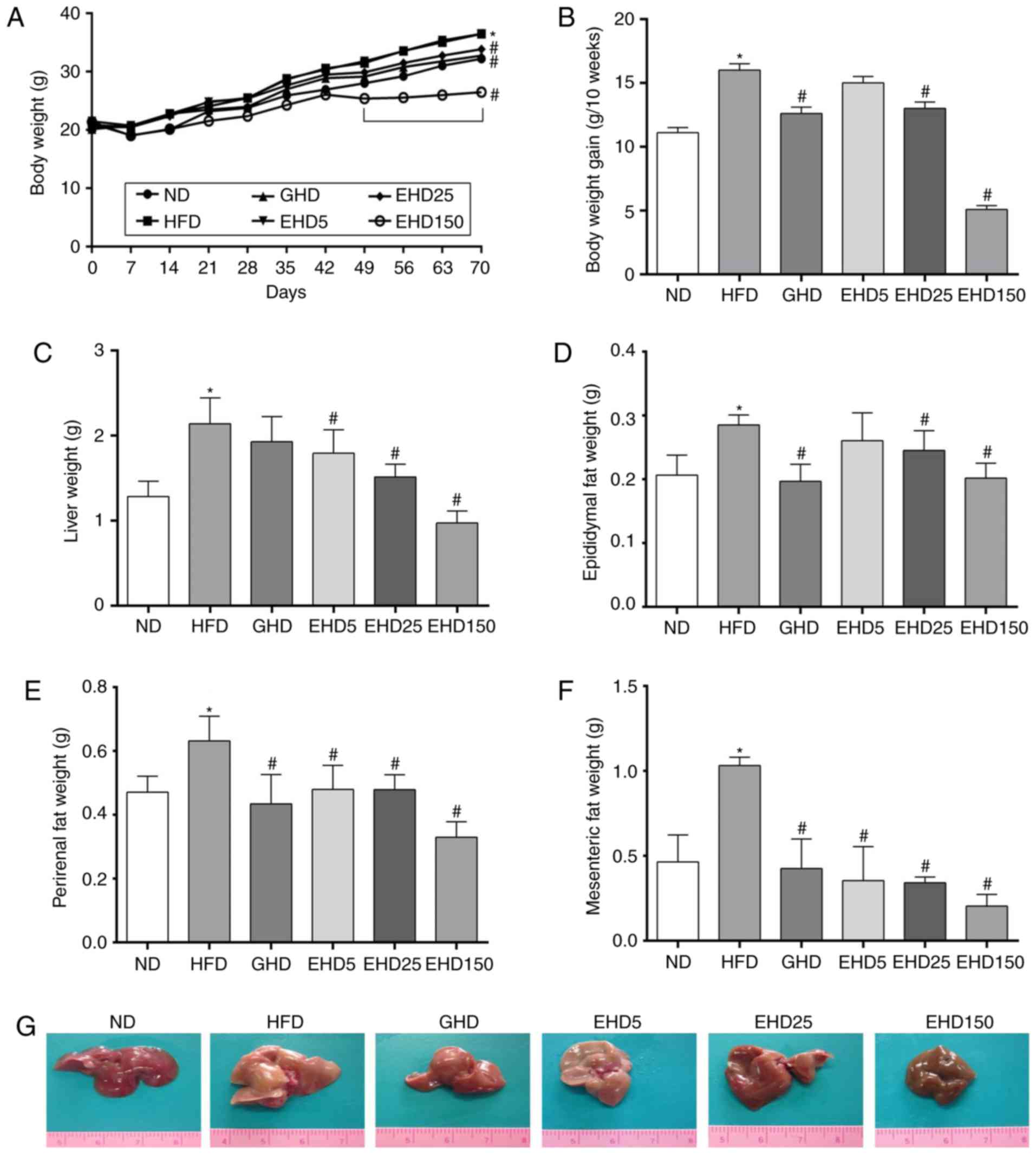
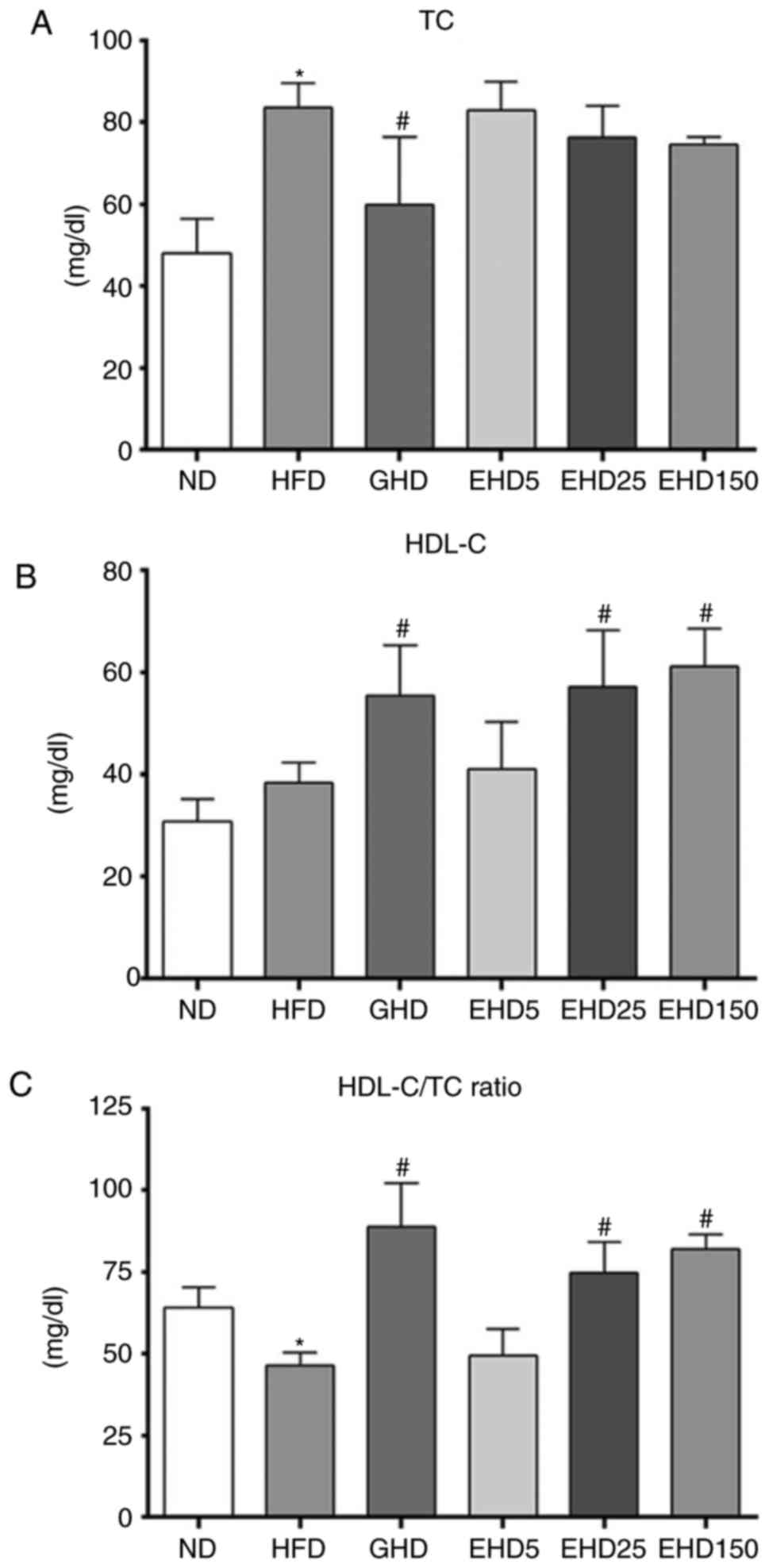
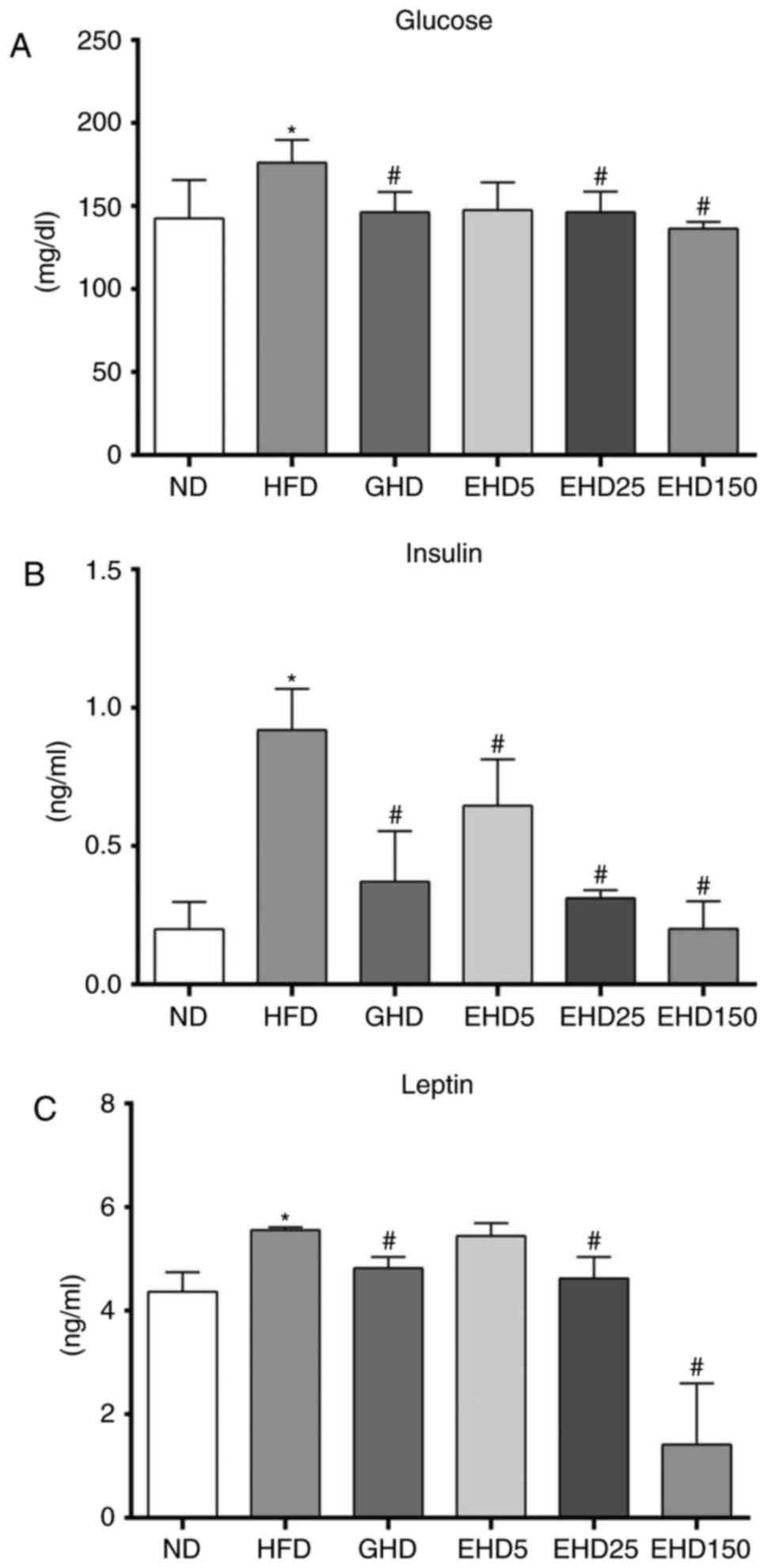
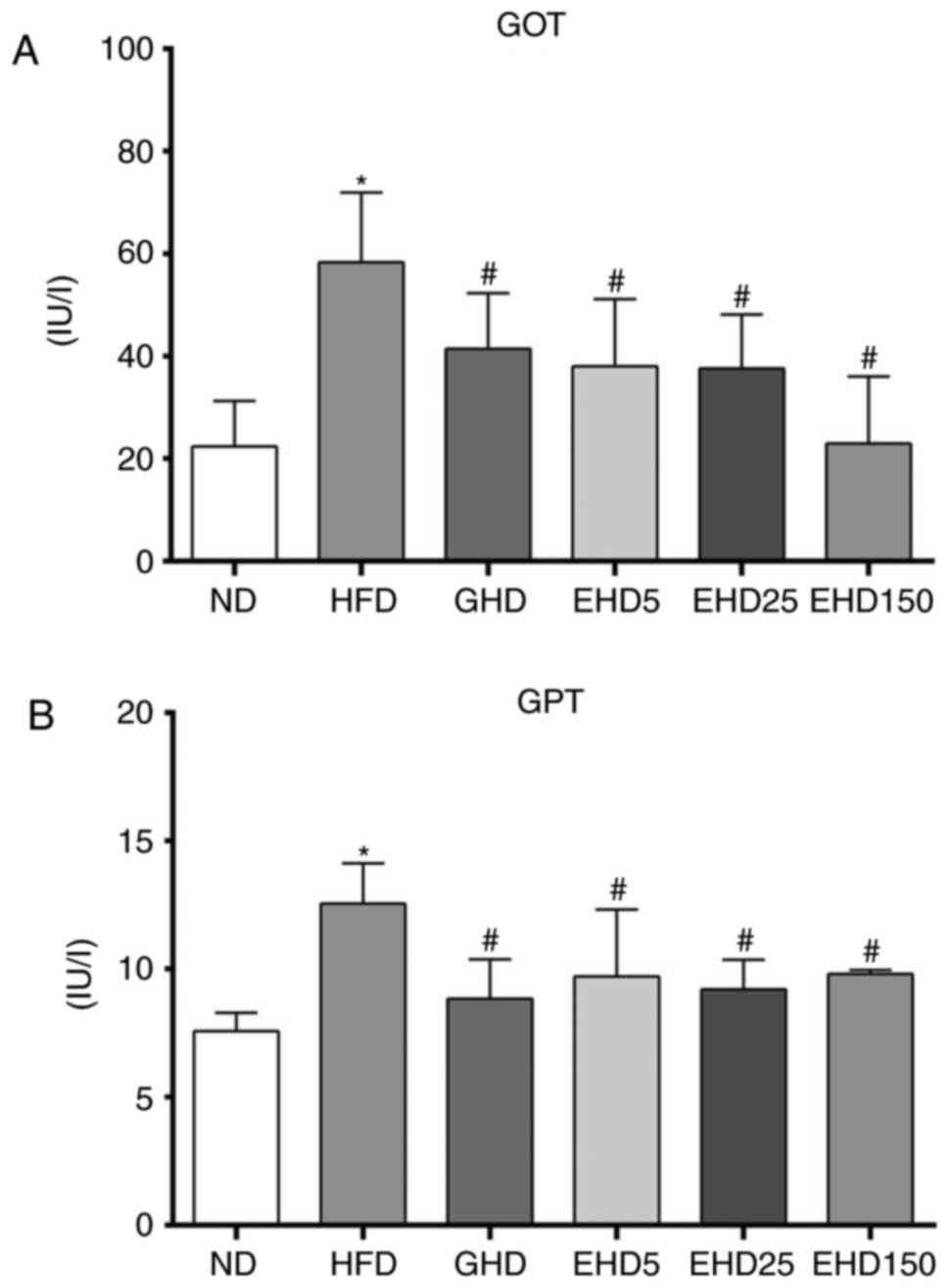
|
1
|
Formiguera X and Cantón A: Obesity:
Epidemiology and clinical aspects. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 18:1125–1146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spieglman BM and Filer JS: Obesity and the
regulation of energy balance. Cell. 104:531–543. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bibiloni Mdel M, Pons A and Tur JA:
Prevalence of overweight and obesity in adolescents: A systematic
review. ISRN Obes. 392747:2013.
|
|
4
|
Obici S and Rossetti L: Minireview:
Nutrient sensing and the regulation of insulin action and energy
balance. Endocrinology. 144:5172–5178. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gurevich-Panigrahi T, Panigrahi S, Wiechec
E and Los M: Obesity: Pathophysiology and clinical management. Curr
Med Chem. 16:506–521. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aggoun Y: Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and
cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Res. 61:653–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Després JP and Lemieux I: Abdominal
obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 444:881–887. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vazzana N, Santilli F, Sestili S,
Cuccurullo C and Davi G: Determinants of increased cardiovascular
disease in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Curr Med Chem.
18:5267–5280. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kopelman PG: Obesity as a medical problem.
Nature. 404:635–643. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abate N: Obesity and cardiovascular
disease. Pathogenetic role of the metabolic syndrome and
therapeutic implications. J Diabetes Complications. 14:154–174.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bray GA and Tartaglia LA: Medicinal
strategies in the treatment of obesity. Nature. 404:672–677. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alemany M, Remesar X and Fernández-López
JA: Drug strategies for the treatment of obesity. IDrugs.
6:566–572. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buyukhatipoglu H: A possibly overlooked
side effect of orlistat: Gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Natl
Med Assoc. 100:12072008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Markowitz GS, Tartini A and D'Agati VD:
Acute interstitial nephritis following treatment with anorectic
agents phentermine and phendimetrazine. Clin Nephrol. 50:252–254.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Onakpoya IJ, Heneghan CJ and Aronson JK:
Post-marketing withdrawal of anti-obesity medicinal products
because of adverse drug reactions: A systematic review. BMC Med.
14:1912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rupérez P: Mineral content of edible
marine seaweeds. Food Chem. 79:23–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Besada V, Andrade JM, Schultze F and
González JJ: Heavy metals in edible seaweeds commercialised for
human consumption. J Mar Syst. 75:305–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rioux LE, Turgeon SL and Beaulieu M:
Effect of season on the composition of bioactive polysaccharides
from the brown seaweed Saccharina longicruris. Phytochemistry.
70:1069–1075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cunha L and Grenha A: Sulfated seaweed
polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery
applications. Mar Drugs. 14:E422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gomes DL, Telles CB, Costa MS,
Almeida-Lima J, Costa LS, Keesen TS and Rocha HA: Methanolic
extracts from brown seaweeds Dictyota cilliolata and Dictyota
menstrualis induce apoptosis in human cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa
cells. Molecules. 20:6573–6591. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Fu Z and Han C: The potential
applications of marine bioactives against diabetes and obesity. Am
J Mar Sci. 2:1–8. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Koh YS, Yoo BS,
Kim JH, Ham YM, Baik JS, Lee NH and Hyun JW: Triphlorethol-A from
Ecklonia cava protects V79.4 lung fibroblast against hydrogen
peroxide induced cell damage. Free Radic Res. 39:883–892. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS,
Lee Y, Kim SY, Kim HS, Joo HG, Park JW, et al: Eckol isolated from
Ecklonia cava attenuates oxidative stress induced cell damage in
lung fibroblast cells. FEBS Lett. 579:6295–6304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang K, Hwang HJ, Hong DH, Park Y, Kim SH,
Lee BH and Shin HC: Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of
ventol, a phlorotannin-rich natural agent derived from Ecklonia
cava, and its effect on proteoglycan degradation in cartilage
explant culture. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 115–116. 77–95.
2004.
|
|
25
|
Wijesekara I, Yoon NY and Kim SK:
Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava (Phaeophyceae): Biological
activities and potential health benefits. Biofactors. 36:408–414.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim BM, Park JH, Kim DS, Kim YM, Jun JY,
Jeong IH and Chi YM: Effects of the polysaccharide from the
sporophyll of brown alga Undaria Pinnatifida on serum lipid profile
and fat tissue accumulation in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Food
Sci. 81:H1840–H1845. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kimura Y, Watanabe K and Okuda H: Effects
of soluble sodium alginate on cholesterol excretion and glucose
tolerance in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 54:47–54. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hernández-Corona DM, Martínez-Abundis E
and González- Ortiz M: Effect of fucoidan administration on insulin
secretion and insulin resistance in overweight or obese adults. J
Med Food. 17:830–832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim MJ, Jeon J and Lee JS: Fucoidan
prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity in animals by suppression of
fat accumulation. Phytother Res. 28:137–143. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wijesinghe WA and Jeon YJ: Exploiting
biological activities of brown seaweed Ecklonia cava for potential
industrial applications: A review. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 63:225–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ham YM, Baik JS, Hyun JW and Lee NH:
Cheminform Abstract: Isolation of a new phlorotannin,
Fucodiphlorethol G, from a brown alga Ecklonia cava. ChemInform.
39:2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Lee SH, Kim MM and
Kim SK: Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in
vitro: An edible marine brown alga Ecklonia cava. Bioorg Med Chem.
17:1963–1973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahn MJ, Yoon KD, Min SY, Lee JS, Kim JH,
Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim NG, Huh H and Kim J: Inhibition of HIV-1
reverse transcriptase and protease by phlorotannins from the brown
alga Ecklonia cava. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:544–547. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang YI, Jung SH, Lee KT and Choi JH:
8.8′-Bieckol, isolated from edible brown algae, exerts its
anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of NF-κB signaling and
ROS production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
23:460–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shin HC, Hwang HJ, Kang KJ and Lee BH: An
anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agent for potential treatment
of osteoarthritis from Ecklonia cava. Arch pharm Res. 29:165–171.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Athukorala Y, Kim KN and Jeon YJ:
Antiproliferative and anti- oxidant properties of an enzymatic
hydrolysate from brown alga Ecklonia cava. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:1065–1074. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park MH, Heo SJ, Park PJ, Moon SH, Sung
SH, Jeon BT and Lee SH: 6,6′-bieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava
protects oxidative stress through inhibiting expression of ROS and
proinflammatory enzymes in high-glucose-induced human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 174:632–643. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim KN, Heo SJ, Song CB, Lee J, Heo MS,
Yeo IK, Kang KA, Hyun JW and Jeon YJ: Protective effect of Ecklonia
cava enzymatic extracts on hydrogen peroxide-induced cell damage.
Process Biochem. 41:2393–2401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang YI, Shin HC, Kim SH, Park WY, Lee KT
and Choi JH: 6,6′-Bieckol, isolated from marine alga Ecklonia cava,
suppressed LPS-induced nitric oxide and PGE2 production and
inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages: The inhibition of
NFκB. Int Immunopharmacol. 12:510–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee W, Oh JY, Kim EA, Kang N, Kim KN, Ahn
G and Jeon YJ: A prebiotic role of Ecklonia cava improves the
mortality of Edwardsiella tarda-infected zebrafish models via
regulating the growth of lactic acid bacteria and pathogen
bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 54:620–628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee W, Ahn G, Oh JY, Kim SM, Kang N, Kim
EA, Kim KN, Jeong JB and Jeon YJ: A prebiotic effect of Ecklonia
cava on the growth and mortality of olive flounder infected with
pathogenic bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 51:313–320. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ahn G, Lee W, Kim KN, Lee JH, Heo SJ, Kang
N, Lee SH, Ahn CB and Jeon YJ: A sulfated polysaccharide of
Ecklonia cava inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells by inducing
apoptosis. EXCLI J. 14:294–306. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ahn JH, Yang YI, Lee KT and Choi JH:
Dieckol, isolated from the edible brown algae Ecklonia cava,
induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells and inhibits tumor
xenograft growth. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:255–268. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Park SJ, Ahn G, Lee NH, Park JW, Jeon YJ
and Jee Y: Phloroglucinol (PG) purified from Ecklonia cava
attenuates radiation-induced apoptosis in blood lympho cytes and
splenocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:2236–2242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shin H, Cho AR, Kim DY, Munkhbayer S, Choi
SJ, Jang S, Kim SH, Shin HC and Kwon O: Enhancement of human hair
growth using Ecklonia cava polyphenols. Ann Dermatol. 28:15–21.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kang JI, Kim SC, Kim MK, Boo HJ, Jeon YJ,
Koh YS, Yoo ES, Kang SM and Kang HK: Effect of dieckol, a component
of Ecklonia cava, on the promotion of hair growth. Int J Mol Sci.
13:6407–6423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Choi BW, Lee HS, Shin HC and Lee BH:
Multifunctional activity of polyphenolic compounds associated with
a potential for Alzheimer's disease therapy from Ecklonia cava.
Phytother Res. 29:549–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kang IJ, Jang BG, In S, Choi B, Kim M and
Kim MJ: Phlorotannin-rich Ecklonia cava reduces the production of
beta-amyloid by modulating alpha- and gamma-secretase expression
and activity. Neurotoxicology. 34:16–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Choi HS, Jeon HJ, Lee OH and Lee BY:
Dieckol, a major phlorotannin in Ecklonia cava, suppresses lipid
accumulation in the adipocytes of high-fat diet-fed zebrafish and
mice: Inhibition of early adipogenesis via cell-cycle arrest and
AMPKα activation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 59:1458–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kang MC, Kim KN, Kang SM, Yang X, Kim EA,
Song CB, Nah JW, Jang MK, Lee JS, Jung WK and Jeon YJ: Protective
effect of dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava against ethanol
caused damage in vitro and in zebrafish model. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:1217–1226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
You HN, Lee HA, Park MH, Lee JH and Han
JS: Phlorofucofuroeckol A isolated from Ecklonia cava alleviates
postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
752:92–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Park EY, Choi H, Yoon JY, Lee IY, Seo Y,
Moon HS, Hwang JH and Jun HS: Polyphenol-rich fraction of Ecklonia
cava improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high fat diet-fed
mice. Mar Drugs. 13:6866–6883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Park EY, Kim EH, Kim MH, Seo YW, Lee JI
and Jun HS: Polyphenol-rich fraction of brown alga Ecklonia cava
collected from Gijang, Korea, reduces obesity and glucose levels in
high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Evi Based Complement Alternat
Med. 418912:2012.
|
|
54
|
Lee SH, Min KH, Han JS, Lee DH, Park DB,
Jung WK, Park PJ, Jeon BT, Kim SK and Jeon YJ: Effects of brown
alga, Ecklonia cava on glucose and lipid metabolism in
C57BL/KsJ–db/db mice, a model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Food
Chem Toxicol. 50:575–582. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kang MC, Wijesinghe WA, Lee SH, Kang SM,
Ko SC, Yang X, Kang N, Jeon BT, Kim J, Lee DH and Jeon YJ: Dieckol
isolated from brown seaweed Ecklonia cava attenuates type ІІ
diabetes in db/db mouse model. Food Chem Toxicol. 53:294–298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kim H, Kong CS, Lee JI, Kim H, Baek S and
Seo Y: Evaluation of inhibitory effect of phlorotannins from
Ecklonia cava on triglyceride accumulation in adipocyte. J Agric
Food Chem. 61:8541–8547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kang C, Jin YB, Lee H, Cha M, Sohn ET,
Moon J, Park C, Chun S, Jung ES, Hong JS, et al: Brown alga
Ecklonia cava attenuates type 1 diabetes by activating AMPK and Akt
signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:509–516. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim IH and Nam TJ: Enzyme-treated Ecklonia
cava extracts inhibits adipogenesis through the downregulation of
C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Med. 39:636–644. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Krishnamoorthy V, Nagappan P, Sereen AK
and Rajendran R: Preliminary phytochemical screening of the fruit
rind of Garcinia cambogia and leaves of Bauhinia variegate-A
comparative study. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 3:479–486.
2014.
|
|
60
|
Rossmeisl M, Rim JS, Koza RA and Kozak LP:
Variation in type 2 diabetes-related traits in mouse strains
susceptible to diet-induced obesity. Diabetes. 52:1958–1966. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bullen JW Jr, Ziotopoulou M, Ungsunan L,
Misra J, Alevizos I, Kokkotou E, Maratos-Flier E, Stephanopoulos G
and Mantzoros CS: Short-term resistance to diet-induced obesity in
A/J mice is not associated with regulation of hypothalamic
neuropeptides. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 287:E662–E670. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Insulin resistance,
inflammation, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 19:371–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
van Herpen NA and Schrauwen-Hinderling VB:
Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol
Behav. 94:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Toye AA, Dumas ME, Blancher C, Rothwell
AR, Fearnside JF, Wilder SP, Bihoreau MT, Cloarec O, Azzouzi I,
Young S, et al: Subtle metabolic and liver gene transcriptional
changes underlie diet-induced fatty liver susceptibility in
insulin-resistant mice. Diabetologia. 50:1867–1879. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Imano H, Noda H, Kitamura A, Sato S,
Kiyama M, Sankai T, Ohira T, Nakamura M, Yamagishi K, Ikeda A, et
al: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of coronary heart
disease among Japanese men and women: The circulatory risk in
communities study (CIRCS). Prev Med. 52:381–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Brewer HB Jr: High-density lipoprotein: A
new potential therapeutic target for the prevention of
cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:387–391.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bonini JA, Colca JR, Dailey C, White M and
Hofmann C: Compensatory alterations for insulin signal transduction
and glucose transport in insulin-resistant diabetes. Am J Physiol.
269:E759–E765. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Park HK and Ahima RS: Physiology of
leptin: Energy homeostasis, neuroendocrine function and metabolism.
Metabolism. 64:24–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Friedman JM and Halaas JL: Leptin and the
regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 395:763–770. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fasshauer M and Paschke R: Regulation of
adipokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 46:1594–1603.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chao J, Huo TI, Cheng HY, Tsai JC, Liao
JW, Lee MS, Qin XM, Hsieh MT, Pao LH and Peng WH: Gallic acid
ameliorated impaired glucose and lipid homeostasis in high fat
diet-induced NAFLD mice. PLoS One. 9:e969692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ye JH, Chao J, Chang ML, Peng WH, Cheng
HY, Liao JW and Pao LH: Pentoxifylline ameliorates non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease in hyperglycaemic and dyslipidaemic mice by
upregulating fatty acid β-oxidation. Sci Rep. 6:331022016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Liu X, Xu J, Xue Y, Gao Z, Li Z, Leng K,
Wang J, Xue C and Wang Y: Sea cucumber cerebrosides and long-chain
bases from Acaudina molpadioides protect against high fat
diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Food Funct. 6:3428–3436.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kuo YH, Lin CH and Shih CC:
Ergostatrien-3β-ol from Antrodia camphorata inhibits diabetes and
hyperlipidemia in high-fat-diet treated mice via regulation of
hepatic related genes, glucose transporter 4, and AMP-activated
protein kinase phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem. 63:2479–2489.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Soret MG, Kupieeki FP and Wyse BM:
Epididymal fat pad alterations in mice with spontaneous obesity and
diabetes and with chemically induced obesity. Diabetologia.
10(Suppl): S639–S648. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Moffat C and Harper ME: Metabolic
functions of AMPK: Aspects of structure and of natural mutations in
the regulatory gamma subunits. IUBMB Life. 62:739–745. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang T, Sawada K, Yamamoto N and Ashida
H: 4-Hydroxyderricin and xanthoangelol from ashitaba (Angelica
keiskei) suppress differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes
via AMPK and MAPK pathways. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:1729–1740.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Schreurs M, Kuipers F and van der Leij FR:
Regulatory enzymes of mitochondrial beta-oxidation as targets for
treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev. 11:380–388. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Eo H, Jeon YJ, Lee M and Lim Y: Brown Alga
Ecklonia cava polyphenol extract ameliorates hepatic lipogenesis,
oxidative stress, and inflammation by activation of AMPK and SIRT1
in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Agric Food Chem. 63:349–359.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Farmer SR: Regulation of PPARgamma
activity during adipogenesis. Int J Obes (Lond). 29(Suppl 1):
S13–S16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ha do T, Trung TN, Phuong TT, Yim N, Chen
QC and Bae K: The selected flavonol glycoside derived from Sophorae
Flos improves glucose uptake and inhibits adipocyte differentiation
via activation AMPK in 3T3-L1 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
20:6076–6081. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Karim S, Adams DH and Lalor PF: Hepatic
expression and cellular distribution of the glucose transporter
family. World J Gastroenterol. 18:6771–6781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Kim S, Jung J, Kim H, Heo RW, Yi CO, Lee
JE, Jeon BT, Kim WH, Hahm JR and Roh GS: Exendin-4 improves
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating glucose transporter
4 expression in ob/ob mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 18:333–339.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|