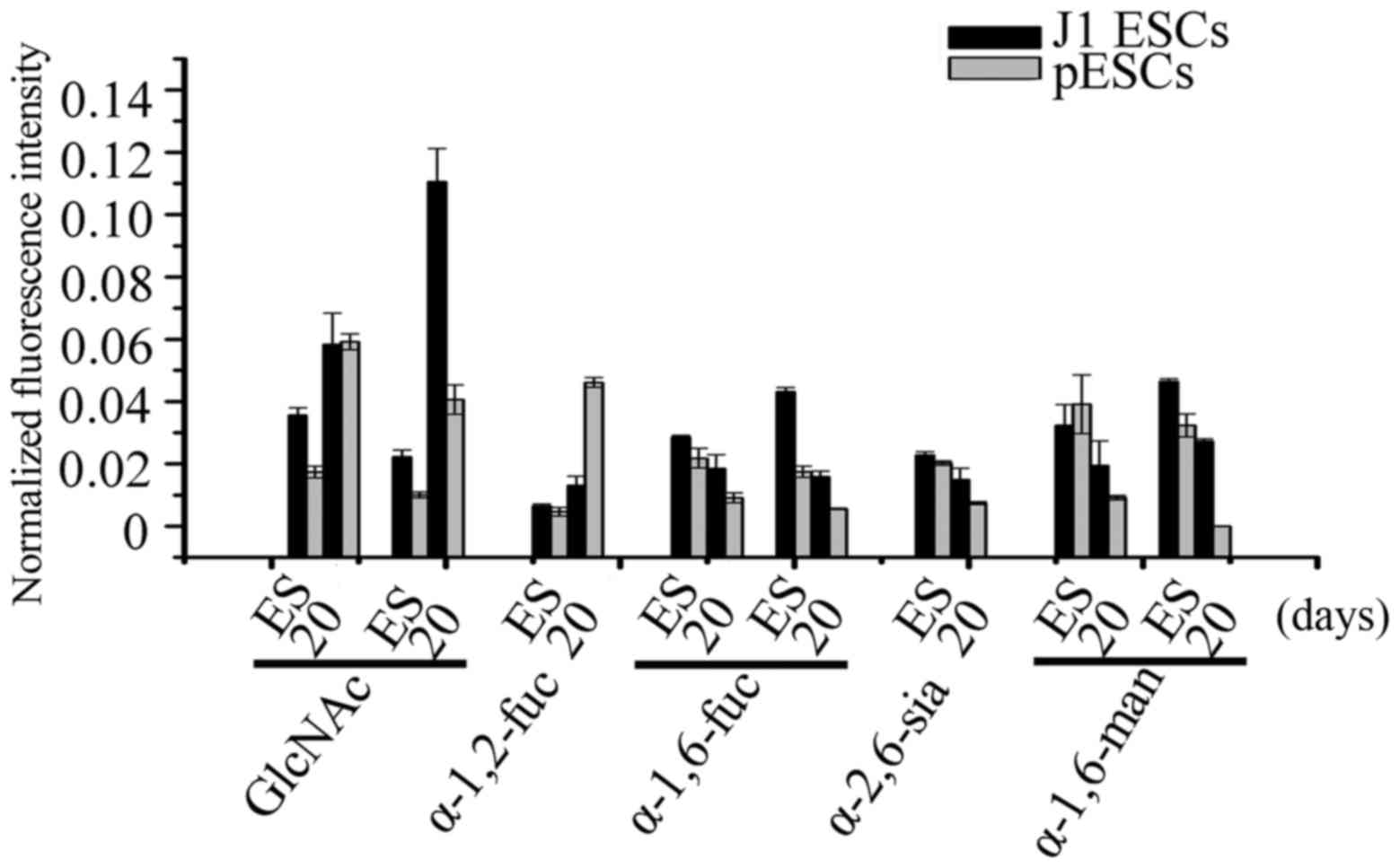
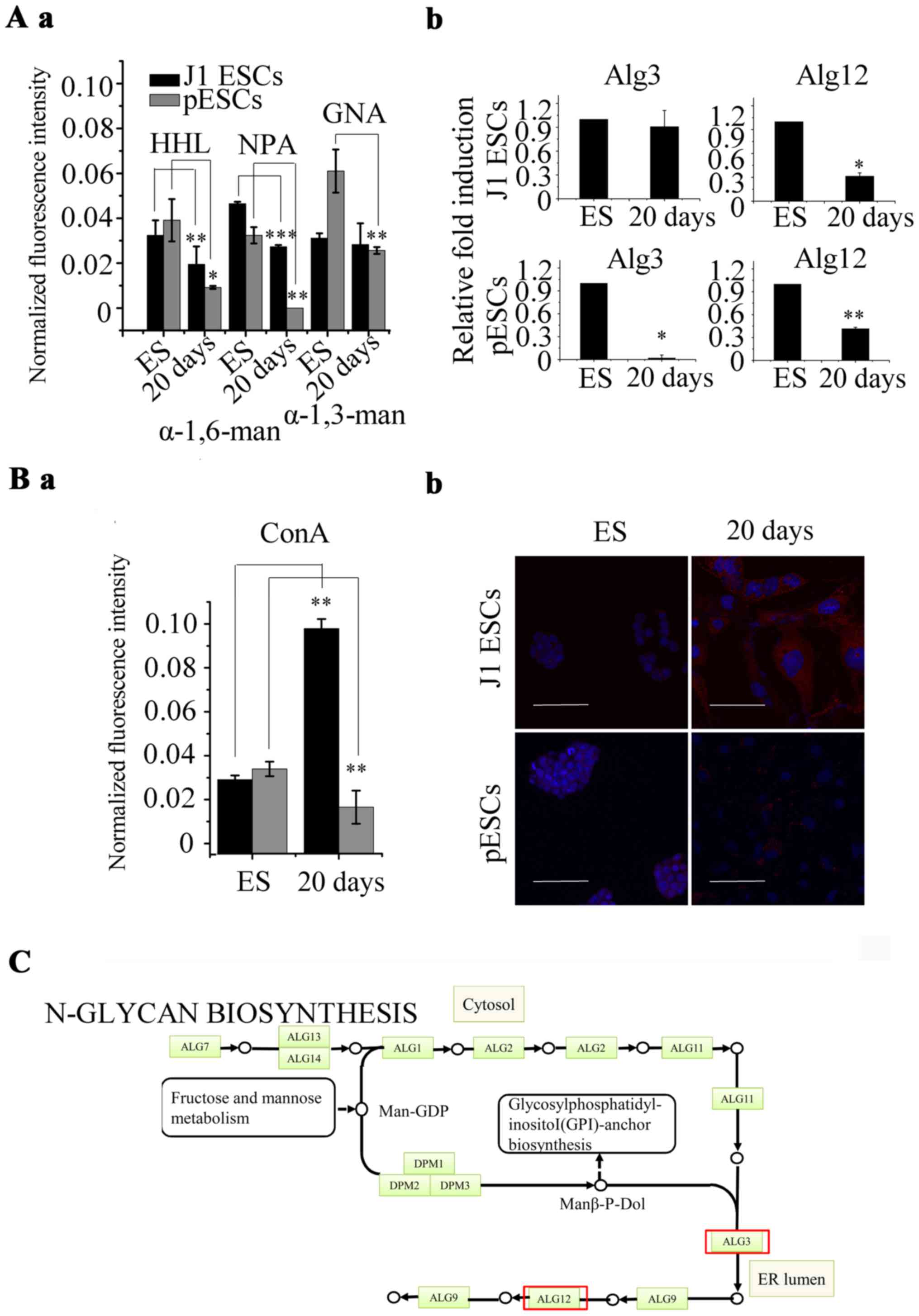
|
1
|
Shepherd PR, Gnudi L, Tozzo E, Yang H,
Leach F and Kahn BB: Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose
disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in
adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 268:22243–22246. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolfgang MJ and Lane MD: Control of energy
homeostasis: role of enzymes and intermediates of fatty acid
metabolism in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Nutr. 26:23–44.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dani C, Smith AG, Dessolin S, Leroy P,
Staccini L, Villageois P, Darimont C and Ailhaud G: Differentiation
of embryonic stem cells into adipocytes in vitro. J Cell Sci.
110:1279–1285. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
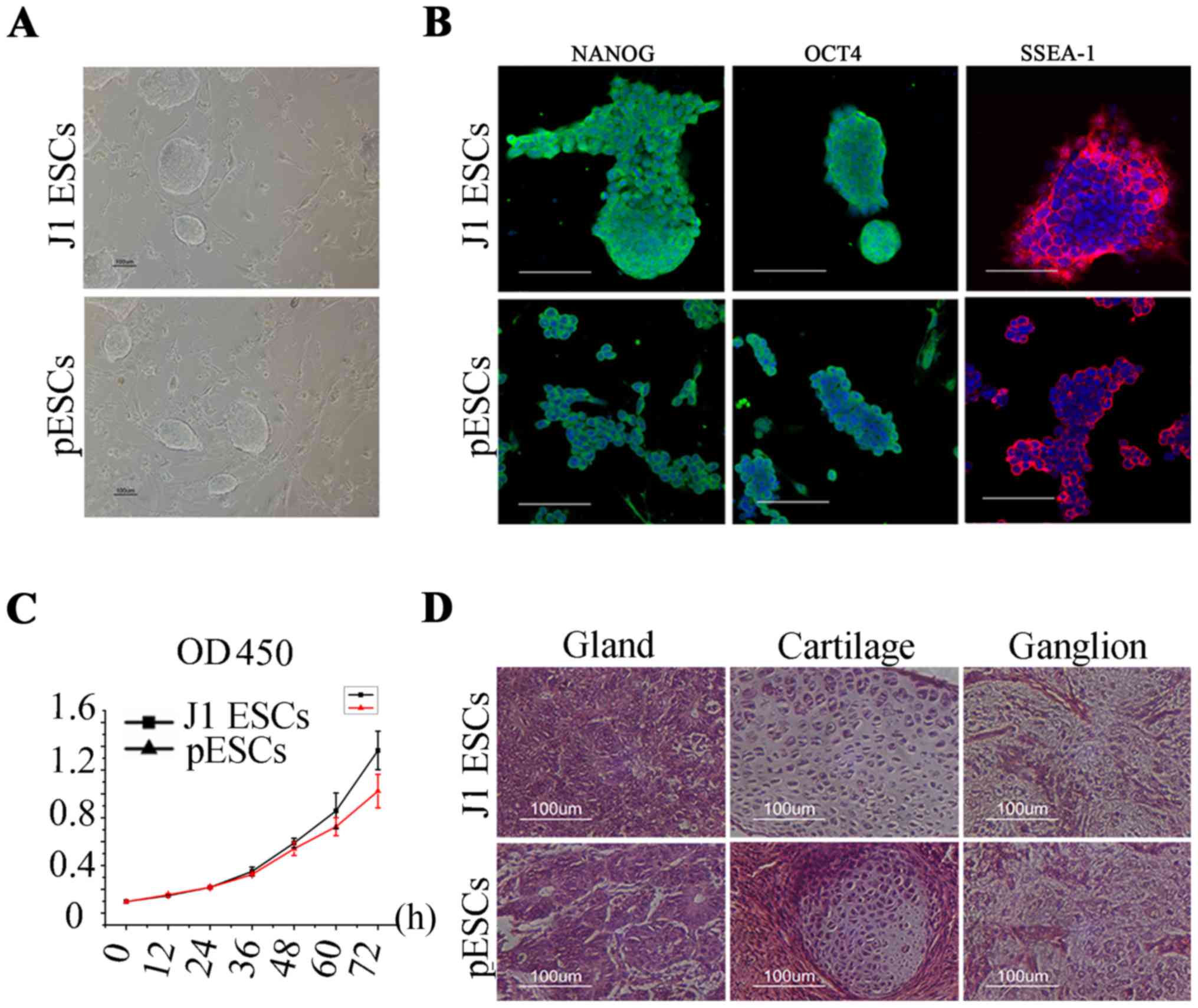
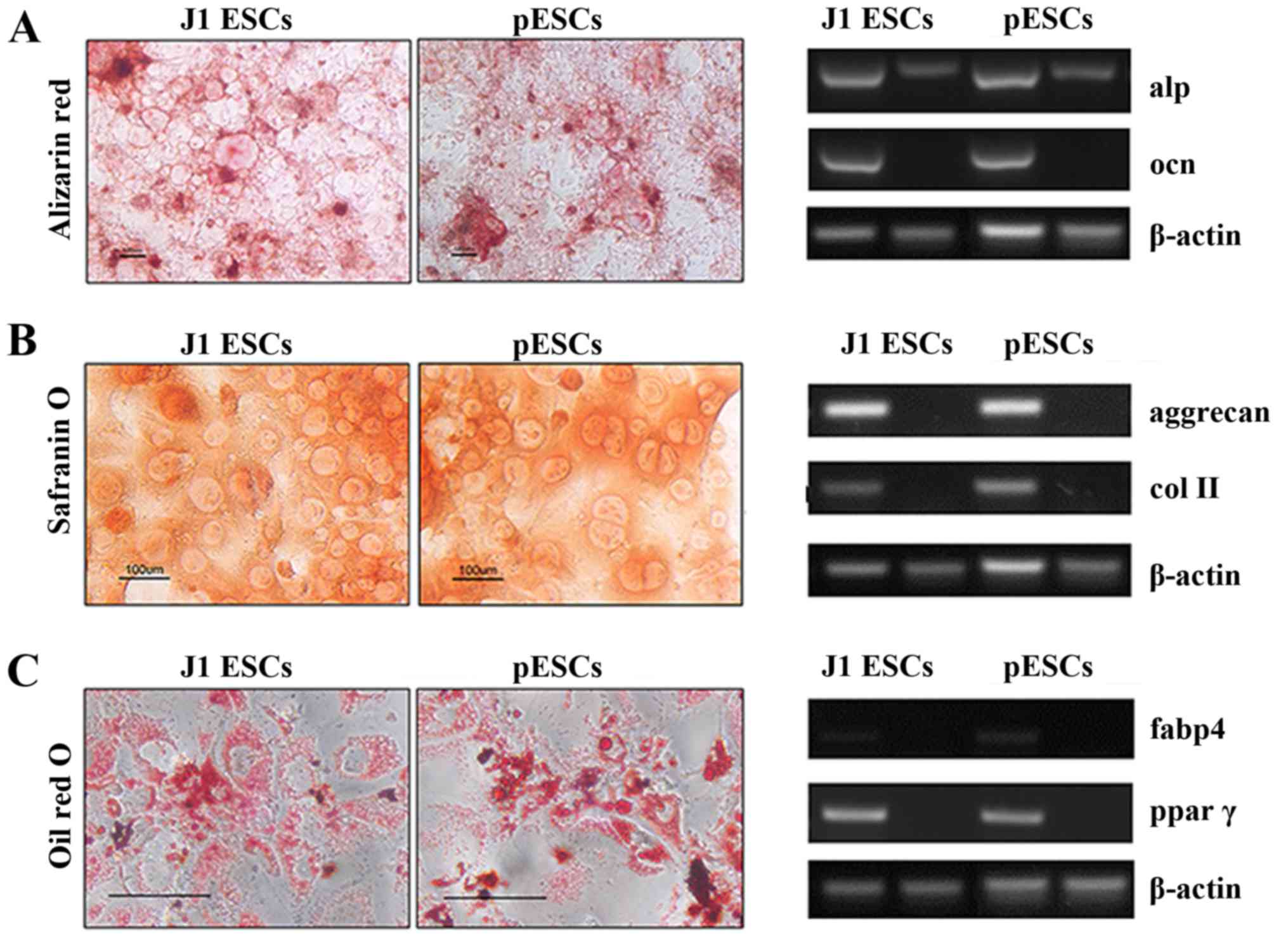
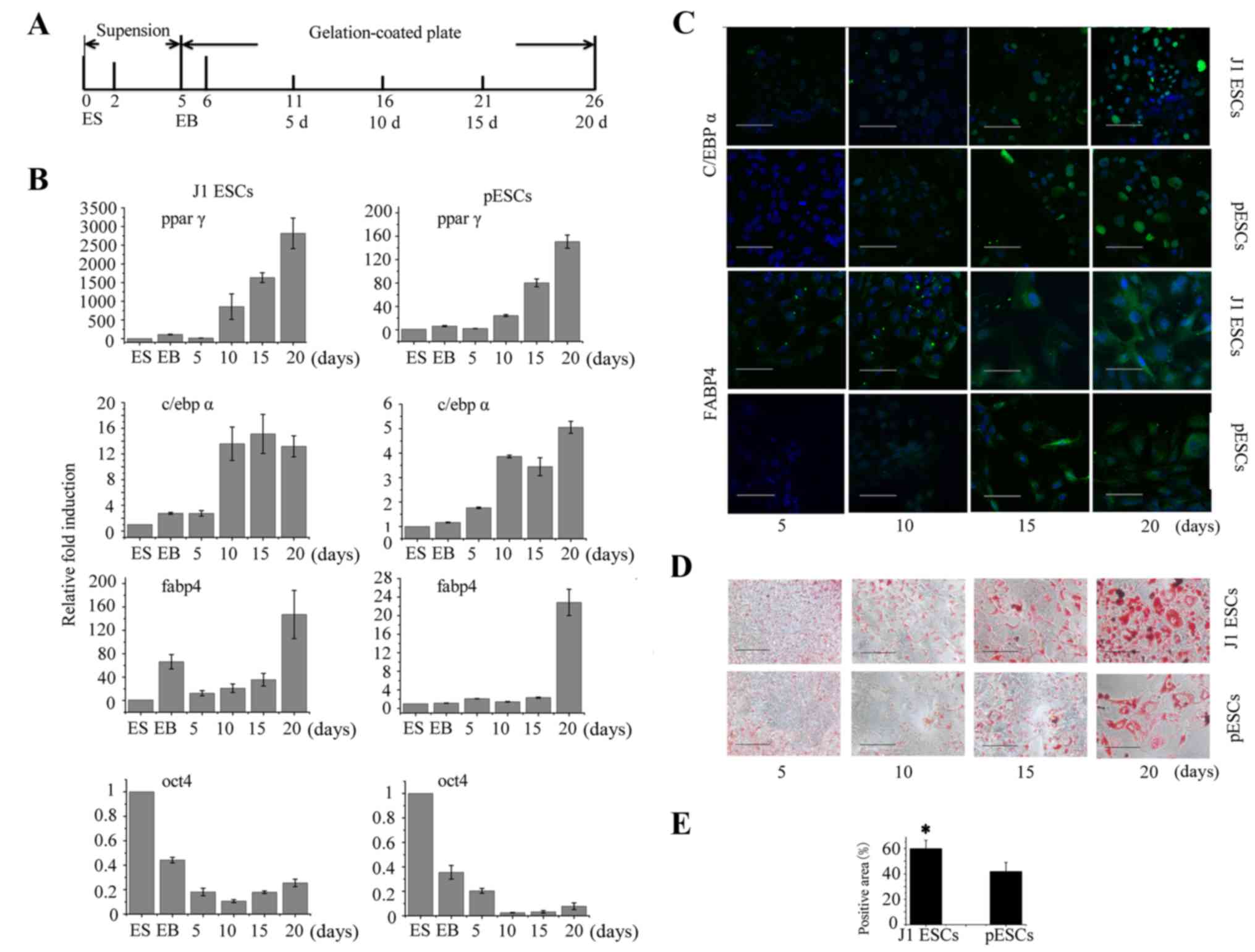
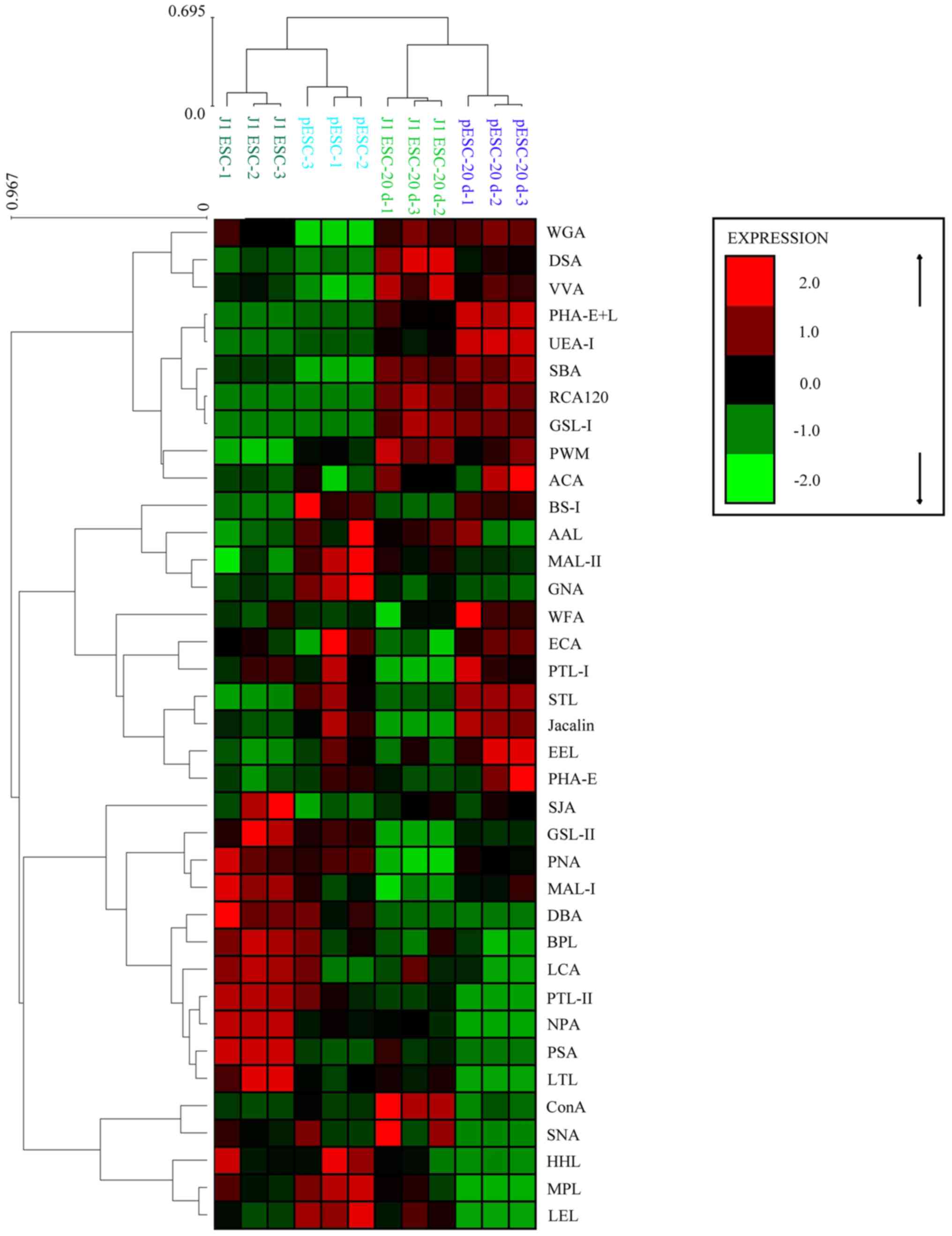
|
Tang QQ, Otto TC and Lane MD: Commitment
of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells to the adipocyte lineage. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9607–9611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Serrero G and Lepak NM: Prostaglandin
F2alpha receptor (FP receptor) agonists are potent adipose
differentiation inhibitors for primary culture of adipocyte
precursors in defined medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
233:200–202. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bowers RR, Kim JW, Otto TC and Lane MD:
Stable stem cell commitment to the adipocyte lineage by inhibition
of DNA methylation: role of the BMP-4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:13022–13027. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bowers RR and Lane MD: Wnt signaling and
adipocyte lineage commitment. Cell Cycle. 7:1191–1196. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Spinella-Jaegle S, Rawadi G, Kawai S,
Gallea S, Faucheu C, Mollat P, Courtois B, Bergaud B, Ramez V,
Blanchet AM, et al: Sonic hedgehog increases the commitment of
pluripotent mesenchymal cells into the osteoblastic lineage and
abolishes adipocytic differentiation. J Cell Sci. 114:2085–2094.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van der Horst G, Farih-Sips H, Löwik CW
and Karperien M: Hedgehog stimulates only osteoblastic
differentiation of undifferentiated KS483 cells. Bone. 33:899–910.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
MacDougald OA and Lane MD: Transcriptional
regulation of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation.
Annu Rev Biochem. 64:345–373. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Student AK, Hsu RY and Lane MD: Induction
of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1
preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 255:4745–4750. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Darlington GJ, Ross SE and MacDougald OA:
The role of C/EBP genes in adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem.
273:30057–30060. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ailhaud G, Grimaldi P and Négrel R:
Cellular and molecular aspects of adipose tissue development. Annu
Rev Nutr. 12:207–233. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Apweiler R, Hermjakob H and Sharon N: On
the frequency of protein glycosylation, as deduced from analysis of
the SWISS-PROT database. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1473:4–8. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lowe JB and Marth JD: A genetic approach
to mammalian glycan function. Annu Rev Biochem. 72:643–691. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang HY, Olson SK, Esko JD and Horvitz
HR: Caenorhabditis elegans early embryogenesis and vulval
morphogenesis require chondroitin biosynthesis. Nature.
423:439–443. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crocker PR: Siglecs: sialic-acid-binding
immunoglobulin-like lectins in cell-cell interactions and
signalling. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 12:609–615. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Collins BE and Paulson JC: Cell surface
biology mediated by low affinity multivalent protein-glycan
interactions. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 8:617–625. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu D, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, El
Shabrawi Y and Sasisekharan R: Tumor cell surface heparan sulfate
as cryptic promoters or inhibitors of tumor growth and metastasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:568–573. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sasisekharan R, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G
and Narayanasami U: Roles of heparan-sulphate glycosaminoglycans in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:521–528. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Muramatsu T and Muramatsu H: Carbohydrate
antigens expressed on stem cells and early embryonic cells.
Glycoconj J. 21:41–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin Y, Zhong Y, Dang L, Zhu M, Yu H, Chen
W, Cui J, Bian H and Li Z: Alteration of protein glycosylation in
human hepatic stellate cells activated with transforming growth
factor-β1. J Proteomics. 75:4114–4123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ito H, Kuno A, Sawaki H, Sogabe M, Ozaki
H, Tanaka Y, Mizokami M, Shoda J, Angata T, Sato T, et al: Strategy
for glycoproteomics: identification of glyco-alteration using
multiple glycan profiling tools. J Proteome Res. 8:1358–1367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu H, Zhu M, Qin Y, Zhong Y, Yan H, Wang
Q, Bian H and Li Z: Analysis of glycan-related genes expression and
glycan profiles in mice with liver fibrosis. J Proteome Res.
11:5277–5285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hwang NS, Kim MS, Sampattavanich S, Baek
JH, Zhang Z and Elisseeff J: Effects of three-dimensional culture
and growth factors on the chondrogenic differentiation of murine
embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 24:284–291. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen Y, Ai A, Tang ZY, Zhou GD, Liu W, Cao
Y and Zhang WJ: Mesenchymal-like stem cells derived from human
parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 21:143–151.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Scillitani G, Zizza S, Liquori GE and
Ferri D: Lectin histochemistry of gastrointestinal glycoconjugates
in the greater horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus ferrumequinum (Schreber,
1774). Acta Histochem. 109:347–357. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moremen KW, Tiemeyer M and Nairn AV:
Vertebrate protein glycosylation: diversity, synthesis and
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:448–462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sasaki N, Okishio K, Ui-Tei K, Saigo K,
Kinoshita-Toyoda A, Toyoda H, Nishimura T, Suda Y, Hayasaka M,
Hanaoka K, et al: Heparan sulfate regulates self-renewal and
pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 283:3594–3606.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Satomaa T, Heiskanen A, Mikkola M, Olsson
C, Blomqvist M, Tiittanen M, Jaatinen T, Aitio O, Olonen A, Helin
J, et al: The N-glycome of human embryonic stem cells. BMC Cell
Biol. 10:422009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paffoni A, Brevini TA, Gandolfi F and
Ragni G: Parthenogenetic activation: biology and applications in
the ART laboratory. Placenta. 29(Suppl B): 121–125. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim K, Lerou P, Yabuuchi A, Lengerke C, Ng
K, West J, Kirby A, Daly MJ and Daley GQ: Histocompatible embryonic
stem cells by parthenogenesis. Science. 315:482–486. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Didié M, Christalla P, Rubart M, Muppala
V, Döker S, Unsöld B, El-Armouche A, Rau T, Eschenhagen T,
Schwoerer AP, et al: Parthenogenetic stem cells for
tissue-engineered heart repair. J Clin Invest. 123:1285–1298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|