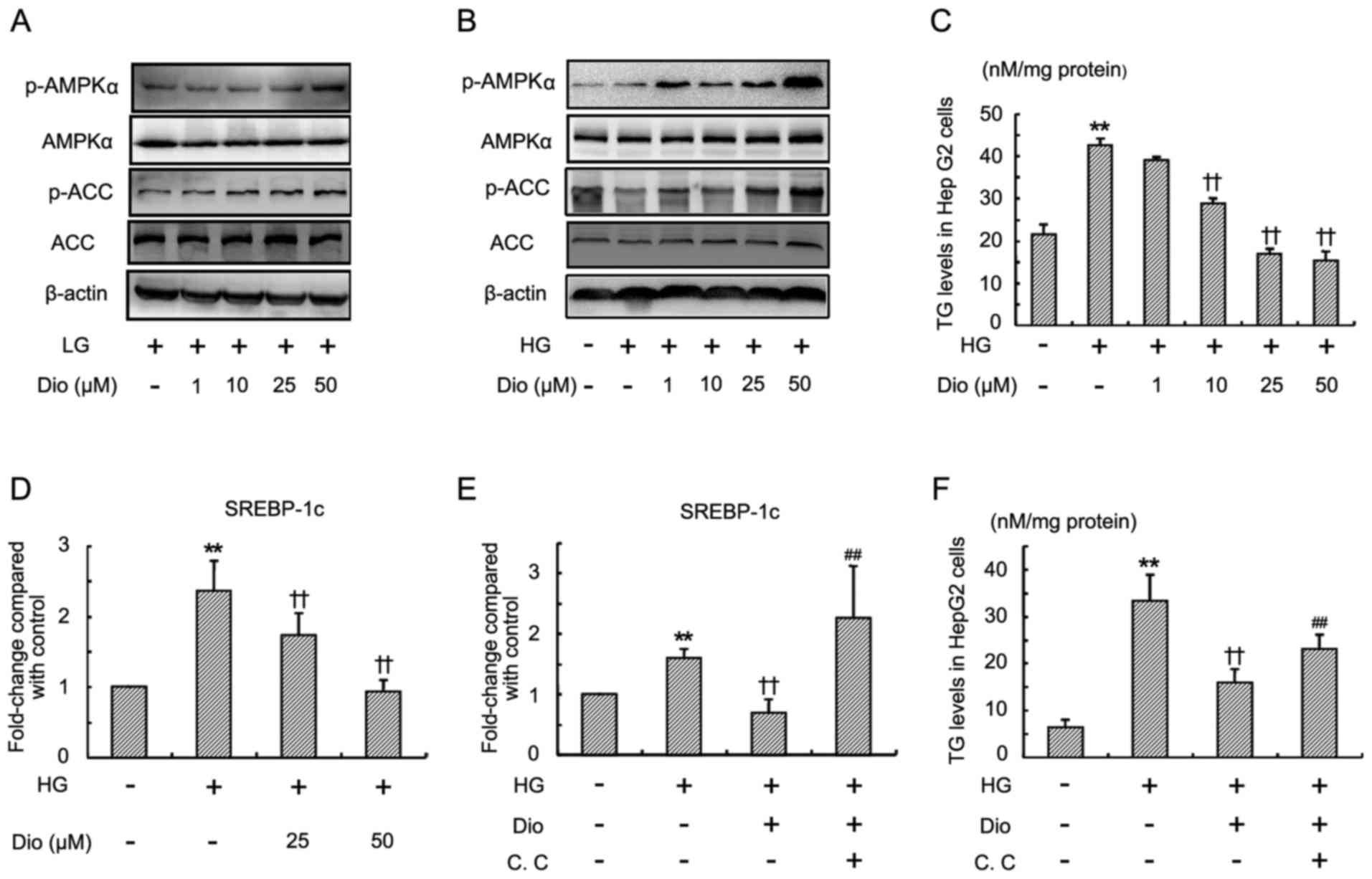
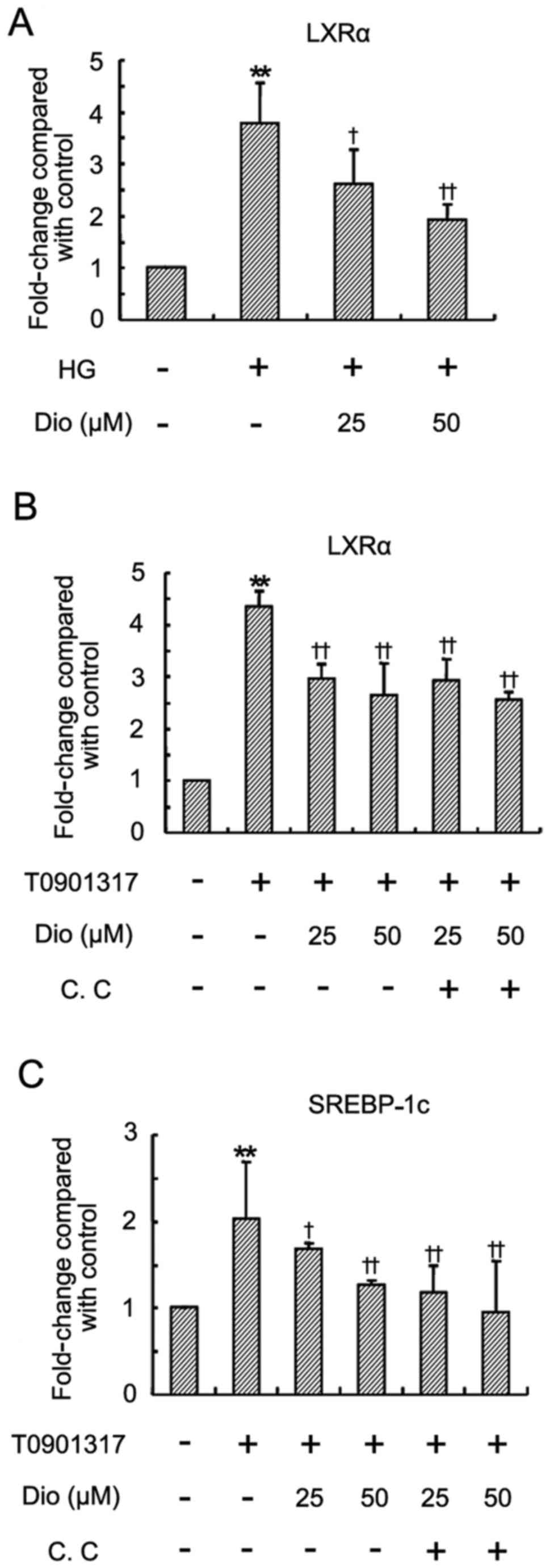
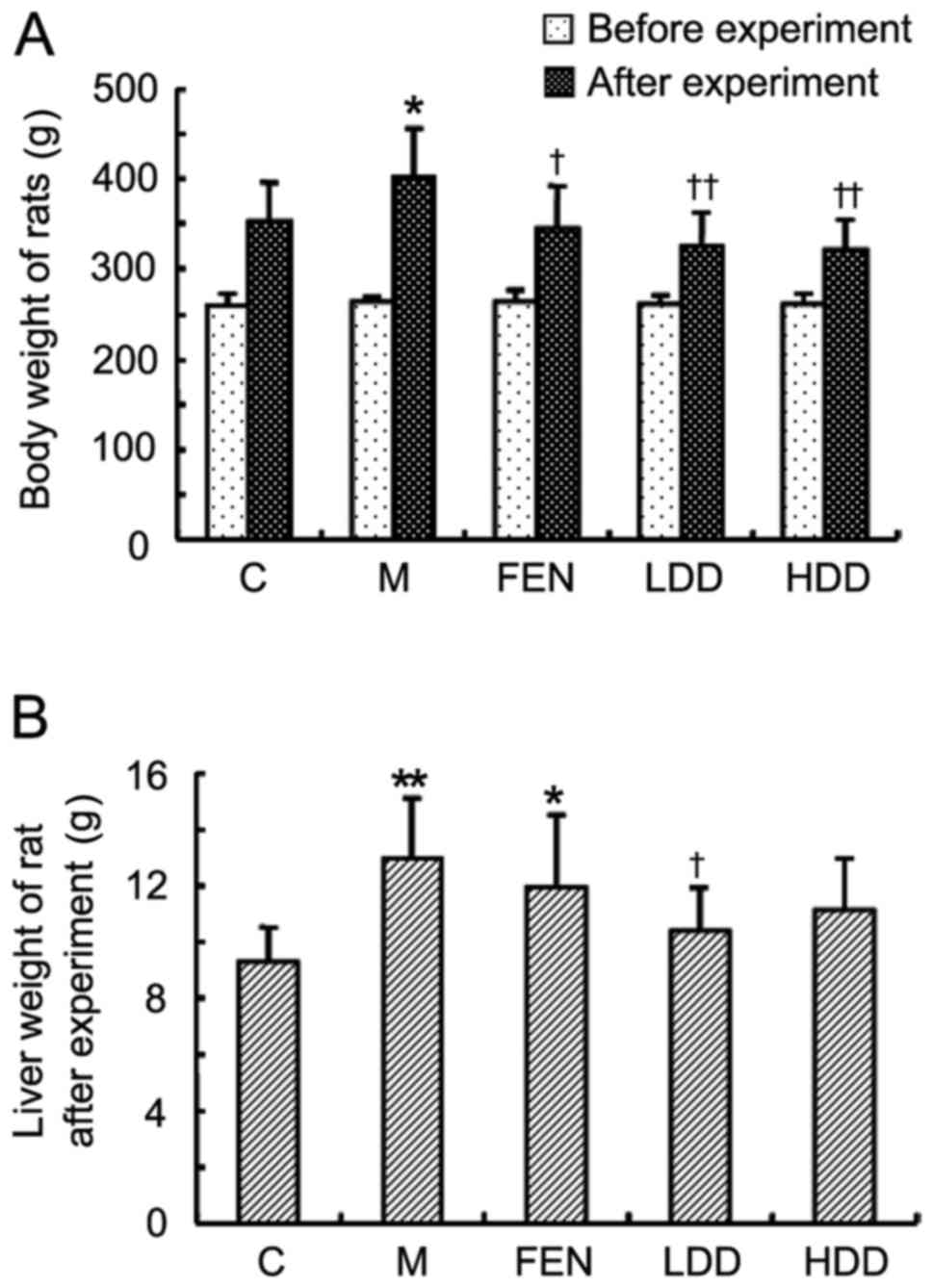
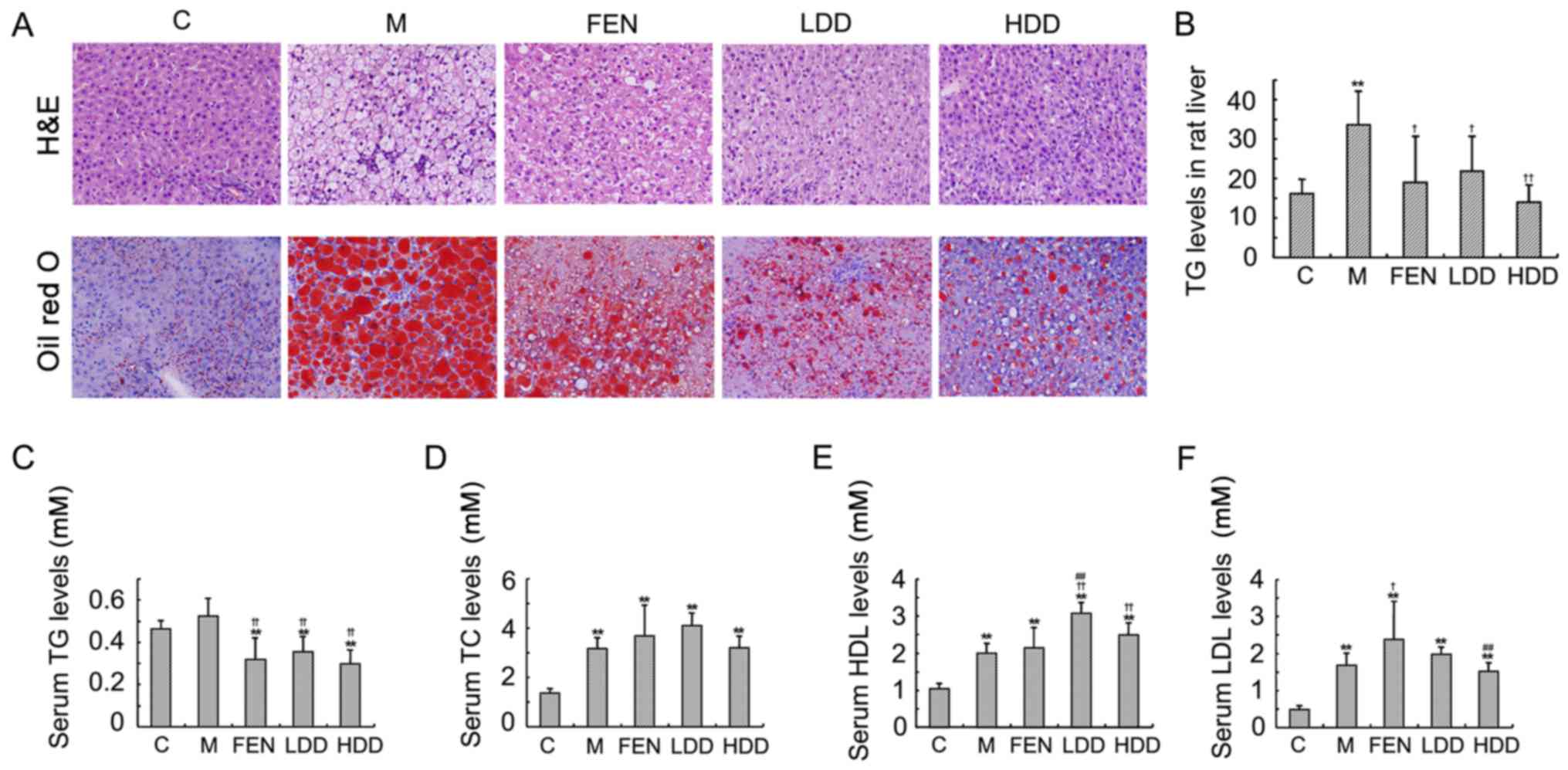
|
1
|
Caballería L, Auladell MA, Torán P,
Miranda D, Aznar J, Pera G, Gil D, Muñoz L, Planas J, Canut S, et
al: Prevalence and factors associated with the presence of non
alcoholic fatty liver disease in an apparently healthy adult
population in primary care units. BMC Gastroenterol. 7:412007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu X, Huang Y, Bao Z, Wang Y, Shi D, Liu
F, Gao Z and Yu X: Prevalence and factors associated with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Shanghai work-units. BMC
Gastroenterol. 12:1232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Welsh JA, Karpen S and Vos MB: Increasing
prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among United States
adolescents, 1988–1994 to 2007–2010. J Pediatr. 162:496–500. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Margini C and Dufour JF: The story of HCC
in NAFLD: from epidemiology, across pathogenesis, to prevention and
treatment. Liver Int. 36:317–324. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated/SNF1 protein
kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:774–785. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Santamarina AB, Oliveira JL, Silva FP,
Carnier J, Mennitti LV, Santana AA, de Souza GH, Ribeiro EB, Oller
do Nascimento CM, Lira FS, et al: Green tea extract rich in
epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents fatty liver by AMPK activation
via LKB1 in mice fed a high-fat diet. PLoS One. 10:e01412272015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li H, Min Q, Ouyang C, Lee J, He C, Zou MH
and Xie Z: AMPK activation prevents excess nutrient-induced hepatic
lipid accumulation by inhibiting mTORC1 signaling and endoplasmic
reticulum stress response. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1842:1844–1854.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Y, Li W, Liu Y, Sun Y, Li Y, Yao Q,
Li J, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Gao L, et al: Alpha-lipoic acid improves
high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis by modulating the
transcription factors SREBP-1, FoxO1 and Nrf2 via the
SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 25:1207–1217. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan H, Weng C, Yang Y, Huang L and Xing
X: Resistin, an adipokine, may affect the improvement of insulin
sensitivity in the metabolic syndrome patient treated with
metformin. Med Hypotheses. 81:969–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
de Mello VD, Kolehmainen M, Pulkkinen L,
Schwab U, Mager U, Laaksonen DE, Niskanen L, Gylling H, Atalay M,
Rauramaa R, et al: Downregulation of genes involved in NFkappaB
activation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells after weight loss
is associated with the improvement of insulin sensitivity in
individuals with the metabolic syndrome: The GENOBIN study.
Diabetologia. 51:2060–2067. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, Huang P, Yang B, Wang X and Xia J:
Roles of CXCL5 on migration and invasion of liver cancer cells. J
Transl Med. 12:1932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Y, Xu X, Zhang Y, Liu K, Huang F, Liu
B and Kou J: Diosgenin regulates adipokine expression in
perivascular adipose tissue and ameliorates endothelial dysfunction
via regulation of AMPK. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 155:155–165.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zang M, Zuccollo A, Hou X, Nagata D, Walsh
K, Herscovitz H, Brecher P, Ruderman NB and Cohen RA: AMP-activated
protein kinase is required for the lipid-lowering effect of
metformin in insulin-resistant human HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem.
279:47898–47905. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uemura T, Goto T, Kang MS, Mizoguchi N,
Hirai S, Lee JY, Nakano Y, Shono J, Hoshino S, Taketani K, et al:
Diosgenin, the main aglycon of fenugreek, inhibits LXRα activity in
HepG2 cells and decreases plasma and hepatic triglycerides in obese
diabetic mice. J Nutr. 141:17–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ghosh S, Sikdar S, Mukherjee A and
Khuda-Bukhsh AR: Evaluation of chemopreventive potentials of
ethanolic extract of Ruta graveolens against A375 skin melanoma
cells in vitro and induced skin cancer in mice in vivo. J Integr
Med. 13:34–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu J, Zhang H, Zheng H and Jiang Y:
Hepatic inflammation scores correlate with common carotid
intima-media thickness in rats with NAFLD induced by a high-fat
diet. BMC Vet Res. 10:1622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akaslan SB, Degertekin CK, Yilmaz G, Cakir
N, Arslan M and Toruner FB: Effects of sitagliptin on nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease in diet-induced obese rats. Metab Syndr Relat
Disord. 11:243–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park KG, Min AK, Koh EH, Kim HS, Kim MO,
Park HS, Kim YD, Yoon TS, Jang BK, Hwang JS, et al: Alpha-lipoic
acid decreases hepatic lipogenesis through adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and
AMPK-independent pathways. Hepatology. 48:1477–1486. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Edwards PA, Kast HR and Anisfeld AM:
BAREing it all: the adoption of LXR and FXR and their roles in
lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 43:2–12. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao M and Liu D: The liver X receptor
agonist T0901317 protects mice from high fat diet-induced obesity
and insulin resistance. AAPS J. 15:258–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Chisholm JW, Hong J, Mills SA and Lawn RM:
The LXR ligand T0901317 induces severe lipogenesis in the db/db
diabetic mouse. J Lipid Res. 44:2039–2048. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jegatheesan P, Beutheu S, Freese K,
Waligora-Dupriet AJ, Nubret E, Butel MJ, Bergheim I and De Bandt
JP: Preventive effects of citrulline on Western diet-induced
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Br J Nutr. 116:191–203.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsujimoto S, Kishina M, Koda M, Yamamoto
Y, Tanaka K, Harada Y, Yoshida A and Hisatome I: Nimesulide, a
cyclo-oxygenase-2 selective inhibitor, suppresses obesity-related
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatic insulin resistance
through the regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ. Int J Mol Med. 38:721–728. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dyck JR, Kudo N, Barr AJ, Davies SP,
Hardie DG and Lopaschuk GD: Phosphorylation control of cardiac
acetyl-CoA carboxylase by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and 5′-AMP
activated protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 262:184–190. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X,
Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, et al: AMPK
phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic
steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant
mice. Cell Metab. 13:376–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schultz JR, Tu H, Luk A, Repa JJ, Medina
JC, Li L, Schwendner S, Wang S, Thoolen M, Mangelsdorf DJ, et al:
Role of LXRs in control of lipogenesis. Genes Dev. 14:2831–2838.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee J, Hong SW, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY,
Oh KW, Park SW and Lee WY: AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses
the expression of LXR/SREBP-1 signaling-induced ANGPTL8 in HepG2
cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 414:148–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cabrera D, Ruiz A, Cabello-Verrugio C,
Brandan E, Estrada L, Pizarro M, Solis N, Torres J, Barrera F and
Arrese M: Diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is
associated with sarcopenia and decreased serum insulin-like growth
factor-1. Dig Dis Sci. 61:3190–3198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Tao Q, Wang X, Wang X and Zhang X:
Impact of high-fat diet on liver genes expression profiles in mice
model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 45:52–62. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu ZJ, Fan JG, Ding XD, Qiao L and Wang
GL: Characterization of high-fat, diet-induced, non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis with fibrosis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 55:931–940.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Jiang SL, Hu XD and Liu P:
Immunomodulation and liver protection of Yinchenhao decoction
against concan-avalin A-induced chronic liver injury in mice. J
Integr Med. 13:262–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moghadam AR, Tutunchi S,
Namvaran-Abbas-Abad A, Yazdi M, Bonyadi F, Mohajeri D, Mazani M,
Marzban H, Łos MJ and Ghavami S: Pre-administration of turmeric
prevents methotrexate-induced liver toxicity and oxidative stress.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:2462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|