Introduction
Lung cancer is among the most common causes of
cancer-associated mortality worldwide. According to a global data
analysis, ~1.5 million new cases are diagnosed annually, with the
majority of cases categorized as non-small cell lung carcinoma
(NSCLC) (1). The detection of
NSCLC at an early stage presents a significant clinical challenge;
in ~70% of newly confirmed cases, the disease has progressed to an
advanced stage, at which the patients have missed the optimal time
window for surgery (2). In
addition to surgery, the use of other therapeutic approaches, such
as adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy, has been common
over the last decades (3).
However, the 5-year relative survival rate of NSCLC patients
remains low (4). The
antineoplastic drug cisplatin (DDP) has been widely used to treat
cancer; however, this drug causes severe side effects, which may
include nephrotoxicity, marrow suppression and considerable
gastrointestinal reactions. Furthermore, patients often experience
physical and mental distress, and DDP treatment contributes so
reducing their quality of life. Therefore, it is of great
significance to identify effective alternatives to DDP in order to
improve the outcome, prognosis and quality of life of patients with
NSCLC.
Phytochemicals are derived from plants and include
traditional herbal remedies that have been used for >2,000 years
to prevent disease or promote health. A number of preclinical
animal models and human epidemiological studies have demonstrated
that certain phytochemicals may have an efficient preventive effect
against human cancer (5).
Hesperidin, a type of flavonoid, is ubiquitous in citrus species,
including orange, lemon and pomelo fruits (6). Recently, the biological properties
and potential therapeutic mechanisms of hesperidin have been widely
tested in laboratory-based studies. Mounting evidence indicates
that hesperidin may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, free
radical-scavenging, anti-diabetic and cardioprotective effects
(7,8), and have proven useful in the
prevention and treatment of cancer (9,10).
Regarding the latter, hesperidin was observed to induce paraptosis
of HepG2 hepatoblastoma cells by activating the mitogen-activated
protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling
pathway, and the mitochondrial and death receptor pathways
(11–13). In addition, hesperidin was able to
trigger the apoptosis of NALM-6 cells (14), Ramos cells (15) and MSTO-211H cells (16) by promoting p53 accumulation,
decreasing constitutive nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity and
inhibiting signaling protein 1. Hesperidin was also reported to
trigger apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway (17) and induce cell cycle arrest via the
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in HeLa cells (18). Saiprasad et al (19) observed that hesperidin initiated
apoptosis and autophagy through mediating Aurora-A-coupled
pro-survival phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of
rapamycin signaling cascades and glycogen synthase kinase-3β
activity to antagonize the effect of azoxymethane on colon
carcinogenesis in a mouse model.
A large number of relevant studies have been
published on the suppression of lung tumorigenesis by hesperidin.
Kohno et al (20) reported
that hesperidin reduced the expression of proliferating cell
nuclear antigen to act against
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced pulmonary
tumorigenesis in mice. Balakrishnan and Menon (21) demonstrated that hesperidin
downregulated the high expression of matrix metalloproteinases
(MMPs) induced by nicotine and decreased the levels of antioxidants
to act against tobacco-associated disease. Kamaraj et al
(22–24) reported several mechanisms for the
protective effects of hesperidin against benzo(a)pyrene-induced
lung carcinogenesis in mice, including an increase in the levels of
antioxidants, modulation of the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and
MMPs, recruitment of mast cells and alteration of the anti-oxidant
and mitochondrial status, comprising major tricarboxylic acid cycle
enzyme activities and electron transport chain complex activities.
Birsu Cincin et al (25)
confirmed that hesperidin had a greater inhibitory effect on A549
and NCI-H358 cells compared with that on MRC-5 normal lung
fibroblasts, and that this effect was associated with the
fibroblast growth factor and NF-κB signal transduction
pathways.
Thus, it has been demonstrated that the antitumor
effects of hesperidin represent a promising strategy for cancer
therapy. The present study was performed to better understand the
pharmacological effects of hesperidin on the alteration of other
molecules and the cell cycle of A549 cells.
Materials and methods
Materials
Hesperidin was purchased from Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). RPMI-1640 basal culture
medium, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) high-glucose
basal culture medium and 0.25% trypsin were purchased from HyClone
(Logan, UT, USA). Fetal bovine serum (FBS) was from Gibco (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer,
phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), broad-spectrum phosphatase
inhibitor, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), MTT and DDP were purchased
from Solarbio (Beijing, China). The bicinchoninic acid (BCA)
protein concentration detection kit was provided by CWBio (Beijing,
China). Cell culture bottles and associated consumables were
purchased from Corning, Inc. (Corning, NY, USA). The Annexin
V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)/propidium iodide (PI) kit (cat.
no. A005-3) and the cell cycle and apoptosis analysis kit (cat. no.
C00150) were supplied by 7 Sea Biotech (Shanghai, China). The
rabbit anti-human antibody against β-actin (cat. no. ab8226) and
horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit
immunoglobulin (Ig)G (cat. no. ab6721) were purchased from Abcam
(Cambridge, UK). Rabbit anti-human antibodies against B-cell
lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2; cat. no. 4223T), Bcl-2-associated X protein
(Bax; cat. no. 5023T), BH3 interacting-domain death agonist
(Bid)/tBid (cat. no. 2002T), B-cell lymphoma extra large protein
(Bcl-xL; cat. no. 2764T), cleaved caspase-3 (cat. no. 9664T),
cleaved caspase-9 (cat. no. 7237T), cleaved poly(adenosine
triphosphate ribose)polymerase (PARP; cat. no. 5625T), p21 (cat.
no. 2947T), p53 (cat. no. 2527T) and cyclin D1 (cat. no. 2978T)
were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA,
USA).
Cell lines and culture conditions
The A549 human NSCLC cell line and the BEAS-2B human
normal lung epithelial cell line were purchased from the Cell Bank
of the Chinese Academy of Medical Science (Shanghai, China). A549
and BEAS-2B cells were respectively cultured in RPMI-1640 and
high-glucose DMEM, each supplemented with a mixture of 10% FBS and
1% penicillin/streptomycin (Solarbio) at 37°C in a humidified
atmosphere containing 5% CO2.
Experimental groups
Hesperidin was dissolved in DMSO to produce a 25
mg/ml stock solution and stored as aliquots in tightly sealed vials
at −20°C. Working solutions were prepared by serial dilutions of
stock solution with whole culture medium. In this study, 7
experimental groups were set as follows: A control group, a 0.5%
DMSO group, several hesperidin groups (50, 75, 100 and 125
µg/ml hesperidin); and a DDP group (1 µg/ml DDP) as a
positive control.
Cell viability assay
The effects of hesperidin on the viability of A549
and BEAS-2B cells were detected by an MTT assay. In brief, each
group of A549 cells (1×104 cells/well) in sextuplicate
wells of a 96-well plate was incubated for 24 h, which was followed
by the addition of hesperidin or DMSO to each group (as stated
above) and incubation for 24, 48 and 72 h. After removal of the
liquid, 180 µl whole culture medium and MTT (20
µl/well; final concentration, 5 mg/ml) were added into each
well for a 4-h treatment. The resulting formazan was dissolved in
100 µl DMSO and the absorbance as the optical density (OD)
at 490 nm for each well was determined with an iMark™ Microplate
Reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The rates of cell
viability inhibition by hesperidin were calculated using the
following formula: (ODcontrol group −
ODexperimental group)/ODcontrol group. In
addition, the morphology of individual groups of cells after the
72-h treatment with hesperidin or DDP (1 µg/ml) was observed
using a microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and the average cell
number in each field of view was counted.
Cell apoptosis assay
A549 or BEAS-2B cells (1×106 cells/well)
were seeded into 6-well plates for 24 h and then treated with DMSO
or hesperidin at varying concentrations (as stated above) for 24,
48 or 72 h. Following treatment with 0.25% trypsin without EDTA,
the supernatant and adherent cells were harvested. Cells were
resuspended and washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
After removal of the supernatant, 400 µl binding buffer from
the Annexin V-FITC/PI kit was added to resuspend the cells.
Subsequently, 5 µl Annexin V-FITC was added, followed by
thorough mixing and incubation for 15 min in the dark at ambient
temperature. Thereafter, the cells were stained with 10 µl
PI and incubated for 5 min in the dark in an ice bath.
Subsequently, the percentage of apoptotic cells was determined
within 30 min by flow cytometric analysis.
Cell cycle analysis
A549 cells (1×106 cells/well) were seeded
into 6-well plates, incubated for 24 h and then treated with
vehicle (DMSO) or hesperidin at varying concentrations (as stated
above) for 72 h. After treatment with 0.25% trypsin, the
supernatant and detached cells were harvested. Cells were
resuspended and washed twice with precooled PBS. After removal of
the supernatant, 1 ml precooled 70% ethyl alcohol was added
followed by gentle mixing and incubation for 30 min at 4°C to fix
the cells. After removal of the supernatant, cells were resuspended
and washed with precooled PBS. Premixed PI working solution (500
µl) was then added to each sample to resuspend the cells,
followed by incubation for 30 min in the dark at 37°C. To produce
the PI working solution, 25 µl PI stock solution and 20
µl RNase A solution (10 mg/ml) were added to 1 ml staining
buffer and mixed gently. Within 5 h, flow cytometric analysis of
the distribution of cells in different phases of the cell cycle was
performed. Red fluorescence was detected at an excitation
wavelength of 488 nm.
Western blot analysis
A549 cells (1×106 cells/well) were seeded
in 6-well plates for 24 h and then treated with vehicle (DMSO) or
hesperidin at varying concentrations (as stated above) for 72 h.
After removal of the supernatant, the cells in the 6-well plates
were put on ice. Fifty microliters RIPA buffer, PMSF and
broad-spectrum phosphatase inhibitor were added to each well. The
cells in the lysis solution were filtered by centrifugation at
12,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. The concentration of total protein
was detected using the BCA protein detection kit and an iMark™
microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Equal volumes of
loading buffer were then added to each sample, followed by boiling
for 5 min, and the samples of denatured protein were stored at
−20°C. Denatured protein (40 µg/lane) from each sample was
separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred onto a polyvinylidene
fluoride membrane (cat. no. 1620177; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) by
wet-transfer. The membranes were blocked for 2 h with 5% bovine
serum albumin (cat. no. A8020; Solarbio) at ambient temperature,
and then incubated with the corresponding pre-diluted rabbit
anti-human primary antibodies (1:2,000 dilution) overnight at 4°C.
Anti-β-actin was used as the control. After washing in
Tris-buffered saline containing Tween-20, the bound antibodies were
probed with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary
antibodies (1:2,000 dilution) by incubation for 2 h at room
temperature. Finally, the bound antibodies were visualized using an
enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) detection reagent (cat. no.
1705060; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). The levels of each target
protein relative to the control were determined by measuring the
integral optical density in a ChemiDoc Touch Imaging system and
quantitatively calculated using Image Laboratory software v. 5.1
(both from Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS
software (version 13.0; SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Pairwise
comparisons were performed by using Student's t-test. The
differences among three or more groups were determined by one-way
analysis of variance followed by a Bonferroni's or Dunnett's test.
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. P<0.05
was regarded to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
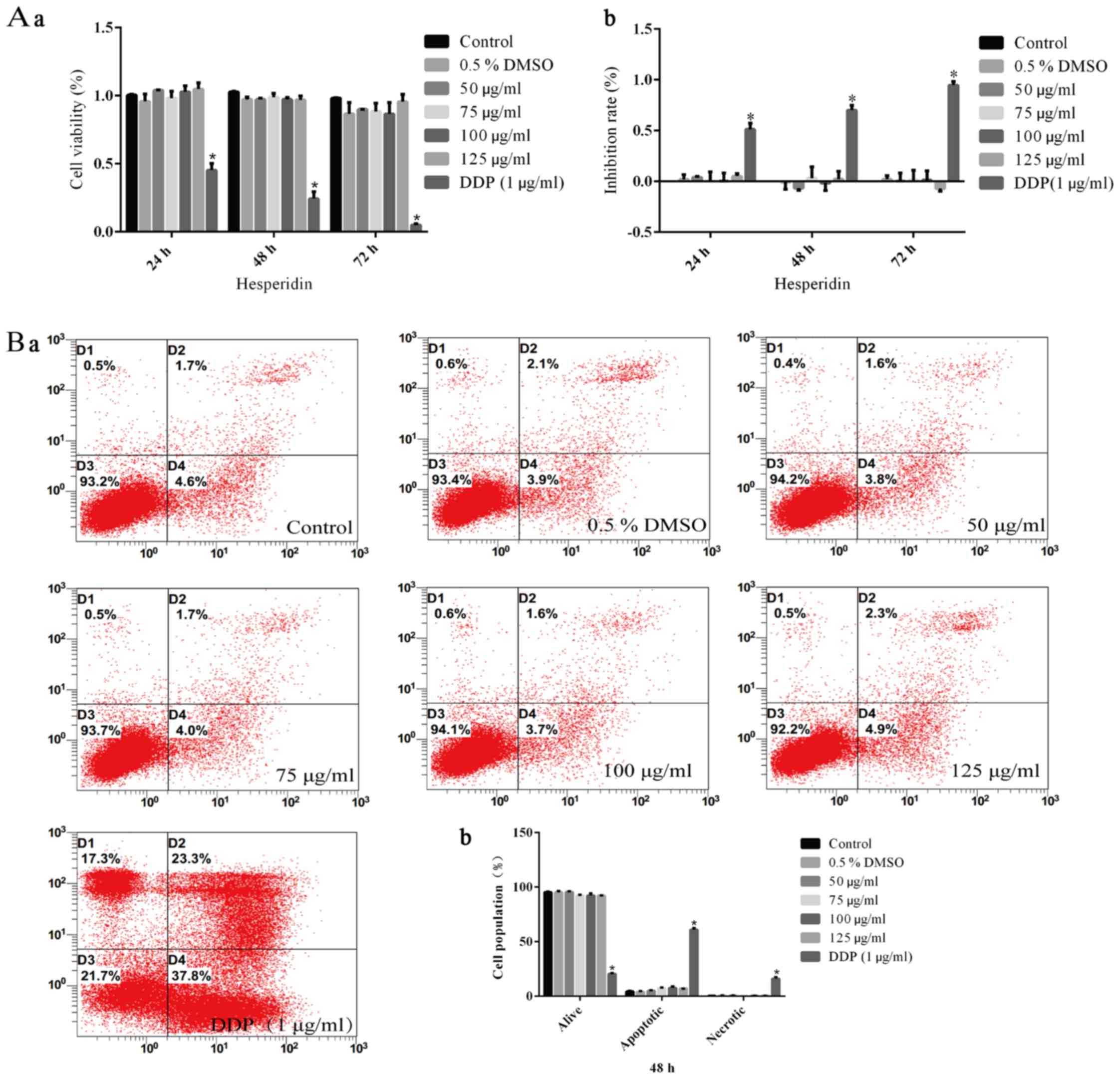
Effects of different concentrations of
hesperidin or DDP on the viability and morphology of A549
cells
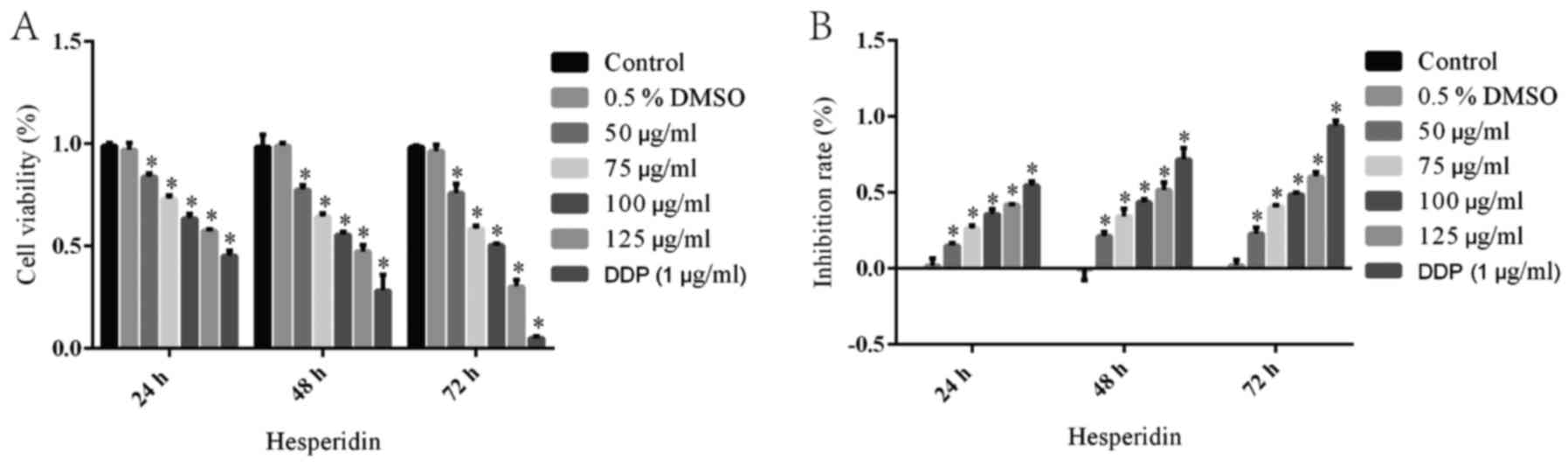
An MTT assay was performed to investigate the
inhibitory effect of hesperidin on the viability of A549 cells. The
cell survival rate of the control group was defined as 100% with an
inhibition ratio of 0%. The cell survival rate and inhibition ratio
in the 0.5% DMSO group was not significantly different from that in
the control group, while DDP (1 µg/ml) treatment caused a
significant decrease in the relative cell survival rate (Fig. 1). Thus, 0.5% DMSO, as the solvent
of hesperidin, had no effect on the viability of A549 cells. In
addition, it was observed that the cell viability in the groups
treated with hesperidin for 24, 48 or 72 h was significantly
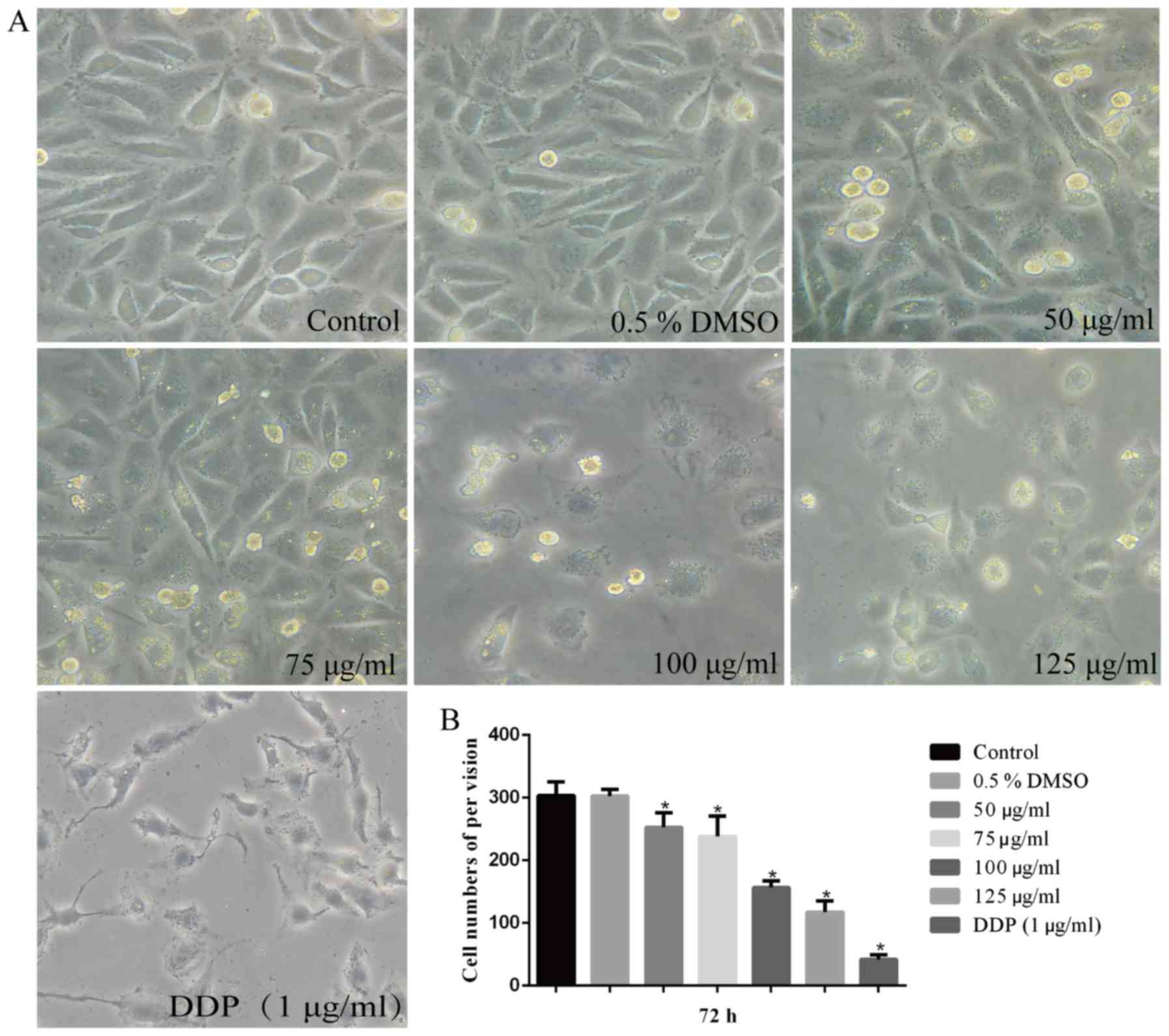
decreased in a time- and dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1). After treatment with 50, 75, 100
and 125 µg/ml hesperidin for 72 h, the morphology of A549
cells was altered and the majority of the cells treated with DDP (1
µg/ml) were apoptotic compared with that in the control
group (Fig. 2A). It was noted
that the cells lost their adherence, appeared shrunken and acquired
a rounded shape. In addition, the cell density per field of view
was significantly decreased compared with that of the control group
(P<0.05). However, the group treated with 0.5% DMSO was not
significantly changed (P>0.05) (Fig. 2B). Thus, it was demonstrated that
the viability of A549 cells was decreased by hesperidin, which
resulted in an alteration of cell morphology.
Effect of different concentrations of
hesperidin and DDP on the induction of apoptosis in A549 cells
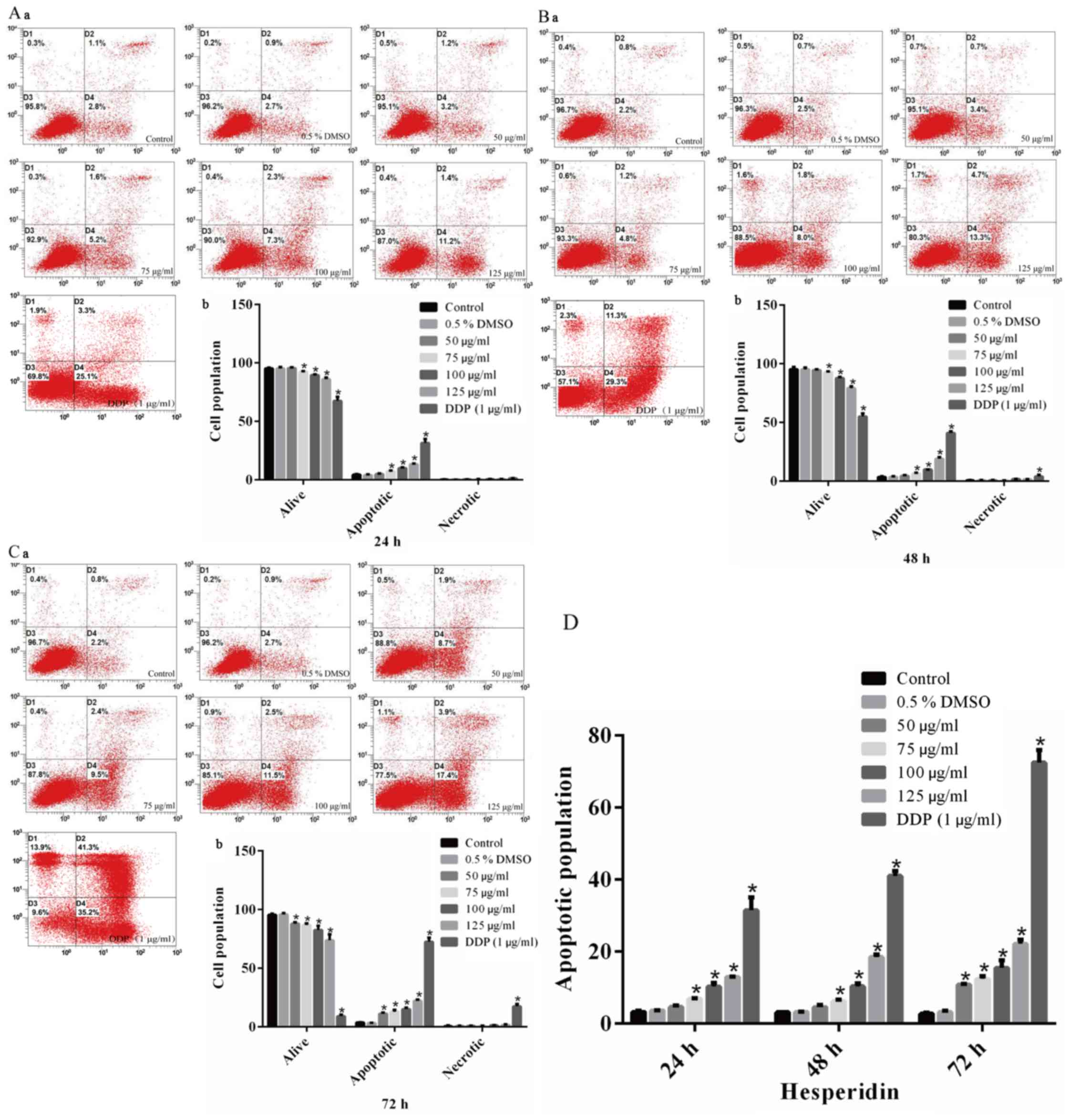
To explore the molecular mechanisms by which
hesperidin reduced the viability of A549 cells, a flow cytometric
apoptosis assay was performed. Cells were treated for 24, 48 or 72
h with different concentrations of hesperidin and stained with
Annexin V-FITC/PI. The results indicated that the apoptotic rate in
the control group was <5%, and the necrotic rate in all groups
was <2%, which was considered acceptable (Fig. 3A–C). The apoptotic rate in the
0.5% DMSO group was not significantly different compared with that
in the control group (Fig. 3),
indicating that 0.5% DMSO (vehicle) had no effect on the survival
rate of A549 cells. The apoptotic rates in the groups treated with
different concentrations of hesperidin for different durations were
increased compared with those in the control group, and this effect
was identified to be time- and dose-dependent (Fig. 3D).
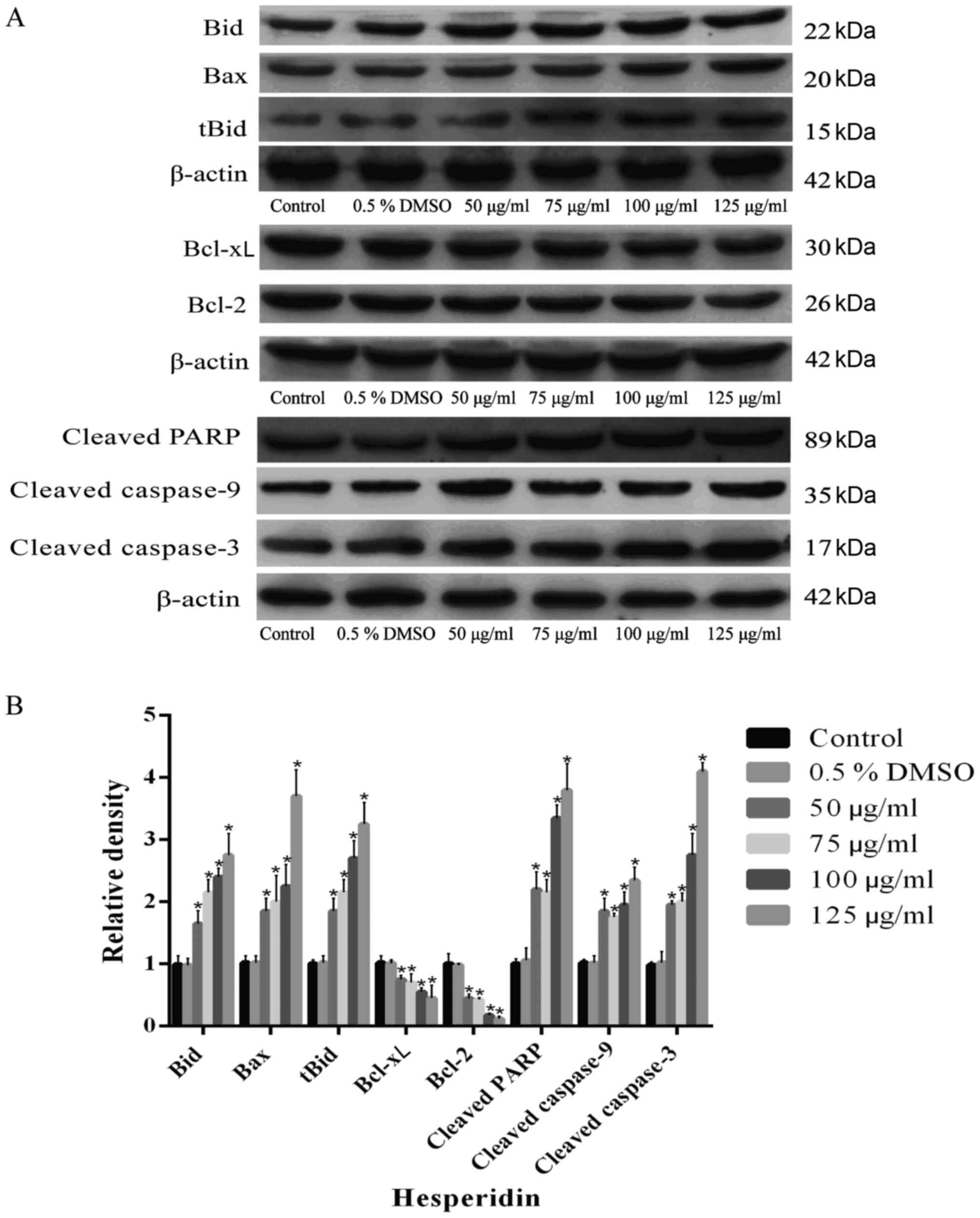
Furthermore, A549 cells were treated with different
concentrations of hesperidin for 72 h. The results confirmed that
hesperidin elevated the expression levels of mitochondrial
apoptotic pathway-associated proteins (Bax, Bid, tBid, cleaved
caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9 and cleaved PARP), while significantly
reducing the expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL compared with
the control in a concentration-dependent manner (P<0.05)
(Fig. 4). The relative expression
levels of mitochondrial apoptotic pathway-associated proteins in
the 0.5% DMSO group were not significantly different compared with
those in the control group (P>0.05) (Fig. 4B), indicating that 0.5% DMSO had
no effect on these proteins in A549 cells. In conclusion, it was
demonstrated that hesperidin induced apoptosis in A549 cells, which
was regulated by the expression of mitochondrial apoptotic
pathway-associated proteins.
Effects of different concentrations of
hesperidin or DDP on the viability and apoptosis of BEAS-2B normal
human lung epithelial cells
BEAS-2B cells were treated with hesperidin or DDP (1
µg/ml) as described above. The results of the MTT and flow
cytometry assays demonstrated that there were no significant
differences between the hesperidin- and 0.5% DMSO-treated cells and
the control group (P>0.05) (Fig.
5A), whereas DDP-treated (1 µg/ml) cells exhibited
significantly decreased viability (P<0.05) (Fig. 5A–a), as well as notably increased
rates of inhibition of proliferation (P<0.05 (Fig. 5A–b) and apoptosis (P<0.05)
(Fig. 5B).
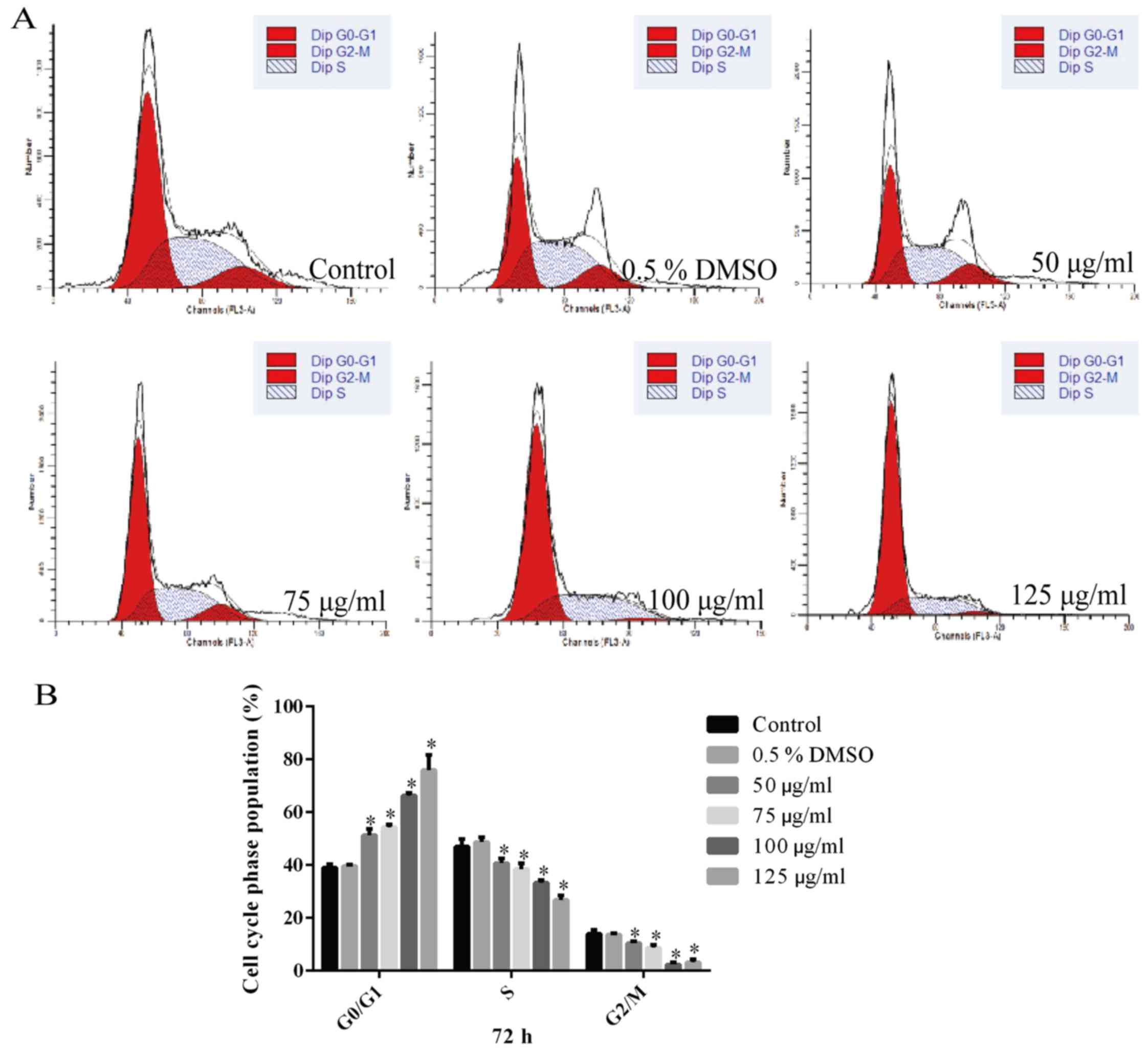
Hesperidin causes G0/G1 phase arrest of
A549 cells
The effect of hesperidin on the cell cycle
distribution of A549 cells was detected by flow cytometry (Fig. 6A). The G0/G1 phase population in
the 0.5% DMSO group was not significantly different from that in
the control group (P>0.05) (Fig.
6B). However, the proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase in the
groups treated with various concentrations of hesperidin for
different durations were significantly increased compared with
those in the control group, indicating cell-cycle/growth arrest in
G0/G1 phase (P<0.05) (Fig.
6B).
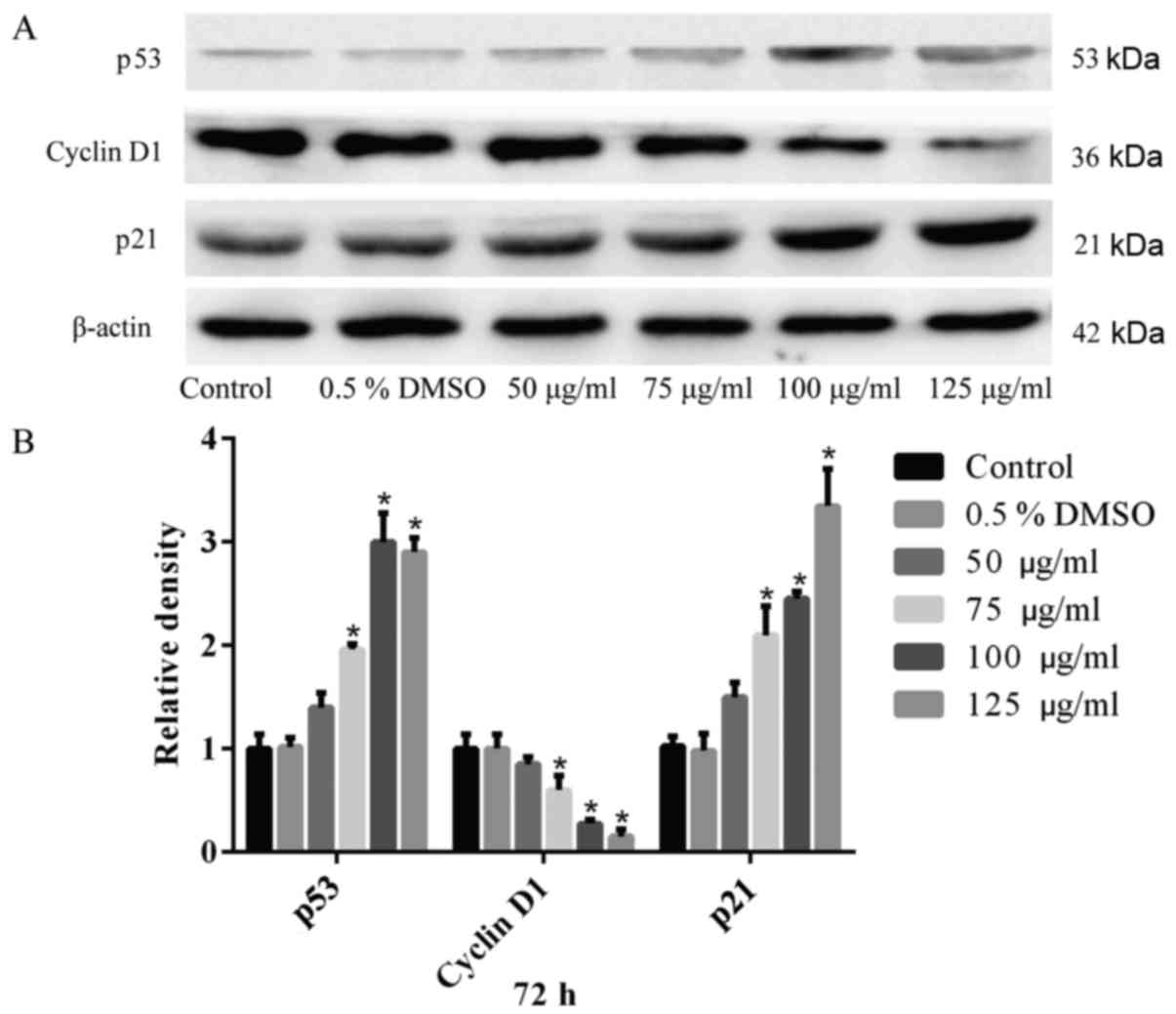
A549 cells were treated with different
concentrations of hesperidin for 72 h and the expression of various
cell cycle-associated proteins was assessed by western blot
analysis. The results confirmed that hesperidin elevated the
relative expression levels of p21 and p53, while reducing the
expression levels of the cell cycle-regulatory protein cyclin D1
(Fig. 7A). Quantitative analysis
revealed significant differences compared with the control
(P<0.05) (Fig. 7B). The 0.5%
DMSO group exhibited no significant differences compared with the
control group (P>0.05) (Fig.
7). These results demonstrated that hesperidin induced G0/G1
phase arrest by regulating the relative expression of cell
cycle-associated proteins in A549 cells.
Discussion
The present study indicated a significant inhibitory
effect of hesperidin on the viability and cell cycle of A549 NSCLC
cells. The cell viability was inhibited by hesperidin through the
mitochondrial apoptotic pathway as well as induction of G0/G1
arrest, accompanied by changes in cell morphology, in a time-and
dose-dependent manner, while not exerting any negative effects on
BEAS-2B human normal lung epithelial cells.
Tumor occurrence and development are associated not
only with dedifferentiation and excessive multiplication of tumor
cells, but are also with the suppression of apoptosis. To
investigate the mechanisms underlying the effect of hesperidin on
apoptosis, apoptosis-associated signaling molecules were detected
in A549 cells, which demonstrated that cell apoptosis was increased
after treatment with hesperidin. Cell apoptosis is regulated by
multiple apoptosis-promoting proteins, such as Bax, Bad and Bid,
and is upregulated by a family of apoptosis-inhibiting proteins,
which include Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. The mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
has a critical role in cell apoptosis. After cytochrome c is
released from the mitochondria into the cytosol, cell apoptosis is
promoted through the activation of caspase-9 and subsequent
downstream factors, such as caspase-3 and cleaved PARP (26). The balance between
apoptosis-promoting and apoptosis-inhibiting proteins is crucial
for the process of apoptosis (26,27). The results of the present study
suggested that the treatment of A549 cells with hesperidin
upregulated the relative levels of mitochondrial apoptotic
pathway-associated proteins, including Bax, Bid, tBid, cleaved
caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-3, while down-regulating the relative
expression levels of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. Furthermore, an increase in
cleaved PARP, which is one of the downstream products of caspase-3,
was observed. These results are in line with those of a previous
study (25). Therefore, it was
indicated that A549 cell apoptosis is induced by hesperidin via
activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Furthermore, cell cycle arrest is associated with
the triggering of cell apoptosis and usually occurs during the
induction of tumor cell apoptosis (28). It was observed that A549 cells
underwent cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase after treatment with
hesperidin. Cell cycle arrest has also been linked to the
inhibition of the proliferation of cancer cells (29). The cell cycle is positively
regulated by certain cell cycle-associated proteins and negatively
regulated by certain inhibitory factors of cyclin-dependent kinases
(CDKs), such as p21, p16 and p27. In the present study, it was
indicated that the expression of p21 was upregulated, while cyclin
D1 was downregulated after the treatment of A549 cells with
hesperidin in a concentration-dependent manner. Cyclin D1 is the
most important protein in the regulation of the G1 phase, and its
expression is altered during tumorigenesis (30). CDKs regulate the cell cycle at
different levels by affecting the assembly of cyclins and CDK
subunits. The G1/S phase transition is negatively regulated by p21
and p27, which is achieved through degrading certain cyclin/CDK
complexes (31). In a previous
study, hesperidin was able to inhibit the G1/S transition by
decreasing the relative expression levels of cyclin D1, while
increasing p21 levels, which was associated with G0/G1 phase arrest
(32). In addition, after
treatment with hesperidin, elevated expression of p53 was observed
in A549 cells, which is also associated with cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis (33–35).
Considering that p53 is an important factor
regulating the expression of p21, it was hypothesized that
hesperidin induced G0/G1 arrest of A549 cells by upregulating the
levels of p53, thereby upregulating the levels of p21 and in turn
inhibiting the conjugation of cyclin D1/CDK complexes. To the best
of our knowledge, the present study was the first to report on the
inhibitory effects of hesperidin on the cell cycle of A549 cells.
However, further study is necessary to elucidate the underlying
mechanisms.
Taken together, the results of the present study
demonstrated that hesperidin induces apoptosis in A549 cells by
activating the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, and inhibits the
proliferation of A549 cells through induction of G0/G1 phase arrest
by significantly upregulating the expression of p21 and p53, as
well as downregulating cyclin D1. Hence, it was indicated that
hesperidin may be developed as a potential therapeutic drug against
NSCLC in the future.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Bo Zhang
(Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Zunyi Medical
College, Zunyi) and Dr Fei He (Translation Medicine Collaborative
Innovation Center of Shenzhen People's Hospital, Shenzhen) for
their efforts in modifying the manuscript and Dr Kuifeng Wang
(Qinhao Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai) for his technical
assistance. This study was financed by the Department of Education
of Guizhou Province [grant no. (2015)375] and the Grant of Key
Subject Construction of Zunyi Medical College (grant no.
SSDJS201623).
References
|
1
|
NSCLC Meta-analysis Collaborative Group:
Preoperative chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data.
Lancet. 383:1561–1571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saintigny P and Burger JA: Recent advances
in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management.
Discov Med. 13:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He J, Shen J, Yang C, Jiang L, Liang W,
Shi X, Xu X and He J: Adjuvant chemotherapy for the completely
resected stage IB nonsmall cell lung cancer: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e9032015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh BN, Singh HB, Singh A, Naqvi AH and
Singh BR: Dietary phytochemicals alter epigenetic events and
signaling pathways for inhibition of metastasis cascade:
Phytoblockers of metastasis cascade. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
33:41–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu Y, Zhang C, Bucheli P and Wei D: Citrus
flavonoids in fruit and traditional Chinese medicinal food
ingredients in China. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 61:57–65. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Molecular mechanisms behind the biological
effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer
and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 124:64–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Knekt P, Kumpulainen J, Järvinen R,
Rissanen H, Heliövaara M, Reunanen A, Hakulinen T and Aromaa A:
Flavonoid intake and risk of chronic diseases. Am J Clin Nutr.
76:560–568. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahmadi A, Shadboorestan A, Nabavi SF,
Setzer WN and Nabavi SM: The role of hesperidin in cell signal
transduction pathway for the prevention or treatment of cancer.
Curr Med Chem. 22:3462–3471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tanaka T, Tanaka T, Tanaka M and Kuno T:
Cancer chemoprevention by citrus pulp and juices containing high
amounts of β-cryptoxanthin and hesperidin. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:5169812012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yumnam S, Hong GE, Raha S, Saralamma VV,
Lee HJ, Lee WS, Kim EH and Kim GS: Mitochondrial dysfunction and
Ca(2+) overload contributes to hesperidin induced paraptosis in
hepatoblastoma cells, HepG2. J Cell Physiol. 231:1261–1268. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Banjerdpongchai R, Wudtiwai B, Khaw-On P,
Rachakhom W, Duangnil N and Kongtawelert P: Hesperidin from Citrus
seed induces human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell apoptosis
via both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Tumour Biol.
37:227–237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Yumnam S, Park HS, Kim MK, Nagappan A,
Hong GE, Lee HJ, Lee WS, Kim EH, Cho JH, Shin SC, et al: Hesperidin
induces paraptosis like cell death in hepatoblastoma, HepG2 cells:
Involvement of ERK1/2 MAPK [corrected]. PLoS One. 9:e1013212014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ghorbani A, Nazari M, Jeddi-Tehrani M and
Zand H: The citrus flavonoid hesperidin induces p53 and inhibits
NF-κB activation in order to trigger apoptosis in NALM-6 cells:
Involvement of PPARγ-dependent mechanism. Eur J Nutr. 51:39–46.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nazari M, Ghorbani A, Hekmat-Doost A,
Jeddi-Tehrani M and Zand H: Inactivation of nuclear factor-κB by
citrus flavanone hesperidin contributes to apoptosis and
chemo-sensitizing effect in Ramos cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
650:526–533. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee KA, Lee SH, Lee YJ, Baeg SM and Shim
JH: Hesperidin induces apoptosis by inhibiting Sp1 and its
regulatory protein in MSTO-211H cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
20:273–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bartoszewski R, Hering A, Marszałł M,
Stefanowicz Hajduk J, Bartoszewska S, Kapoor N, Kochan K and
Ochocka R: Mangiferin has an additive effect on the apoptotic
properties of hesperidin in Cyclopia sp tea extracts. PLoS One.
9:e921282014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, Yu H, Zhang J, Gao J, Ge X and Lou
G: Hesperidin inhibits HeLa cell proliferation through apoptosis
mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways and cell cycle
arrest. BMC Cancer. 15:6822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saiprasad G, Chitra P, Manikandan R and
Sudhandiran G: Hesperidin induces apoptosis and triggers autophagic
markers through inhibition of Aurora-A mediated
phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin and
glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta signalling cascades in experimental
colon carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 50:2489–2507. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kohno H, Taima M, Sumida T, Azuma Y, Ogawa
H and Tanaka T: Inhibitory effect of mandarin juice rich in
beta-cryptoxanthin and hesperidin on
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced pulmonary
tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Lett. 174:141–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Balakrishnan A and Menon VP: Effect of
hesperidin on matrix metalloproteinases and antioxidant status
during nicotine-induced toxicity. Toxicology. 238:90–98. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kamaraj S, Anandakumar P, Jagan S,
Ramakrishnan G and Devaki T: Hesperidin attenuates mitochondrial
dysfunction during benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in
mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 25:91–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kamaraj S, Anandakumar P, Jagan S,
Ramakrishnan G and Devaki T: Modulatory effect of hesperidin on
benzo(a)pyrene induced experimental lung carcinogenesis with
reference to COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:320–327.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kamaraj S, Ramakrishnan G, Anandakumar P,
Jagan S and Devaki T: Antioxidant and anticancer efficacy of
hesperidin in benzo(a)pyrene induced lung carcinogenesis in mice.
Invest New Drugs. 27:214–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Birsu Cincin Z, Unlu M, Kiran B, Sinem
Bireller E, Baran Y and Cakmakoglu B: Anti-proliferative, apoptotic
and signal transduction effects of hesperidin in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 38:195–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Eichhorn JM, Alford SE, Sakurikar N and
Chambers TC: Molecular analysis of functional redundancy among
ant-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and its role in cancer cell survival.
Exp Cell Res. 322:415–424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Silva RD, Manon S, Gonçalves J, Saraiva L
and Côrte-Real M: The importance of humanized yeast to better
understand the role of bcl-2 family in apoptosis: Finding of novel
therapeutic opportunities. Curr Pharm Des. 17:246–255. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dai HY, Liu L, Qin SK, He XM and Li SY:
Lobaplatin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in the
human colorectal carcinoma cell Line LOVO in vitro. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:137–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu Z, Liu B, e C, Liu J, Zhang Q, Liu J,
Chen N, Chen R and Zhu R: Resveratrol inhibits the proliferation of
human melanoma cells by inducing G1/S cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 11:400–404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim JK and Diehl JA: Nuclear cyclin D1: An
oncogenic driver in human cancer. J Cell Physiol. 220:292–296.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Orlando S, Gallastegui E, Besson A, Abril
G, Aligué R, Pujol MJ and Bachs O: p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 collaborate
in the regulation of transcription by recruiting cyclin-Cdk
complexes on the promoters of target genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:6860–6873. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shaltiel IA, Krenning L, Bruinsma W and
Medema RH: The same, only different - DNA damage checkpoints and
their reversal throughout the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 128:607–620.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li L, Dai HJ, Ye M, Wang SL, Xiao XJ,
Zheng J, Chen HY, Luo YH and Liu J: Lycorine induces cell-cycle
arrest in the G0/G1 phase in K562 cells via HDAC inhibition. Cancer
Cell Int. 12:492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaplon J, van Dam L and Peeper D: Two-way
communication between the metabolic and cell cycle machineries: The
molecular basis. Cell Cycle. 14:2022–2032. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Zhang X, Teng L and Legerski RJ:
DNA damage checkpoint recovery and cancer development. Exp Cell
Res. 334:350–358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|