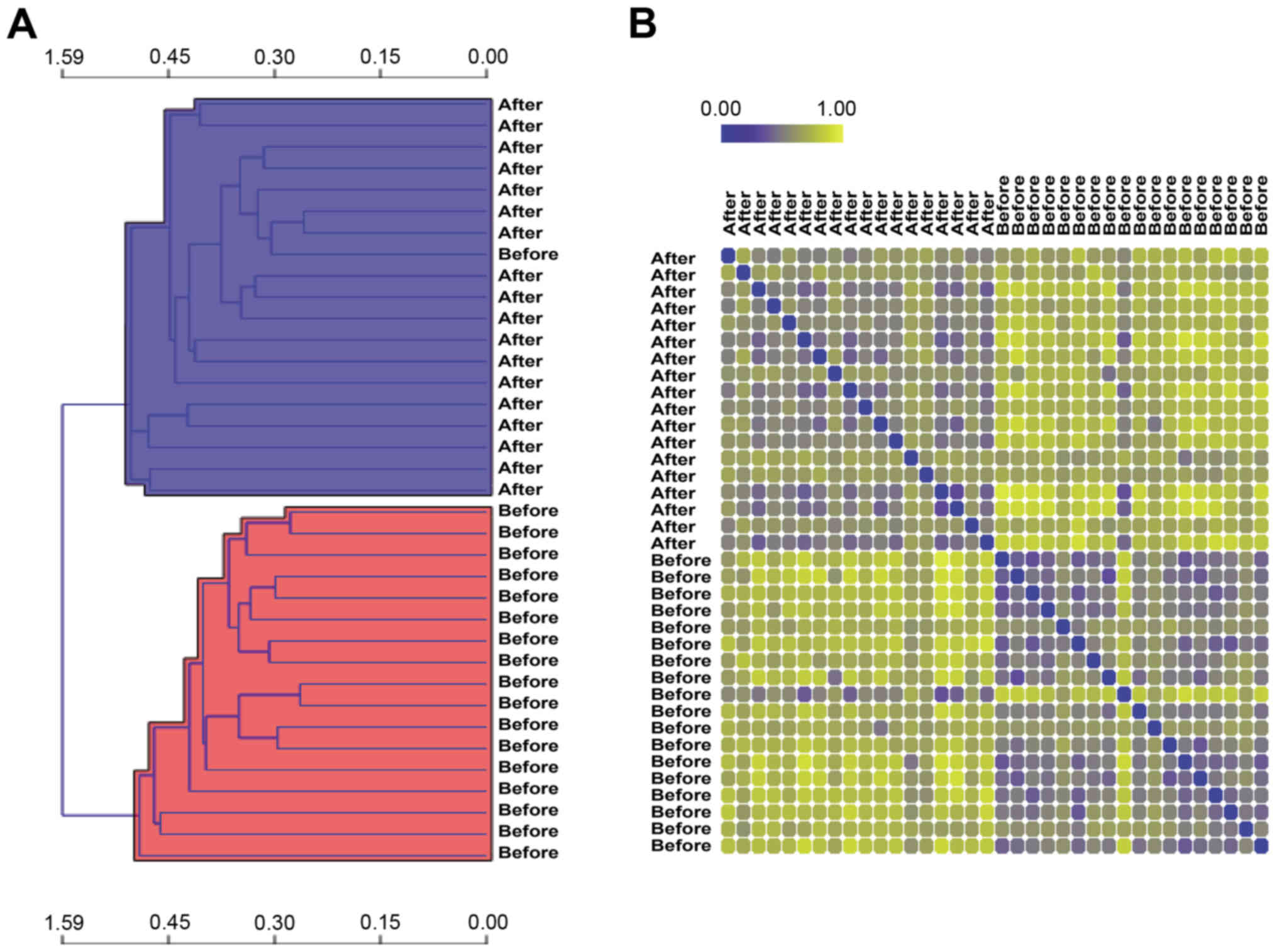
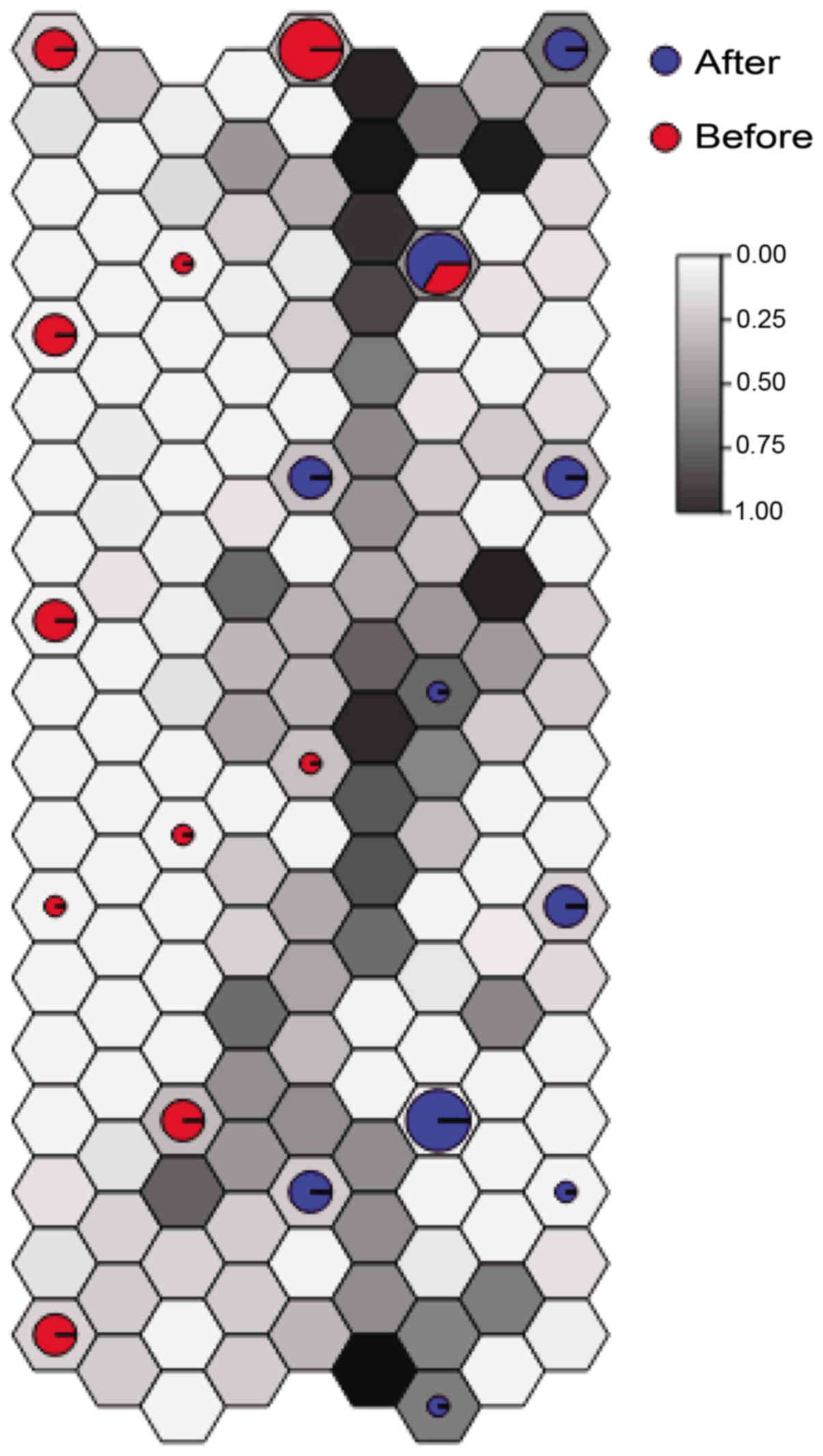
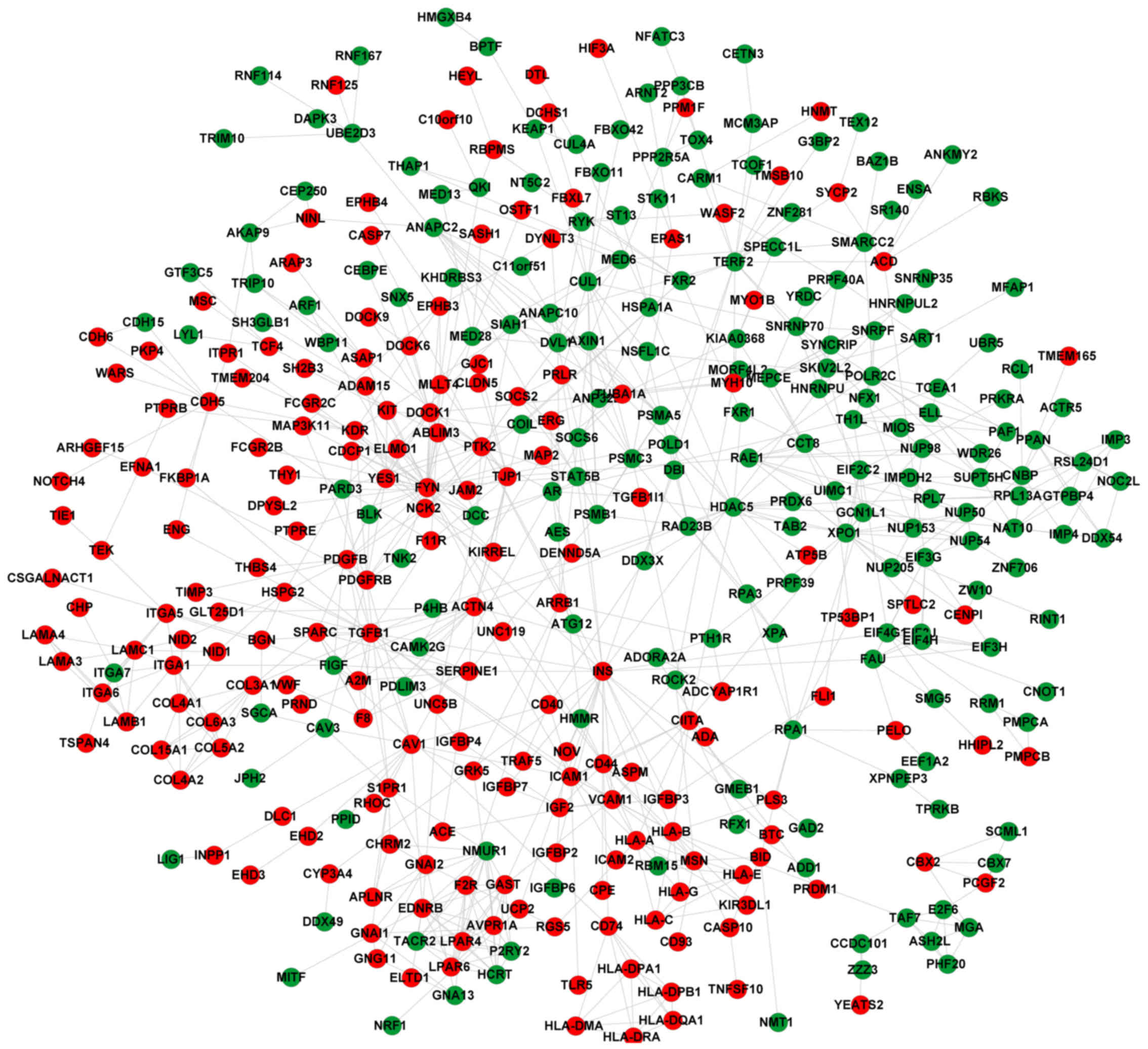
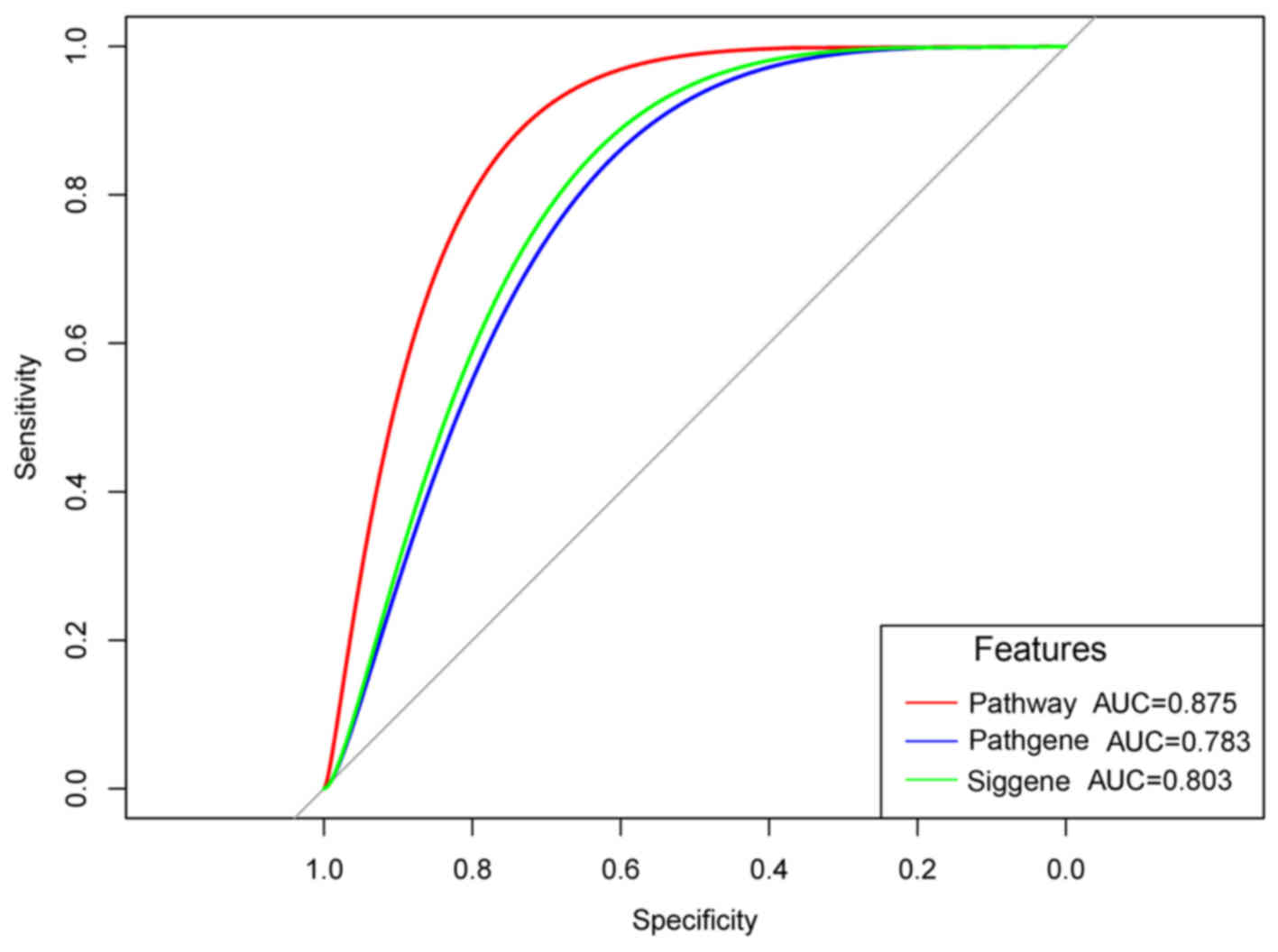
|
1
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment - where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G, Jaffe N, Eftekhari F, Raymond
AK and Yasko AW: Pediatric and Adolescent Osteosarcoma. Springer;
New York, NY: 2010
|
|
3
|
Ritter J and Bielack SS: Osteosarcoma. Ann
Oncol. 21(Suppl 7): vii320–vii325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Geller DS and Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: a
review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin Adv
Hematol Oncol. 8:705–718. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Mavrogenis AF, Abati CN, Romagnoli C and
Ruggieri P: Similar survival but better function for patients after
limb salvage versus amputation for distal tibia osteosarcoma. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 470:1735–1748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong Y, Liang G, Yuan B, Yang C, Gao R and
Zhou X: MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol.
36:1477–1486. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang JH, Kang XH, Lu P, Miao ZH, Sun GS,
Cao XJ and Cao F: Expression of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in
osteosarcoma and its effect on invasiveness and metastatic
potential of osteosarcoma cells. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi.
45:561–565. 2016.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hou CH, Lin FL, Tong KB, Hou SM and Liu
JF: Transforming growth factor alpha promotes osteosarcoma
metastasis by ICAM-1 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biochem
Pharmacol. 89:453–463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Z, Wu MS, Zou C, Tang Q, Lu J, Liu D,
Wu Y, Yin J, Xie X, Shen J, et al: Downregulation of MCT1 inhibits
tumor growth, metastasis and enhances chemotherapeutic efficacy in
osteosarcoma through regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett.
342:150–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao S, Kurenbekova L, Gao Y, Roos A,
Creighton CJ, Rao P, Hicks J, Man TK, Lau C, Brown AM, et al: NKD2,
a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, suppresses tumor growth and
metastasis in osteosarcoma. Oncogene. 34:5069–5079. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun XZ, Liao Y and Zhou CM: NKD2 a novel
marker to study the progression of osteosarcoma development. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2799–2804. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qian M, Yang X, Li Z, Jiang C, Song D, Yan
W, Liu T, Wu Z, Kong J, Wei H, et al: p50-associated COX-2
extragenic RNA (PACER) overexpression promotes proliferation and
metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by activating COX-2 gene. Tumour
Biol. 37:3879–3886. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kelly AD, Haibe-Kains B, Janeway KA, Hill
KE, Howe E, Goldsmith J, Kurek K, Perez-Atayde AR, Francoeur N, Fan
JB, et al: MicroRNA paraffin-based studies in osteosarcoma reveal
reproducible independent prognostic profiles at 14q32. Genome Med.
5:22013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Demšar J, Curk T, Erjavec A, Gorup Č,
Hočevar T, Milutinovič M, Možina M, Polajnar M, Toplak M, Starič A,
et al: Orange: Data mining toolbox in Python. J Mach Learn Res.
14:2349–2353. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Man D, Uda K, Ito Y and Nakano K:
Accelerating computation of Euclidean distance map using the GPU
with efficient memory access. Int J Parallel Emergent Distrib Syst.
28:383–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nahler G: Pearson correlation coefficient.
Springer Top Signal Process. 2:1–4. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zha W, Li M and Fu Y: Empirical analysis
of highway traffic accident in average linkage clustering method.
ECJTU. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Kohonen T: The self-organization map. Adv
Inf Knowl Process. 1:3–17. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Tweedie S, Ashburner M, Falls K, Leyland
P, McQuilton P, Marygold S, Millburn G, Osumi-Sutherland D,
Schroeder A, Seal R, et al FlyBase Consortium: FlyBase: Enhancing
Drosophila gene ontology annotations. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:D555–D559. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC, et al: DAVID
Bioinformatics Resources: Expanded annotation database and novel
algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic
Acids Res. 35:W169–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chatr-Aryamontri A, Breitkreutz BJ,
Oughtred R, Boucher L, Heinicke S, Chen D, Stark C, Breitkreutz A,
Kolas N, O’Donnell L, et al: The BioGRID interaction database: 2015
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D470–D478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Keshava Prasad TS, Goel R, Kandasamy K,
Keerthikumar S, Kumar S, Mathivanan S, Telikicherla D, Raju R,
Shafreen B, Venugopal A, et al: Human Protein Reference Database -
2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D767–D772. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide to
Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Langfelder P, Mischel PS and Horvath S:
When is hub gene selection better than standard meta-analysis? PLoS
One. 8:e615052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roush ET, Das T and Nandana P: Cluster
software upgrades. Journal. 2009.
|
|
28
|
May WL: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis.
Encyclopedia of Cancer. 1934–1937. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yoshii T, Geng Y, Peyton S, Mercurio AM
and Rotello VM: Biochemical and biomechanical drivers of cancer
cell metastasis, drug response and nanomedicine. Drug Discov Today.
21:1489–1494. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stoehlmacher J, Park DJ, Zhang W, Yang D,
Groshen S, Zahedy S and Lenz HJ: A multivariate analysis of genomic
polymorphisms: Prediction of clinical outcome to 5-FU/oxaliplatin
combination chemotherapy in refractory colorectal cancer. Br J
Cancer. 91:344–354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reed E: Platinum-DNA adduct, nucleotide
excision repair and platinum based anti-cancer chemotherapy. Cancer
Treat Rev. 24:331–344. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Biason P, Hattinger CM, Innocenti F,
Talamini R, Alberghini M, Scotlandi K, Zanusso C, Serra M and
Toffoli G: Nucleotide excision repair gene variants and association
with survival in osteosarcoma patients treated with neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics J. 12:476–483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cai Y, Cai T and Chen Y: Wnt pathway in
osteosarcoma, from oncogenic to therapeutic. J Cell Biochem.
115:625–631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lin CH, Ji T, Chen CF and Hoang BH: Wnt
signaling in osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 804:33–45. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du X, Yang J, Yang D, Tian W and Zhu Z:
The genetic basis for inactivation of Wnt pathway in human
osteosarcoma. BMC Cancer. 14:4502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu JF, Tsao YT and Hou CH:
Fractalkine/CX3CL1 induced intercellular adhesion
molecule-1-dependent tumor metastasis through the
CX3CR1/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in human osteosarcoma. Oncotarget.
8:54136–54148. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Liu JF, Tsao YT and Hou CH: Amphiregulin
enhances inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and promotes
tumor metastasis in human osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 6:40880–40895.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin YM, Chang ZL, Liao YY, Chou MC and
Tang CH: IL-6 promotes ICAM-1 expression and cell motility in human
osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 328:135–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kubo T, Piperdi S, Rosenblum J, Antonescu
CR, Chen W, Kim HS, Huvos AG, Sowers R, Meyers PA, Healey JH, et
al: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor as a prognostic marker
and a therapeutic target for imatinib mesylate therapy in
osteosarcoma. Cancer. 112:2119–2129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Takagi S, Takemoto A, Takami M, Oh-Hara T
and Fujita N: Platelets promote osteosarcoma cell growth through
activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor-Akt
signaling axis. Cancer Sci. 105:983–988. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu S, Yang S, Sun G, Huang W and Zhang Y:
Transforming growth factor-beta polymorphisms and serum level in
the development of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 33:802–806. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nikitovic D, Chalkiadaki G, Berdiaki A,
Aggelidakis J, Katonis P, Karamanos NK and Tzanakakis GN: Lumican
regulates osteosarcoma cell adhesion by modulating TGFβ2 activity.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:928–935. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu Y, Zhao J and He M: Correlation between
TGF-β1 gene 29 T>C single nucleotide polymorphism and
clinicopathological characteristics of osteosarcoma. Tumour Biol.
36:5149–5156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun Y, Xia P, Zhang H, Liu B and Shi Y:
P53 is required for Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via the TGF-beta
signaling pathway in osteosarcoma-derived cells. Am J Cancer Res.
6:114–125. 2015.
|
|
45
|
Bao TZ, Zao HW, Zheng QX, Liu W and Liu Y:
Effects of antisense transforming growth factor-β1 on the factors
related to metastasis in osteosarcoma. Chin J Exp Surg. 4:477–478.
2005.
|