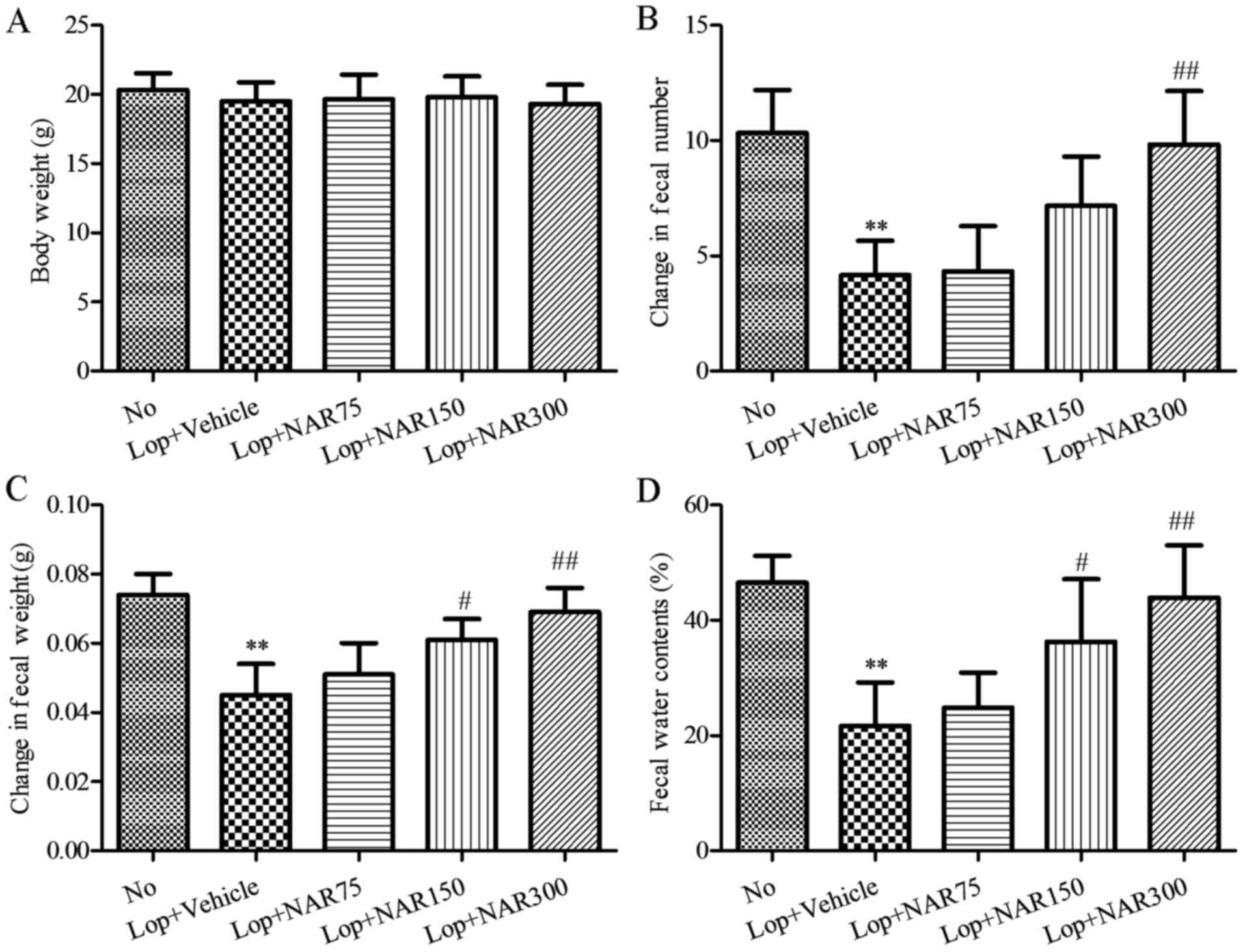
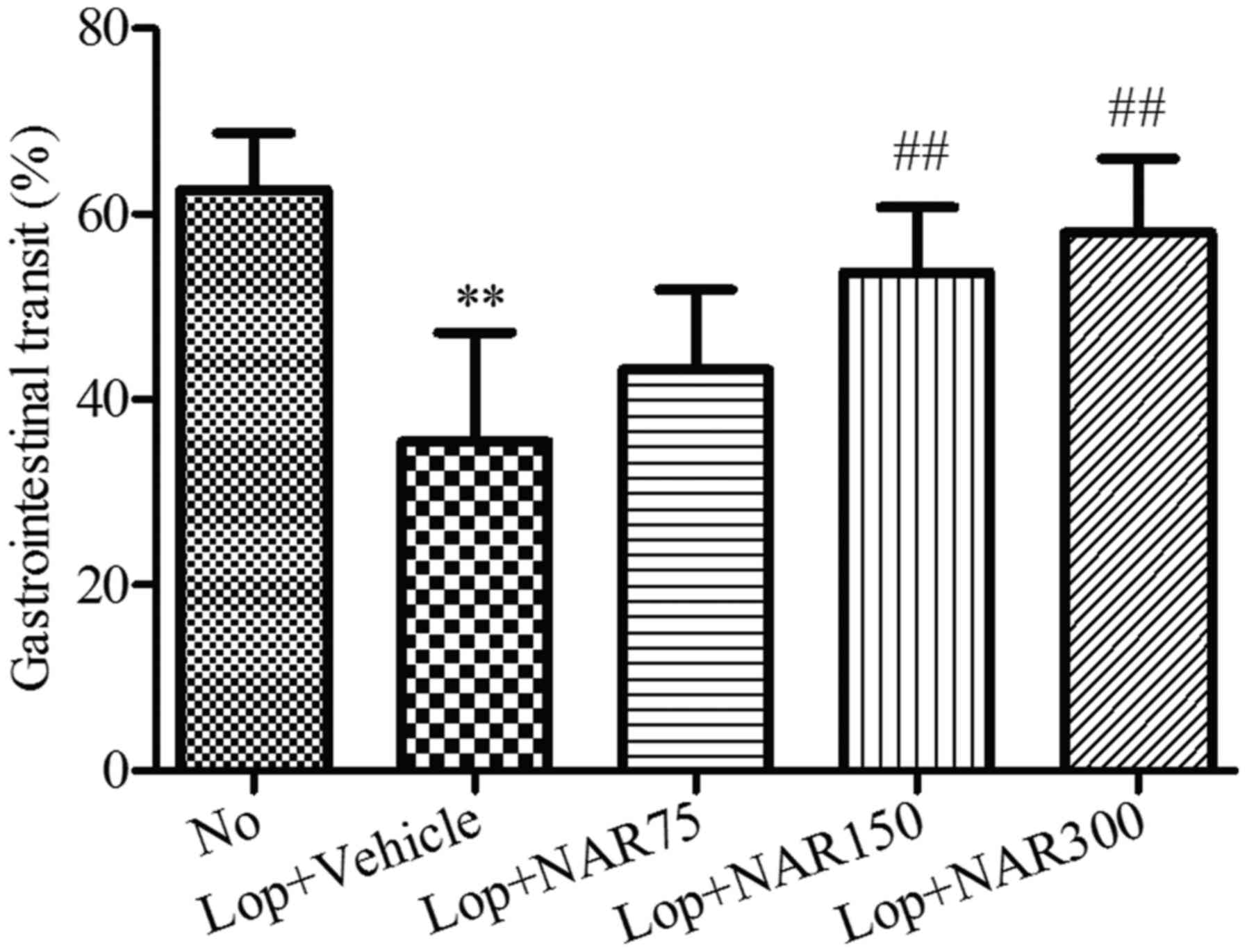
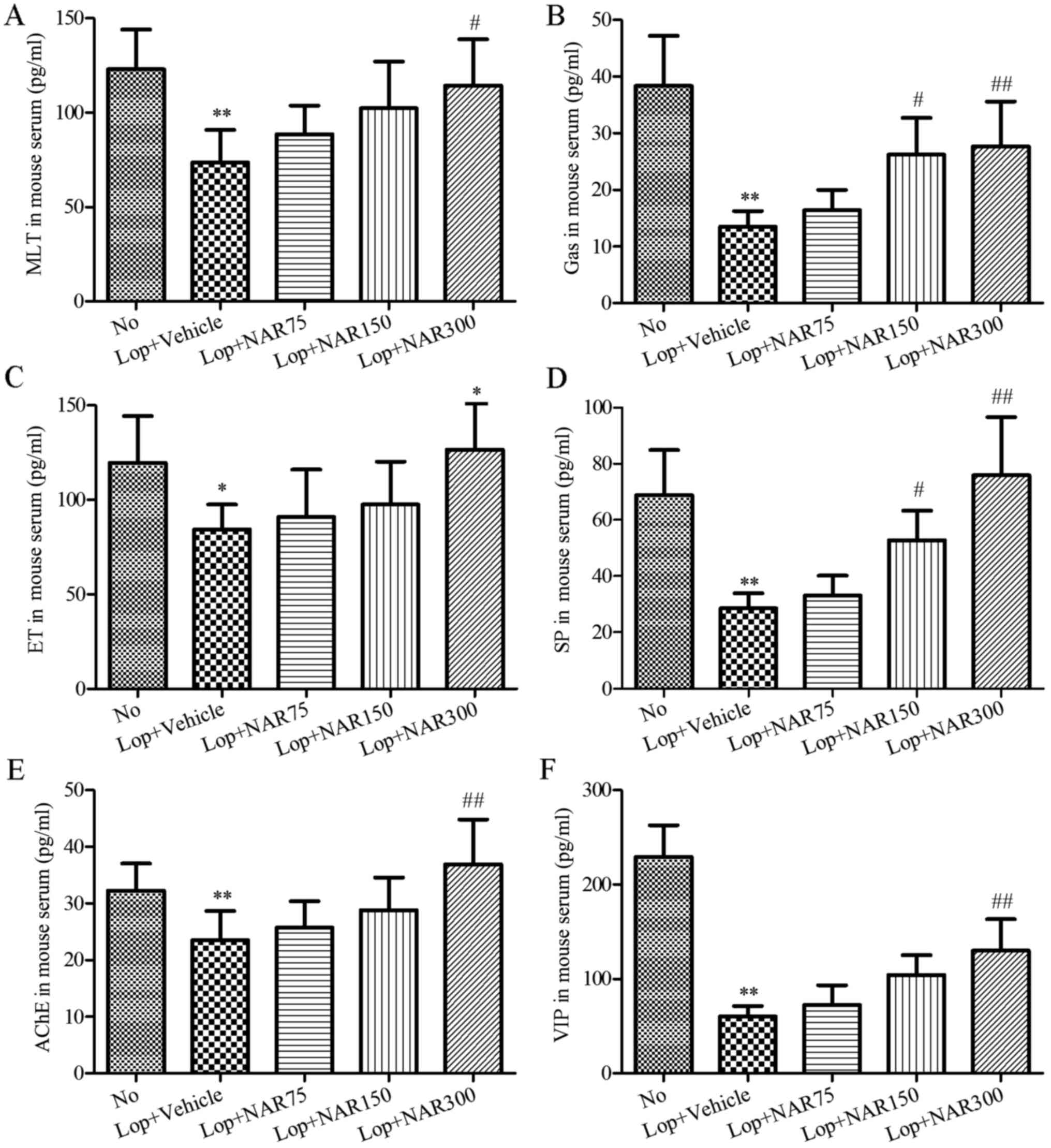
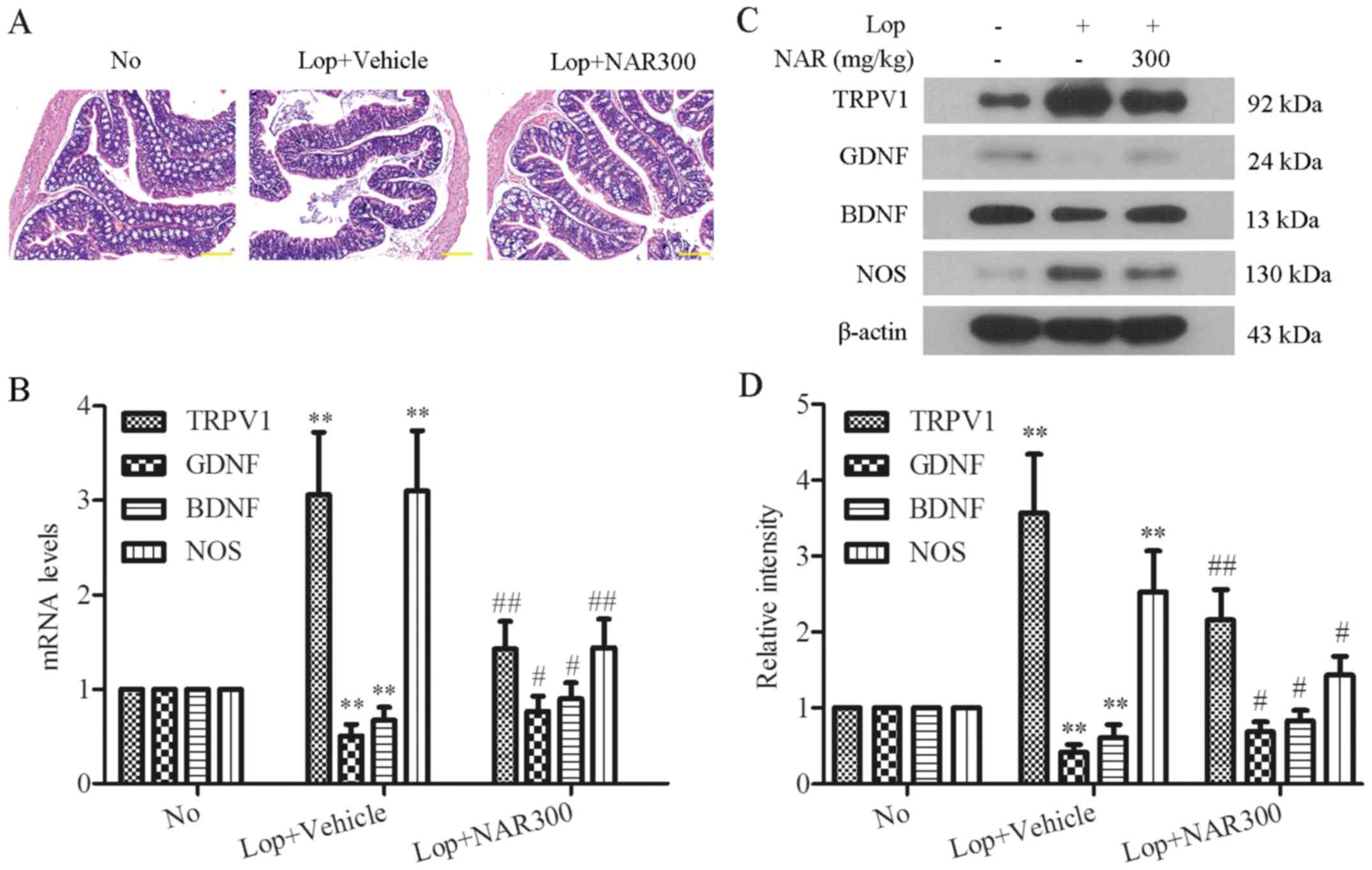
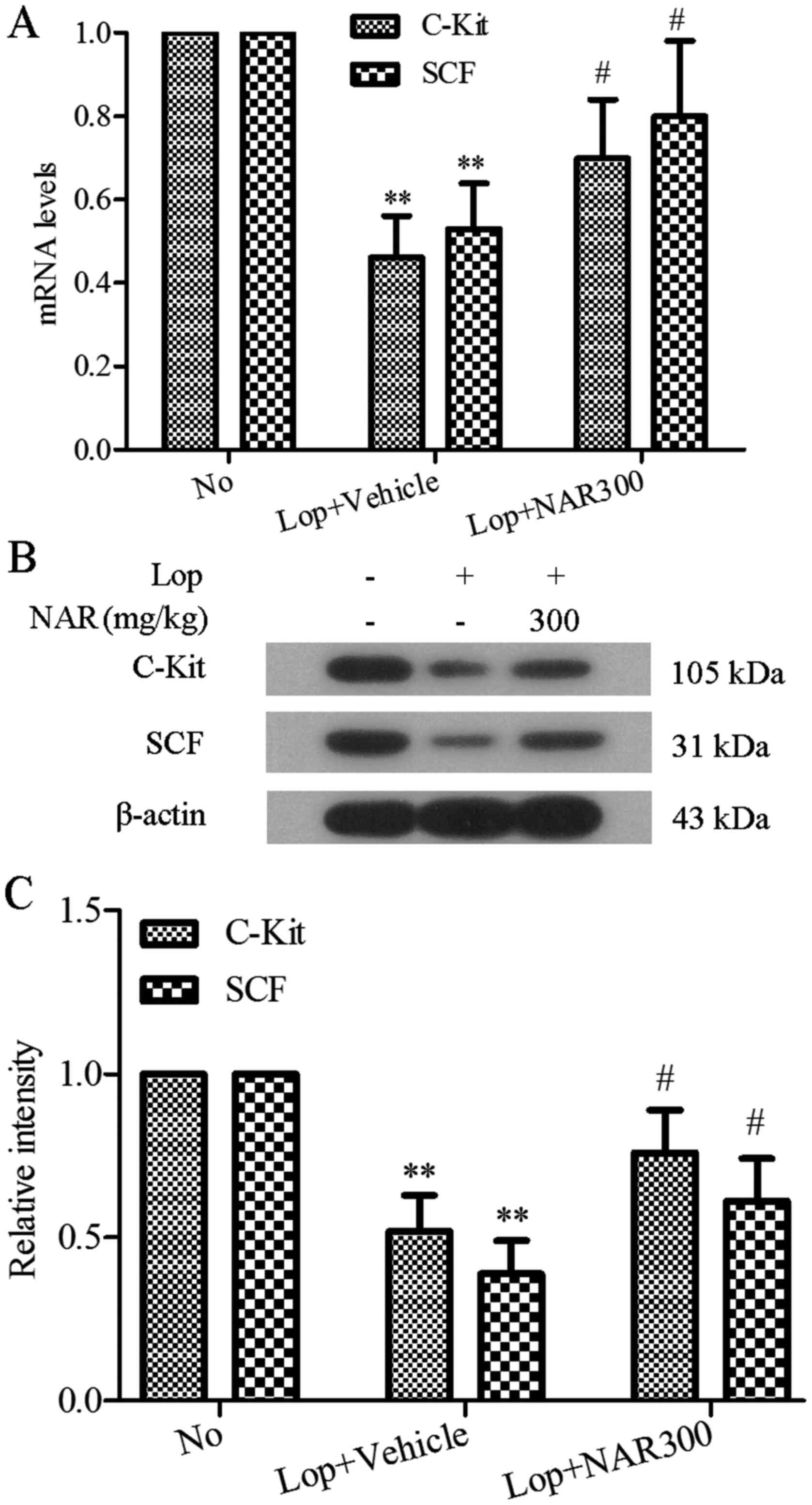
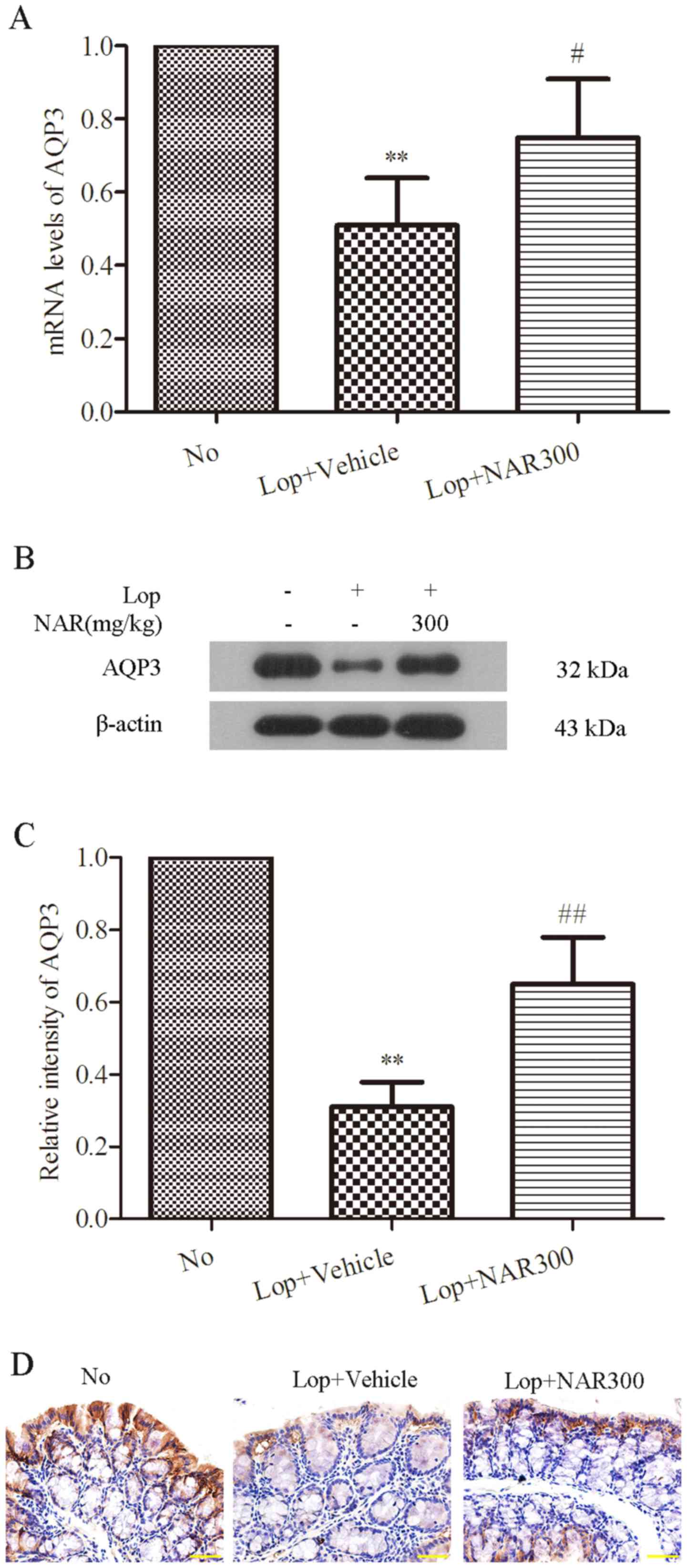
|
1
|
Bassotti G and Blandizzi C: Understanding
and treating refractory constipation. World J Gastrointest
Pharmacol Ther. 5:77–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bassotti G: Understanding constipation
treatment: do we need to strain to obtain better results? Expert
Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 9:387–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mostafa SM, Bhandari S, Ritchie G, Gratton
N and Wenstone R: Constipation and its implications in the
critically ill patient. Br J Anaesth. 91:815–819. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouyang A and Locke GR 3rd: Overview of
neurogastroenterology-gastrointestinal motility and functional GI
disorders: classification, prevalence, and epidemiology.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 36:485–498. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang HL: Understanding the pathogenesis of
slow-transit constipation: one step forward. Dig Dis Sci.
60:2216–2218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He CL, Burgart L, Wang L, Pemberton J,
Young-Fadok T, Szurszewski J and Farrugia G: Decreased interstitial
cell of cajal volume in patients with slow-transit constipation.
Gastroenterology. 118:14–21. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Andromanakos NP, Pinis SI and Kostakis AI:
Chronic severe constipation: current pathophysiological aspects,
new diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic options. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:204–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chan OT, Chiles L, Levy M, Zhai J, Yerian
LM, Xu H, Xiao SY, Soffer EE, Conklin JL, Dhall D, et al:
Smoothelin expression in the gastrointestinal tract: implication in
colonic inertia. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 21:452–459.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Renugadevi J and Prabu SM: Cadmium-induced
hepatotoxicity in rats and the protective effect of naringenin. Exp
Toxicol Pathol. 62:171–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ekambaram G, Rajendran P, Magesh V and
Sakthisekaran D: Naringenin reduces tumor size and weight lost in
N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric carcinogenesis
in rats. Nutr Res. 28:106–112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang ZH, Yu HJ, Pan A, Du JY, Ruan YC, Ko
WH, Chan HC and Zhou WL: Cellular mechanisms underlying the
laxative effect of flavonol naringenin on rat constipation model.
PLoS On. 3:pp. e33482008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yamamoto T, Watabe K, Nakahara M, Ogiyama
H, Kiyohara T, Tsutsui S, Tamura S, Shinomura Y and Hayashi N:
Disturbed gastrointestinal motility and decreased interstitial
cells of Cajal in diabetic db/db mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:660–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chai Y, Huang Y, Tang H, Tu X, He J, Wang
T, Zhang Q, Xiong F, Li D and Qiu Z: Role of stem cell growth
factor/c-Kit in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Exp
Ther Med. 13:1187–1193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wald A: Chronic constipation: advances in
management. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 19:4–10. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wintola OA, Sunmonu TO and Afolayan AJ:
The effect of Aloe ferox Mill. in the treatment of
loperamide-induced constipation in Wistar rats. BMC Gastroenterol.
10:952010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kakino M, Tazawa S, Maruyama H, Tsuruma K,
Araki Y, Shimazawa M and Hara H: Laxative effects of agarwood on
low-fiber diet-induced constipation in rats. BMC Complemen. Altern
Med. 10:682010.
|
|
17
|
Hughes S, Higgs NB and Turnberg LA:
Loperamide has antisecretory activity in the human jejunum in vivo.
Gut. 25:931–935. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamada K and Onoda Y: Comparison of the
effects of T-1815, yohimbine and naloxone on mouse colonic
propulsion. J Smooth Muscle Res. 29:47–53. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sohji Y, Kawashima K and Shimizu M:
[Pharmacological studies of loperamide, an anti-diarrheal agent.
II. Effects on peristalsis of the small intestine and colon in
guinea pigs (author's transl)]. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi.
74:155–163. 1978.In Japanese. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HY, Kim JH, Jeung HW, Lee CU, Kim DS,
Li B, Lee GH, Sung MS, Ha KC, Back HI, et al: Effects of Ficus
carica paste on loperamide-induced constipation in rats. Food Chem
Toxicol. 50:895–902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kakino M, Izuta H, Ito T, Tsuruma K, Araki
Y, Shimazawa M, Oyama M, Iinuma M and Hara H: Agarwood induced
laxative effects via acetylcholine receptors on loperamide-induced
constipation in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:1550–1555.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Zhao XR, Wang R, Qiu GQ and Zhang
M: Effect of Zhizhuwan on gastrointestinal peptide concentrations
in plasma of diabetic gastroenteropathy with constipation patients.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 33:2966–2968. 2008.In Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Suo H, Zhao X, Qian Y, Li G, Liu Z, Xie J
and Li J: Therapeutic effect of activated carbon-induced
constipation mice with Lactobacillus fermentum Suo on treatment.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:21875–21895. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iijima K, Koike T, Abe Y and Shimosegawa
T: Cutoff serum pepsinogen values for predicting gastric acid
secretion status. Tohoku J Exp Med. 232:293–300. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fevang J, Ovrebø K, Myking O, Grong K and
Svanes K: Role of endothelin in the circulatory changes associated
with small bowel strangulation obstruction in pigs: effects of the
endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan. J Surg Res. 96:224–232.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yik YI, Farmer PJ, King SK, Chow CW,
Hutson JM and Southwell BR: Gender differences in reduced substance
P (SP) in children with slow-transit constipation. Pediatr Surg
Int. 27:699–704. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moriya R, Fujikawa T, Ito J, Shirakura T,
Hirose H, Suzuki J, Fukuroda T, Macneil DJ and Kanatani A:
Pancreatic polypeptide enhances colonic muscle contraction and
fecal output through neuropeptide Y Y4 receptor in mice.
Eur J Pharmacol. 627:258–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
King SK, Sutcliffe JR, Ong SY, Lee M, Koh
TL, Wong SQ, Farmer PJ, Peck CJ, Stanton MP, Keck J, et al:
Substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide are reduced in right
transverse colon in pediatric slow-transit constipation.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 22:883–892. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geppetti P and Trevisani M: Activation and
sensitisation of the vanilloid receptor: role in gastrointestinal
inflammation and function. Br J Pharmacol. 141:1313–1320. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rodrigues DM, Li AY, Nair DG and
Blennerhassett MG: Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is a
key neurotrophin in the postnatal enteric nervous system.
Neurogastroenterol Moti. 23:e44–e56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Saffrey MJ: Cellular changes in the
enteric nervous system during ageing. Dev Biol. 382:344–355. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen F, Yu Y, Wang P, Dong Y, Wang T, Zuo
X and Li Y: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor accelerates gut
motility in slow-transit constipation. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 212:pp.
226–238. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Peregud DI, Yakovlev AA, Stepanichev MY,
Onufriev MV, Panchenko LF and Gulyaeva V: Expression of BDNF and
TrkB phosphorylation in the rat frontal cortex during morphine
withdrawal are NO dependent. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 36:839–849. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tomita R, Igarashi S, Fujisaki S and
Tanjoh K: The effects of neurotensin in the colon of patients with
slow transit constipation. Hepatogastroenterology. 54:1662–1666.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu J, Chen Y, Liu S and Hou X:
Electroacupuncture regulates apoptosis/proliferation of
intramuscular interstitial cells of cajal and restores colonic
motility in diabetic constipation rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 584179:2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Farrugia G: Interstitial cells of Cajal in
health and disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 20:54–63. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yu CS, Kim HC, Hong HK, Chung DH, Kim HJ,
Kang GH and Kim JC: Evaluation of myenteric ganglion cells and
interstitial cells of Cajal in patients with chronic idiopathic
constipation. Int J Colorectal Dis. 17:253–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mostafa RM, Moustafa YM and Hamdy H:
Interstitial cells of Cajal, the Maestro in health and disease.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:3239–3248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Parthasarathy G, Chen J, Chia N, O'Connor
HM, Gaskins HR and Bharucha AE: Reproducibility of assessing fecal
microbiota in chronic constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
29:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Silberstein C, Kierbel A, Amodeo G, Zotta
E, Bigi F, Berkowski D and Ibarra C: Functional characterization
and localization of AQP3 in the human colon. Braz J Med Biol Res.
32:1303–1313. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kon R, Ikarashi N, Hayakawa A, Haga Y,
Fueki A, Kusunoki Y, Tajima M, Ochiai W, Machida Y and Sugiyama K:
Morphine-induced constipation develops with increased aquaporin-3
expression in the colon via increased serotonin secretion. Toxicol
Sci. 145:337–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|