishimura T, Yamazaki S, Yamaguchi
T, Kawana-Tachikawa A, Hayama T, Nakauchi Y, Ando J, Ota Y,
Takahashi S, et al: A Safeguard system for induced pluripotent stem
cell-derived rejuvenated T cell therapy. Stem Cell Reports.
5:597–608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|