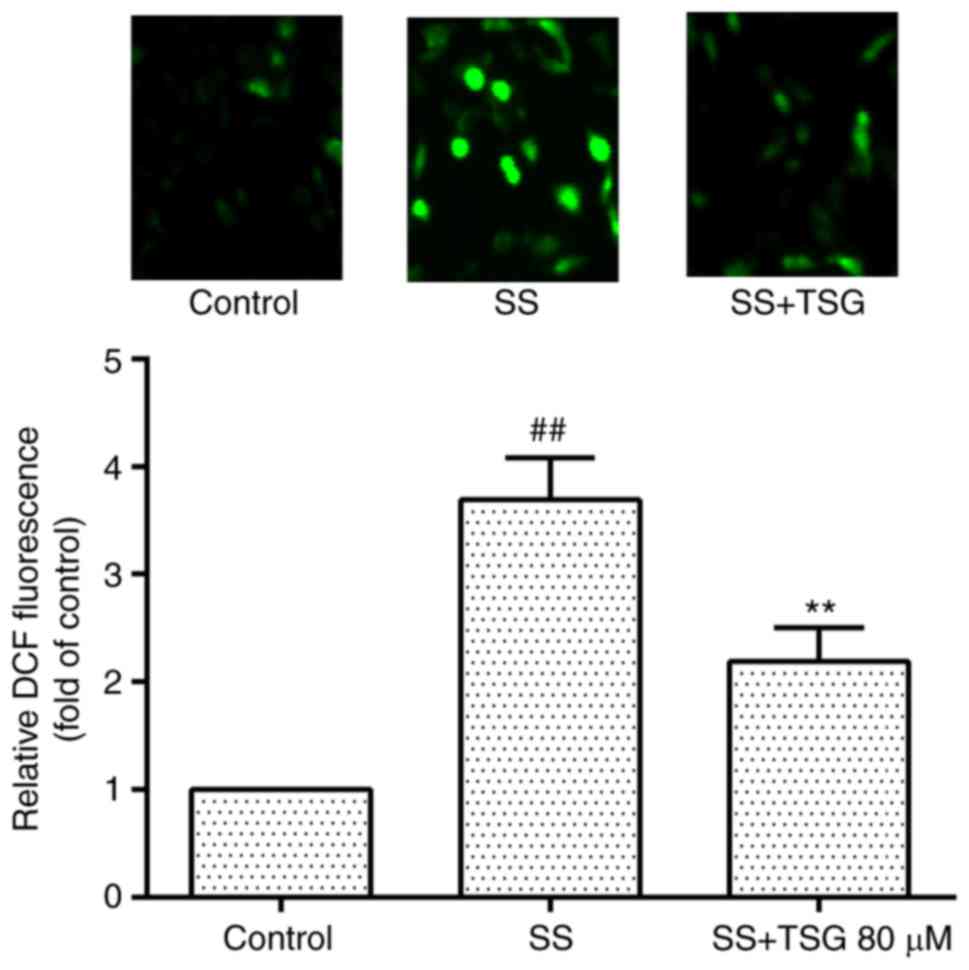
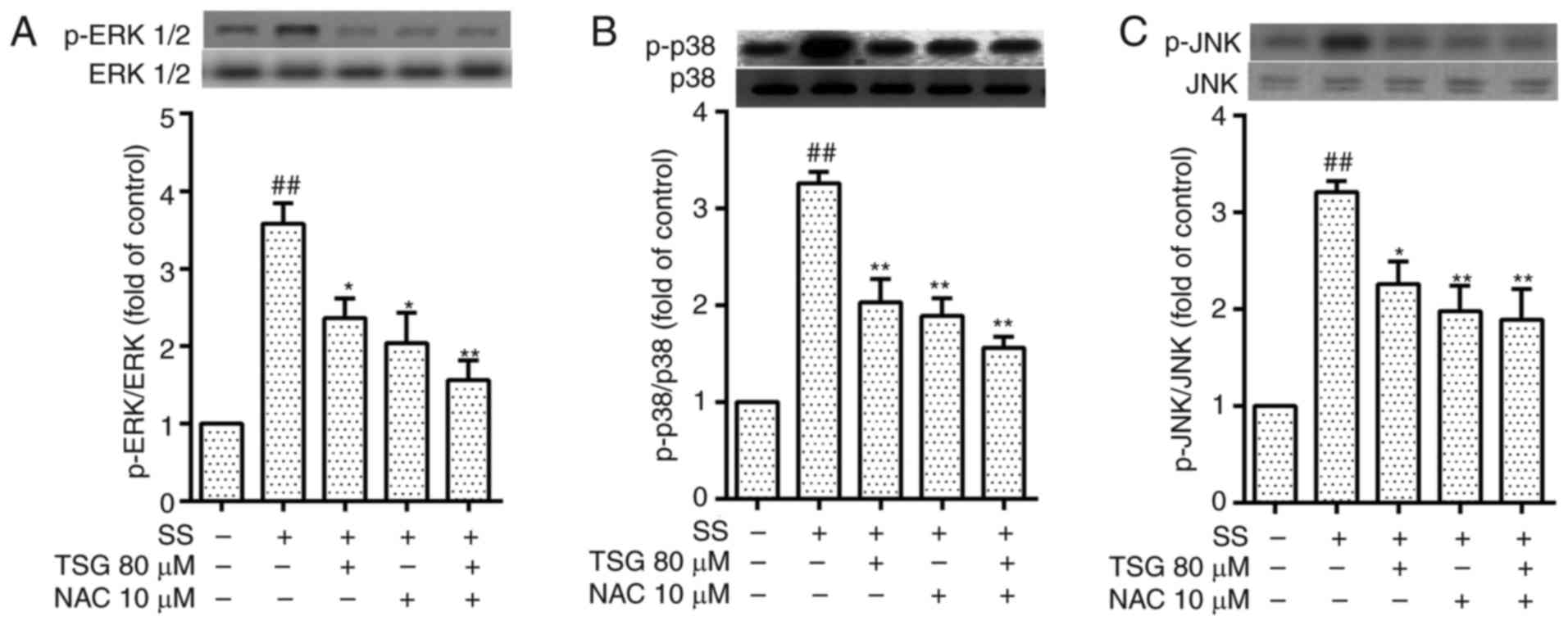
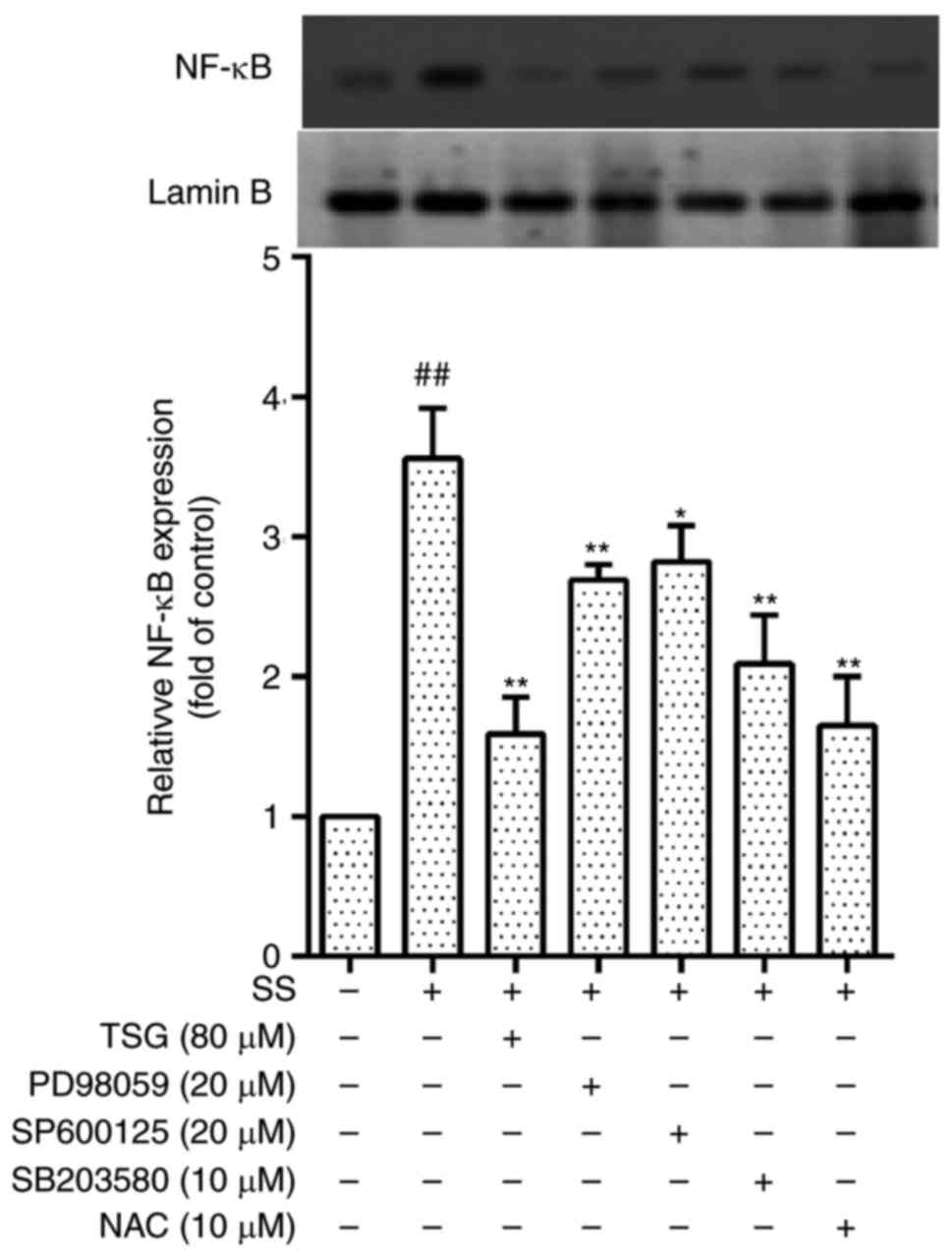
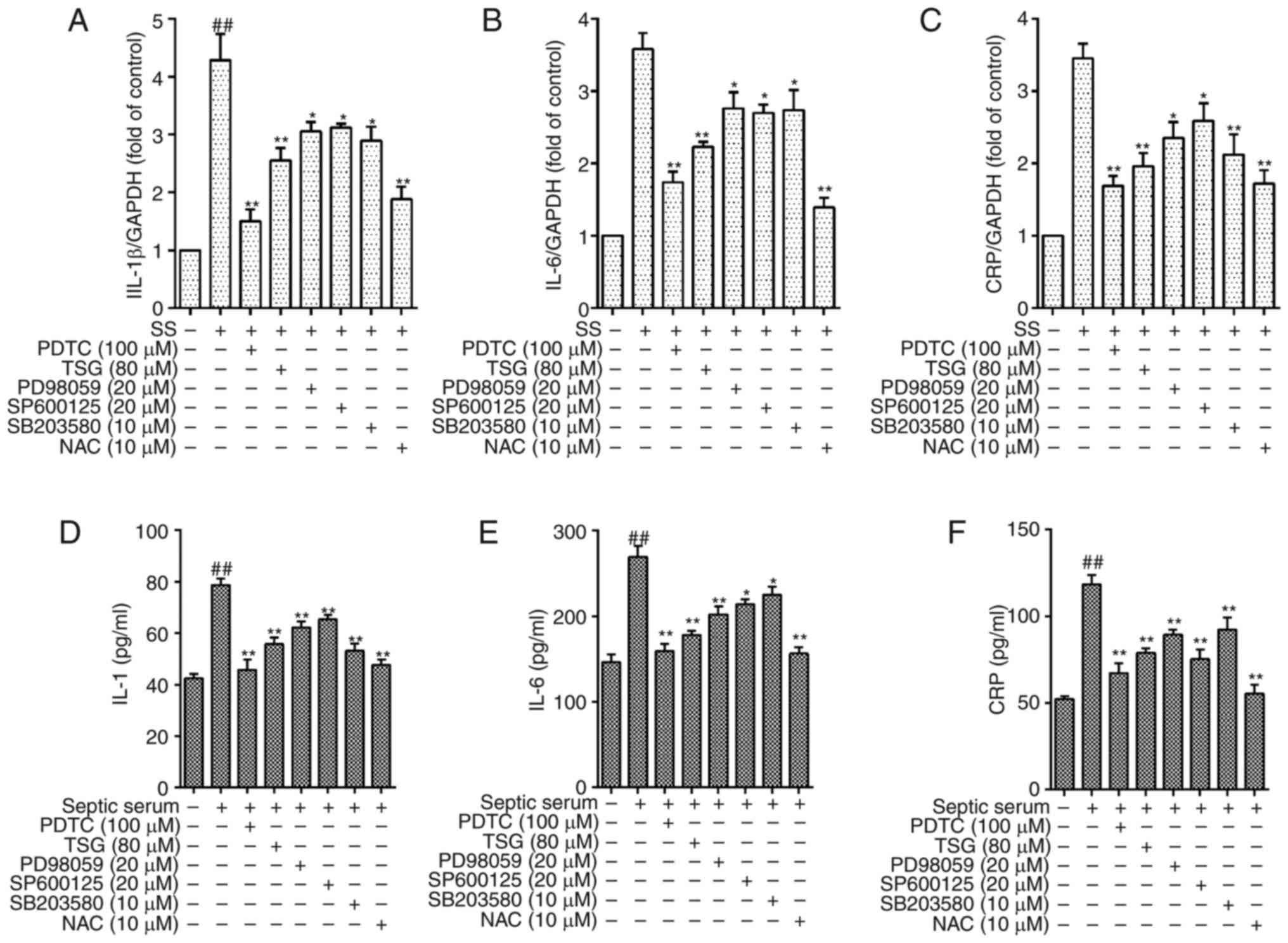
|
1
|
Churpek MM, Snyder A, Han X, Sokol S,
Pettit N, Howell MD and Edelson DP: Quick sepsis-related organ
failure assessment, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and
early warning scores for detecting clinical deterioration in
infected patients outside the intensive care unit. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 195:906–911. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Colbert JF, Schmidt EP, Faubel S and Ginde
AA: Severe sepsis outcomes among hospitalizations with inflammatory
bowel disease. Shock. 47:128–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kanashiro A, Sônego F, Ferreira RG,
Castanheira FV, Leite CA, Borges VF, Nascimento DC, Cólon DF,
Alves-Filho JC, Ulloa L and Cunha FQ: Therapeutic potential and
limitations of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in sepsis.
Pharmacol Res. 117:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Martin JB and Badeaux JE: Interpreting
laboratory tests in infection: Making sense of biomarkers in sepsis
and systemic inflammatory response syndrome for intensive care unit
patients. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 29:119–130. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Md Ralib A, Mat Nor MB and Pickering JW:
Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin diagnosed acute
kidney injury in patients with systemic inflammatory disease and
sepsis. Nephrology (Carlton). 22:412–419. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Arcêncio L and Evora PR: The lack of
clinical applications would be the cause of low interest in an
endothelial dysfunction classification. Arq Bras Cardiol.
108:97–99. 2017.In English, Portuguese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Downey RM, Liao P, Millson EC, Quyyumi AA,
Sher S and Park J: Endothelial dysfunction correlates with
exaggerated exercise pressor response during whole body maximal
exercise in chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
312:F917–F924. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Graw JA, Yu B, Rezoagli E, Warren HS, Buys
ES, Bloch DB and Zapol WM: Endothelial dysfunction inhibits the
ability of haptoglobin to prevent hemoglobin-induced hypertension.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 312:H1120–H1127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hashemi M, Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Zarean
E, Baktash F and Mortazavi ZS: Evaluation of the effect of
high-dose folic acid on endothelial dysfunction in pre-eclamptic
patients: A randomized clinical trial. J Res Med Sci. 21:1142016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rothenbach PA, Dahl B, Schwartz JJ,
O'Keefe GE, Yamamoto M, Lee WM, Horton JW, Yin HL and Turnage RH:
Recombinant plasma gelsolin infusion attenuates burn-induced
pulmonary microvascular dysfunction. J Appl Physiol (1985).
96:25–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tsukamoto M, Tampo Y, Sawada M and Yonaha
M: Paraquat-induced membrane dysfunction in pulmonary microvascular
endothelial cells. Pharmacol Toxicol. 86:102–109. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tsukamoto M, Tampo Y, Sawada M and Yonaha
M: Paraquat-induced oxidative stress and dysfunction of the
glutathione redox cycle in pulmonary microvascular endothelial
cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 178:82–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Farley KS, Wang LF, Law C and Mehta S:
Alveolar macrophage inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent
pulmonary micro-vascular endothelial cell septic barrier
dysfunction. Microvasc Res. 76:208–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang MJ, Xiao JH, Wang Y, Yan YL, Yang J
and Wang JL: 2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-D-glucoside
improves gastrointestinal motility disorders in STZ-induced
diabetic mice. PLoS One. 7:e502912012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
He H, Wang S, Tian J, Chen L, Zhang W,
Zhao J, Tang H, Zhang X and Chen J: Protective effects of
2,3,5,4′-tetrahydro xystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in the
MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease: Involvement of
reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK, P38 and mitochondrial
pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 767:175–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin CL, Hsieh SL, Leung W, Jeng JH, Huang
GC, Lee CT and Wu CC: 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-gluc
oside suppresses human colorectal cancer cell metastasis through
inhibiting NF-κB activation. Int J Oncol. 49:629–638. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ling S, Duan J, Ni R and Xu JW:
2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene -2-O-β-D-glucoside promotes
expression of the longevity gene klotho. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:31282352016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ling S and Xu JW: Biological Activities of
2,3,5,4′-tetrah ydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside in antiaging and
anti-aging-related disease treatments. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:49732392016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Peng Y, Zeng Y, Xu J, Huang XL, Zhang W
and Xu XL: PPAR-gamma is involved in the protective effect of
2,3,4′,5-tetra-hydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-D-glucoside against cardiac
fibrosis in pressure-overloaded rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:105–114.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lambertucci F, Motiño O, Villar S, Rigalli
JP, de Luján Alvarez M, Catania VA, Martín-Sanz P, Carnovale CE,
Quiroga AD, Francés DE and Ronco MT: Benznidazole, the trypanocidal
drug used for chagas disease, induces hepatic NRF2 activation and
attenuates the inflammatory response in a murine model of sepsis.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 315:12–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li HR, Liu J, Zhang SL, Luo T, Wu F, Dong
JH, Guo YJ and Zhao L: Corilagin ameliorates the extreme
inflammatory status in sepsis through TLR4 signaling pathways. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park SY, Jin ML, Wang Z, Park G and Choi
YW: 2,3,4′,5-tetrahyd roxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside exerts
anti-inflammatory effects on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
microglia by inhibiting NF-κB and activating AMPK/Nrf2 pathways.
Food Chem Toxicol. 97:159–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang M, Yu LM, Zhao H, Zhou XX, Yang Q,
Song F, Yan L, Zhai ME, Li BY, Zhang B, et al:
2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbe ne-2-O-β-D-glucoside protects murine
hearts against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating
Notch1/Hes1 signaling and attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:317–330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W, Chen XF, Huang YJ, Chen QQ, Bao
YJ and Zhu W: 2,3,4′,5-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside
inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibroblast proliferation
via suppression of the reactive oxygen species-extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:429–437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao J, Xu S, Song F, Nian L, Zhou X and
Wang S: 2,3,5,4′-tetr ahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside protects
human umbilical vein endothelial cells against
lysophosphatidylcholine-induced apoptosis by upregulating
superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase. IUBMB Life.
66:711–722. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng G, Wen X, Shi Y, Jiang Y, Hu G, Zhou
Y and Ran P: Development of a new method for the isolation and
culture of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells from rat pulmonary
arteries. J Vasc Res. 50:468–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niwa H, Ogawa Y, Kido Y, Abe Y, Kobayashi
M, Mori T and Tanaka T: The rate of lipid oxidation in septic rat
models. Jpn J Surg. 19:439–445. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cepinskas G and Wilson JX: Inflammatory
response in micro-vascular endothelium in sepsis: Role of oxidants.
J Clin Biochem Nutr. 42:175–184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Garrean S, Gao XP, Brovkovych V, Shimizu
J, Zhao YY and Vogel SM: Caveolin-1 regulates NF-kappaB activation
and lung inflammatory response to sepsis induced by
lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 177:4853–4860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McCuskey RS, Nishida J, McDonnell D, Baker
GL, Urbaschek R and Urbaschek B: Effect of immunoglobulin G on the
hepatic microvascular inflammatory response during sepsis. Shock.
5:28–33. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Orfanos SE, Kotanidou A, Glynos C,
Athanasiou C, Tsigkos S, Dimopoulou I, Sotiropoulou C, Zakynthinos
S, Armaganidis A, Papapetropoulos A and Roussos C: Angiopoietin-2
is increased in severe sepsis: Correlation with inflammatory
mediators. Crit Care Med. 35:199–206. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Biegańska-Hensoldt S and Rosolowska-Huszcz
D: Polyphenols in preventing endothelial dysfunction. Postepy Hig
Med Dosw (Online). 71:227–235. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Moussa MD, Santonocito C, Fagnoul D,
Donadello K, Pradier O, Gaussem P, De Backer D and Vincent JL:
Evaluation of endothelial damage in sepsis-related ARDS using
circulating endothelial cells. Intensive Care Med. 41:231–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Schlichting DE, Waxman AB, O'Brien LA,
Wang T, Naum CC, Rubeiz GJ, Um SL, Williams M and Yan SC:
Circulating endothelial and endothelial progenitor cells in
patients with severe sepsis. Microvasc Res. 81:216–221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lush CW and Kvietys PR: Microvascular
dysfunction in sepsis. Microcirculation. 7:83–101. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vincent JL and De Backer D: Microvascular
dysfunction as a cause of organ dysfunction in severe sepsis. Crit
Care. 9(Suppl 4): S9–S12. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nishida J, Ekataksin W, McDonnell D,
Urbaschek R, Urbaschek B and McCuskey RS: Ethanol exacerbates
hepatic microvascular dysfunction, endotoxemia, and lethality in
septic mice. Shock. 1:413–418. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Armour J, Tyml K, Lidington D and Wilson
JX: Ascorbate prevents microvascular dysfunction in the skeletal
muscle of the septic rat. J Appl Physiol (1985). 90:795–803. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
De Blasi RA, Palmisani S, Alampi D,
Mercieri M, Romano R, Collini S and Pinto G: Microvascular
dysfunction and skeletal muscle oxygenation assessed by
phase-modulation near-infrared spectroscopy in patients with septic
shock. Intensive Care Med. 31:1661–1668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Constantino L, Goncalves RC, Giombelli VR,
Tomasi CD, Vuolo F, Kist LW, de Oliveira GM, Pasquali MA, Bogo MR,
Mauad T, et al: Regulation of lung oxidative damage by endogenous
superoxide dismutase in sepsis. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2:172014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Schwalm MT, Pasquali M, Miguel SP, Dos
Santos JP, Vuolo F, Comim CM, Petronilho F, Quevedo J, Gelain DP,
Moreira JC, et al: Acute brain inflammation and oxidative damage
are related to long-term cognitive deficits and markers of
neurodegeneration in sepsis-survivor rats. Mol Neurobiol.
49:380–385. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Taner G, Aydin S, Bacanli M, Sarıgöl Z,
Sahin T, Başaran AA and Başaran N: Modulating effects of
pycnogenol® on oxidative stress and DNA damage induced
by sepsis in rats. Phytother Res. 28:1692–1700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
O'Sullivan AW, Wang JH and Redmond HP:
NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK inhibition improve survival in endotoxin
shock and in a cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis in
combination with antibiotic therapy. J Surg Res. 152:46–53. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ronco MT, Manarin R, Francés D, Serra E,
Revelli S and Carnovale C: Benznidazole treatment attenuates liver
NF-κB activity and MAPK in a cecal ligation and puncture model of
sepsis. Mol Immunol. 48:867–873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Chaudry IH and Ayala A:
Immune suppression in polymicrobial sepsis: differential regulation
of Th1 and Th2 responses by p38 MAPK. J Surg Res. 91:141–146. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Jarrar D, Chaudry IH
and Ayala A: Evolution of an immune suppressive macrophage
phenotype as a product of P38 MAPK activation in polymicrobial
sepsis. Shock. 15:42–48. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Song GY, Chung CS, Jarrar D, Cioffi WG and
Ayala A: Mechanism of immune dysfunction in sepsis: Inducible
nitric oxide-meditated alterations in p38 MAPK activation. J
Trauma. 53:276–2832. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun Y, Li YH, Wu XX, Zheng W, Guo ZH, Li
Y, Chen T, Hua ZC and Xu Q: Ethanol extract from Artemisia vestita,
a traditional Tibetan medicine, exerts anti-sepsis action through
down-regulating the MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Int J Mol Med.
17:957–962. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|