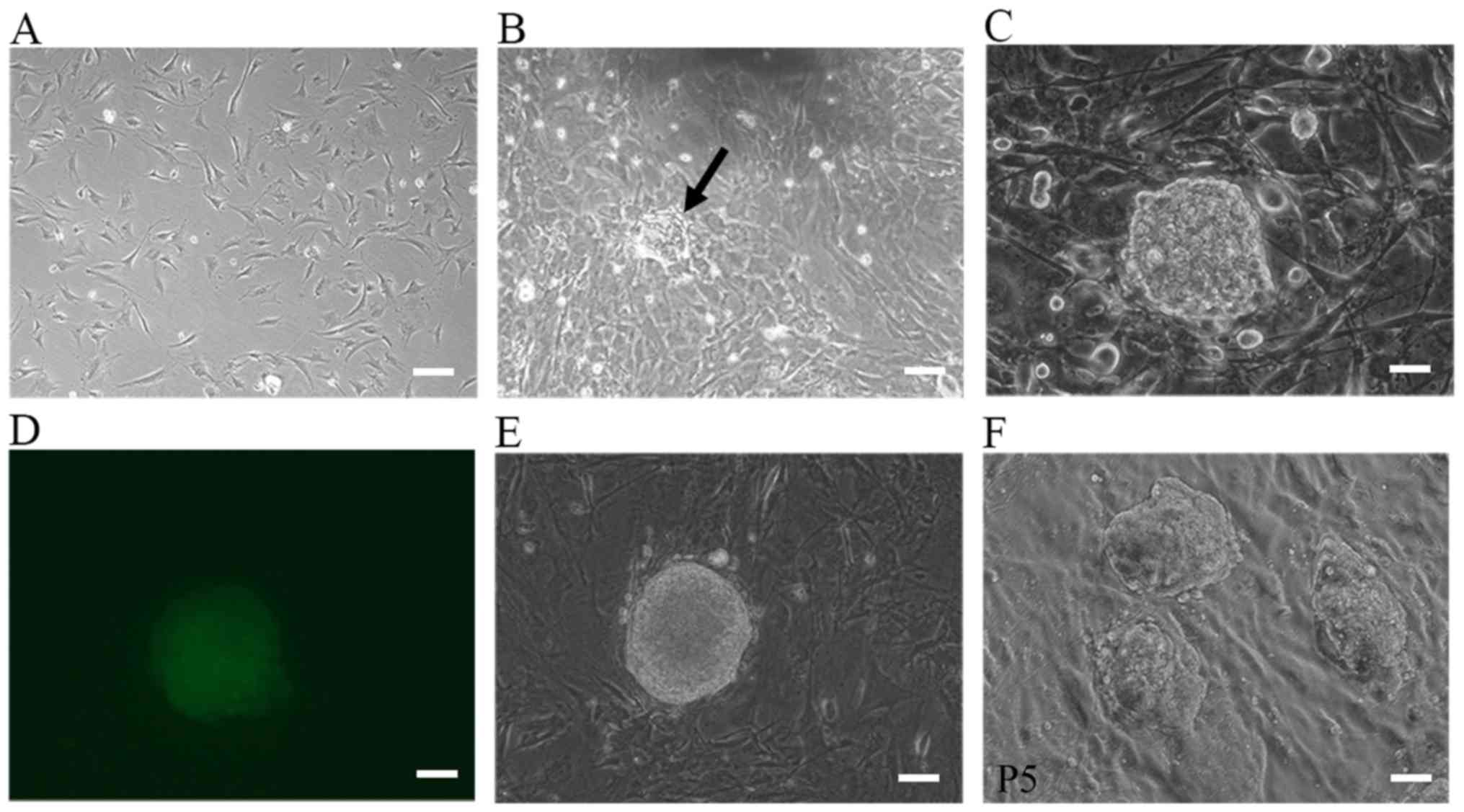
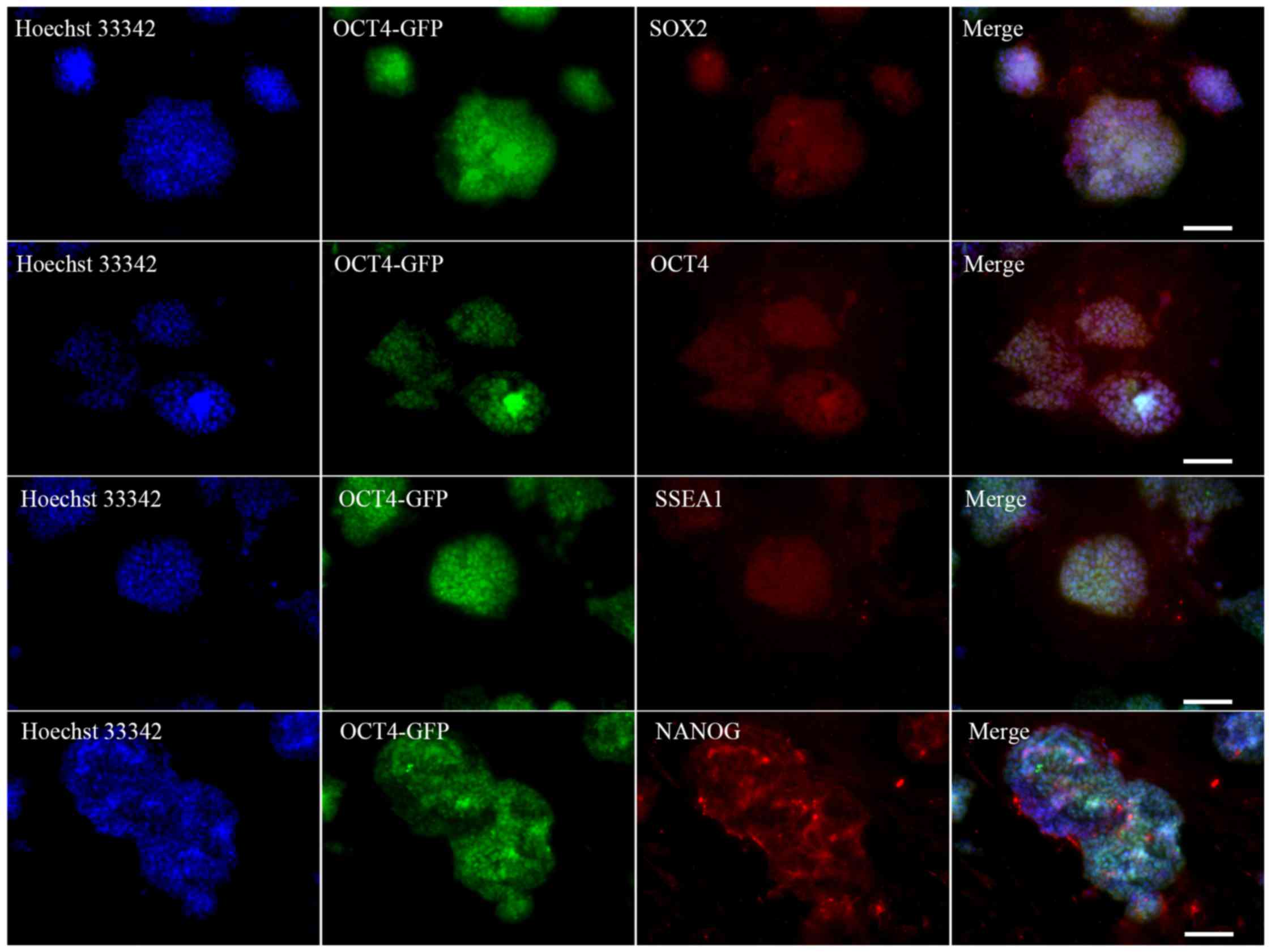
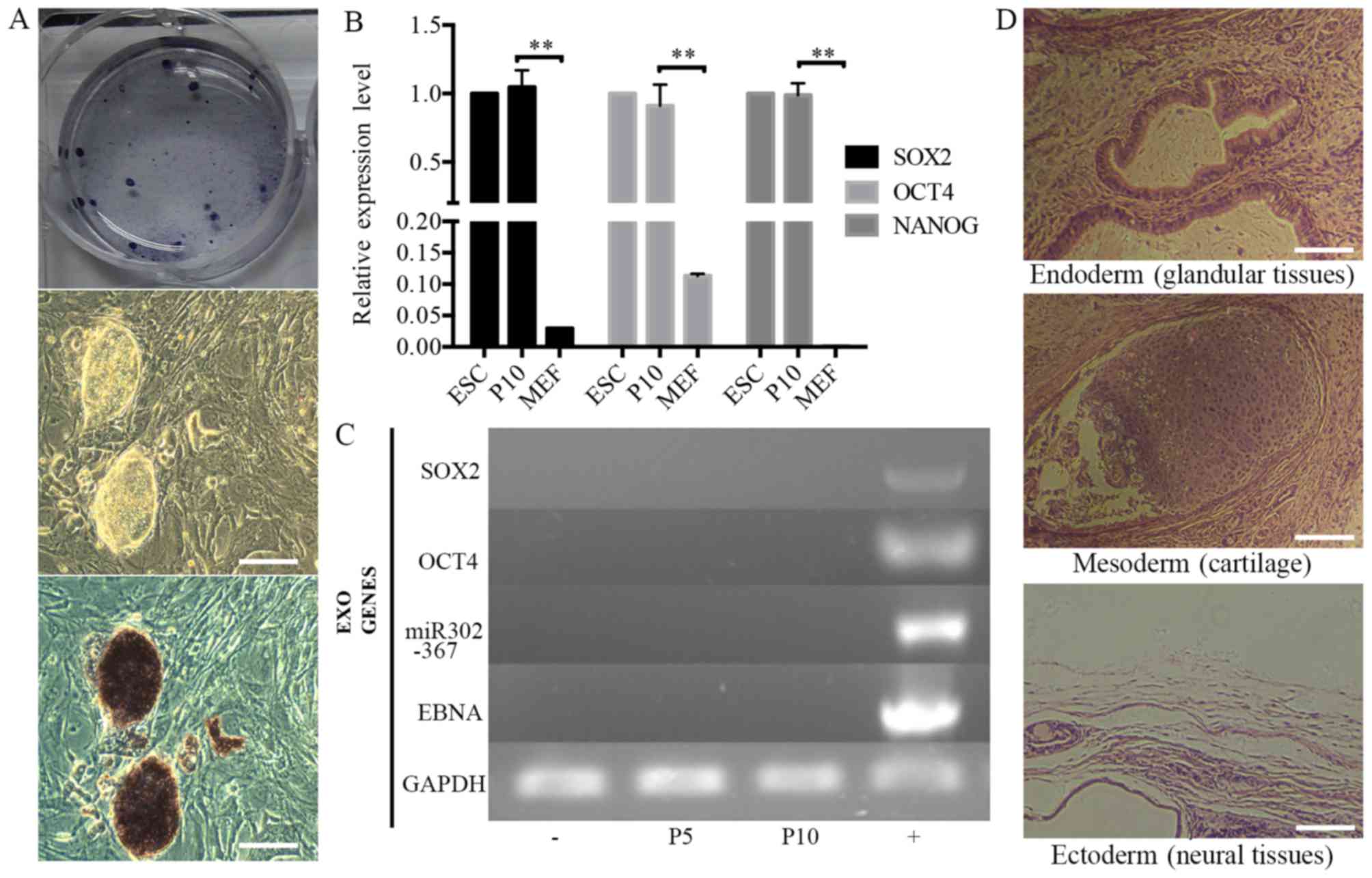
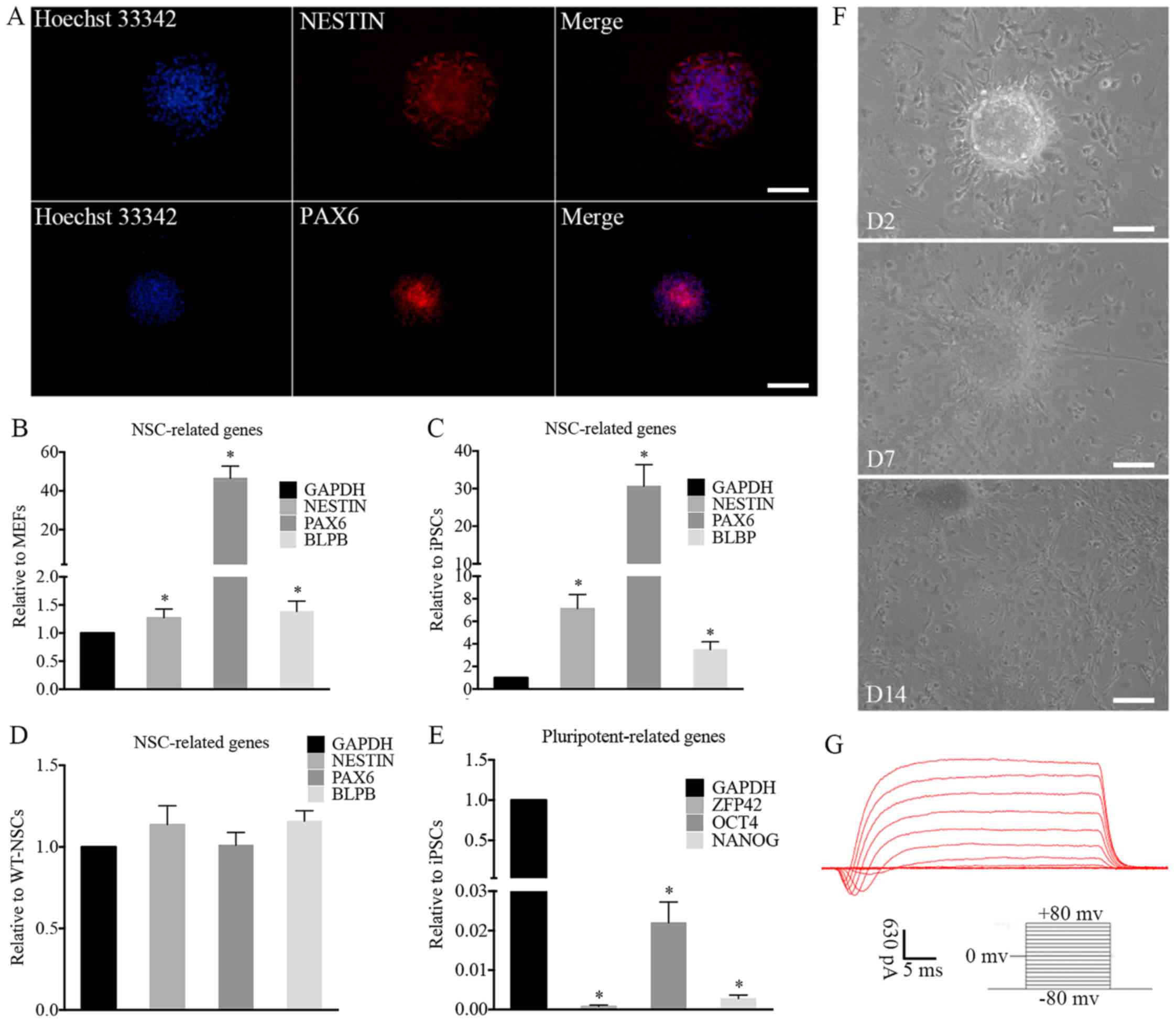
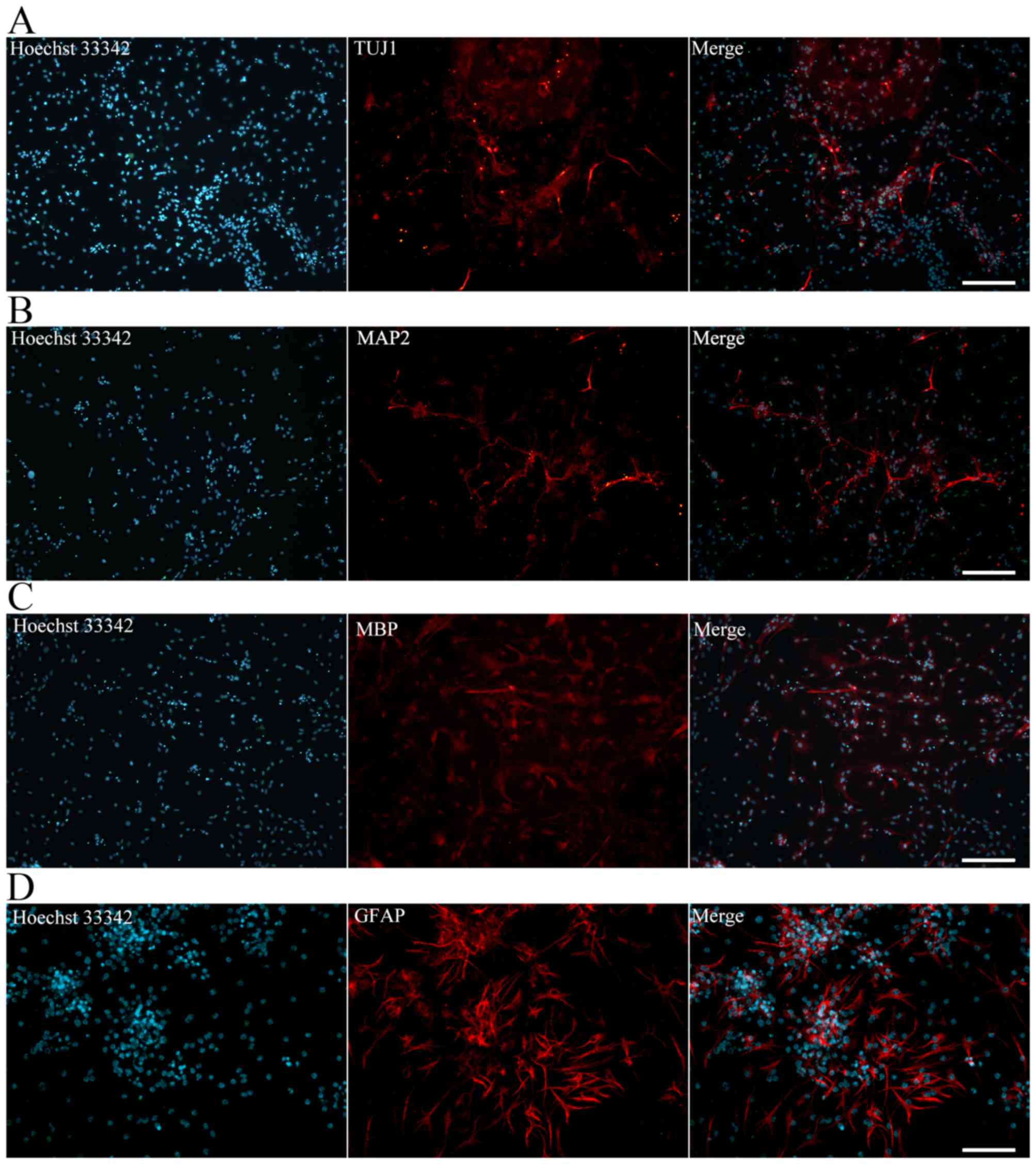
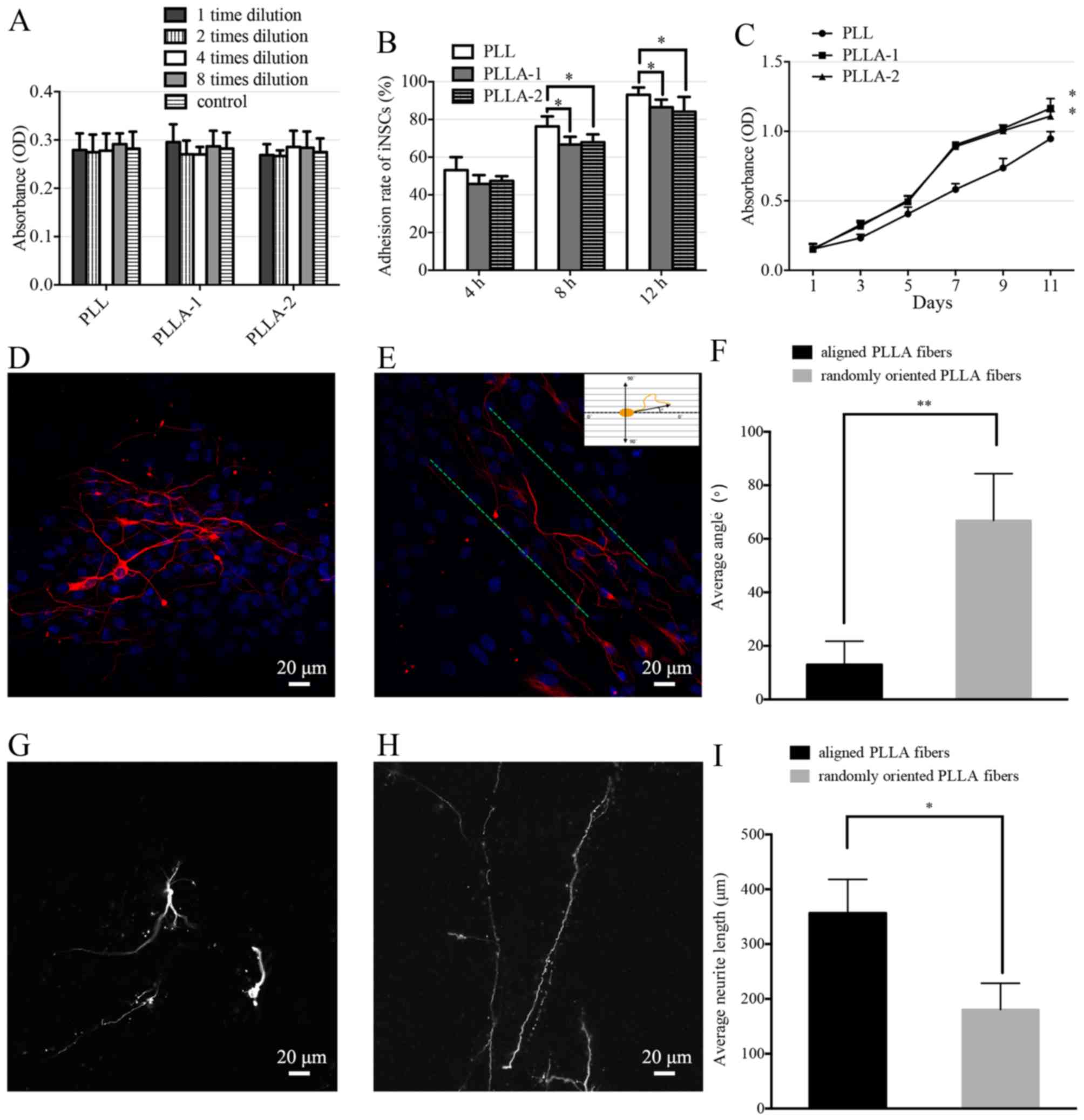
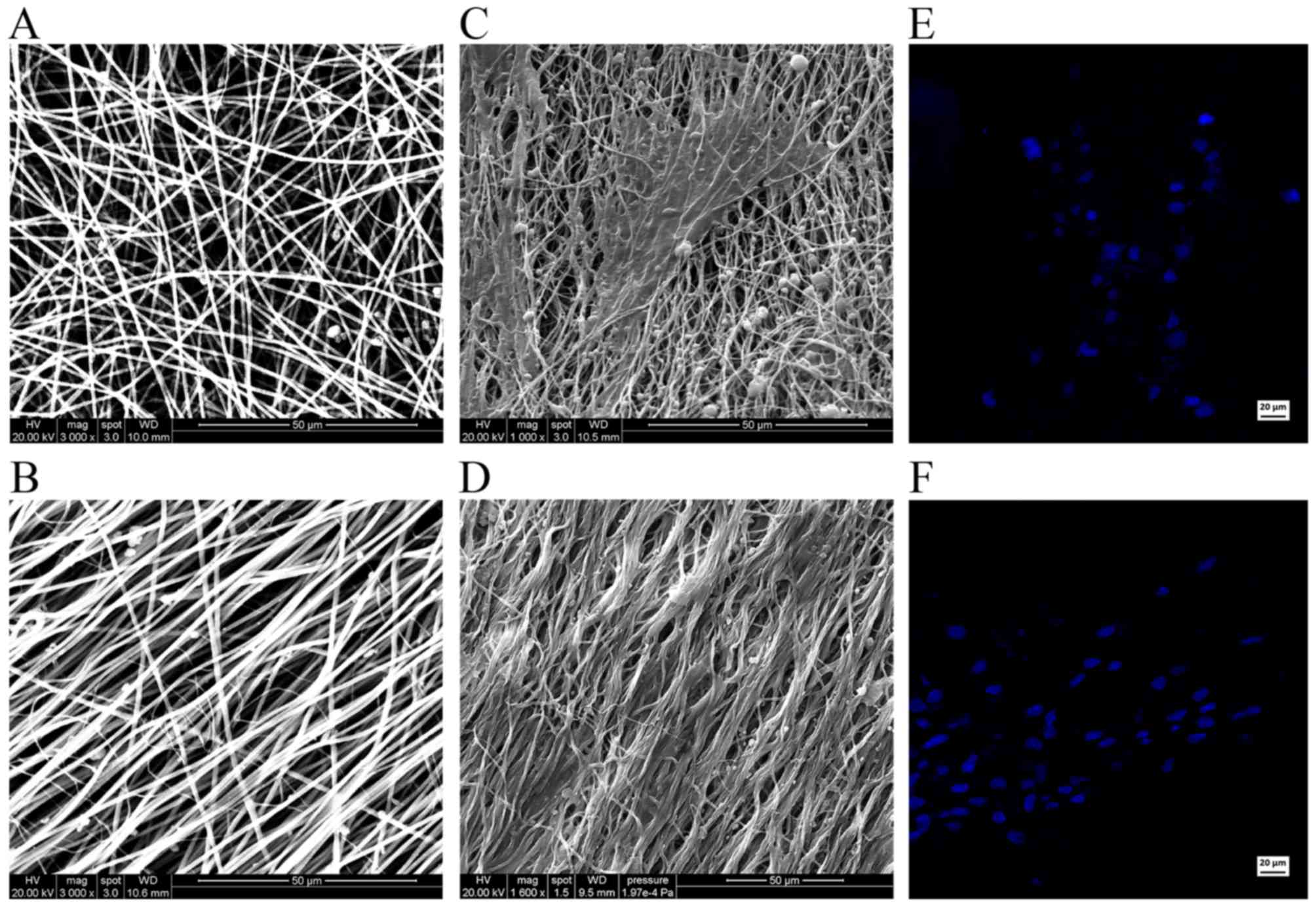
|
1
|
Nichols CM, Brenner MJ, Fox IK, Tung TH,
Hunter DA, Rickman SR and Mackinnon SE: Effects of motor versus
sensory nerve grafts on peripheral nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol.
190:347–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
IJkema-Paassen J, Jansen K, Gramsbergen A
and Meek MF: Transection of peripheral nerves, bridging strategies
and effect evaluation. Biomaterials. 25:1583–1592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Evans NR, Davies EM, Dare CJ and Oreffo
RO: Tissue engineering strategies in spinal arthrodesis: the
clinical imperative and challenges to clinical translation. Regen
Med. 8:49–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ziv Y, Avidan H, Pluchino S, Martino G and
Schwartz M: Synergy between immune cells and adult neural
stem/progenitor cells promotes functional recovery from spinal cord
injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:13174–13179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu Y and Wang MY: Neural stem cell grafts
for complete spinal cord injury. Neurosurgery. 71:N13–N15. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Piltti KM, Salazar DL, Uchida N, Cummings
BJ and Anderson AJ: Safety of human neural stem cell
transplantation in chronic spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Transl
Med. 2:961–974. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choi HW, Kim JS, Choi S, Hong YJ, Kim MJ,
Seo HG and Do JT: Neural stem cells differentiated from iPS cells
spontaneously regain pluripotency. Stem Cells. 32:2596–2604. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen X, Gu Q, Wang X, Ma Q, Tang H, Yan X,
Guo X, Yan H, Hao J and Zeng F: Directed neuronal differentiation
of mouse embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells and their
gene expression profiles. Int J Mol Med. 32:25–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okita K, Ichisaka T and Yamanaka S:
Generation of germ-line-competent induced pluripotent stem cells.
Nature. 448:313–317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Briggs JA, Sun J, Shepherd J, Ovchinnikov
DA, Chung TL, Nayler SP, Kao LP, Morrow CA, Thakar NY, Soo SY, et
al: Integration-free induced pluripotent stem cells model genetic
and neural developmental features of down syndrome etiology. Stem
Cells. 31:467–478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hoveizi E, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Tavakol S
and Sanamiri K: In vitro differentiation of human iPS cells into
neural like cells on a biomimetic polyurea. Mol Neurobiol.
54:601–607. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pham QP, Sharma U and Mikos AG:
Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering
applications: a review. Tissue Eng. 12:1197–1211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ebrahimi-Barough S, Hoveizi E, Norouzi
Javidan A and Ai J: Investigating the neuroglial differentiation
effect of neuroblastoma conditioned medium in human endometrial
stem cells cultured on 3D nanofibrous scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 103:2621–2627. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang HB, Mullins ME, Cregg JM, McCarthy CW
and Gilbert RJ: Varying the diameter of aligned electrospun fibers
alters neurite outgrowth and Schwann cell migration. Acta Biomater.
6:2970–2978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kabiri M, Oraee-Yazdani S, Shafiee A,
Hanaee-Ahvaz H, Dodel M, Vaseei M and Soleimani M:
Neuroregenerative effects of olfactory ensheathing cells
transplanted in a multi-layered conductive nanofibrous conduit in
peripheral nerve repair in rats. J Biomed Sci. 22:352015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lim SH and Mao HQ: Electrospun scaffolds
for stem cell engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:1084–1096. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L, Prabhakaran MP,
Morshed M, Nasr-Esfahani MH and Ramakrishna S: Electrospun
poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve
tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 29:4532–4539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu Y, Lü X and Ding F: influence of
poly(L-lactic acid) aligned nanofibers on C12 differentiation. J
Biomed Nanotechnol. 11:816–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Huang Y, Pang M, Yang Y, Li S, Liu
L, Shu T, Zhou W, Wang X, Rong L, et al: Tissue-engineered
regeneration of completely transected spinal cord using induced
neural stem cells and gelatin-electrospun poly
(lactide-co-glycolide)/polyethylene glycol scaffolds. PLoS One.
10:pp. e01177092015, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meijering E, Jacob M, Sarria JC, Steiner
P, Hirling H and Unser M: Design and validation of a tool for
neurite tracing and analysis in fluorescence microscopy images.
Cytometry A. 58:167–176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
22(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
David S and Aguayo AJ: Axonal elongation
into peripheral nervous system 'bridges' after central nervous
system injury in adult rats. Science. 214:931–933. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Johnson EO, Zoubos AB and Soucacos PN:
Regeneration and repair of peripheral nerves. Injury. 36(Suppl 4):
S24–S29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Darsalia V, Kallur T and Kokaia Z:
Survival, migration and neuronal differentiation of human fetal
striatal and cortical neural stem cells grafted in stroke-damaged
rat striatum. Eur J Neurosci. 26:605–614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paul C, Samdani AF, Betz RR, Fischer I and
Neuhuber B: Grafting of human bone marrow stromal cells into spinal
cord injury: a comparison of delivery methods. Spine. 34:328–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu G, Cheng Y, Guo S, Feng Y, Li Q, Jia
H, Wang Y, Tong L and Tong X: Transplantation of adipose-derived
stem cells for peripheral nerve repair. Int J Mol Med. 28:565–572.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park Ki, Teng YD and Snyder EY: The
injured brain interacts reciprocally with neural stem cells
supported by scaffolds to reconstitute lost tissue. Nat Biotechnol.
20:1111–1117. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ring KL, Tong LM, Balestra ME, Javier R,
Andrews-Zwilling Y, Li G, Walker D, Zhang WR, Kreitzer AC and Huang
Y: Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into
multi-potent neural stem cells with a single factor. Cell Stem
Cell. 11:100–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Elkabetz Y and Studer L: Human ESC-derived
neural rosettes and neural stem cell progression. Cold Spring Harb
Symp Quant Biol. 73:377–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi Y, Okada Y, Itakura G, Iwai H,
Nishimura S, Yasuda A, Nori S, Hikishima K, Konomi T, Fujiyoshi K,
et al: Pre-evaluated safe human iPSC-derived neural stem cells
promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury in common
marmoset without tumorigenicity. PloS one. 7:e527872012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aboody K, Capela A, Niazi N, Stern JH and
Temple S: Translating stem cell studies to the clinic for CNS
repair: current state of the art and the need for a Rosetta stone.
Neuron. 70:597–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okita K, Matsumura Y, Sato Y, Okada A,
Morizane A, Okamoto S, Hong H, Nakagawa M, Tanabe K, Tezuka K, et
al: A more efficient method to generate integration-free human iPS
cells. Nat Methods. 8:409–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fusaki N, Ban H, Nishiyama A, Saeki K and
Hasegawa M: Efficient induction of transgene-free human pluripotent
stem cells using a vector based on Sendai virus, an RNA virus that
does not integrate into the host genome. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 85:348–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Talluri TR, Kumar D, Glage S, Garrels W,
Ivics Z, Debowski K, Behr R and Kues WA: Non-viral reprogramming of
fibroblasts into induced pluripotent stem cells by Sleeping Beauty
and piggyBac transposons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:581–587.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jia F, Wilson KD, Sun N, Gupta DM, Huang
M, Li Z, Panetta NJ, Chen ZY, Robbins RC, Kay MA, et al: A nonviral
minicircle vector for deriving human iPS cells. Nat Methods.
7:197–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim D, Kim CH, Moon Ji, Chung YG, Chang
MY, Han BS, Ko S, Yang E, Cha KY, Lanza R, et al: Generation of
human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of
reprogramming proteins. Cell Stem Cell. 4:472–476. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu S, Wilson KD, Ghosh Z, Han L, Wang Y,
Lan F, Ransohoff KJ, Burridge P and Wu JC: MicroRNA-302 increases
repro gramming efficiency via repression of NR2F2. Stem Cells.
31:259–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Yu J, Hu K, Smuga-Otto K, Tian S, Stewart
R, Slukvin II and Thomson JA: Human induced pluripotent stem cells
free of vector and transgene sequences. Science. 324:797–801. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wrobel MR and Sundararaghavan HG: Directed
migration in neural tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
20:93–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hoveizi E, Tavakol S and Ebrahimi-Barough
S: Neuroprotective effect of transplanted neural precursors
embedded on PLA/CS scaffold in an animal model of multiple
sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol. 51:1334–1342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li J and Shi R: Fabrication of patterned
multi-walled poly-l-lactic acid conduits for nerve regeneration. J
Neurosci Methods. 165:257–264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hurtado A, Cregg JM, Wang HB, Wendell DF,
Oudega M, Gilbert RJ and McDonald JW: Robust CNS regeneration after
complete spinal cord transection using aligned poly-L-lactic acid
microfibers. Biomaterials. 32:6068–6079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|