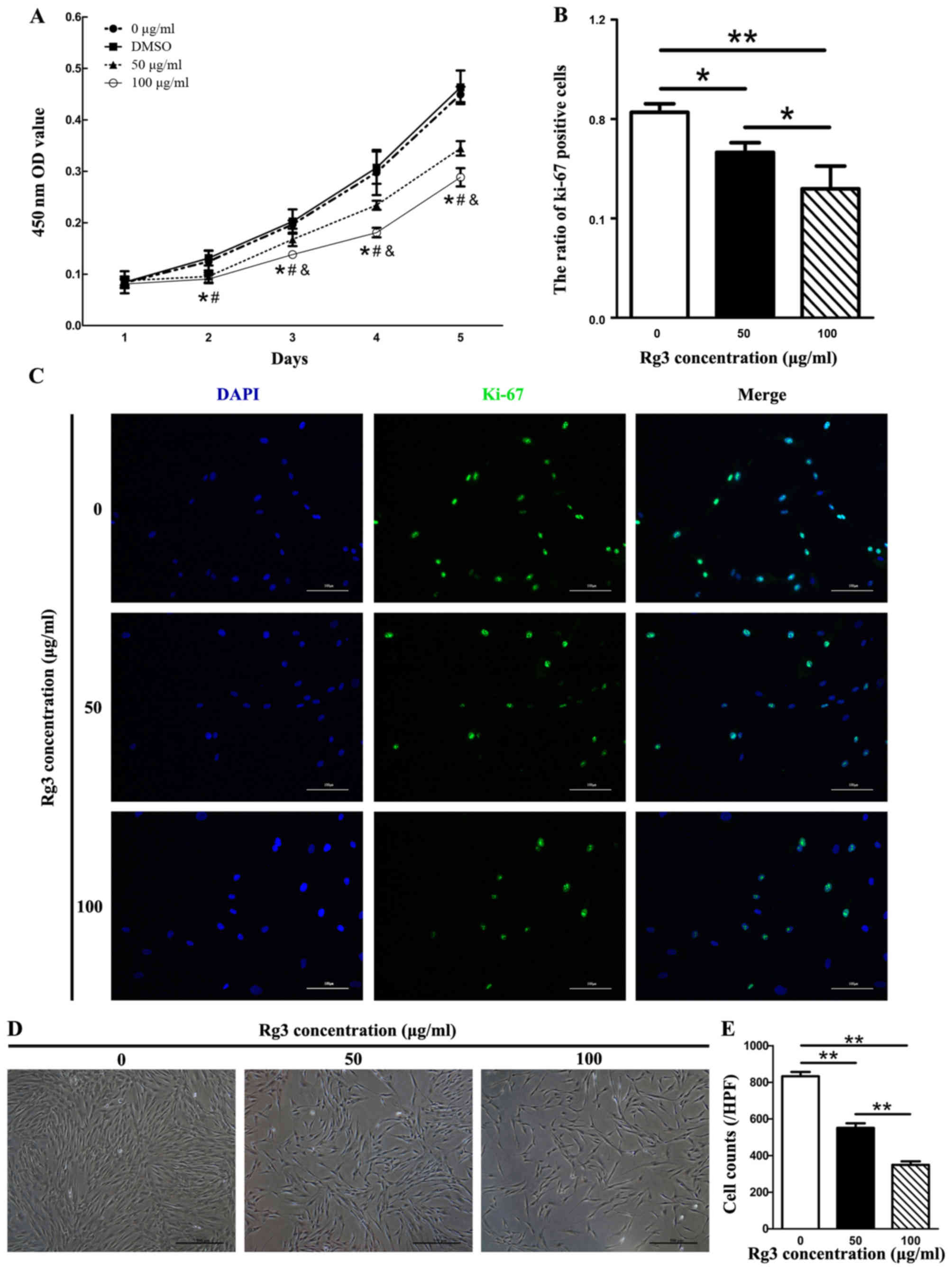
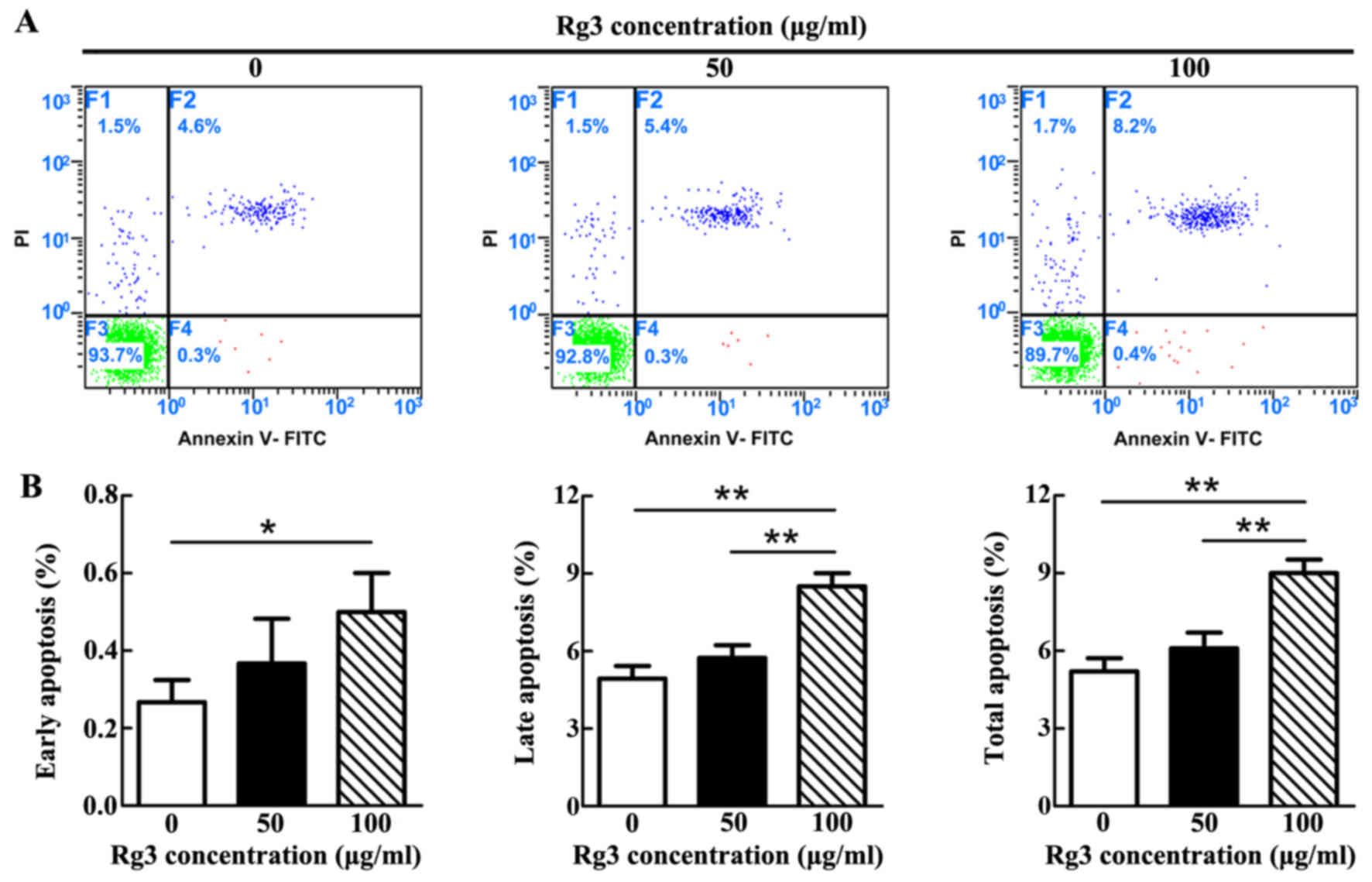
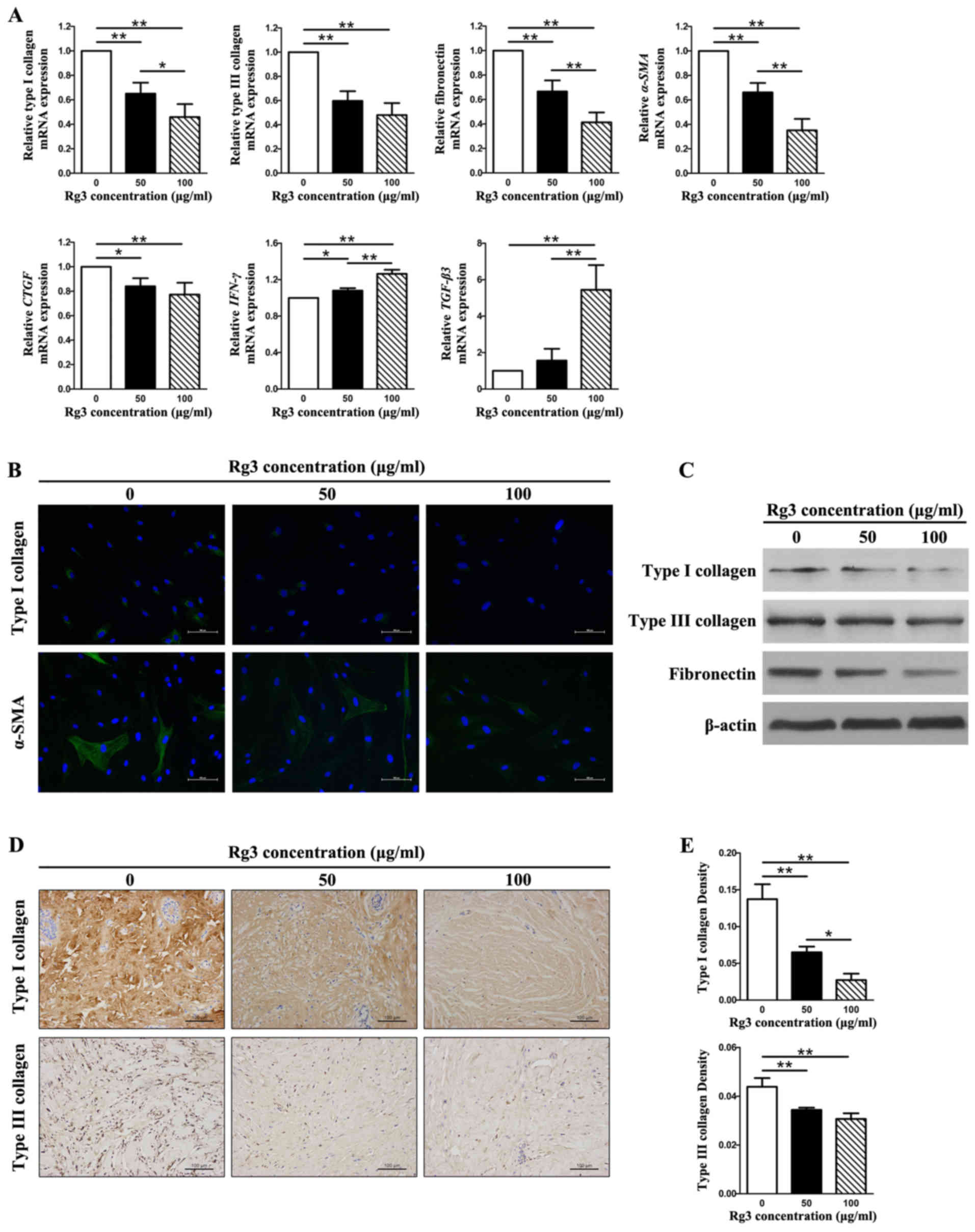
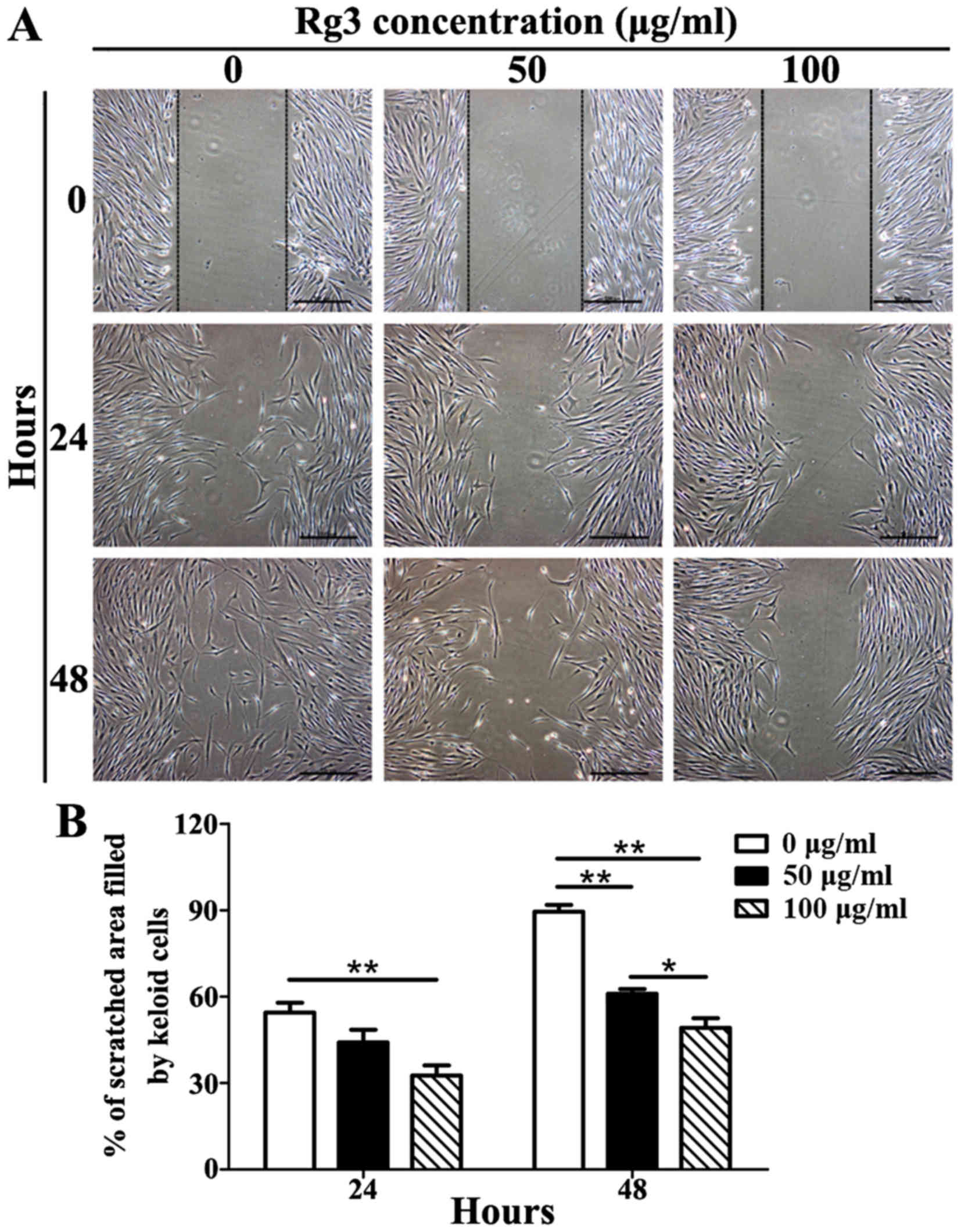
|
1
|
Trace AP, Enos CW, Mantel A and Harvey VM:
Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Spectrum of Clinical Challenges.
Am J Clin Dermatol. 17:201–223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
English RS and Shenefelt Pd: Keloids and
hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg. 25:631–638. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang R, Chen J, Zhang Z and Cen Y: Role of
chymase in the local renin-angiotensin system in keloids:
Inhibition of chymase may be an effective therapeutic approach to
treat keloids. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:4979–4988. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu WS, Zheng XD, Yao XH and Zhang LF:
Clinical and epidemiological analysis of keloids in Chinese
patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 307:109–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Butler PD, Longaker MT and Yang GP:
Current progress in keloid research and treatment. J Am Coll Surg.
206:731–741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bijlard E, Steltenpool S and Niessen FB:
Intralesional 5-fluorouracil in keloid treatment: A systematic
review. Acta Derm Venereol. 95:778–782. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ud-Din S and Bayat A: Strategic management
of keloid disease in ethnic skin: A structured approach supported
by the emerging literature. Br J Dermatol. 169(Suppl 3): 71–81.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu T, Peng YF, Jia C, Yang BH, Tao X, Li
J and Fang X: Ginsenoside Rg3 improves erectile function in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Sex Med. 12:611–620. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yuan HD, Quan HY, Zhang Y, Kim SH and
Chung SH: 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3-induced apoptosis in HT-29 colon
cancer cells is associated with AMPK signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 3:825–831. 2010.
|
|
10
|
He BC, Gao JL, Luo X, Luo J, Shen J, Wang
L, Zhou Q, Wang YT, Luu HH, Haydon RC, et al: Ginsenoside Rg3
inhibits colorectal tumor growth through the downregulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 38:437–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang JH, Nao JF, Zhang M and He P:
20(s)-ginsenoside Rg3 promotes apoptosis in human ovarian cancer
HO-8910 cells through PI3K/Akt and XIAP pathways. Tumour Biol.
35:11985–11994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Joo SS, Yoo YM, Ahn BW, Nam SY, Kim YB,
Hwang KW and Lee DI: Prevention of inflammation-mediated
neurotoxicity by Rg3 and its role in microglial activation. Biol
Pharm Bull. 31:1392–1396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen QJ, Zhang MZ and Wang LX: Gensenoside
Rg3 inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression in human cancer cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 26:849–858. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pazyar N, Omidian M and Jamshydian N:
Ginseng as a potential novel addition to the antikeloid weaponry.
Phytother Res. 26:1579–1580. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JP, Lu D, Nicholson RC, Zhao WJ, Li PY
and Wang F: Toxicity of a novel anti-tumor agent 20(S)-ginsenoside
Rg3: A 26-week intramuscular repeated administration study in rats.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3388–3396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SM, Lee SY, Cho JS, Son SM, Choi SS,
Yun YP, Yoo HS, Yoon DY, Oh KW, Han SB, et al: Combination of
ginsenoside Rg3 with docetaxel enhances the susceptibility of
prostate cancer cells via inhibition of NF-kappaB. Eur J Pharmacol.
631:1–9. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lan CC, Liu IH, Fang AH, Wen CH and Wu CS:
Hyperglycaemic conditions decrease cultured keratinocyte mobility:
Implications for impaired wound healing in patients with diabetes.
Br J Dermatol. 159:1103–1115. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin JU, Lee WJ, Tran TN, Jung I and Lee
JH: Hsp70 knockdown by siRNA decreased collagen production in
keloid fibroblasts. Yonsei Med J. 56:1619–1626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gill SE and Parks WC: Metalloproteinases
and their inhibitors: Regulators of wound healing. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 40:1334–1347. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liang CJ, Yen YH, Hung LY, Wang SH, Pu CM,
Chien HF, Tsai JS, Lee CW, Yen FL and Chen YL: Thalidomide inhibits
fibronectin production in TGF-β1-treated normal and keloid
fibroblasts via inhibition of the p38/Smad3 pathway. Biochem
Pharmacol. 85:1594–1602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schäfer M and Werner S: Cancer as an
overhealing wound: An old hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 9:628–638. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shin YM, Jung HJ, Choi WY and Lim CJ:
Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitory activities of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 in cultured
mammalian cell lines. Mol Biol Rep. 40:269–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Dong X, Mao S and Wen H: Upregulation of
proinflammatory genes in skin lesions may be the cause of keloid
formation (Review). Biomed Rep. 1:833–836. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lee WJ, Ahn HM, Roh H, Na Y, Choi IK, Lee
JH, Kim Yo, Lew DH and Yun CO: Decorin-expressing adenovirus
decreases collagen synthesis and upregulates MMP expression in
keloid fibroblasts and keloid spheroids. Exp Dermatol. 24:591–597.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao KB, Malathi N, Narashiman S and Rajan
ST: Evaluation of myofibroblasts by expression of alpha smooth
muscle actin: A marker in fibrosis, dysplasia and carcinoma. J Clin
Diagn Res. 8:ZC14–ZC17. 2014.
|
|
27
|
Chipev CC, Simman R, Hatch G, Katz AE,
Siegel DM and Simon M: Myofibroblast phenotype and apoptosis in
keloid and palmar fibroblasts in vitro. Cell death differ.
7:166–176. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mun JH, Kim YM, Kim BS, Kim JH, Kim MB and
Ko HC: Simvastatin inhibits transforming growth factor-β1-induced
expression of type I collagen, CTGF, and α-SMA in keloid
fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 22:125–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu R, Yue B, Yang Q, Ma Y, Huang G, Guan
M, Avram MM and Lu Z: The effect of 595 nm pulsed dye laser on
connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) expression in cultured
keloid fibroblasts. Lasers Surg Med. 47:203–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Khoo YT, Ong CT, Mukhopadhyay A, Han HC,
Do DV, Lim IJ and Phan TT: Upregulation of secretory connective
tissue growth factor (CTGF) in keratinocyte-fibroblast coculture
contributes to keloid pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 208:336–343.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duncan MR and Berman B: Differential
regulation of glycosaminoglycan, fibronectin, and collagenase
production in cultured human dermal fibroblasts by
interferon-alpha, -beta, and -gamma. Arch Dermatol Res. 281:11–18.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Y, Peng Y, Gao D, Feng C, Yuan X, Li H,
Wang Y, Yang L, Huang S and Fu X: Mesenchymal stem cells suppress
fibroblast proliferation and reduce skin fibrosis through a
TGF-β3-dependent activation. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 14:50–62.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yoshimoto H, Ishihara H, Ohtsuru A, Akino
K, Murakami R, Kuroda H, Namba H, Ito M, Fujii T and Yamashita S:
Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-I) receptor and
the invasiveness of cultured keloid fibroblasts. Am J Pathol.
154:883–889. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma H, Cai H, Zhang Y, Wu J, Liu X, Zuo J,
Jiang W, Ji G, Zhang Y, Liu C, et al: Membrane palmitoylated
protein 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and
invasion via upregulating matrix metalloproteinase 1. Cancer Lett.
344:74–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fujiwara M, Muragaki Y and Ooshima A:
Keloid-derived fibroblasts show increased secretion of factors
involved in collagen turnover and depend on matrix
metalloproteinase for migration. Br J Dermatol. 153:295–300. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Uchida G, Yoshimura K, Kitano Y, Okazaki M
and Harii K: Tretinoin reverses upregulation of matrix
metalloproteinase-13 in human keloid-derived fibroblasts. Exp
dermatol. 12(Suppl 2): 35–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee CH, Hong CH, Chen YT, Chen YC and Shen
MR: TGF-beta1 increases cell rigidity by enhancing expression of
smooth muscle actin: Keloid-derived fibroblasts as a model for
cellular mechanics. J Dermatol Sci. 67:173–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Song R, Li G and Li S: Aspidin PB, a novel
natural anti-fibrotic compound, inhibited fibrogenesis in
TGF-β1-stimulated keloid fibroblasts via PI-3K/Akt and Smad
signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 238:66–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Branton MH and Kopp JB: TGF-β and
fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1:1349–1365. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Morén A, Nakayama T,
Christian JL, Heuchel R, Itoh S, Kawabata M, Heldin NE, Heldin CH,
et al: Identification of Smad7, a TGFbeta-inducible antagonist of
TGF-beta signalling. Nature. 389:631–635. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fujiwara M, Muragaki Y and Ooshima A:
Upregulation of transforming growth factor-beta1 and vascular
endothelial growth factor in cultured keloid fibroblasts: relevance
to angiogenic activity. Arch Dermatol Res. 297:161–169. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu Y, Zhang Q, Ann DK, Akhondzadeh A,
Duong HS, Messadi DV and Le AD: Increased vascular endothelial
growth factor may account for elevated level of plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 via activating eRK1/2 in keloid fibroblasts.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C905–C912. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
He S, Yang Y, Liu X, Huang W and Zhang X,
Yang S and Zhang X: Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza
extract inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and collagen
synthesis in keloid fibroblasts by mediating transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway. Br J Dermatol. 166:564–574. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tuan TL, Wu H, Huang EY, Chong SS, Laug W,
Messadi D, Kelly P and Le A: Increased plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 in keloid fibroblasts may account for their elevated
collagen accumulation in fibrin gel cultures. Am J Pathol.
162:1579–1589. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|