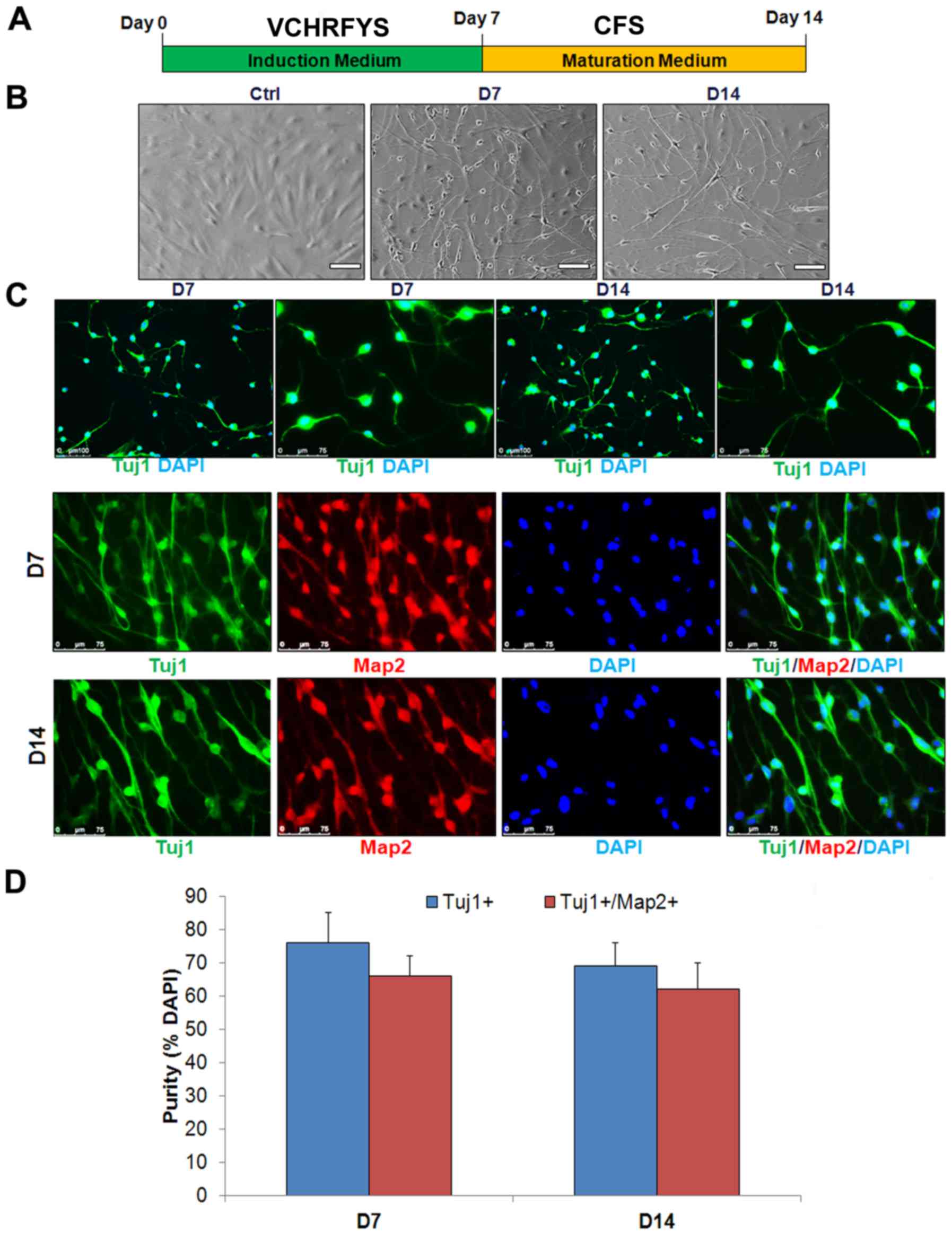
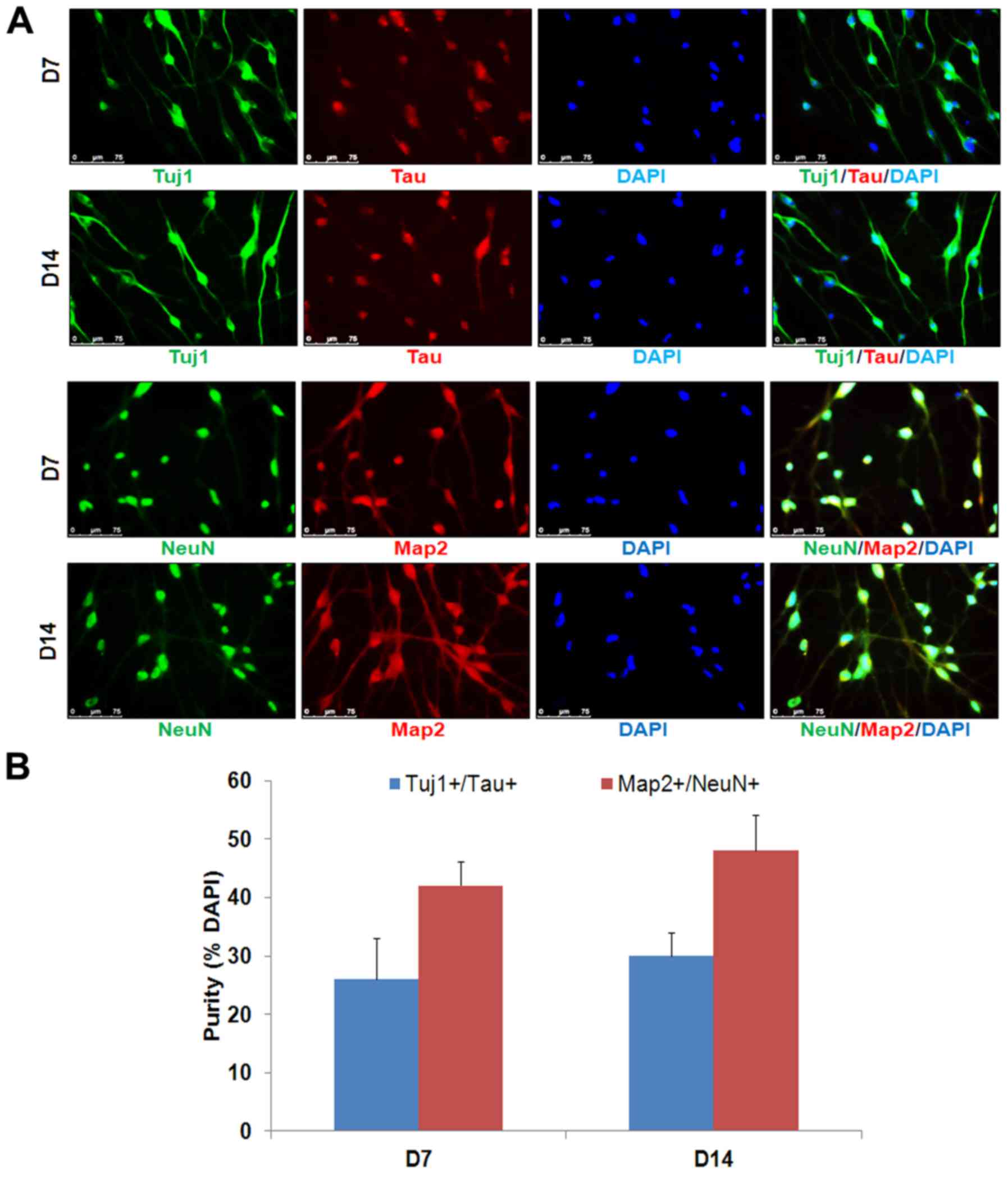
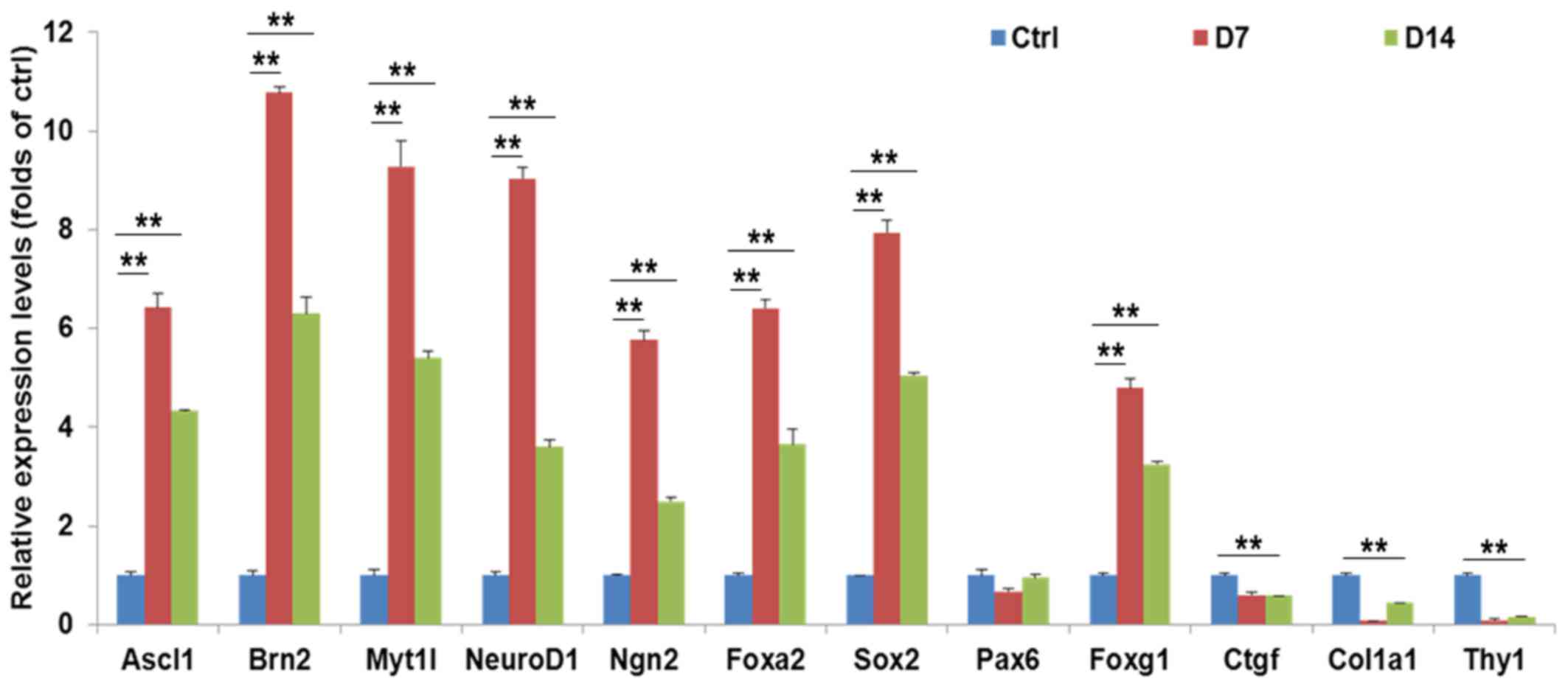
|
1
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu J, Du Y and Deng H: Direct lineage
reprogramming: Strategies, mechanisms, and applications. Cell Stem
Cell. 16:119–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yashar M, Kalani S and Martirosyan N:
Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons. World
Neurosurg. 77:7–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP,
Kokubu Y, Südhof TC and Wernig M: Direct conversion of fibroblasts
to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 463:1035–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, Shcheglovitov A,
Portmann T, Li Y, Lee-Messer C, Dolmetsch RE, Tsien RW and Crabtree
GR: MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons.
Nature. 476:228–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng L, Hu W, Qiu B, Zhao J, Yu Y, Guan
W, Wang M, Yang W and Pei G: Generation of neural progenitor cells
by chemical cocktails and hypoxia. Cell Res. 25:645–646. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li X, Zuo X, Jing J, Ma Y, Wang J, Liu D,
Zhu J, Du X, Xiong L, Du Y, et al: Small-molecule-driven direct
reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts into functional neurons. Cell
Stem Cell. 17:195–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu W, Qiu B, Guan W, Wang Q, Wang M, Li W,
Gao L, Shen L, Huang Y, Xie G, et al: Direct Conversion of normal
and Alzheimer's disease human fibroblasts into neuronal cells by
small molecules. Cell Stem Cell. 17:204–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jacobs JP, Jones CM and Baille JP:
Characteristics of a human diploid cell designated MRC-5. Nature.
227:168–170. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao Y, Wang J, Yan W, Zhou Y, Chen Y,
Zhou K, Wen J, Wang Y and Cai W: Dysregulated miR-124 and miR-200
expression contribute to cholangiocyte proliferation in the
cholestatic liver by targeting IL-6/STAT3 signalling. J Hepatol.
62:889–896. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hotta R, Pepdjonovic L, Anderson RB, Zhang
D, Bergner AJ, Leung J, Pébay A, Young HM, Newgreen DF and Dottori
M: Small-molecule induction of neural crest-like cells derived from
human neural progenitors. Stem Cells. 27:2896–2905. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rawal N, Parish C, Castelo-Branco G and
Arenas E: Inhibition of JNK increases survival of transplanted
dopamine neurons in Parkinsonian rats. Cell Death Differ.
14:381–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Neely MD, Litt MJ, Tidball AM, et al:
DMH1, a highly selective small molecule BMP inhibitor promotes
neurogenesis of hiPSCs: comparison of AX6 and SOX1 expression
during neural induction. ACS Chem Neurosci. 3(6): 482–91. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim BW, Yang S, Lee CH and Son H: A
critical time window for the survival of neural progenitor cells by
HDAC inhibitors in the hippocampus. Mol Cells. 31:159–164. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jeong SG, Ohn T, Kim SH and Cho GW:
Valproic acid promotes neuronal differentiation by induction of
neuroprogenitors in human bone-marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.
Neurosci Lett. 554:22–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu J, Liu H, Huang CT, Chen H, Du Z, Liu
Y, Sherafat MA and Zhang SC: Generation of integration-free and
region-specific neural progenitors from primate fibroblasts. Cell
Rep. 3:1580–1591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chambers SM, Qi Y, Mica Y, Lee G, Zhang
XJ, Niu L, Bilsland J, Cao L, Stevens E, Whiting P, et al: Combined
small-molecule inhibition accelerates developmental timing and
converts human pluripotent stem cells into nociceptors. Nat
Biotechnol. 30:715–720. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Babos K and Ichida JK: Small molecules
take a big step by converting fibroblasts into neurons. Cell Stem
Cell. 17:127–129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu ML, Zang T, Zou Y, Chang JC, Gibson
JR, Huber KM and Zhang CL: Small molecules enable neurogenin 2 to
efficiently convert human fibroblasts into cholinergic neurons. Nat
Commun. 4:21832013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Victor MB, Richner M, Hermanstyne TO, et
al: Generation of human striatal neurons by microRNA-dependent
direct conversion of fibroblasts. Neuron. 84(2): 311–23. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huangfu D, Maehr R, Guo W, et al:
Induction of pluripotent stem cells by defined factors is greatly
improved by small-molecule compounds. Nat Biotechnol. 26(7): 795–7.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ladewig J, Mertens J, Kesavan J, et al:
Small molecules enable highly efficient neuronal conversion of
human fibroblasts. Nat Methods. (6): 575–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xi G, Hu P, Qu C, et al: Induced neural
stem cells generated from rat fibroblasts. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 11(5): 312–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Zhu S, Ambasudhan R, Sun W, et al: Small
molecules enable OCT4-mediated direct reprogramming into expandable
human neural stem cells. Cell Res. 24(1): 126–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Ichida JK, Blanchard J, Lam K, et al: A
small-molecule inhibitor of tgf-Beta signaling replaces sox2 in
reprogramming by inducing nanog. Cell Stem Cell. 5:491–503. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chambers SM, Fasanob CA, Papapetrou EP, et
al: Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by
dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol. 27:275–280.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|