|
1
|
Kandahari AM, Yang X, Laroche KA, Dighe
AS, Pan D and Cui Q: A review of UHMWPE wear-induced osteolysis:
the role for early detection of the immune response. Bone Res.
4:160142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
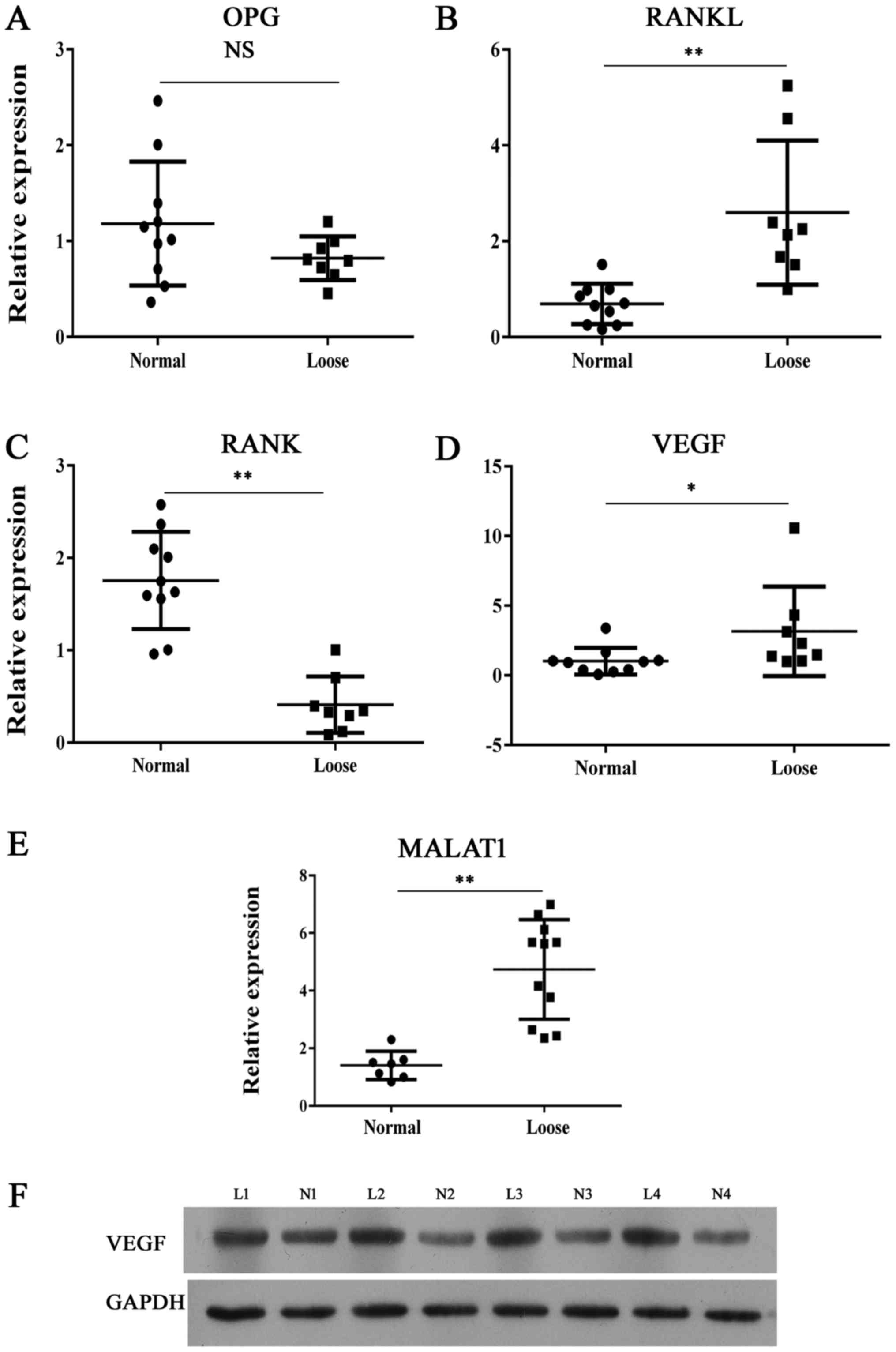
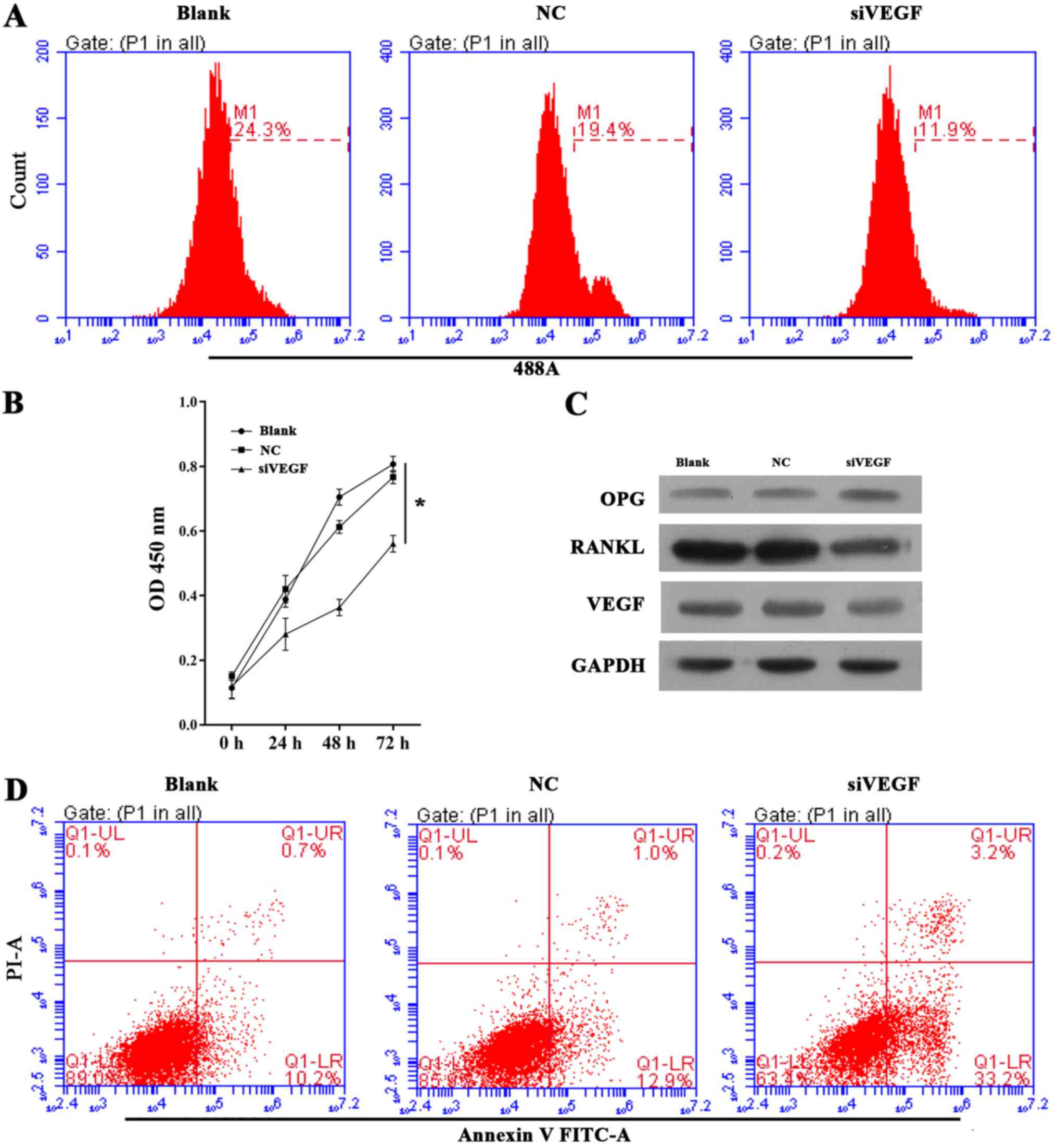
2
|
Harris WH: Wear and periprosthetic
osteolysis: the problem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 393:66–70. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fu C, Xie J, Hu N, Liang X, Chen R, Wang
C, Chen C, Xu C, Huang W and Paul Sung KL: Titanium particles
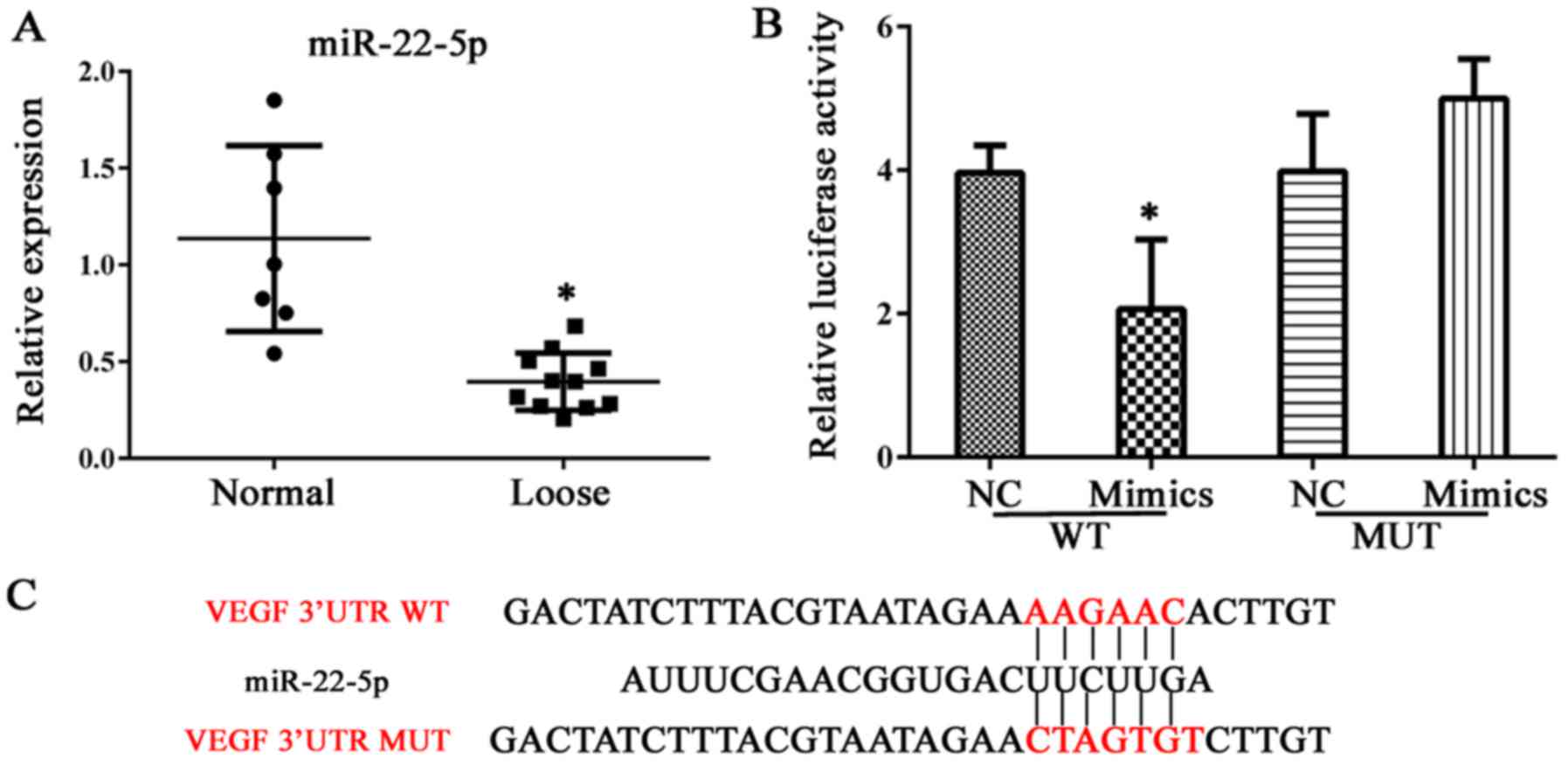
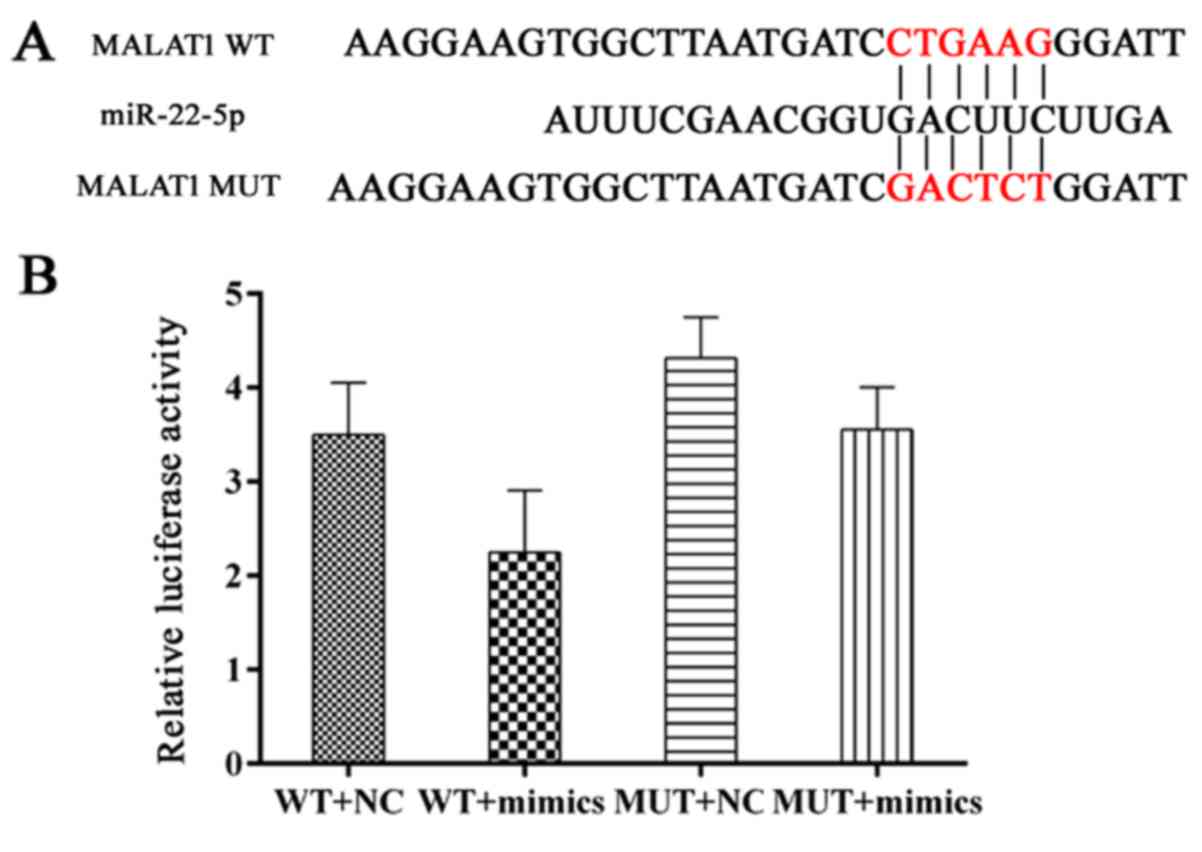
up-regulate the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human
synovial cells. Int Orthop. 38:1091–1098. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
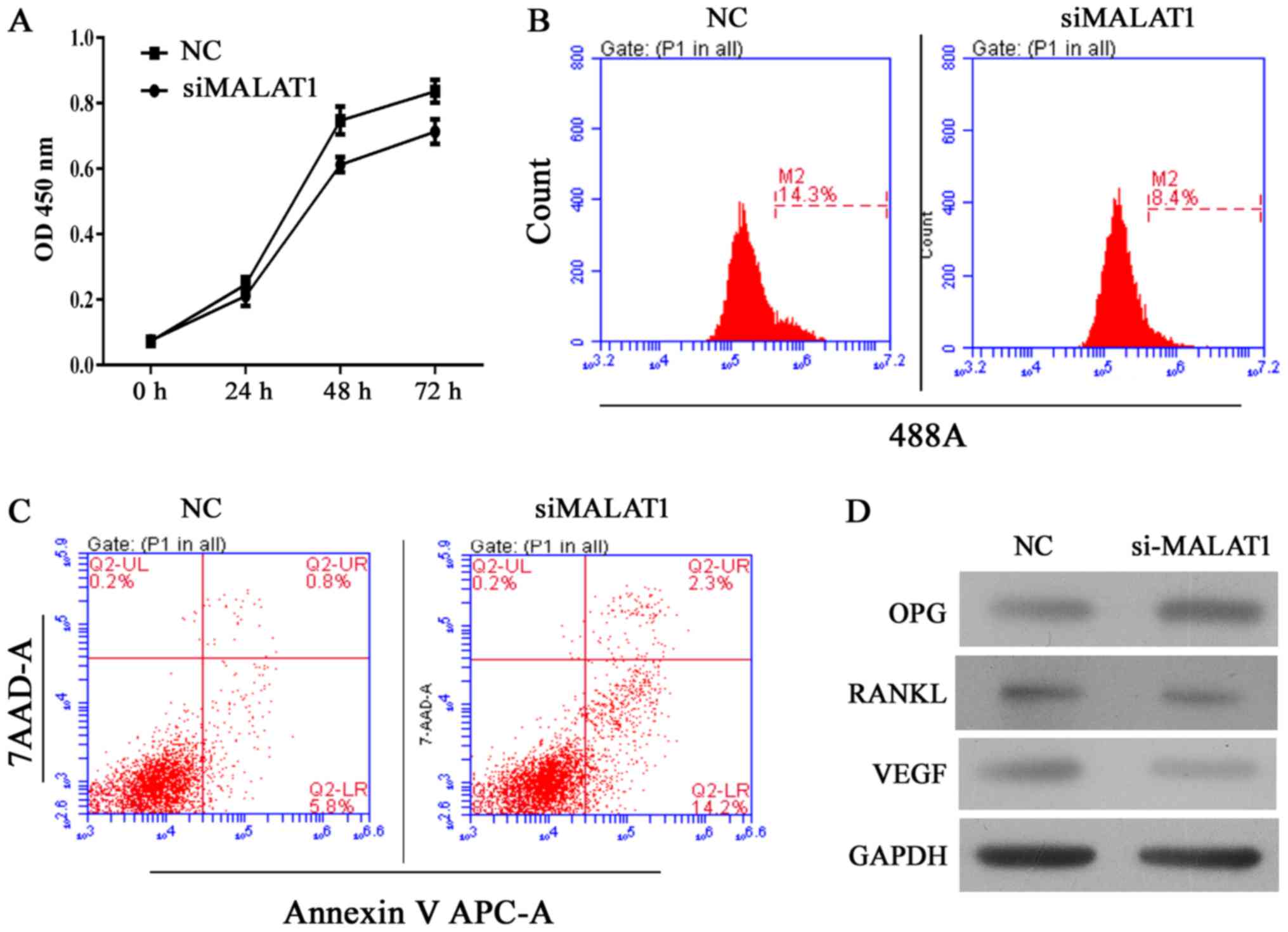
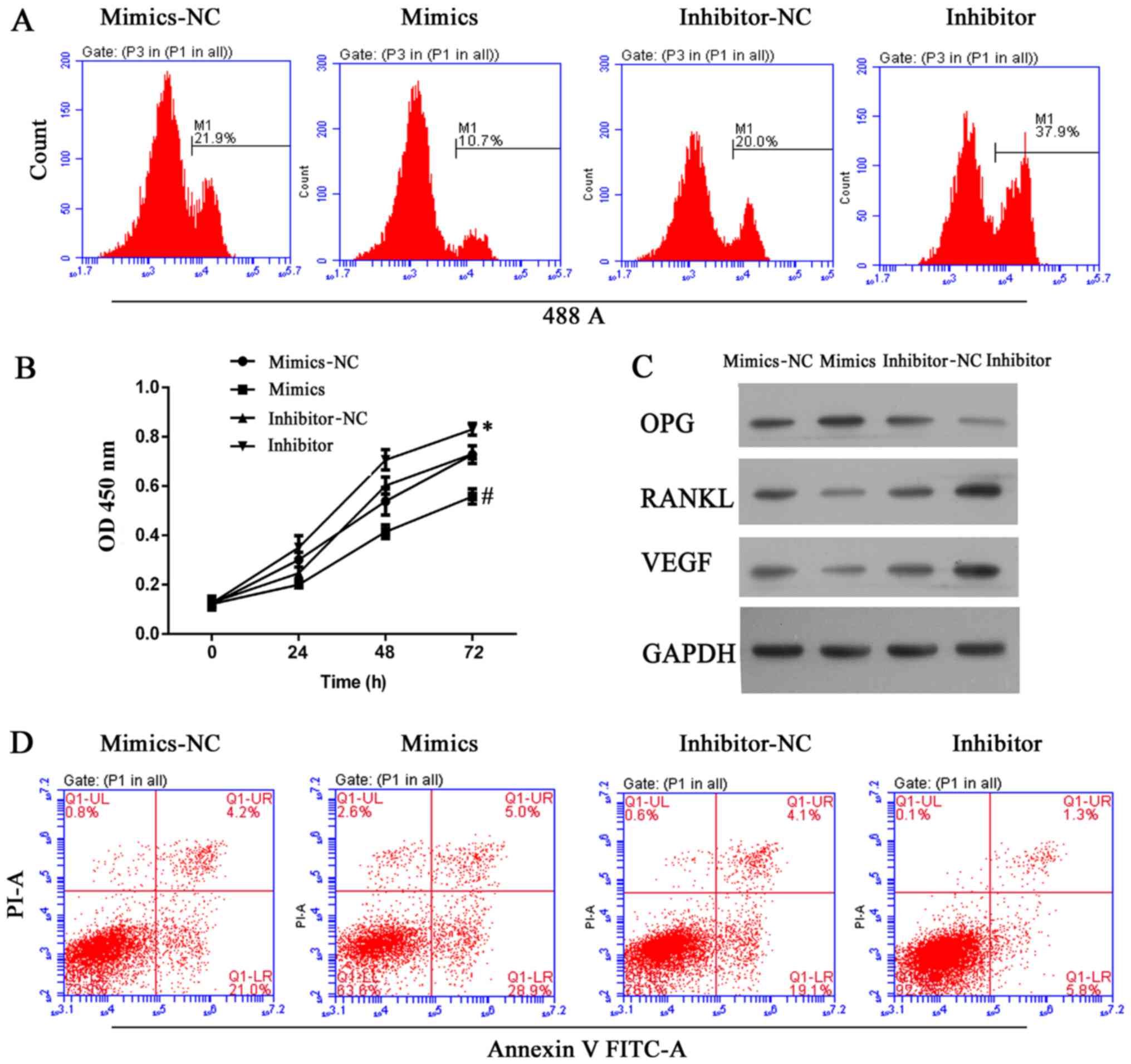
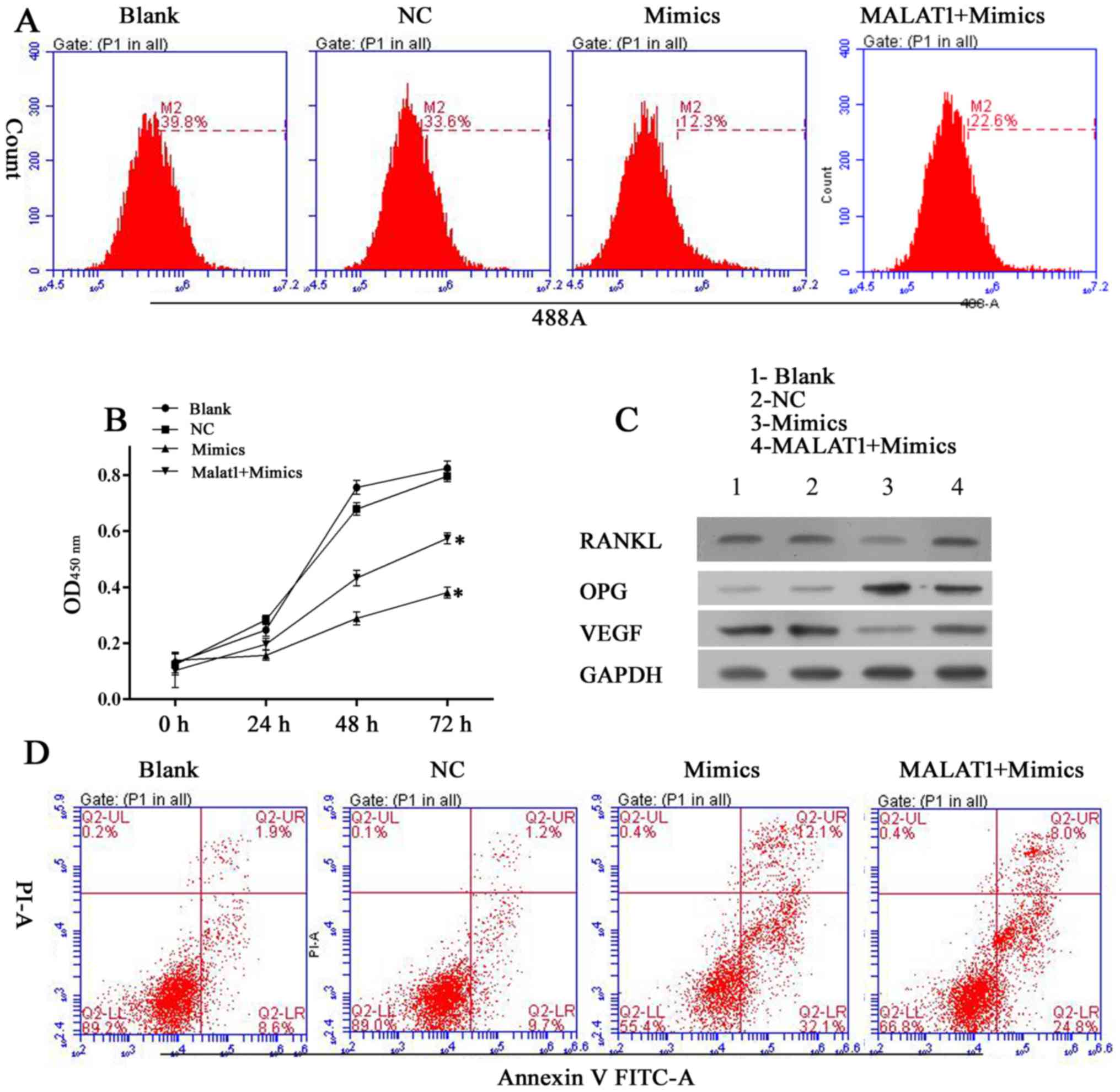
|
|
4
|
Katsuyama E, Miyamoto H, Kobayashi T, Sato
Y, Hao W, Kanagawa H, Fujie A, Tando T, Watanabe R, Morita M, et
al: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK4) promotes
inflammatory osteolysis by activating osteoclasts and inhibiting
formation of foreign body giant cells. J Biol Chem. 290:716–726.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Vallés G, Pérez C, Boré A, Martín-Saavedra
F, Saldaña L and Vilaboa N: Simvastatin prevents the induction of
interleukin-6 gene expression by titanium particles in human
osteoblastic cells. Acta Biomater. 9:4916–4925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Beck RT, Illingworth KD and Saleh KJ:
Review of periprosthetic osteolysis in total joint arthroplasty: an
emphasis on host factors and future directions. J Orthop Res.
30:541–546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wooley PH and Schwarz EM: Aseptic
loosening. Gene Ther. 11:402–407. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang Y, Jia T, Wooley PH and Yang SY:
Current research in the pathogenesis of aseptic implant loosening
associated with particulate wear debris. Acta Orthop Belg. 79:1–9.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakagawa M, Kaneda T, Arakawa T, Morita S,
Sato T, Yomada T, Hanada K, Kumegawa M and Hakeda Y: Vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) directly enhances osteoclastic
bone resorption and survival of mature osteoclasts. FEBS Lett.
473:161–164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Favus MJ: Primer on the Metabolic Bone
Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism. Rittenhouse Book
Distributors. 2006.
|
|
11
|
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel
DV and Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted
angiogenic mitogen. Science. 246:1306–1309. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goad DL, Rubin J, Wang H, Tashjian AH Jr
and Patterson C: Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor in human SaOS-2 osteoblast-like cells and murine osteoblasts
induced by insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology.
137:2262–2268. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gerber HP, Vu TH, Ryan AM, Kowalski J,
Werb Z and Ferrara N: VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage
remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone
formation. Nat Med. 5:623–628. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Henriksen K, Karsdal M, Delaisse JM and
Engsig MT: RANKL and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
induce osteoclast chemotaxis through an ERK1/2-dependent mechanism.
J Biol Chem. 278:48745–48753. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gibb EA, Vucic EA, Enfield KS, Stewart GL,
Lonergan KM, Kennett JY, Becker-Santos DD, MacAulay CE, Lam S,
Brown CJ, et al: Human cancer long non-coding RNA transcriptomes.
PLoS One. 6:e259152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu B, Peng XC, Zheng XL, Wang J and Qin
YW: miR-126 restoration down-regulate VEGF and inhibit the growth
of lung cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer.
66:169–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cascio S, D'Andrea A, Ferla R, Surmacz E,
Gulotta E, Amodeo V, Bazan V, Gebbia N and Russo A: miR-20b
modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:242–249.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lei Z, Li B, Yang Z, Fang H, Zhang GM,
Feng ZH and Huang B: Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b
tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen
concentration. PLoS One. 4:e76292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamakuchi M, Yagi S, Ito T and Lowenstein
CJ: MicroRNA-22 regulates hypoxia signaling in colon cancer cells.
PLoS One. 6:e202912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang S, Wang S, Bian C, Yang Z, Zhou H,
Zeng Y, Li H, Han Q and Zhao RC: Upregulation of miR-22 promotes
osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation
of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by
repressing HDAC6 protein expression. Stem Cells Dev. 21:2531–2540.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Che W, Dong Y and Quan HB: RANKL inhibits
cell proliferation by regulating MALAT1 expression in a human
osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19. Cell Mol Biol. 61:7–14.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Jin X, Xiang Y, Chen Y, Shen CX,
Zhang YC and Li YG: The lncRNA MALAT1 protects the endothelium
against ox-LDL-induced dysfunction via upregulating the expression
of the miR-22-3p target genes CXCR2 and AKT. FEBS Lett.
589:3189–3196. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kauther MD, Xu J and Wedemeyer C:
Alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide can reverse the catabolic
influence of UHMWPE particles on RANKL expression in primary human
osteoblasts. Int J Biol Sci. 6:525–536. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao S, Liu D, Pan F and Wise GE: Effect of
vascular endothelial growth factor on RANK gene expression in
osteoclast precursors and on osteoclastogenesis. Arch Oral Biol.
51:596–602. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley
M, Chang MS, Lüthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, et
al: Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the
regulation of bone density. Cell. 89:309–319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tripathi V, Ellis JD, Shen Z, Song DY, Pan
Q, Watt AT, Freier SM, Bennett CF, Sharma A, Bubulya PA, et al: The
nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative
splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol
Cell. 39:925–938. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thum T and Fiedler J: LINCing MALAT1 and
angiogenesis. Circ Res. 114:1366–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi
K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A,
et al: Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for
osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is
identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:3597–3602.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takahashi N, Udagawa N and Suda T: A new
member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family,
ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and
function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 256:449–455. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Berendsen AD, Jia S, Lotinun S,
Baron R, Ferrara N and Olsen BR: Intracellular VEGF regulates the
balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin
Invest. 122:3101–3113. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu K and Olsen BR: Osteoblast-derived VEGF
regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone
repair. J Clin Invest. 126:509–526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tombran-Tink J and Barnstable CJ:
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts express PEDF, VEGF-A isoforms, and VEGF
receptors: possible mediators of angiogenesis and matrix remodeling
in the bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 316:573–579. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hendrickson DG, Hogan DJ, McCullough HL,
Myers JW, Herschlag D, Ferrell JE and Brown PO: Concordant
regulation of translation and mRNA abundance for hundreds of
targets of a human microRNA. PLoS Biol. 7:e10002382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G,
Kostoulas N, Reczko M, Maragkakis M, Dalamagas TM and Hatzigeorgiou
AG: DIANA-LncBase: experimentally verified and computationally
predicted microRNA targets on long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41:D239–D245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language. Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Seitz H: Redefining microRNA targets. Curr
Biol. 19:870–873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Q, Guo R, Lu Y, Zhao L, Zhou Q,
Schwarz EM, Huang J, Chen D, Jin ZG, Boyce BF, et al: VEGF-C, a
lymphatic growth factor, is a RANKL target gene in osteoclasts that
enhances osteoclastic bone resorption through an autocrine
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 283:13491–13499. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|