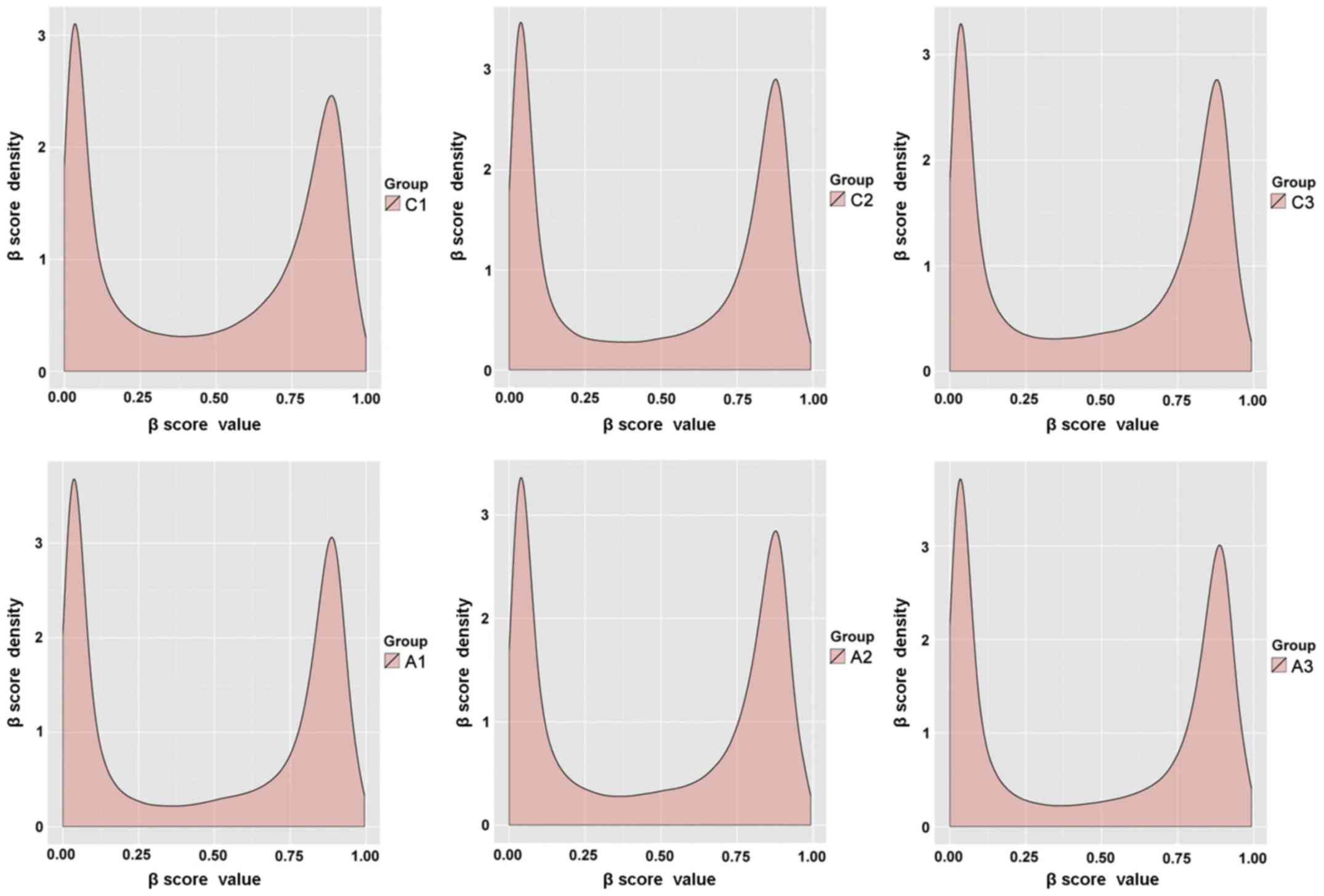
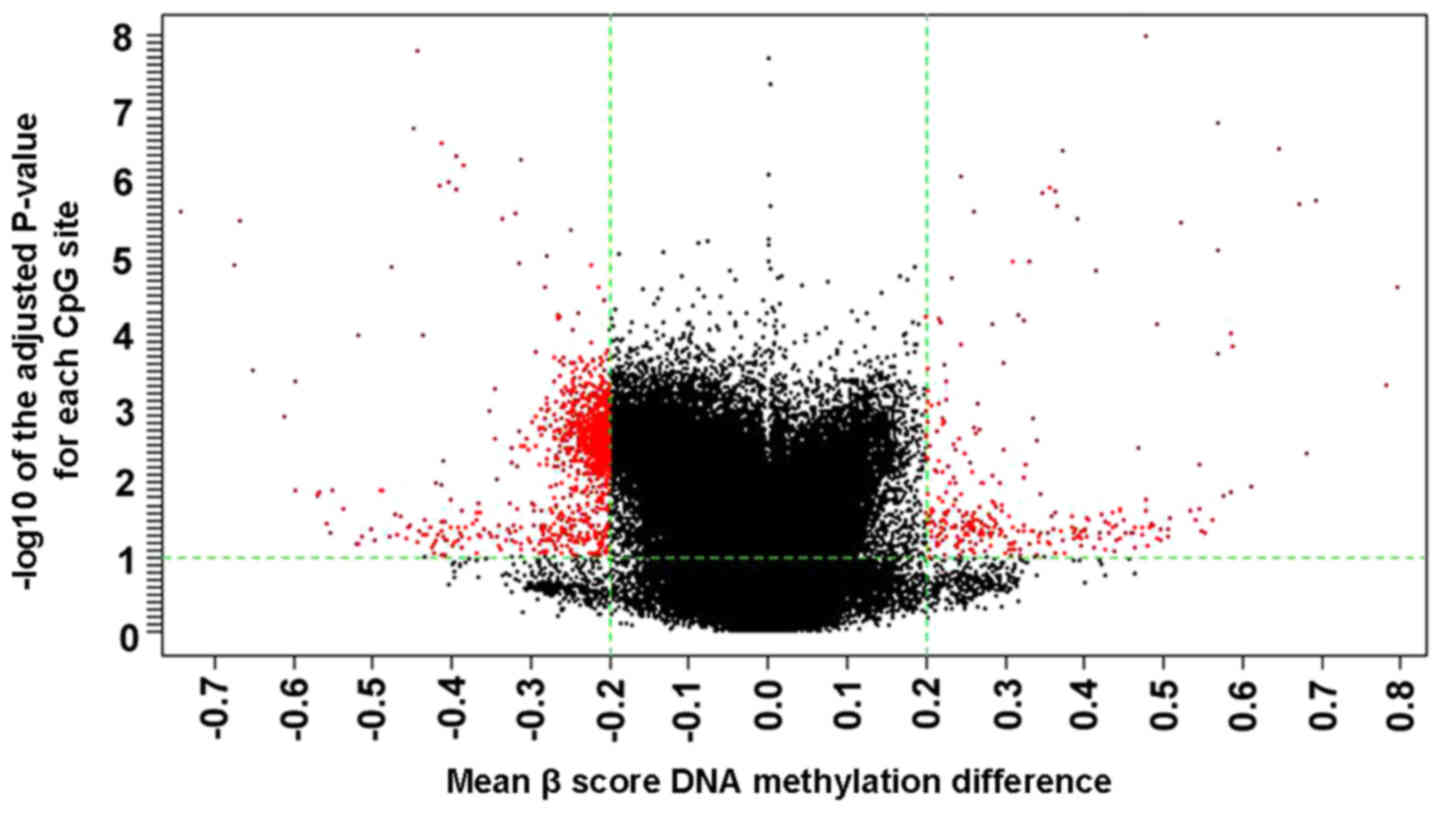
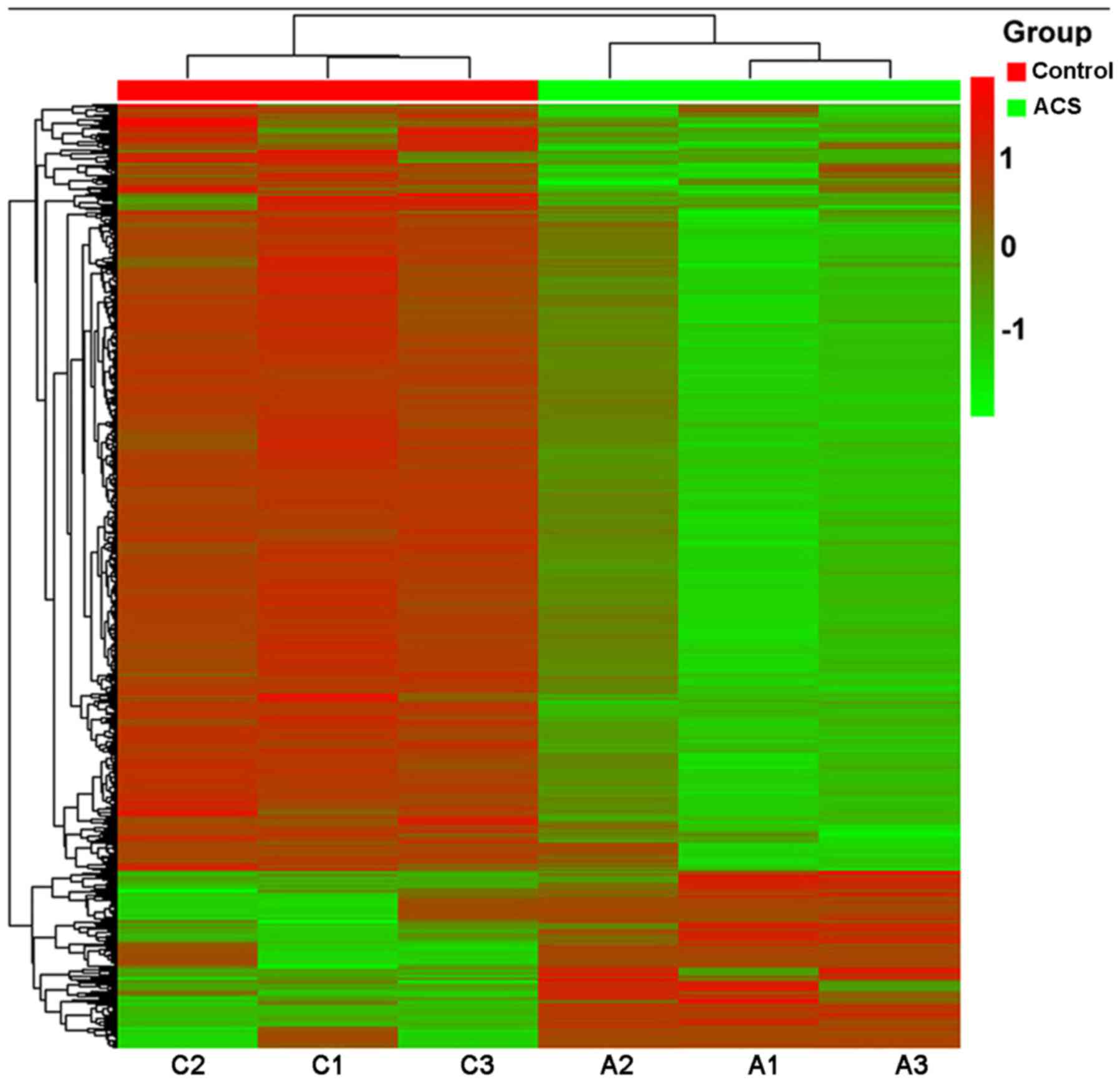
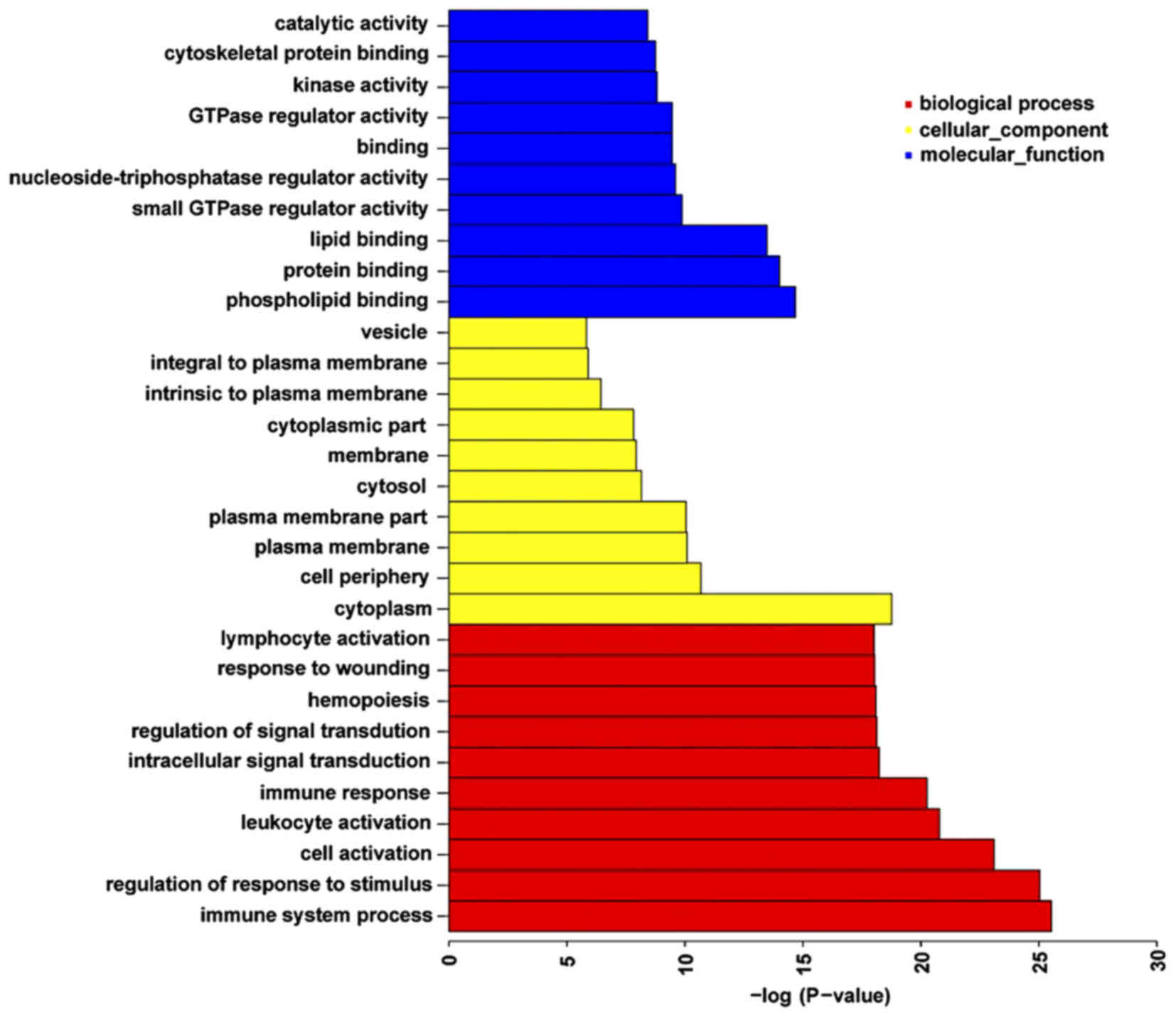
|
1
|
Falk E, Nakano M, Bentzon JF, Finn AV and
Virmani R: Update on acute coronary syndromes: The pathologists'
view. Eur Heart J. 34:719–728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Corcoran D, Grant P and Berry C: Risk
stratification in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: Risk
scores, biomarkers and clinical judgment. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc.
8:131–137. 2015.
|
|
3
|
O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey
DE Jr, MK, de Lemos JA, Ettinger SM, Fang JC, Fesmire FM, Franklin
BA, et al; American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart
Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA
guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction:
A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American
Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation.
127:e362–e425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Redfors B, Råmunddal T, Angerås O, Dworeck
C, Haraldsson I, Ioanes D, Petursson P, Libungan B, Odenstedt J,
Stewart J, et al: Angiographic findings and survival in patients
undergoing coronary angiography due to sudden cardiac arrest in
western Sweden. Resuscitation. 90:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hofer TP, Frankenberger M, Mages J, Lang
R, Meyer P, Hoffmann R, Colige A and Ziegler-Heitbrock L:
Tissue-specific induction of ADAMTS2 in monocytes and macrophages
by glucocorticoids. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:323–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
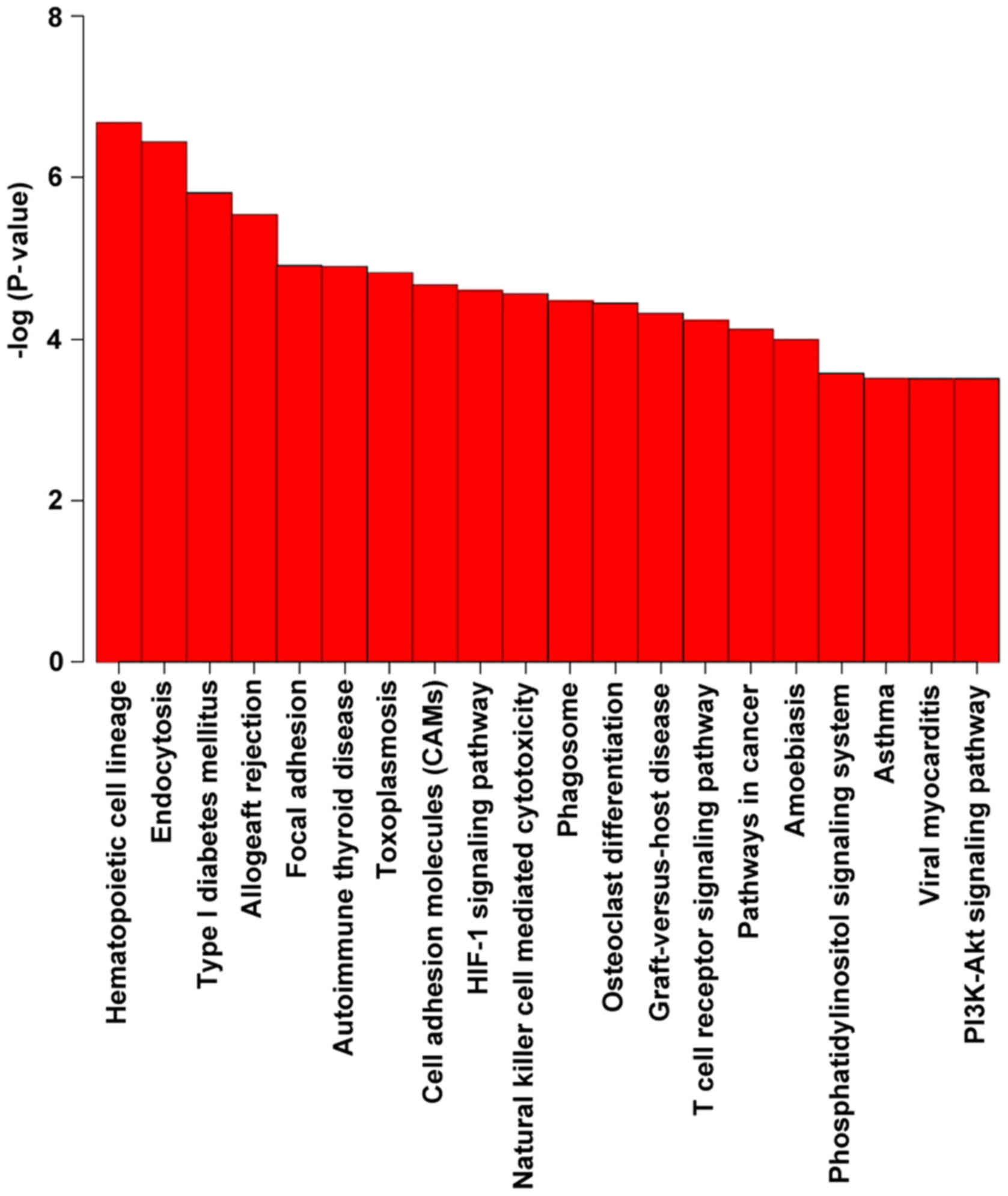
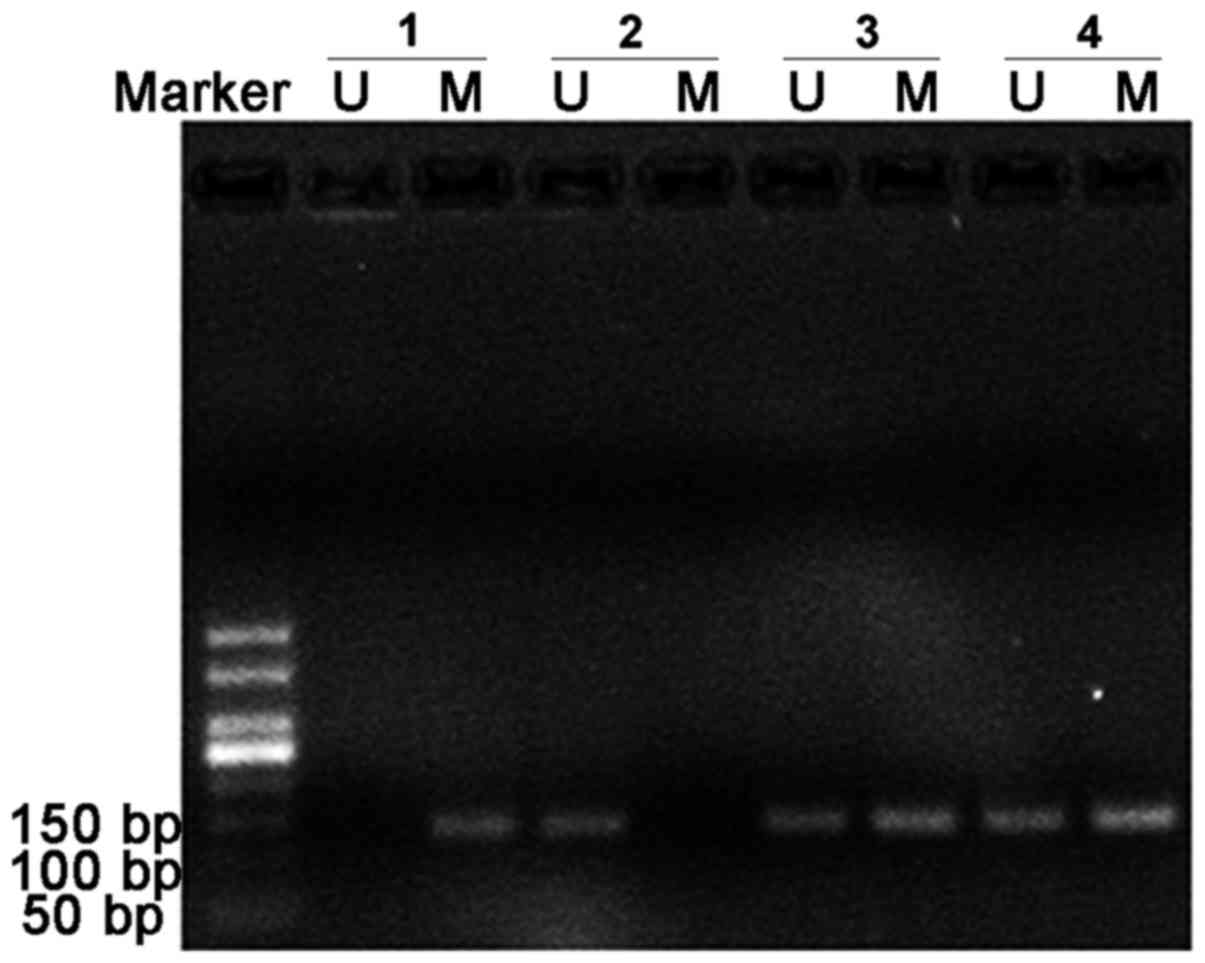
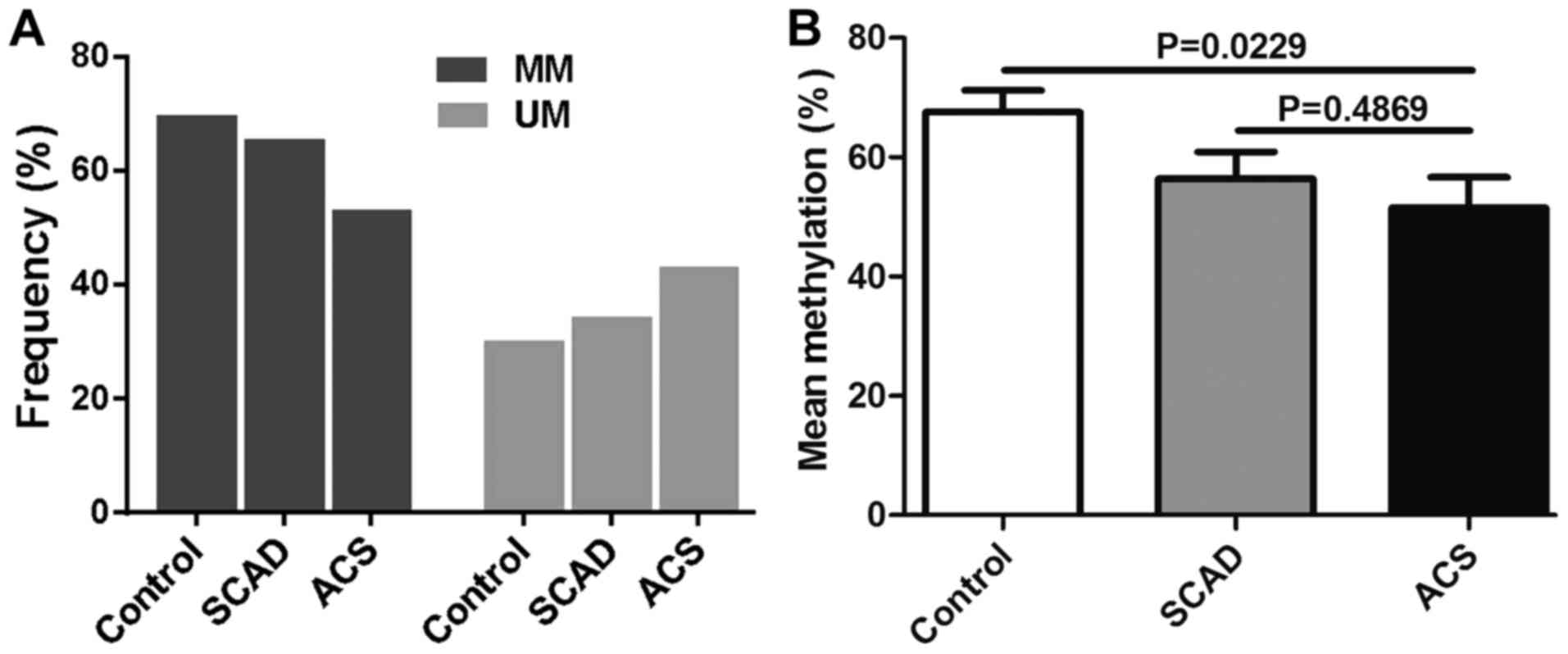
|
|
6
|
Tomson T, Surges R, Delamont R, Haywood S
and Hesdorffer DC: Who to target in sudden unexpected death in
epilepsy prevention and how? Risk factors, biomarkers, and
intervention study designs. Epilepsia. 57(Suppl 1): 4–16. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mosleh W, Abdel-Qadir H and Farkouh M:
Biomarkers in the emergency workup of chest pain: Uses,
limitations, and future. Cleve Clin J Med. 80:589–598. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu SS, Lin X, Yuan LQ and Liao EY: The
role of epigenetics in arterial calcification. BioMed Res Int.
2015:3208492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heyn H and Esteller M: DNA methylation
profiling in the clinic: Applications and challenges. Nat Rev
Genet. 13:679–692. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Handy DE, Castro R and Loscalzo J:
Epigenetic modifications: Basic mechanisms and role in
cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 123:2145–2156. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wallace RG, Twomey LC, Custaud MA, Moyna
N, Cummins PM, Mangone M and Murphy RP: Potential diagnostic and
prognostic biomarkers of epigenetic drift within the cardiovascular
compartment. BioMed Res Int. 2016:24657632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Loscalzo J and Handy DE: Epigenetic
modifications: Basic mechanisms and role in cardiovascular disease
(2013 Grover Conference series). Pulm Circ. 4:169–174. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turgeon PJ, Sukumar AN and Marsden PA:
Epigenetics of cardiovascular disease - A new 'Beat' in coronary
artery disease. Med Epigenet. 2:37–52. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kandi V and Vadakedath S: Effect of DNA
methylation in various diseases and the probable protective role of
nutrition: A mini-review. Cureus. 7:e3092015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Razin A, Webb C, Szyf M, Yisraeli J,
Rosenthal A, Naveh-Many T, Sciaky-Gallili N and Cedar H: Variations
in DNA methylation during mouse cell differentiation in vivo and in
vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:2275–2279. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Afzali M, Nakhaee A, Tabatabaei SP,
Tirgar-Fakheri K and Hashemi M: Aberrant promoter methylation
profile of Niemann-pick type C1 gene in cardiovascular disease.
Iran Biomed J. 17:77–83. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nazarenko MS, Markov AV, Lebedev IN,
Freidin MB, Sleptcov AA, Koroleva IA, Frolov AV, Popov VA,
Barbarash OL and Puzyrev VP: A comparison of genome-wide DNA
methylation patterns between different vascular tissues from
patients with coronary heart disease. PLoS One. 10:e01226012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Liu Y, Strickland FM and Richardson
B: Age-dependent decreases in DNA methyltransferase levels and low
transmethylation micronutrient levels synergize to promote
overexpression of genes implicated in autoimmunity and acute
coronary syndromes. Exp Gerontol. 45:312–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Kim JM, Stewart R, Kang HJ, Bae KY, Kim
SW, Shin IS, Hong YJ, Ahn Y, Jeong MH and Yoon JS: BDNF methylation
and depressive disorder in acute coronary syndrome: The K-DEPACS
and EsDEPACS studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 62:159–165. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lü CX, Xu RD, Cao M, Wang G, Yan FQ, Shang
SS, Wu XF, Ruan L, Quan XQ and Zhang CT: FOXP3 demethylation as a
means of identifying quantitative defects in regulatory T cells in
acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 229:263–270. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang LN, Liu PP, Wang L, Yuan F, Xu L,
Xin Y, Fei LJ, Zhong QL, Huang Y, Xu L, et al: Lower ADD1 gene
promoter DNA methylation increases the risk of essential
hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e634552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim JD, Lee A, Choi J, Park Y, Kang H,
Chang W, Lee MS and Kim J: Epigenetic modulation as a therapeutic
approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Exp Mol Med.
47:e1752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Zheng Y, Hou C, Yang L, Li X, Lin
J, Huang G, Lu Q, Wang CY and Zhou Z: DNA methylation impairs TLR9
induced Foxp3 expression by attenuating IRF-7 binding activity in
fulminant type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun. 41:50–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pasquier J, Hoarau-Véchot J, Fakhro K,
Rafii A and Abi Khalil C: Epigenetics and cardiovascular disease in
diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 15:1082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Babu M, Durga Devi T, Mäkinen P, Kaikkonen
M, Lesch HP, Junttila S, Laiho A, Ghimire B, Gyenesei A and
Ylä-Herttuala S: Differential promoter methylation of macrophage
genes is associated with impaired vascular growth in ischemic
muscles of hyperlipidemic and type 2 diabetic mice: Genome-wide
promoter methylation study. Circ Res. 117:289–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yip L, Fuhlbrigge R, Taylor C, Creusot RJ,
Nishikawa-Matsumura T, Whiting CC, Schartner JM, Akter R, von
Herrath M and Fathman CG: Inflammation and hyperglycemia mediate
Deaf1 splicing in the pancreatic lymph nodes via distinct pathways
during type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 64:604–617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Hiltunen MO, Turunen MP, Häkkinen TP,
Rutanen J, Hedman M, Mäkinen K, Turunen AM, Aalto-Setälä K and
Ylä-Herttuala S: DNA hypomethylation and methyltransferase
expression in atherosclerotic lesions. Vasc Med. 7:5–11. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Castillo-Díaz SA, Garay-Sevilla ME,
Hernández-González MA, Solís-Martínez MO and Zaina S: Extensive
demethylation of normally hypermethylated CpG islands occurs in
human atherosclerotic arteries. Int J Mol Med. 26:691–700.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang YZ, Manduchi E, Stoeckert CJ Jr and
Davies PF: Arterial endothelial methylome: Differential DNA
methylation in atherosusceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo.
BMC Genomics. 16:5062015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A and Jaenisch
R: Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA
hypomethylation. Science. 300:4552003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Virani S, Rentschler KM, Nishijo M,
Ruangyuttikarn W, Swaddiwudhipong W, Basu N and Rozek LS: DNA
methylation is differentially associated with environmental cadmium
exposure based on sex and smoking status. Chemosphere. 145:284–290.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Zhu X, Li J, Deng S, Yu K, Liu X, Deng Q,
Sun H, Zhang X, He M, Guo H, et al: Genome-wide analysis of DNA
methylation and cigarette smoking in a chinese population. Environ
Health Perspect. 124:966–973. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: The Gene Ontology Consortium: Gene ontology: Tool for the
unification of biology. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
McLean CY, Bristor D, Hiller M, Clarke SL,
Schaar BT, Lowe CB, Wenger AM and Bejerano G: GREAT improves
functional interpretation of cis-regulatory regions. Nat
Biotechnol. 28:495–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim M, Long TI, Arakawa K, Wang R, Yu MC
and Laird PW: DNA methylation as a biomarker for cardiovascular
disease risk. PLoS One. 5:e96922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ramos RB, Fabris V, Lecke SB, Maturana MA
and Spritzer PM: Association between global leukocyte DNA
methylation and cardiovascular risk in postmenopausal women. BMC
Med Genet. 17:712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zaina S, Heyn H, Carmona FJ, Varol N,
Sayols S, Condom E, Ramírez-Ruz J, Gomez A, Gonçalves I, Moran S,
et al: DNA methylation map of human atherosclerosis. Circ
Cardiovasc Genet. 7:692–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li J, Chen L, Du L and Li M: Cage the
firefly luciferin! - a strategy for developing bioluminescent
probes. Chem Soc Rev. 42:662–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sharma P, Kumar J, Garg G, Kumar A,
Patowary A, Karthikeyan G, Ramakrishnan L, Brahmachari V and
Sengupta S: Detection of altered global DNA methylation in coronary
artery disease patients. DNA Cell Biol. 27:357–365. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bockmühl Y, Patchev AV, Madejska A,
Hoffmann A, Sousa JC, Sousa N, Holsboer F, Almeida OF and Spengler
D: Methylation at the CpG island shore region upregulates Nr3c1
promoter activity after early-life stress. Epigenetics. 10:247–257.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao X, Gu J, Li M, Xi J, Sun W, Song G
and Liu G: Pathway analysis of body mass index genome-wide
association study highlights risk pathways in cardiovascular
disease. Sci Rep. 5:130252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zidar DA, Mudd JC, Juchnowski S, Lopes JP,
Sparks S, Park SS, Ishikawa M, Osborne R, Washam JB, Chan C, et al:
Altered maturation status and possible immune exhaustion of CD8 T
lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients presenting with
acute coronary syndromes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
36:389–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Arbel Y, Finkelstein A, Halkin A, Birati
EY, Revivo M, Zuzut M, Shevach A, Berliner S, Herz I, Keren G, et
al: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is related to the severity of
coronary artery disease and clinical outcome in patients undergoing
angiography. Atherosclerosis. 225:456–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang JJ, Zhang CN, Meng Y, Han AZ, Gong JB
and Li K: Elevated concentrations of oxidized lipoprotein(a) are
associated with the presence and severity of acute coronary
syndromes. Clin Chim Acta. 408:79–82. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang JJ, Han AZ, Meng Y, Gong JB, Zhang
CN, Li K and Liu YX: Measurement of oxidized lipoprotein (a) in
patients with acute coronary syndromes and stable coronary artery
disease by 2 ELISAs: Using different capture antibody against
oxidized lipoprotein (a) or oxidized LDL. Clin Biochem. 43:571–575.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee AM, Shimizu C, Oharaseki T, Takahashi
K, Daniels LB, Kahn A, Adamson R, Dembitsky W, Gordon JB and Burns
JC: Role of TGF-β signaling in remodeling of noncoronary artery
aneurysms in kawasaki disease. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 18:310–317.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Turner AW, Nikpay M, Silva A, Lau P,
Martinuk A, Linseman TA, Soubeyrand S and McPherson R: Functional
interaction between COL4A1/COL4A2 and SMAD3 risk loci for coronary
artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 242:543–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng Q, Deng Y, Yang X, Leng X, Yang Y and
Liu H: Genetic variants of ADAM17 are implicated in the
pathological process of Kawasaki disease and secondary coronary
artery lesions via the TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling pathway. Eur J
Pediatr. 175:705–713. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lusis AJ: Cardiovascular disease genes
come together. Atherosclerosis. 242:630–631. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Turner AW, Martinuk A, Silva A, Lau P,
Nikpay M, Eriksson P, Folkersen L, Perisic L, Hedin U, Soubeyrand
S, et al: Functional analysis of a novel genome-wide association
study signal in SMAD3 that confers protection from coronary artery
disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:972–983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saito Y, Kondo H and Hojo Y: Granzyme B as
a novel factor involved in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiol.
57:141–147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
van der Burgh R, Meeldijk J, Jongeneel L,
Frenkel J, Bovenschen N, van Gijn M and Boes M: Reduced
serpinB9-mediated caspase-1 inhibition can contribute to
autoinflammatory disease. Oncotarget. 7:19265–19271. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hata J, Kubo M and Kiyohara Y: Genome-wide
association study for ischemic stroke based on the Hisayama study.
Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 66:47–52. 2011.In Japanese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wu L, Xi B, Hou D, Zhao X, Liu J, Cheng H,
Zhou X, Shen Y, Wang X and Mi J: The SNP (rs2230500) in PRKCH
decreases the risk of carotid intima-media thickness in a Chinese
young adult population. PLoS One. 7:e406062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu L, Shen Y, Liu X, Ma X, Xi B, Mi J,
Lindpaintner K, Tan X and Wang X: The 1425G/A SNP in PRKCH is
associated with ischemic stroke and cerebral hemorrhage in a
Chinese population. Stroke. 40:2973–2976. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|